文章目录
- 一、FileStream和StreamWriter理解
-
- 1.1、具体关系解析
- 1.2、类比理解
- 1.3、总结
- 1.4、示例代码
- [1.5、 WriteLine()和 Write()的区别](#1.5、 WriteLine()和 Write()的区别)
- [1.6、 StreamWriter.Close的作用](#1.6、 StreamWriter.Close的作用)
- 二、List<Dictionary<string,string>>与控件DataGrid用法
-
- 2.1、DataGrid
- [2.2、 List<Dictionary<string,string>>](#2.2、 List<Dictionary<string,string>>)
- [三、 字符串切割函数 Split() 用法](#三、 字符串切割函数 Split() 用法)
一、FileStream和StreamWriter理解
在 C# 中,StreamWriter 和 FileStream 是 协作关系 ,二者共同完成文件的文本写入操作,但职责不同。简单来说:
FileStream 负责底层的 字节级文件操作 (如打开、读取、写入字节),而 StreamWriter 基于 FileStream 提供 文本编码转换和便捷的文本写入功能(如直接写入字符串、换行等)。
1.1、具体关系解析
-
依赖关系
StreamWriter的构造函数需要接收一个Stream类型的参数(FileStream是Stream的子类),即StreamWriter必须依赖一个底层流(如FileStream)才能工作。例:
new StreamWriter(aFile)中,aFile(FileStream)是StreamWriter的"数据源/目标"。 -
功能分工
FileStream:处理与操作系统交互的底层细节,比如:- 打开文件并获取文件句柄
- 以字节(
byte)为单位读写数据 - 控制文件的打开模式(
FileMode)、访问权限(FileAccess)、共享模式(FileShare)等。
StreamWriter:在FileStream之上封装了文本处理逻辑,比如:- 将字符串自动编码为字节(默认 UTF-8,可指定编码)
- 提供
WriteLine()等便捷方法(自动处理换行符\r\n) - 内部维护缓冲区,减少频繁的底层 IO 操作,提升性能。
-
生命周期关联
当
StreamWriter被释放(如using语句结束)时,会自动刷新缓冲区并关闭其依赖的FileStream(除非构造时指定leaveOpen: true)。例:若希望释放
StreamWriter后仍保留FileStream用于其他操作,可这样写:csharpusing (FileStream aFile = new FileStream("Log.txt", FileMode.OpenOrCreate)) { // leaveOpen: true 表示释放 StreamWriter 时不关闭 FileStream using (StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(aFile, leaveOpen: true)) { sw.WriteLine("Hello"); } // 此时 aFile 仍可继续使用(如读取字节) }
1.2、类比理解
可以把二者的关系类比为"水管"和"水龙头":
FileStream是 水管:负责连接水源(文件),提供原始的水流(字节)传输通道。StreamWriter是 带过滤功能的水龙头:安装在水管上,将原始水流(字节)转换为符合需求的"饮用水"(字符串),并提供便捷的开关(写入方法)。
1.3、总结
FileStream是底层字节流,处理文件的物理操作;StreamWriter是高层文本包装器,依赖FileStream实现字符串到字节的转换和便捷写入。- 二者结合使用,既利用了
FileStream的底层控制能力,又通过StreamWriter简化了文本处理。
1.4、示例代码
csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.IO;
namespace StreamWrite
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
FileStream aFile = new FileStream("Log.txt", FileMode.OpenOrCreate);
StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(aFile);
bool truth = true;
// Write data to file.
