本章共12踢,分上下两篇。
1.修改程序清单10.7的rain.c程序,用指针进行计算(仍然要声明并初始化数组)。
cpp
#define MONTHS 12 //一年的月份数
#define YEARS 5 //年数
int main(void)
{
//用2010~2014年的降水量初始化数组
const float rain[YEARS][MONTHS] = {
{ 4.3, 4.3, 4.3, 3.0, 2.0, 1.2, 0.2, 0.2, 0.4, 2.4, 3.5, 6.6 },
{ 8.5, 8.2, 1.2, 1.6, 2.4, 0.0, 5.2, 0.9, 0.3, 0.9, 1.4, 7.3 },
{ 9.1, 8.5, 6.7, 4.3, 2.1, 0.8, 0.2, 0.2, 1.1, 2.3, 6.1, 8.4 },
{ 7.2, 9.9, 8.4, 3.3, 1.2, 0.8, 0.4, 0.0, 0.6, 1.7, 4.3, 6.2 },
{ 7.6, 5.6, 3.8, 2.8, 3.8, 0.2, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.3, 2.6, 5.2 }
};
float subtot = 0.0, total = 0.0;
printf(" Year RAINFALL(inches)\n");
for (int year = 0; year < YEARS; year++)
{
subtot = 0.0;
for(int month = 0; month < MONTHS; month++)
subtot += *(*(rain + year) + month);
printf("%5d %15.1f\n", year + 2010, subtot);
total += subtot;
}
printf("\nThe yearly average is %.1f inches.\n\n", total / YEARS);
printf("MONTHLY AVERAGES:\n\n");
printf(" Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct ");
printf(" Nov Dec\n");
for (int month = 0; month < MONTHS; month++)
{
subtot = 0.0;
for (int year = 0; year < YEARS; year++)
{
subtot += *(*(rain + year) + month);
}
printf(" % 4.1f ", subtot / YEARS);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
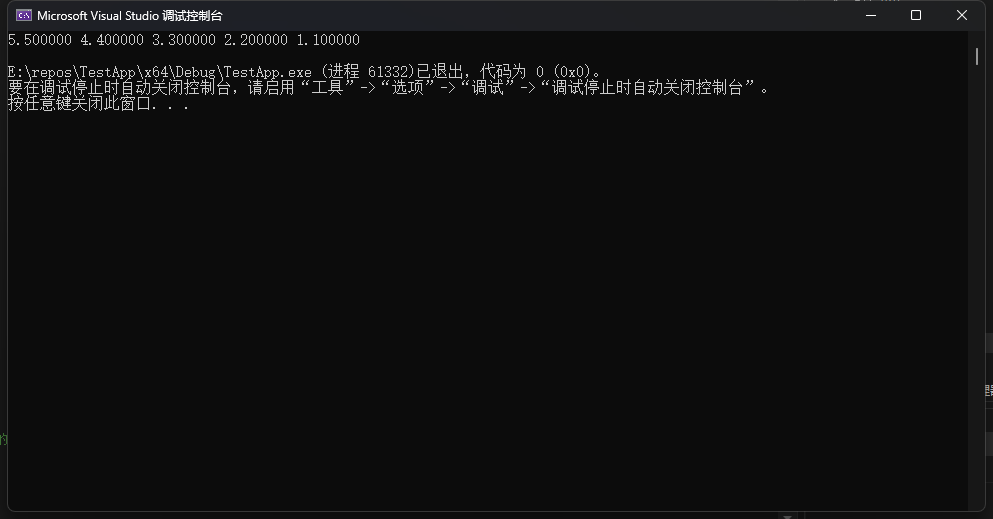
}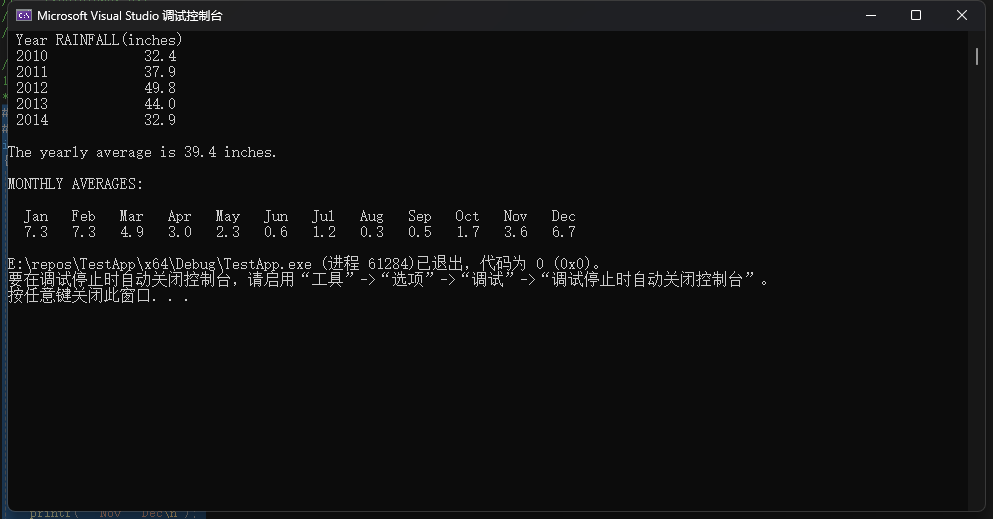
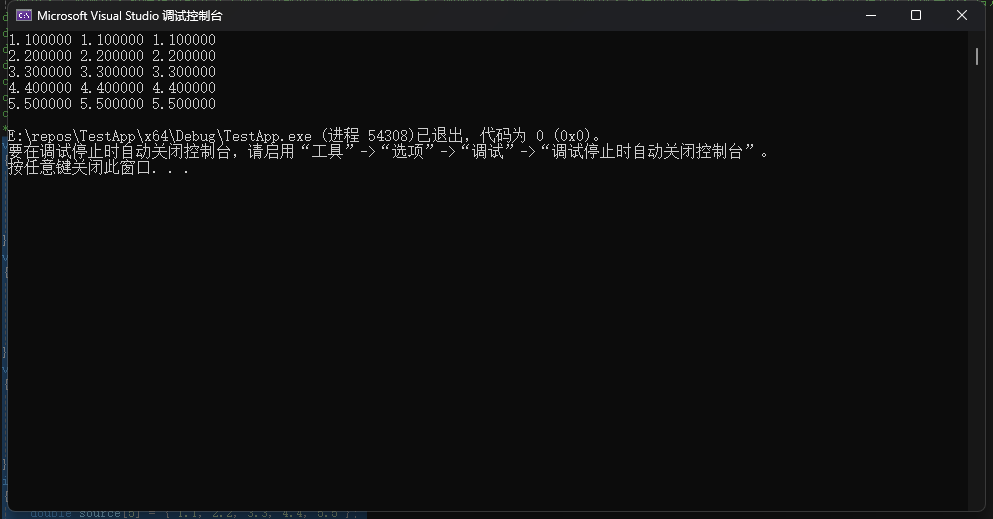
