
MCP工具开发实战:打造智能体的"超能力"
🌟 Hello,我是摘星!
🌈 在彩虹般绚烂的技术栈中,我是那个永不停歇的色彩收集者。
🦋 每一个优化都是我培育的花朵,每一个特性都是我放飞的蝴蝶。
🔬 每一次代码审查都是我的显微镜观察,每一次重构都是我的化学实验。
🎵 在编程的交响乐中,我既是指挥家也是演奏者。让我们一起,在技术的音乐厅里,奏响属于程序员的华美乐章。
目录
[1. MCP工具概念与设计原则](#1. MCP工具概念与设计原则)
[1.1 工具概念的本质理解](#1.1 工具概念的本质理解)
[1.2 核心设计原则](#1.2 核心设计原则)
[1.3 工具分类与应用场景](#1.3 工具分类与应用场景)
[2. 参数验证与错误处理机制](#2. 参数验证与错误处理机制)
[2.1 多层次参数验证体系](#2.1 多层次参数验证体系)
[2.2 错误处理策略](#2.2 错误处理策略)
[2.3 错误恢复机制](#2.3 错误恢复机制)
[3. 异步工具调用与性能优化](#3. 异步工具调用与性能优化)
[3.1 异步调用模式设计](#3.1 异步调用模式设计)
[3.2 性能优化策略](#3.2 性能优化策略)
[3.3 监控与性能分析](#3.3 监控与性能分析)
[4. 工具组合与链式调用实现](#4. 工具组合与链式调用实现)
[4.1 工具组合设计模式](#4.1 工具组合设计模式)
[4.2 链式调用执行器](#4.2 链式调用执行器)
[4.4 工具组合最佳实践](#4.4 工具组合最佳实践)
[5. 实战案例:构建智能数据分析工具链](#5. 实战案例:构建智能数据分析工具链)
[5.1 需求分析与架构设计](#5.1 需求分析与架构设计)
[5.2 数据清洗工具实现](#5.2 数据清洗工具实现)
[5.3 完整工具链集成](#5.3 完整工具链集成)
[6. 测试与质量保证](#6. 测试与质量保证)
[6.1 单元测试框架](#6.1 单元测试框架)
[6.2 集成测试与端到端测试](#6.2 集成测试与端到端测试)
[7. 部署与运维](#7. 部署与运维)
[7.1 生产环境部署](#7.1 生产环境部署)
[7.2 监控与告警](#7.2 监控与告警)
摘要
作为一名深耕AI技术领域多年的博主摘星,我深刻认识到工具(Tools)在现代智能体系统中的核心地位。在Anthropic推出的Model Context Protocol(MCP)框架下,工具不再是简单的功能模块,而是赋予AI智能体真正"超能力"的关键组件。通过深入研究MCP工具开发的各个层面,我发现这一技术正在重新定义人机交互的边界。MCP工具开发不仅仅是编写几个函数那么简单,它涉及复杂的参数验证机制、精密的错误处理策略、高效的异步调用模式,以及优雅的工具组合设计。在实际项目中,我见证了许多开发者因为缺乏对MCP工具设计原则的深入理解,导致开发出的工具要么性能低下,要么稳定性差,要么无法与其他工具有效协作。本文将从工具概念的本质出发,深入探讨MCP工具开发的核心技术要点,包括如何设计符合MCP规范的工具接口、如何实现健壮的参数验证与错误处理、如何优化异步工具调用的性能表现,以及如何构建可组合、可扩展的工具生态系统。通过理论与实践相结合的方式,我将为读者呈现一个完整的MCP工具开发实战指南,帮助开发者真正掌握这一前沿技术,为智能体注入强大的能力扩展机制。
1. MCP工具概念与设计原则
1.1 工具概念的本质理解
在MCP(Model Context Protocol)框架中,工具(Tools)是连接AI智能体与外部世界的桥梁。与传统的API调用不同,MCP工具具有更强的语义化特征和上下文感知能力。
python
// MCP工具的基本结构定义
interface MCPTool {
name: string; // 工具名称
description: string; // 工具描述
inputSchema: JSONSchema; // 输入参数模式
handler: ToolHandler; // 工具处理函数
metadata?: ToolMetadata; // 工具元数据
}
interface ToolHandler {
(params: any, context: MCPContext): Promise<ToolResult>;
}
interface ToolResult {
content: ToolContent[]; // 工具执行结果
isError?: boolean; // 是否为错误结果
metadata?: Record<string, any>; // 结果元数据
}1.2 核心设计原则
MCP工具开发遵循以下核心设计原则:
|----------|----------------|---------------|
| 设计原则 | 描述 | 实现要点 |
| 单一职责 | 每个工具只负责一个明确的功能 | 避免功能耦合,提高可维护性 |
| 幂等性 | 相同输入产生相同输出 | 确保工具调用的可预测性 |
| 可组合性 | 工具间可以灵活组合使用 | 标准化输入输出格式 |
| 错误透明 | 错误信息清晰可理解 | 提供详细的错误上下文 |
| 性能优先 | 优化执行效率和资源使用 | 异步处理和缓存机制 |
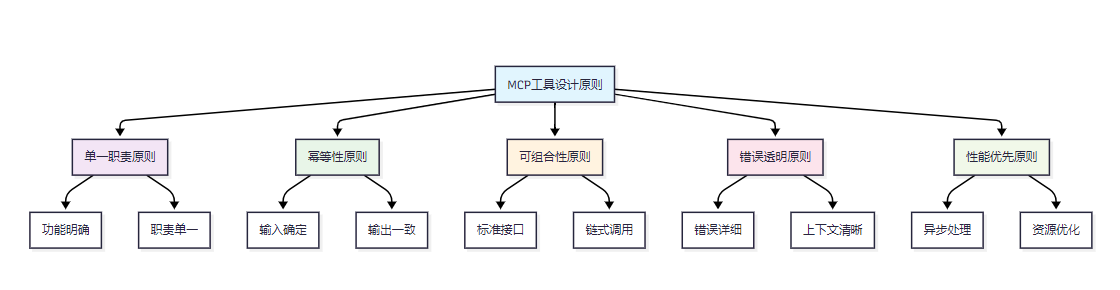
图1 MCP工具设计原则架构图
1.3 工具分类与应用场景
根据功能特性,MCP工具可以分为以下几类:
python
// 数据处理工具示例
class DataProcessingTool implements MCPTool {
name = "data_processor";
description = "处理和转换数据格式";
inputSchema = {
type: "object",
properties: {
data: { type: "array", description: "待处理的数据" },
operation: {
type: "string",
enum: ["filter", "transform", "aggregate"],
description: "处理操作类型"
}
},
required: ["data", "operation"]
};
async handler(params: any, context: MCPContext): Promise<ToolResult> {
const { data, operation } = params;
try {
let result;
switch (operation) {
case "filter":
result = this.filterData(data, context.filterCriteria);
break;
case "transform":
result = this.transformData(data, context.transformRules);
break;
case "aggregate":
result = this.aggregateData(data, context.aggregateFunction);
break;
default:
throw new Error(`不支持的操作类型: ${operation}`);
}
return {
content: [{
type: "text",
text: `数据处理完成,处理了 ${data.length} 条记录`
}, {
type: "json",
data: result
}]
};
} catch (error) {
return {
content: [{
type: "text",
text: `数据处理失败: ${error.message}`
}],
isError: true
};
}
}
}2. 参数验证与错误处理机制
2.1 多层次参数验证体系