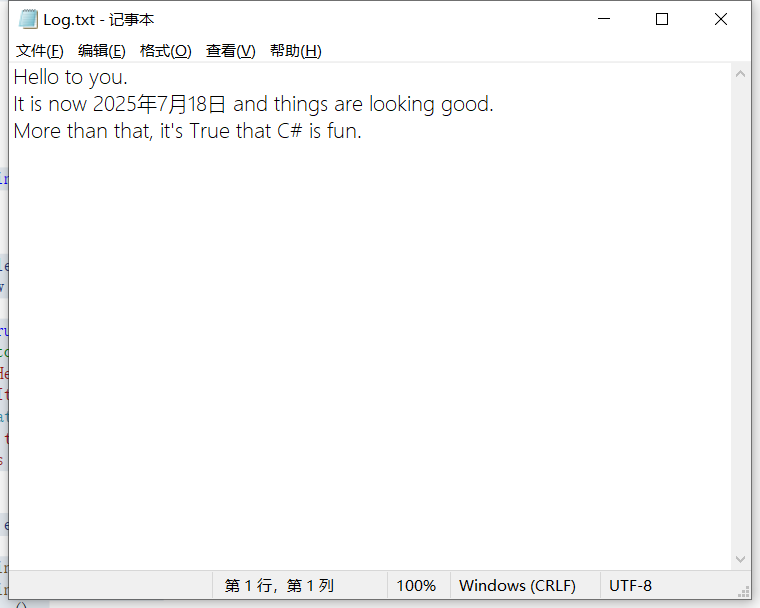
sw.WriteLine("Hello to you.");
sw.WriteLine("It is now {0} and things are looking good.",
DateTime.Now.ToLongDateString());
sw.Write("More than that,");
sw.Write(" it's {0} that C# is fun.", truth);
sw.Close();
}
catch(IOException e)
{
Console.WriteLine("An IO exception has been thrown!");
Console.WriteLine(e.ToString());
Console.ReadLine();
return;
}
}
}
}
1.5、 WriteLine()和 Write()的区别
csharp
sw.WriteLine("Hello to you.");
sw.WriteLine("It is now {0} and things are looking good.",
DateTime.Now.ToLongDateString());
sw.Write("More than that,");在 C# 的 StreamWriter 类中,WriteLine() 和 Write() 是两个常用的写入方法,它们的核心区别在于 是否自动添加换行符。以下是详细对比:
一、核心区别
| 方法 | 是否添加换行符 | 写入后光标位置 | 示例代码效果 |
|---|---|---|---|
WriteLine() |
✅ 自动添加 | 移至下一行开头 | sw.WriteLine("A"); sw.WriteLine("B"); → 文件内容: A B |
Write() |
❌ 不添加 | 留在当前行末尾 | sw.Write("A"); sw.Write("B"); → 文件内容: AB |
二、示例对比
假设你有以下代码:
csharp
using (StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter("test.txt"))
{
sw.Write("第一行");
sw.WriteLine("第二行");
sw.Write("第三行");
sw.WriteLine("第四行");
}生成的 test.txt 文件内容为:
第一行第二行
第三行第四行三、使用场景建议
-
逐行写入文本 (如日志、CSV):
使用
WriteLine(),例如:csharpsw.WriteLine("Name, Age"); sw.WriteLine("Alice, 30"); sw.WriteLine("Bob, 25"); -
格式化输出 (如拼接字符串):
使用
Write()配合WriteLine(),例如:csharpsw.Write("Total: "); sw.WriteLine(100.50); // 输出:Total: 100.50 -
手动控制换行 :
使用
Write()并显式添加换行符(\n或Environment.NewLine),例如:csharpsw.Write("第一部分内容\n"); // 等效于 sw.WriteLine("第一部分内容"); sw.Write("第二部分内容" + Environment.NewLine); // 跨平台换行符
四、性能差异
两者的性能差异极小,可忽略不计。但在大量写入时:
-
WriteLine()可能略微慢于Write()(多一次换行符写入)。 -
建议结合
BufferedStream提升整体性能:csharpusing (FileStream fs = new FileStream("test.txt", FileMode.Create)) using (BufferedStream bs = new BufferedStream(fs, 8192)) // 8KB 缓冲区 using (StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(bs)) { // 批量写入 }
五、注意事项
-
换行符的平台差异:
- Windows 默认使用
\r\n(回车+换行)。 - Linux/macOS 使用
\n(换行)。 WriteLine()会根据当前操作系统自动选择换行符(通过Environment.NewLine)。
- Windows 默认使用
-
与
Console.WriteLine()的类比:StreamWriter的WriteLine()和Console.WriteLine()逻辑一致,只是输出目标不同(文件 vs 控制台)。
六、总结
- 用
WriteLine():当需要每行独立时(如日志、配置文件)。 - 用
Write():当需要自定义格式或拼接内容时(如 JSON、HTML)。 - 混用:当需要灵活控制换行位置时(如表格输出)。
合理选择方法可以让代码更简洁、输出更易读。
1.6、 StreamWriter.Close的作用
在 C# 中,sw.Close() 的作用是 释放 StreamWriter 占用的系统资源 (如文件句柄、网络连接等)。如果不调用 Close(),会导致以下问题:
一、不调用 Close() 的后果
-
资源泄漏
- 文件句柄不会立即释放,其他程序无法访问该文件(如无法删除或修改)。
- 若频繁创建
StreamWriter而不关闭,可能耗尽系统资源(如文件句柄上限)。
-
数据丢失风险
StreamWriter有 缓冲区(默认 4KB),数据会先写入缓冲区,而非直接写入文件。- 若不调用
Close()或Flush(),缓冲区中的数据可能 不会被写入文件。
-
异常处理不完善