2.编写一个程序,初始化一个double数组,然后把该数组的内容拷贝至3个其他数组中(在main()中声明这4个数组)。使用带数组表示发的函数进行第1份拷贝。使用带指针表示法和指针递增的函数进行第2份拷贝。把目标数组名、源数组名和待拷贝的元素个数作为前两个函数的参数。第3个函数以目标数组名、源数组名和指向源数组最后一个元素后面的元素指针。也就是说,给定以下声明,则函数调用如下所示:
double source[5] = {1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4, 5.5};
double target1[5];
double target2[5];
double target3[5];
copy_arr(target1, source, 5);
copy_ptr(target2, source, 5);
copy_ptrs(target3, source, source + 5);
cpp
void copy_arr(double target[], double source[], int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
target[i] = source[i];
}
}
void copy_ptr(double* target, double* source, int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
*target++ = *source++;
}
}
void copy_ptrs(double* target, double* source, double* end)
{
for (double *p = source; source < end; source++)
{
*target++ = *source;
}
}
int main(void)
{
double source[5] = { 1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4, 5.5 };
double target1[5];
double target2[5];
double target3[5];
copy_arr(target1, source, 5);
copy_ptr(target2, source, 5);
copy_ptrs(target3, source, source + 5);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
printf("%f %f %f\n", target1[i], target2[i], target3[i]);
}
return 0;
}
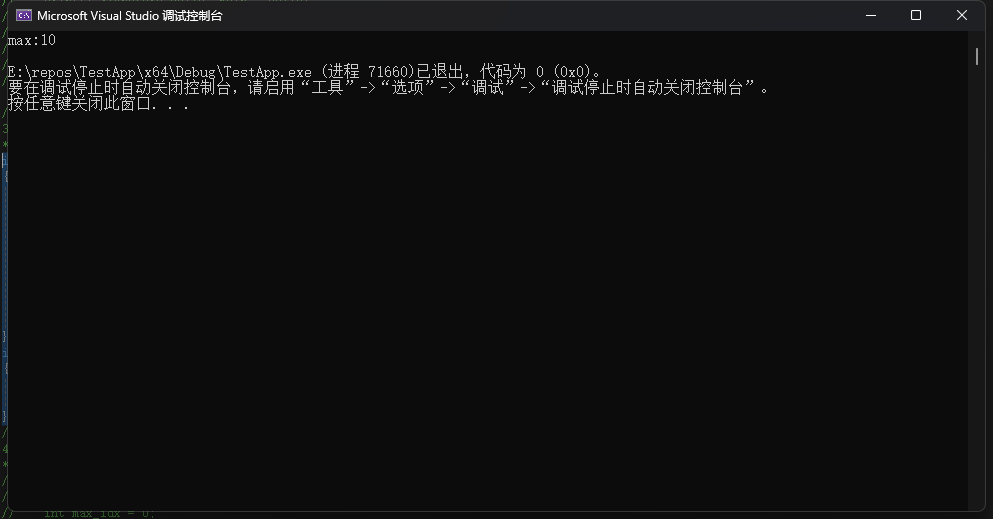
3.编写一个函数,返回存储在int类型数组中的最大值,并在一个简单的程序中测试该函数。
cpp
int max_array(int a[], int n)
{
int max = a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
if (a[i] > max)
{
max = a[i];
}
}
return max;
}
int main()
{