MCP工具的参数验证需要建立多层次的验证体系,确保输入数据的完整性和正确性。
python
// 参数验证器接口定义
interface ParameterValidator {
validate(params: any, schema: JSONSchema): ValidationResult;
}
interface ValidationResult {
isValid: boolean;
errors: ValidationError[];
sanitizedParams?: any;
}
interface ValidationError {
path: string;
message: string;
code: string;
severity: 'error' | 'warning';
}
// 实现多层次验证器
class MultiLevelValidator implements ParameterValidator {
private validators: Map<string, ValidatorFunction> = new Map();
constructor() {
this.initializeValidators();
}
private initializeValidators() {
// 基础类型验证
this.validators.set('type', this.validateType.bind(this));
// 格式验证
this.validators.set('format', this.validateFormat.bind(this));
// 业务规则验证
this.validators.set('business', this.validateBusinessRules.bind(this));
// 安全性验证
this.validators.set('security', this.validateSecurity.bind(this));
}
validate(params: any, schema: JSONSchema): ValidationResult {
const errors: ValidationError[] = [];
let sanitizedParams = { ...params };
// 第一层:基础类型验证
const typeErrors = this.validateType(params, schema);
errors.push(...typeErrors);
// 第二层:格式验证
if (errors.length === 0) {
const formatErrors = this.validateFormat(params, schema);
errors.push(...formatErrors);
}
// 第三层:业务规则验证
if (errors.length === 0) {
const businessErrors = this.validateBusinessRules(params, schema);
errors.push(...businessErrors);
}
// 第四层:安全性验证
if (errors.length === 0) {
const securityResult = this.validateSecurity(params, schema);
errors.push(...securityResult.errors);
sanitizedParams = securityResult.sanitizedParams || sanitizedParams;
}
return {
isValid: errors.filter(e => e.severity === 'error').length === 0,
errors,
sanitizedParams
};
}
private validateType(params: any, schema: JSONSchema): ValidationError[] {
// 实现类型验证逻辑
const errors: ValidationError[] = [];
if (schema.type === 'object' && typeof params !== 'object') {
errors.push({
path: '$',
message: '参数必须是对象类型',
code: 'TYPE_MISMATCH',
severity: 'error'
});
}
return errors;
}
private validateSecurity(params: any, schema: JSONSchema): {
errors: ValidationError[];
sanitizedParams: any;
} {
const errors: ValidationError[] = [];
const sanitized = this.sanitizeInput(params);
// 检查潜在的安全风险
if (this.containsSqlInjection(params)) {
errors.push({
path: '$',
message: '检测到潜在的SQL注入风险',
code: 'SECURITY_RISK',
severity: 'error'
});
}
return { errors, sanitizedParams: sanitized };
}
}2.2 错误处理策略
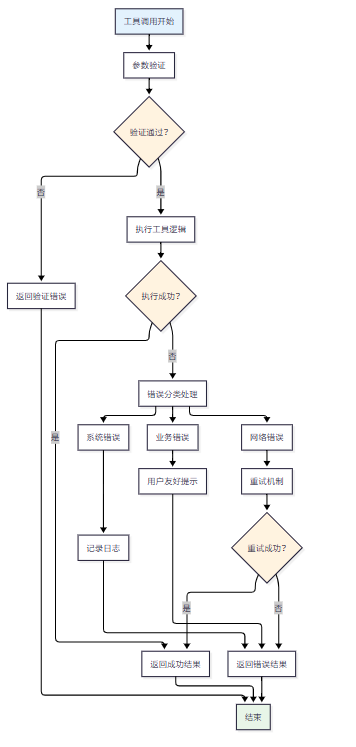
图2 MCP工具错误处理流程图
python
// 错误处理管理器
class ErrorHandler {
private static instance: ErrorHandler;
private errorStrategies: Map<string, ErrorStrategy> = new Map();
static getInstance(): ErrorHandler {
if (!ErrorHandler.instance) {
ErrorHandler.instance = new ErrorHandler();
}
return ErrorHandler.instance;
}
constructor() {
this.initializeStrategies();
}
private initializeStrategies() {
// 系统错误策略
this.errorStrategies.set('SYSTEM_ERROR', {
handle: this.handleSystemError.bind(this),
shouldRetry: false,
logLevel: 'error'
});
// 网络错误策略
this.errorStrategies.set('NETWORK_ERROR', {
handle: this.handleNetworkError.bind(this),
shouldRetry: true,
maxRetries: 3,
logLevel: 'warn'
});
// 业务错误策略
this.errorStrategies.set('BUSINESS_ERROR', {
handle: this.handleBusinessError.bind(this),
shouldRetry: false,
logLevel: 'info'
});
}
async handleError(error: Error, context: ErrorContext): Promise<ToolResult> {
const errorType = this.classifyError(error);