- 若写入过程中发生异常,
Close()可能不会被执行,导致资源无法释放。
- 若写入过程中发生异常,
二、Close() 的底层逻辑
Close() 方法实际上做了两件事:
Flush():将缓冲区中的数据强制写入文件。Dispose():释放非托管资源(如文件句柄),并标记对象已销毁。
三、推荐替代方案:using 语句
C# 提供了 using 语句,它会自动调用 Dispose() 方法(等价于 Close()),即使发生异常也能确保资源释放。
示例对比:
csharp
// 不使用 using(需手动 Close())
StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter("test.txt");
sw.WriteLine("Hello");
sw.Close(); // 必须显式调用,否则资源泄漏
// 使用 using(自动释放资源)
using (StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter("test.txt"))
{
sw.WriteLine("Hello");
// 无需调用 Close(),using 块结束时自动释放
}四、为什么示例代码中不调用 Close() 仍"正常"?
-
程序退出时系统回收资源
若程序立即退出,操作系统会强制释放文件句柄,但这是不可控的行为,不推荐依赖。
-
缓冲区自动刷新
- 缓冲区满时(默认 4KB)会自动刷新。
- 若写入的数据量很小(如示例中的几行文本),可能未填满缓冲区,导致数据丢失。
五、最佳实践
-
永远使用
using语句避免手动调用
Close(),让using自动管理资源。 -
显式调用
Flush()(可选)若需要立即写入数据(如实时日志),可调用
Flush():csharpusing (StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter("log.txt")) { sw.WriteLine("重要日志"); sw.Flush(); // 立即写入文件,不等待缓冲区满 } -
处理大文件时增大缓冲区
通过构造函数调整缓冲区大小(如 64KB),减少 IO 次数:
csharpusing (FileStream fs = new FileStream("large.txt", FileMode.Create)) using (StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(fs, Encoding.UTF8, 65536)) { // 写入大量数据 }
六、总结
Close()的作用:释放资源并确保数据写入文件。- 不调用的风险:资源泄漏、数据丢失。
- 推荐方案 :使用
using语句替代手动Close(),提升代码安全性和简洁性。
二、List<Dictionary<string,string>>与控件DataGrid用法
2.1、DataGrid
WPF(Windows Presentation Foundation)中的DataGrid是一个强大的控件,用于显示和编辑表格数据。下面我将介绍它的基本用法、常见属性和事件,并通过示例代码演示。
1. 基本用法
DataGrid通常与数据绑定一起使用,可绑定到任何实现了IEnumerable接口的集合(如List<T>、ObservableCollection<T>)。
XAML 示例
xml
<DataGrid ItemsSource="{Binding Employees}"
AutoGenerateColumns="True"
SelectionMode="Single"
SelectionUnit="FullRow"
CanUserAddRows="True"
CanUserDeleteRows="True"
HorizontalAlignment="Stretch"
VerticalAlignment="Stretch"/>关键属性说明
ItemsSource:绑定数据源。AutoGenerateColumns:是否自动生成列(默认True)。SelectionMode:选择模式(Single、Extended、Multiple)。SelectionUnit:选择单位(FullRow、Cell、CellOrRowHeader)。CanUserAddRows:是否允许用户添加行。CanUserDeleteRows:是否允许用户删除行。
2. 自定义列
若要控制列的显示方式,可手动定义列:
xml
<DataGrid ItemsSource="{Binding Employees}"
AutoGenerateColumns="False">
<DataGrid.Columns>
<!-- 文本列 -->
<DataGridTextColumn Header="ID"
Binding="{Binding Id}"
Width="SizeToHeader"/>
<!-- 绑定到复杂属性 -->
<DataGridTextColumn Header="姓名"
Binding="{Binding Name}"
Width="*"/>
<!-- 复选框列 -->
<DataGridCheckBoxColumn Header="在职"
Binding="{Binding IsActive}"
Width="Auto"/>
<!-- 模板列(自定义显示) -->
<DataGridTemplateColumn Header="操作">
<DataGridTemplateColumn.CellTemplate>
<DataTemplate>
<Button Content="编辑"
Click="EditButton_Click"/>
</DataTemplate>