int a[] = { 1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 9, 10, 4, 5, 6 };
printf("max:%d\n", max_array(a, 10));
}
4.编写一个函数,返回存储在double类型数组中最大值的下标,并在一个简单的程序中测试该函数。
cpp
int max_array(double a[], int n)
{
int max_idx = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
if (a[i] > a[max_idx])
{
max_idx = i;
}
}
return max_idx;
}
int main()
{
double a[10] = { 1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4, 5.5, 6.6, 7.7, 8.8, 9.9, 10.1 };
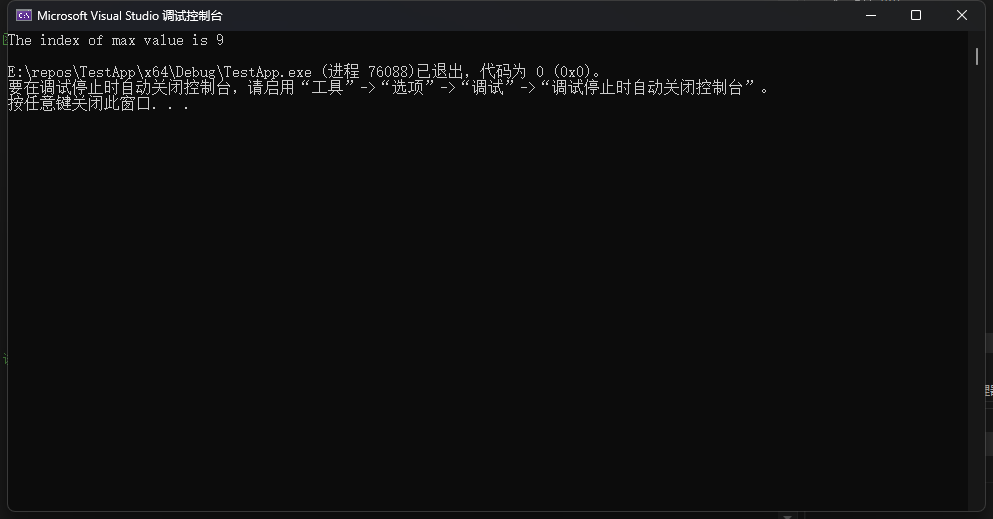
printf("The index of max value is %d\n", max_array(a, 10));
}
5.编写一个函数,返回存储在double数组中最大值和最小值的差,并在一个简单的程序中测试该函数。
cpp
double max_min_diff(double a[], int n)
{
double max = a[0];
double min = a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
if (a[i] > max)
{
max = a[i];
}
else if (a[i] < min)
{
min = a[i];
}
}
return max - min;
}
int main()
{
double a[10] = { 1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4, 5.5, 6.6, 7.7, 8.8, 9.9, 10.1 };
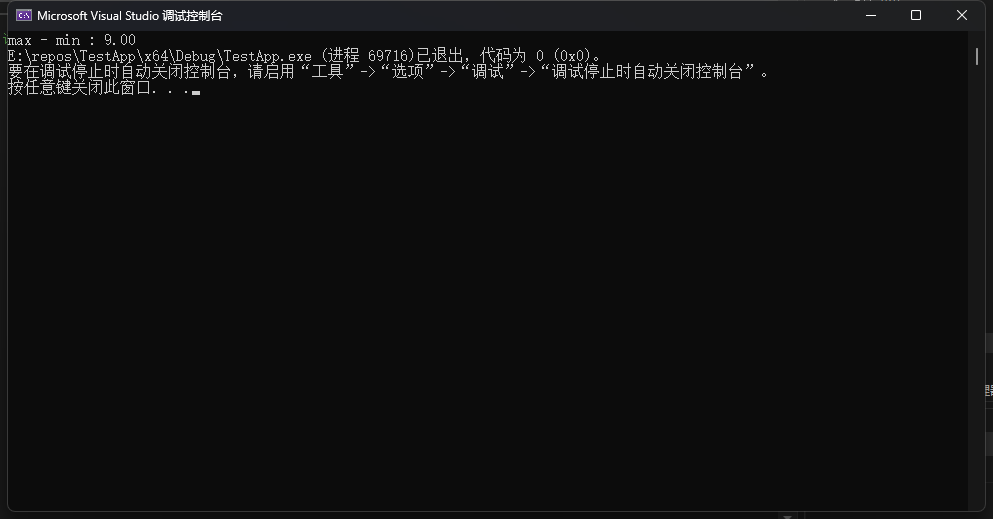
printf("max - min : %.2f", max_min_diff(a, 10));
}
6.编写一个程序,把double类型数组中的数据倒叙排列,并在一个简单的程序中测试该函数。
cpp
void DescSort(double a[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (a[i] < a[j])
{
double temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
double a[5] = { 2.2, 1.1, 4.4, 5.5, 3.3 };
DescSort(a, 5);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
printf("%f ", a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}