const strategy = this.errorStrategies.get(errorType);
if (!strategy) {
return this.handleUnknownError(error, context);
}
// 记录错误日志
this.logError(error, context, strategy.logLevel);
// 执行错误处理策略
return await strategy.handle(error, context);
}
private handleNetworkError(error: Error, context: ErrorContext): Promise<ToolResult> {
return {
content: [{
type: "text",
text: `网络连接异常,请检查网络设置后重试。错误详情: ${error.message}`
}],
isError: true,
metadata: {
errorType: 'NETWORK_ERROR',
retryable: true,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString()
}
};
}
}2.3 错误恢复机制
"优秀的错误处理不是避免错误,而是优雅地从错误中恢复。" ------ 软件工程最佳实践
python
// 错误恢复管理器
class RecoveryManager {
private recoveryStrategies: Map<string, RecoveryStrategy> = new Map();
constructor() {
this.initializeRecoveryStrategies();
}
private initializeRecoveryStrategies() {
// 自动重试策略
this.recoveryStrategies.set('AUTO_RETRY', {
canRecover: (error) => error.code === 'TEMPORARY_FAILURE',
recover: this.autoRetryRecover.bind(this)
});
// 降级策略
this.recoveryStrategies.set('FALLBACK', {
canRecover: (error) => error.code === 'SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE',
recover: this.fallbackRecover.bind(this)
});
// 缓存策略
this.recoveryStrategies.set('CACHE_FALLBACK', {
canRecover: (error) => error.code === 'DATA_SOURCE_ERROR',
recover: this.cacheRecover.bind(this)
});
}
async attemptRecovery(error: Error, context: RecoveryContext): Promise<ToolResult | null> {
for (const [name, strategy] of this.recoveryStrategies) {
if (strategy.canRecover(error)) {
try {
const result = await strategy.recover(error, context);
if (result) {
console.log(`错误恢复成功,使用策略: ${name}`);
return result;
}
} catch (recoveryError) {
console.warn(`恢复策略 ${name} 执行失败:`, recoveryError);
}
}
}
return null; // 无法恢复
}
}3. 异步工具调用与性能优化
3.1 异步调用模式设计
现代MCP工具必须支持异步调用以提高系统整体性能。以下是几种主要的异步调用模式:
python
// 异步工具调用管理器
class AsyncToolManager {
private executionPool: Map<string, Promise<ToolResult>> = new Map();
private concurrencyLimit: number = 10;
private semaphore: Semaphore;
constructor(concurrencyLimit: number = 10) {
this.concurrencyLimit = concurrencyLimit;
this.semaphore = new Semaphore(concurrencyLimit);
}
// 并发执行多个工具
async executeParallel(toolCalls: ToolCall[]): Promise<ToolResult[]> {
const promises = toolCalls.map(async (call) => {
await this.semaphore.acquire();
try {
return await this.executeSingleTool(call);
} finally {
this.semaphore.release();
}
});
return Promise.all(promises);
}
// 流水线执行工具链
async executePipeline(toolChain: ToolCall[]): Promise<ToolResult> {
let currentResult: ToolResult | null = null;
for (const toolCall of toolChain) {
// 将前一个工具的输出作为当前工具的输入
if (currentResult) {
toolCall.params = this.mergeParams(toolCall.params, currentResult);
}
currentResult = await this.executeSingleTool(toolCall);
// 如果某个工具执行失败,中断流水线
if (currentResult.isError) {
break;
}
}
return currentResult!;
}
// 条件执行工具
async executeConditional(
condition: ConditionFunction,
trueTool: ToolCall,
falseTool?: ToolCall
): Promise<ToolResult> {
const shouldExecuteTrue = await condition();
const toolToExecute = shouldExecuteTrue ? trueTool : falseTool;
if (!toolToExecute) {
return {
content: [{
type: "text",
text: "条件不满足,跳过工具执行"
}]
};
}
return this.executeSingleTool(toolToExecute);
}
}3.2 性能优化策略
|----------|-------------|--------|-------|
| 优化策略 | 适用场景 | 性能提升 | 实现复杂度 |
| 缓存机制 | 重复调用相同参数的工具 | 80-95% | 中等 |
| 连接池 | 频繁的数据库或网络操作 | 60-80% | 中等 |
| 批量处理 | 大量相似的小任务 | 70-90% | 低 |