</DataGridTemplateColumn.CellTemplate>
</DataGridTemplateColumn>
</DataGrid.Columns>
</DataGrid>3. 数据模型与视图模型
假设我们有一个员工类:
csharp
public class Employee
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public bool IsActive { get; set; }
public DateTime HireDate { get; set; }
}在窗口的代码-behind中设置数据源:
csharp
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public ObservableCollection<Employee> Employees { get; set; }
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
// 初始化数据
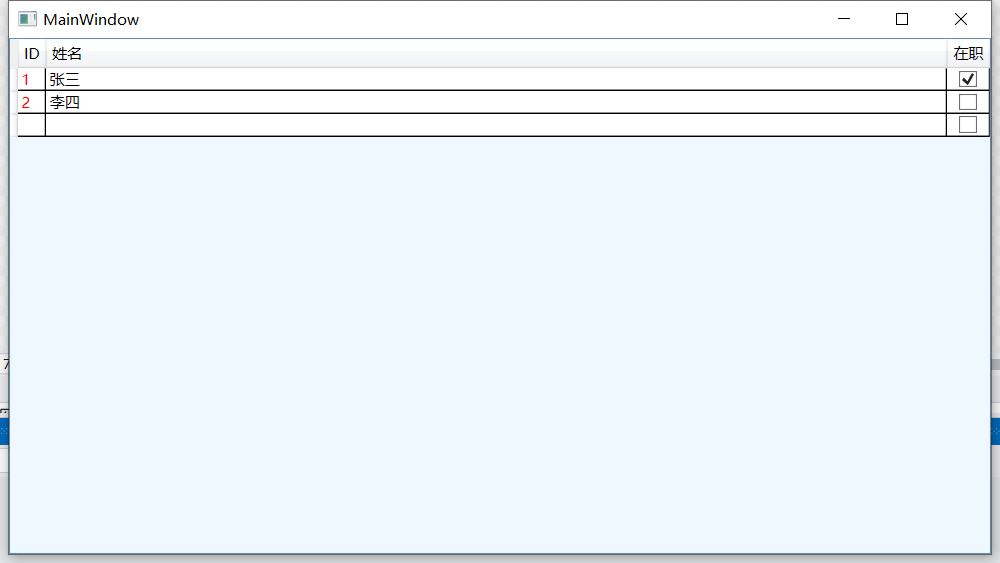
Employees = new ObservableCollection<Employee>
{
new Employee { Id = 1, Name = "张三", IsActive = true, HireDate = DateTime.Now.AddYears(-2) },
new Employee { Id = 2, Name = "李四", IsActive = false, HireDate = DateTime.Now.AddYears(-1) }
};
// 设置DataContext
DataContext = this;
}
}4. 常见事件
SelectionChanged:选择项变更时触发。CellEditEnding:单元格编辑结束时触发。RowEditEnding:行编辑结束时触发。
事件处理示例
xml
<DataGrid SelectionChanged="DataGrid_SelectionChanged"
CellEditEnding="DataGrid_CellEditEnding"/>
csharp
private void DataGrid_SelectionChanged(object sender, SelectionChangedEventArgs e)
{
var selectedEmployee = (sender as DataGrid)?.SelectedItem as Employee;
if (selectedEmployee != null)
{
// 处理选中项
}
}
private void DataGrid_CellEditEnding(object sender, DataGridCellEditEndingEventArgs e)
{
// 处理单元格编辑结束事件
if (e.EditAction == DataGridEditAction.Commit)
{
var editedEmployee = e.Row.Item as Employee;
// 更新数据
}
}5. 高级用法
(1)样式定制
通过Style属性自定义外观:
xml
<DataGrid.Resources>
<Style TargetType="DataGridCell">
<Setter Property="Foreground" Value="Black"/>
<Setter Property="Background" Value="LightGray"/>
</Style>
</DataGrid.Resources>(2)分组与排序
通过视图模型实现分组:
csharp
// 获取集合视图
var view = CollectionViewSource.GetDefaultView(Employees);
view.SortDescriptions.Add(new SortDescription("HireDate", ListSortDirection.Descending));
// 分组
PropertyGroupDescription groupDescription = new PropertyGroupDescription("IsActive");
view.GroupDescriptions.Add(groupDescription);总结
DataGrid是WPF中展示表格数据的核心控件,通过数据绑定、自定义列和事件处理,可实现复杂的表格交互功能。建议结合MVVM模式使用,将数据逻辑与UI分离。
其他功能(如筛选、分页),待完善····
简单示例代码
xml
<Window x:Class="practice_DataGrig.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:practice_DataGrig"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="MainWindow" Height="450" Width="800">
<DataGrid ItemsSource="{Binding Employees}"
AutoGenerateColumns="False" Background="AliceBlue">
<DataGrid.Columns>
<!-- 文本列 -->
<DataGridTextColumn Header="ID"
Binding="{Binding Id}"
Width="SizeToHeader" Foreground="Red"/>
<!-- 绑定到复杂属性 -->
<DataGridTextColumn Header="姓名"
