


专栏:JavaEE初阶起飞计划
个人主页:手握风云
目录
[1.1. 定时器](#1.1. 定时器)
一、多线程案例
1.1. 定时器
定时器是软件开发的一个重要组件,是一种能够按照预设的时间间隔或在特定时间点执行某个任务或代码片段的机制。你可以把它想象成一个闹钟,只不过这个"闹钟"不是提醒你去起床,而是提醒计算机去执行某个特定的操作。定时器与阻塞队列一致,也会被单独封装成一个或一组服务器来使用。
- 标准库中的定时器
java
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
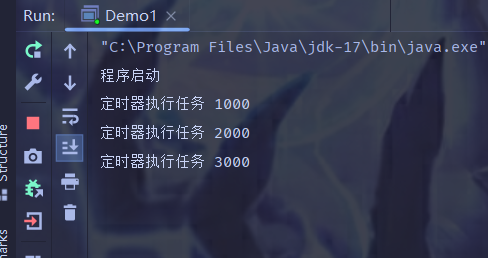
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Timer timer = new Timer();
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("定时器执行任务 3000");
}
}, 3000);
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("定时器执行任务 2000");
}
}, 2000);
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("定时器执行任务 1000");
}
}, 1000);
System.out.println("程序启动");
}
}
- 定时器的实现
对于自主实现的定时器,需要指定等待的最大时间,如果等不到,还需要执行其他的操作。
java
class MyTimer {
public MyTimer() {
}
//向定时器中添加任务
public void schedule(Runnable runnable, long delay) {
}
}这里注意,TimerTask类实现的是Runnable接口,所以我们在schedule方法里面添加的也是Runnable类型的参数。既然要对任务进行组织管理,就得使用合适的数据结构,比如顺序表、栈。但是这些任务不一定是按照时间顺序添加的,并且添加的顺序和执行顺序没太大关系。如果使用顺序表,执行任务时,就需要遍历来找到时间最小的任务,效率太低。这时我们就可以使用堆来解决。
对于堆所存放的泛型参数,这里不能添加成Runnable,因为堆里面的任务不只是内容,还需要考虑任务的时间。
java
class MyTimerTask {
private Runnable task;
// 这个地方为了和当前时间对比,确认任务是否执行,需要保存绝对的时间戳
private long time;
public MyTimerTask(Runnable task, long delay) {
this.task = task;
this.time = System.currentTimeMillis() + delay;
}
public Runnable getTask() {
return task;
}
public long getTime() {
return time;
}
}
class MyTimer {
private PriorityQueue<MyTimerTask> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
public MyTimer() {
}
//向定时器中添加任务
public void schedule(Runnable runnable, long delay) {
queue.offer(new MyTimerTask(runnable, delay));
}
}由于MyTimerTask是放在优先级队列中,所以我们还需要写出比较规则。
java
class MyTimerTask implements Comparable<MyTimerTask>{
private Runnable task;
// 这个地方为了和当前时间对比,确认任务是否执行,需要保存绝对的时间戳
private long time;
public MyTimerTask(Runnable task, long delay) {
this.task = task;
this.time = System.currentTimeMillis() + delay;
}
public Runnable getTask() {
return task;
}
public long getTime() {
return time;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(MyTimerTask o) {
return (int) (this.time - o.time);
}
}接下来就是创建线程,让线程来检测任务是否到时间了,以及去执行这个任务。我们需要循环从队列中取出元素,判断是否到时间了,如果到达就出队列,没有就不做处理。
java
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
class MyTimerTask implements Comparable<MyTimerTask>{
private Runnable task;
// 这个地方为了和当前时间对比,确认任务是否执行,需要保存绝对的时间戳
private long time;
public MyTimerTask(Runnable task, long delay) {
this.task = task;
this.time = System.currentTimeMillis() + delay;
}
public Runnable getTask() {
return task;
}
public long getTime() {
return time;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(MyTimerTask o) {
return (int) (this.time - o.time);
}
}
class MyTimer {
private PriorityQueue<MyTimerTask> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
public MyTimer() {
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
if (queue.isEmpty()) {
continue;
}
MyTimerTask task = queue.peek();
long curTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (curTime < task.getTime()) {
continue;
} else {
task.getTask().run();
queue.poll();
}
}
});
t.start();
}
//向定时器中添加任务
public void schedule(Runnable runnable, long delay) {
queue.offer(new MyTimerTask(runnable, delay));
}
}
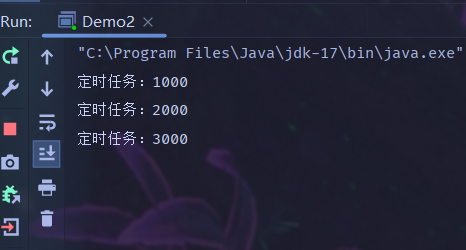
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyTimer timer = new MyTimer();
timer.schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("定时任务:3000");
}
}, 3000);
timer.schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("定时任务:2000");
}
}, 2000);
timer.schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("定时任务:1000");
}
}, 1000);
}
}
虽然执行效果没有什么问题,但上面的操作对于同一个队列进行出入,所以线程是不安全的。那我们就需要在入队列和出队列的操作里面都要进行加锁。第二个问题,就是忙等出现饿死。如上面的代码,当队列为空或者没到时间时,不做任何处理,只消耗CPU资源,没有任何实质性的进展。尤其是第二个continue,这里就相当于30分钟之后要去执行某项任务,每隔1分钟就得看一下时间,当我们设计了等待时间之后,到时间自动唤醒或者有优先级更高的任务要去执行。
完整代码:
java
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
class MyTimerTask implements Comparable<MyTimerTask>{
private Runnable task;
// 这个地方为了和当前时间对比,确认任务是否执行,需要保存绝对的时间戳
private long time;
public MyTimerTask(Runnable task, long delay) {
this.task = task;
this.time = System.currentTimeMillis() + delay;
}
public Runnable getTask() {
return task;
}
public long getTime() {
return time;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(MyTimerTask o) {
return (int) (this.time - o.time);
}
}
class MyTimer {
private PriorityQueue<MyTimerTask> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
private Object locker = new Object();
public MyTimer() {
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
try {
synchronized (locker) {
if (queue.isEmpty()) {
locker.wait();
}
MyTimerTask task = queue.peek();
long curTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (curTime < task.getTime()) {
locker.wait(task.getTime() - curTime);
} else {
task.getTask().run();
queue.poll();
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
t.start();
}
//向定时器中添加任务
public void schedule(Runnable runnable, long delay) {
synchronized (locker) {
queue.offer(new MyTimerTask(runnable, delay));
locker.notify();
}
}
}
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyTimer timer = new MyTimer();
timer.schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("定时任务:3000");
}
}, 3000);
timer.schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("定时任务:2000");
}
}, 2000);
timer.schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("定时任务:1000");
}
}, 1000);
}
}