| 预加载 | 可预测的资源需求 | 50-70% | 高 |
| 懒加载 | 按需加载大型资源 | 40-60% | 中等 |
python
// 性能优化工具包装器
class OptimizedToolWrapper {
private cache: LRUCache<string, ToolResult>;
private connectionPool: ConnectionPool;
private batchProcessor: BatchProcessor;
constructor(tool: MCPTool, options: OptimizationOptions) {
this.cache = new LRUCache({
max: options.cacheSize || 1000,
ttl: options.cacheTTL || 300000 // 5分钟
});
this.connectionPool = new ConnectionPool({
min: options.minConnections || 2,
max: options.maxConnections || 10
});
this.batchProcessor = new BatchProcessor({
batchSize: options.batchSize || 50,
flushInterval: options.flushInterval || 1000
});
}
async execute(params: any, context: MCPContext): Promise<ToolResult> {
// 1. 检查缓存
const cacheKey = this.generateCacheKey(params);
const cachedResult = this.cache.get(cacheKey);
if (cachedResult && this.isCacheValid(cachedResult, context)) {
return cachedResult;
}
// 2. 批量处理优化
if (this.canBatch(params)) {
return this.batchProcessor.add(params, context);
}
// 3. 连接池优化
const connection = await this.connectionPool.acquire();
try {
const result = await this.executeWithConnection(params, context, connection);
// 4. 缓存结果
if (this.shouldCache(result)) {
this.cache.set(cacheKey, result);
}
return result;
} finally {
this.connectionPool.release(connection);
}
}
private generateCacheKey(params: any): string {
return crypto
.createHash('sha256')
.update(JSON.stringify(params))
.digest('hex');
}
}3.3 监控与性能分析
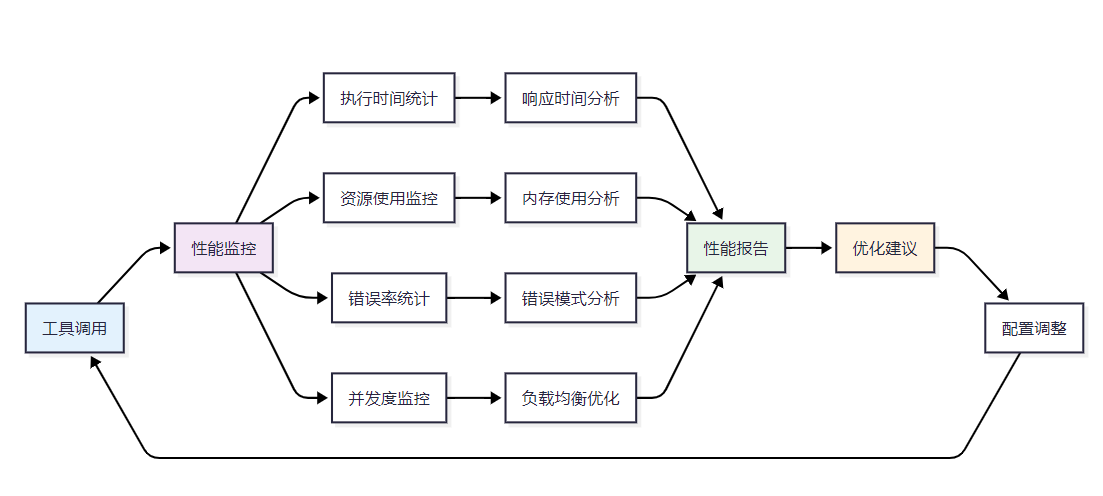
图3 MCP工具性能监控体系架构图
python
// 性能监控器
class PerformanceMonitor {
private metrics: Map<string, ToolMetrics> = new Map();
private alertThresholds: AlertThresholds;
constructor(thresholds: AlertThresholds) {
this.alertThresholds = thresholds;
}
startMonitoring(toolName: string, params: any): MonitoringSession {
const session = new MonitoringSession(toolName, params);
session.start();
return session;
}
recordExecution(session: MonitoringSession, result: ToolResult): void {
session.end();
const toolName = session.toolName;
const metrics = this.metrics.get(toolName) || new ToolMetrics(toolName);
// 更新性能指标
metrics.addExecution({
duration: session.duration,
success: !result.isError,
memoryUsage: session.memoryUsage,
timestamp: session.startTime
});
this.metrics.set(toolName, metrics);
// 检查性能阈值
this.checkThresholds(toolName, metrics);
}
private checkThresholds(toolName: string, metrics: ToolMetrics): void {
const avgResponseTime = metrics.getAverageResponseTime();
const errorRate = metrics.getErrorRate();
if (avgResponseTime > this.alertThresholds.maxResponseTime) {
this.triggerAlert('HIGH_RESPONSE_TIME', {
toolName,
currentValue: avgResponseTime,
threshold: this.alertThresholds.maxResponseTime
});
}
if (errorRate > this.alertThresholds.maxErrorRate) {
this.triggerAlert('HIGH_ERROR_RATE', {
toolName,
currentValue: errorRate,
threshold: this.alertThresholds.maxErrorRate
});
}
}
generatePerformanceReport(): PerformanceReport {
const report = new PerformanceReport();
for (const [toolName, metrics] of this.metrics) {
report.addToolReport({
toolName,
totalExecutions: metrics.getTotalExecutions(),
averageResponseTime: metrics.getAverageResponseTime(),
errorRate: metrics.getErrorRate(),
throughput: metrics.getThroughput(),
recommendations: this.generateRecommendations(metrics)
});
}
return report;
}
}4. 工具组合与链式调用实现
4.1 工具组合设计模式
工具组合是MCP生态系统中的高级特性,允许将多个简单工具组合成复杂的工作流。
python
// 工具组合器接口
interface ToolComposer {