Binding="{Binding Name}"
Width="*"/>
<!-- 复选框列 -->
<DataGridCheckBoxColumn Header="在职"
Binding="{Binding IsActive}"
Width="Auto"/>
<!-- 模板列(自定义显示) --><!--
<DataGridTemplateColumn Header="操作">
<DataGridTemplateColumn.CellTemplate>
<DataTemplate>
<Button Content="编辑"
Click="EditButton_Click"/>
</DataTemplate>
</DataGridTemplateColumn.CellTemplate>
</DataGridTemplateColumn>-->
</DataGrid.Columns>
</DataGrid>
</Window>
csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Collections.ObjectModel;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Data;
using System.Windows.Documents;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Imaging;
using System.Windows.Navigation;
using System.Windows.Shapes;
namespace practice_DataGrig
{
public class Employee
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public bool IsActive { get; set; }
public DateTime HireDate { get; set; }
}
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public ObservableCollection<Employee> Employees { get; set; }
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
// 初始化数据
Employees = new ObservableCollection<Employee>
{
new Employee { Id = 1, Name = "张三", IsActive = true, HireDate = DateTime.Now.AddYears(-2) },
new Employee { Id = 2, Name = "李四", IsActive = false, HireDate = DateTime.Now.AddYears(-1) }
};
// 设置DataContext
DataContext = this;
}
}
}2.2、 List<Dictionary<string,string>>
在WPF(Windows Presentation Foundation)应用程序里,List<Dictionary<string, string>> 属于复合数据结构。
结构剖析
- Dictionary<string, string> :
- 这是一个键值对集合,其中键(Key)和值(Value)均为字符串类型。
- 它和数据表中的"行"概念类似,键的作用等同于列名,值则相当于单元格数据。
- List<...> :
- 该列表用于存放多个
Dictionary<string, string>对象。 - 可以把它想象成由行构成的集合,类似于数据表。
- 该列表用于存放多个
应用场景
在WPF程序中,这种数据结构主要有以下两种应用场景:
- 动态数据处理 :
- 当数据的结构(列)在运行时才会确定,或者可能发生变化时,就可以使用这种数据结构。
- 比如从CSV文件、JSON数据或者数据库查询结果中获取的数据。
- 数据绑定 :
- 能够将其绑定到WPF的控件上,像DataGrid、ListView等。
- 键(Key)会被当作列标题,值(Value)则作为单元格内容。
示例代码
下面通过一段示例代码,展示该数据结构的创建和使用方法:
csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Windows;
namespace WpfApp1
{
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
// 创建数据
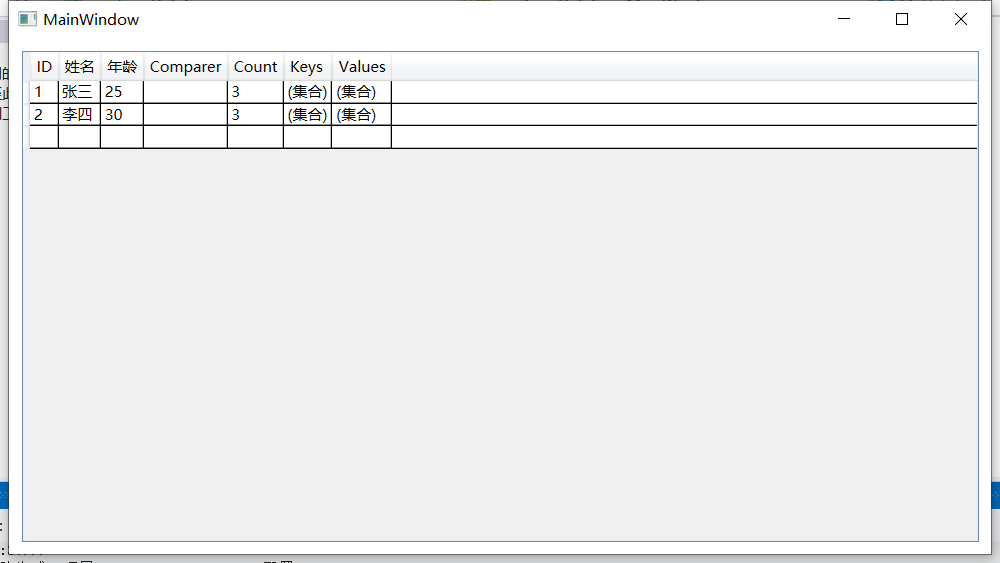
var data = new List<Dictionary<string, string>>
{
new Dictionary<string, string>
{
{ "ID", "1" },
{ "Name", "张三" },
{ "Age", "25" }
},
new Dictionary<string, string>
{
{ "ID", "2" },
{ "Name", "李四" },
{ "Age", "30" }
}
};
// 绑定到DataGrid(假设XAML中已有DataGrid控件,名称为MyDataGrid)
MyDataGrid.ItemsSource = data;
}
}
}优缺点分析
优点:
- 具有很强的灵活性,适合处理结构不固定的数据。
- 不需要预先定义类,使用起来较为便捷。
缺点:
- 类型安全方面存在不足,因为值都是字符串类型。
- 缺乏编译时检查,容易引发运行时错误。
- 对于复杂的业务逻辑,维护起来比较困难。
替代方案
如果数据结构是固定的,建议使用强类型集合,例如:
csharp
public class Person
{
public string ID { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Age { get; set; }
}
// 使用 List<Person>
var people = new List<Person>
{
new Person { ID = "1", Name = "张三", Age = "25" },
new Person { ID = "2", Name = "李四", Age = "30" }
};强类型集合的优势在于类型安全,还能利用Visual Studio的智能提示功能。
示例代码
xml
<Window x:Class="practice_DataGrig.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:practice_DataGrig"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="MainWindow" Height="450" Width="800">
<DataGrid x:Name="MyDataGrid"
HorizontalAlignment="Stretch"
VerticalAlignment="Stretch"
Margin="10">
<DataGrid.Columns>
<DataGridTextColumn Header="ID" Binding="{Binding [ID]}" />
<DataGridTextColumn Header="姓名" Binding="{Binding [Name]}" />
<DataGridTextColumn Header="年龄" Binding="{Binding [Age]}" />
</DataGrid.Columns>
</DataGrid>
</Window>注意此处的Binding="{Binding [ID]}
在WPF的数据绑定中,{Binding [Key]} 这种语法里的方括号有着特殊的用途
方括号的作用
在绑定路径里使用方括号 [],意味着要通过索引器(Indexer)来访问集合或字典中的元素。
针对 Dictionary<string, string> 的绑定
对于 Dictionary<string, string> 类型的对象,WPF没办法直接识别它的键(Key)。所以,要通过索引器来访问对应键的值。
{Binding [ID]}这种写法,实际上等同于在代码里调用dictionary["ID"]。- 如果是强类型属性,不添加方括号,则相当于
Person.ID - 这里的
[ID]表示以字符串"ID"作为键,去获取字典里对应的值。
对比强类型属性绑定
假设使用的是强类型对象,比如 Person 类,那绑定语法就会有所不同:
xml
<DataGridTextColumn Header="ID" Binding="{Binding ID}" />在这个例子中:
{Binding ID}表示直接访问Person类的ID属性。- 因为
Person是强类型,WPF能够直接识别它的属性。
总结
| 数据类型 | 绑定语法示例 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Dictionary<string, T> | {Binding [Key]} |
通过索引器访问键对应的值 |
| 强类型对象(如Person) | {Binding PropertyName} |
直接访问对象的属性 |
所以,在绑定 Dictionary<string, string> 时,必须使用 [Key] 这种语法,这样WPF才能正确获取到字典里的值。
csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Collections.ObjectModel;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Data;
using System.Windows.Documents;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Imaging;
using System.Windows.Navigation;
using System.Windows.Shapes;
namespace practice_DataGrig
{
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
// 创建数据
var data = new List<Dictionary<string, string>>
{
new Dictionary<string, string>
{
{ "ID", "1" },
{ "Name", "张三" },
{ "Age", "25" }
},
new Dictionary<string, string>
{
{ "ID", "2" },
{ "Name", "李四" },
{ "Age", "30" }
}
};
// 绑定到DataGrid(假设XAML中已有DataGrid控件,名称为MyDataGrid)
MyDataGrid.ItemsSource = data;
}
}
}三、 字符串切割函数 Split() 用法
在 C# 中,Split() 是 string 类的一个非常实用的方法,用于将字符串按指定的分隔符拆分成多个子字符串。下面为你详细介绍它的各种用法:
一、按字符数组拆分
这种方式可以根据多个不同的字符来拆分字符串。
csharp
string str = "Hello,World!This is a test.";