compose(tools: MCPTool[], composition: CompositionStrategy): ComposedTool;
}
// 组合策略枚举
enum CompositionStrategy {
SEQUENTIAL = 'sequential', // 顺序执行
PARALLEL = 'parallel', // 并行执行
CONDITIONAL = 'conditional', // 条件执行
PIPELINE = 'pipeline', // 流水线执行
TREE = 'tree' // 树形执行
}
// 组合工具实现
class ComposedTool implements MCPTool {
name: string;
description: string;
inputSchema: JSONSchema;
private tools: MCPTool[];
private strategy: CompositionStrategy;
private executor: CompositionExecutor;
constructor(
tools: MCPTool[],
strategy: CompositionStrategy,
metadata: CompositionMetadata
) {
this.tools = tools;
this.strategy = strategy;
this.name = metadata.name;
this.description = metadata.description;
this.inputSchema = this.generateComposedSchema(tools);
this.executor = CompositionExecutorFactory.create(strategy);
}
async handler(params: any, context: MCPContext): Promise<ToolResult> {
try {
// 验证组合工具的输入参数
const validationResult = this.validateComposedParams(params);
if (!validationResult.isValid) {
return this.createErrorResult(validationResult.errors);
}
// 执行工具组合
const result = await this.executor.execute(
this.tools,
params,
context
);
return result;
} catch (error) {
return this.handleCompositionError(error, context);
}
}
private generateComposedSchema(tools: MCPTool[]): JSONSchema {
// 合并所有工具的输入模式
const properties: Record<string, any> = {};
const required: string[] = [];
tools.forEach((tool, index) => {
const toolPrefix = `tool_${index}_`;
if (tool.inputSchema.properties) {
Object.entries(tool.inputSchema.properties).forEach(([key, value]) => {
properties[`${toolPrefix}${key}`] = value;
});
}
if (tool.inputSchema.required) {
tool.inputSchema.required.forEach(key => {
required.push(`${toolPrefix}${key}`);
});
}
});
return {
type: "object",
properties,
required
};
}
}4.2 链式调用执行器
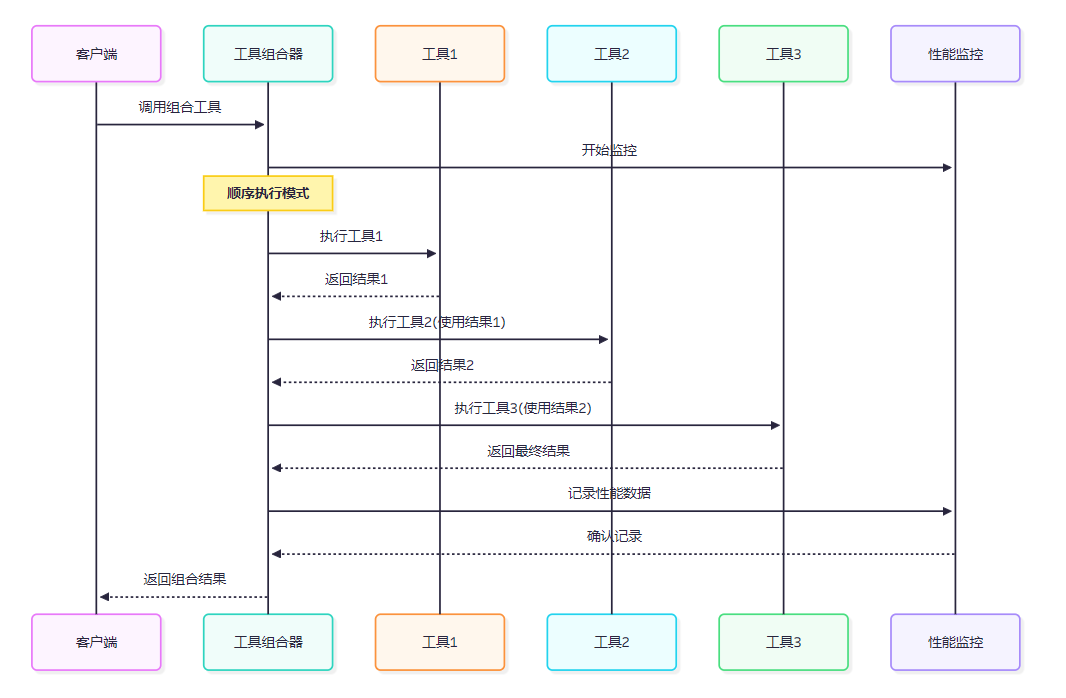
图4 MCP工具链式调用执行序列图
python
// 链式调用执行器
class ChainExecutor implements CompositionExecutor {
async execute(
tools: MCPTool[],
params: any,
context: MCPContext
): Promise<ToolResult> {
const executionChain = new ExecutionChain();
let currentResult: ToolResult | null = null;
for (let i = 0; i < tools.length; i++) {
const tool = tools[i];
const toolParams = this.extractToolParams(params, i);
// 如果不是第一个工具,将前一个工具的输出合并到当前参数中
if (currentResult && i > 0) {
toolParams = this.mergeWithPreviousResult(toolParams, currentResult);
}
// 创建执行节点
const node = new ExecutionNode(tool, toolParams, context);
executionChain.addNode(node);
try {
// 执行当前工具
currentResult = await tool.handler(toolParams, context);
// 记录执行结果
node.setResult(currentResult);
// 如果工具执行失败,中断链式调用
if (currentResult.isError) {
break;
}
} catch (error) {
// 处理工具执行异常
currentResult = {
content: [{
type: "text",
text: `工具 ${tool.name} 执行失败: ${error.message}`
}],
isError: true
};
node.setResult(currentResult);
break;
}
}
return currentResult || {
content: [{
type: "text",
text: "工具链执行完成,但未产生结果"
}],
isError: true
};
}
private extractToolParams(params: any, toolIndex: number): any {
const toolPrefix = `tool_${toolIndex}_`;
const toolParams: any = {};
Object.entries(params).forEach(([key, value]) => {
if (key.startsWith(toolPrefix)) {
const actualKey = key.substring(toolPrefix.length);
toolParams[actualKey] = value;
}
});
return toolParams;
}
private mergeWithPreviousResult(params: any, previousResult: ToolResult): any {
// 将前一个工具的输出合并到当前参数中
const mergedParams = { ...params };
// 如果前一个结果包含JSON数据,将其合并