char[] separators = { ',', '!', ' ' };
string[] result = str.Split(separators);结果:
["Hello", "World", "This", "is", "a", "test."]二、按字符串数组拆分
使用这种方法,能够以特定的字符串作为分隔符来拆分字符串。
csharp
string str = "Hello--World--CSharp";
string[] separators = { "--" };
string[] result = str.Split(separators, StringSplitOptions.None);结果:
["Hello", "World", "CSharp"]三、限制拆分结果数量
通过设置 count 参数,可以控制拆分后得到的子字符串的最大数量。
csharp
string str = "A,B,C,D,E";
string[] result = str.Split(',', 3);结果:
["A", "B", "C,D,E"]四、移除空条目
使用 StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries 选项,能够过滤掉拆分结果中的空字符串。
csharp
string str = "A,,B,,,C";
string[] result = str.Split(new char[] { ',' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);结果:
["A", "B", "C"]五、按行拆分(处理换行符)
利用换行符(\n、\r 或 \r\n)可以将文本拆分成多行。
csharp
string str = "Line1\r\nLine2\nLine3";
string[] result = str.Split(new[] { '\r', '\n' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);结果:
["Line1", "Line2", "Line3"]六、从字符串末尾开始拆分
结合 Reverse() 和 Take() 方法,可以从字符串末尾开始进行拆分操作。
csharp
string str = "192.168.1.1";
string[] parts = str.Split('.');
string lastPart = parts.Reverse().Take(1).First();结果:
lastPart = "1"七、处理复杂分隔符(使用正则表达式)
当需要处理复杂的分隔符模式时,可以借助正则表达式的 Split 方法。
csharp
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
string str = "Hello123World456CSharp";
string[] result = Regex.Split(str, @"\d+");结果:
["Hello", "World", "CSharp"]八、在WPF数据绑定中使用
可以通过创建值转换器,在WPF的数据绑定过程中使用 Split 方法。
csharp
public class SplitConverter : IValueConverter
{
public object Convert(object value, Type targetType, object parameter, CultureInfo culture)
{
if (value is string str && parameter is string separator)
{
return str.Split(new[] { separator }, StringSplitOptions.None);
}
return null;
}
public object ConvertBack(object value, Type targetType, object parameter, CultureInfo culture)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}九、性能优化(针对大量数据)
在处理大量数据时,StringSplitEnumerator 能提供更好的性能。
csharp
string str = "A,B,C,D";
var enumerator = str.AsSpan().Split(',');
foreach (var part in enumerator)
{
Console.WriteLine(part.ToString());
}十、注意事项
-
空字符串处理:
- 当字符串以分隔符开头或结尾时,拆分结果的开头或结尾可能会出现空字符串。
- 可以使用
StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries来过滤这些空字符串。
-
文化敏感性:
- 处理国际字符串时,要留意不同文化对字符的解释可能存在差异。
-
正则表达式的替代方案:
- 对于复杂的分隔符模式,建议使用
Regex.Split方法。
- 对于复杂的分隔符模式,建议使用
-
内存效率:
- 在 .NET Core 3.0 及更高版本中,
StringSplitEnumerator能减少内存分配,提升性能。
- 在 .NET Core 3.0 及更高版本中,
-
字符串长度限制:
- 拆分超长字符串时,可能会消耗大量内存,需要谨慎处理。
-
不可变特性:
Split方法不会修改原字符串,而是返回一个新的字符串数组。
如果你在实际使用过程中有特定的场景或问题,可以进一步提供详细信息,以便我给出更具针对性的解决方案。