previousResult.content.forEach(content => {
if (content.type === 'json' && content.data) {
Object.assign(mergedParams, content.data);
}
});
return mergedParams;
}
}4.4 工具组合最佳实践
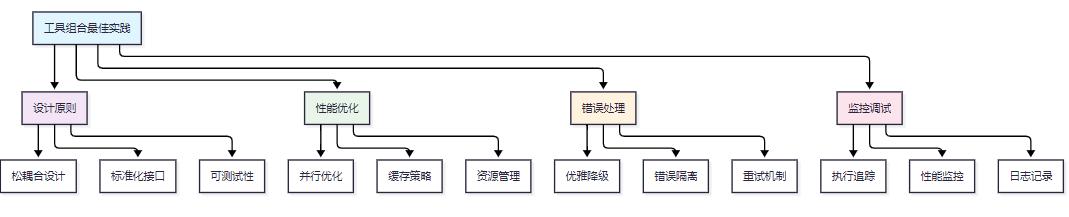
图5 工具组合最佳实践架构图
5. 实战案例:构建智能数据分析工具链
5.1 需求分析与架构设计
让我们通过一个实际案例来展示MCP工具开发的完整流程。我们将构建一个智能数据分析工具链,包含数据获取、清洗、分析和可视化四个核心工具。
python
// 数据分析工具链架构
interface DataAnalysisChain {
dataFetcher: DataFetcherTool; // 数据获取工具
dataCleaner: DataCleanerTool; // 数据清洗工具
dataAnalyzer: DataAnalyzerTool; // 数据分析工具
dataVisualizer: DataVisualizerTool; // 数据可视化工具
}
// 数据获取工具实现
class DataFetcherTool implements MCPTool {
name = "data_fetcher";
description = "从各种数据源获取数据";
inputSchema = {
type: "object",
properties: {
source: {
type: "string",
enum: ["database", "api", "file", "stream"],
description: "数据源类型"
},
config: {
type: "object",
description: "数据源配置信息"
},
query: {
type: "string",
description: "查询条件或SQL语句"
}
},
required: ["source", "config"]
};
async handler(params: any, context: MCPContext): Promise<ToolResult> {
const { source, config, query } = params;
try {
let data;
switch (source) {
case "database":
data = await this.fetchFromDatabase(config, query);
break;
case "api":
data = await this.fetchFromAPI(config, query);
break;
case "file":
data = await this.fetchFromFile(config);
break;
case "stream":
data = await this.fetchFromStream(config);
break;
default:
throw new Error(`不支持的数据源类型: ${source}`);
}
return {
content: [{
type: "text",
text: `成功获取 ${data.length} 条数据记录`
}, {
type: "json",
data: {
records: data,
metadata: {
source,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString(),
count: data.length
}
}
}]
};
} catch (error) {
return {
content: [{
type: "text",
text: `数据获取失败: ${error.message}`
}],
isError: true
};
}
}
private async fetchFromDatabase(config: any, query: string): Promise<any[]> {
// 实现数据库查询逻辑
const connection = await this.createDatabaseConnection(config);
const result = await connection.query(query);
await connection.close();
return result.rows;
}
private async fetchFromAPI(config: any, query?: string): Promise<any[]> {
// 实现API调用逻辑
const url = query ? `${config.endpoint}?${query}` : config.endpoint;
const response = await fetch(url, {
headers: config.headers || {},
method: config.method || 'GET'
});
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error(`API调用失败: ${response.status} ${response.statusText}`);
}
const data = await response.json();
return Array.isArray(data) ? data : [data];
}
}5.2 数据清洗工具实现
// 数据清洗工具
class DataCleanerTool implements MCPTool {
name = "data_cleaner";
description = "清洗和预处理数据";
inputSchema = {
type: "object",
properties: {
records: {
type: "array",
description: "待清洗的数据记录"
},
rules: {
type: "array",
items: {
type: "object",
properties: {
type: {
type: "string",
enum: ["remove_null", "remove_duplicates", "normalize", "validate", "transform"]
},
field: { type: "string" },
config: { type: "object" }
}
},
description: "清洗规则配置"
}
},
required: ["records", "rules"]
};
async handler(params: any, context: MCPContext): Promise<ToolResult> {
const { records, rules } = params;
try {
let cleanedData = [...records];
const cleaningReport = {
originalCount: records.length,
operations: [],
finalCount: 0
};
// 按顺序应用清洗规则
for (const rule of rules) {
const beforeCount = cleanedData.length;
cleanedData = await this.applyCleaningRule(cleanedData, rule);
const afterCount = cleanedData.length;
cleaningReport.operations.push({
type: rule.type,
field: rule.field,
beforeCount,
afterCount,
removedCount: beforeCount - afterCount
});
}
cleaningReport.finalCount = cleanedData.length;
return {
content: [{
type: "text",
text: `数据清洗完成,从 ${cleaningReport.originalCount} 条记录清洗为 ${cleaningReport.finalCount} 条记录`
}, {
type: "json",
data: {
cleanedRecords: cleanedData,
cleaningReport
}
}]
};
} catch (error) {
return {
content: [{
type: "text",
text: `数据清洗失败: ${error.message}`
}],
isError: true
};
}
}
private async applyCleaningRule(data: any[], rule: any): Promise<any[]> {
switch (rule.type) {
case "remove_null":
return data.filter(record =>
rule.field ? record[rule.field] != null :
Object.values(record).every(value => value != null)
);
case "remove_duplicates":
const seen = new Set();
return data.filter(record => {
const key = rule.field ? record[rule.field] : JSON.stringify(record);
if (seen.has(key)) {
return false;
}
seen.add(key);
return true;
});
case "normalize":
return data.map(record => {
if (rule.field && record[rule.field]) {
record[rule.field] = this.normalizeValue(record[rule.field], rule.config);
}
return record;
});
case "validate":
return data.filter(record =>
this.validateRecord(record, rule.field, rule.config)
);
case "transform":
return data.map(record =>
this.transformRecord(record, rule.field, rule.config)
);
default:
throw new Error(`不支持的清洗规则类型: ${rule.type}`);
}
}
}5.3 完整工具链集成
python
// 智能数据分析工具链
class IntelligentDataAnalysisChain {
private tools: Map<string, MCPTool> = new Map();
private executor: ChainExecutor;
private monitor: PerformanceMonitor;
constructor() {
this.initializeTools();
this.executor = new ChainExecutor();
this.monitor = new PerformanceMonitor({
maxResponseTime: 5000,
maxErrorRate: 0.05
});
}
private initializeTools() {
this.tools.set('fetcher', new DataFetcherTool());
this.tools.set('cleaner', new DataCleanerTool());
this.tools.set('analyzer', new DataAnalyzerTool());
this.tools.set('visualizer', new DataVisualizerTool());
}
async executeAnalysis(request: AnalysisRequest): Promise<AnalysisResult> {
const session = this.monitor.startMonitoring('data_analysis_chain', request);
try {
// 构建工具调用链
const toolChain: ToolCall[] = [
{
tool: this.tools.get('fetcher')!,
params: request.dataSource
},
{
tool: this.tools.get('cleaner')!,
params: request.cleaningRules
},
{
tool: this.tools.get('analyzer')!,
params: request.analysisConfig
},
{
tool: this.tools.get('visualizer')!,
params: request.visualizationConfig
}
];
// 执行工具链
const result = await this.executor.executePipeline(toolChain);
this.monitor.recordExecution(session, result);
return this.formatAnalysisResult(result);
} catch (error) {
const errorResult: ToolResult = {
content: [{
type: "text",
text: `分析链执行失败: ${error.message}`
}],
isError: true
};
this.monitor.recordExecution(session, errorResult);
throw error;
}
}
private formatAnalysisResult(result: ToolResult): AnalysisResult {
// 格式化分析结果
const jsonContent = result.content.find(c => c.type === 'json');
return {
success: !result.isError,
data: jsonContent?.data || null,
visualizations: this.extractVisualizations(result),
metadata: result.metadata || {}
};
}
}6. 测试与质量保证
6.1 单元测试框架
python
// MCP工具测试框架
class MCPToolTester {
private testSuites: Map<string, TestSuite> = new Map();
// 注册测试套件
registerTestSuite(toolName: string, suite: TestSuite) {
this.testSuites.set(toolName, suite);
}
// 执行所有测试
async runAllTests(): Promise<TestReport> {
const report = new TestReport();
for (const [toolName, suite] of this.testSuites) {
console.log(`运行 ${toolName} 工具测试...`);
const suiteResult = await this.runTestSuite(toolName, suite);
report.addSuiteResult(toolName, suiteResult);
}
return report;
}
// 执行单个测试套件
private async runTestSuite(toolName: string, suite: TestSuite): Promise<SuiteResult> {
const result = new SuiteResult(toolName);
for (const testCase of suite.testCases) {
try {
const testResult = await this.runTestCase(testCase);
result.addTestResult(testResult);
} catch (error) {
result.addTestResult({
name: testCase.name,
passed: false,
error: error.message,
duration: 0
});
}
}
return result;
}
// 执行单个测试用例
private async runTestCase(testCase: TestCase): Promise<TestResult> {
const startTime = Date.now();
try {
// 准备测试环境
const context = await this.prepareTestContext(testCase);
// 执行工具
const result = await testCase.tool.handler(testCase.params, context);
// 验证结果
const passed = await testCase.validator(result, testCase.expected);
return {
name: testCase.name,
passed,
duration: Date.now() - startTime,
result
};
} catch (error) {
return {
name: testCase.name,
passed: false,
error: error.message,
duration: Date.now() - startTime
};
}
}
}
// 数据处理工具测试示例
describe('DataProcessingTool', () => {
let tool: DataProcessingTool;
let tester: MCPToolTester;
beforeEach(() => {
tool = new DataProcessingTool();
tester = new MCPToolTester();
});
test('should filter data correctly', async () => {
const testCase: TestCase = {
name: 'filter_operation',
tool,
params: {
data: [
{ id: 1, value: 10 },
{ id: 2, value: 20 },
{ id: 3, value: 30 }
],
operation: 'filter'
},
expected: {
filteredCount: 2
},
validator: (result, expected) => {
const jsonContent = result.content.find(c => c.type === 'json');
return jsonContent?.data?.length === expected.filteredCount;
}
};
const result = await tester.runTestCase(testCase);
expect(result.passed).toBe(true);
});
test('should handle invalid operation', async () => {
const testCase: TestCase = {
name: 'invalid_operation',
tool,
params: {
data: [],
operation: 'invalid'
},
expected: {
isError: true
},
validator: (result, expected) => {
return result.isError === expected.isError;
}
};
const result = await tester.runTestCase(testCase);
expect(result.passed).toBe(true);
});
});6.2 集成测试与端到端测试
python
// 工具链集成测试
class ToolChainIntegrationTest {
private chain: IntelligentDataAnalysisChain;
constructor() {
this.chain = new IntelligentDataAnalysisChain();
}
async testCompleteWorkflow(): Promise<void> {
const request: AnalysisRequest = {
dataSource: {
source: 'api',
config: {
endpoint: 'https://api.example.com/data',
headers: { 'Authorization': 'Bearer test-token' }
}
},
cleaningRules: [
{ type: 'remove_null', field: 'value' },
{ type: 'remove_duplicates', field: 'id' }
],
analysisConfig: {
type: 'statistical',
metrics: ['mean', 'median', 'std']
},
visualizationConfig: {
type: 'chart',
chartType: 'line'
}
};
const result = await this.chain.executeAnalysis(request);
// 验证结果
expect(result.success).toBe(true);
expect(result.data).toBeDefined();
expect(result.visualizations).toHaveLength(1);
}
async testErrorHandling(): Promise<void> {
const invalidRequest: AnalysisRequest = {
dataSource: {
source: 'invalid',
config: {}
},
cleaningRules: [],
analysisConfig: {},
visualizationConfig: {}
};
try {
await this.chain.executeAnalysis(invalidRequest);
fail('应该抛出错误');
} catch (error) {
expect(error).toBeDefined();
}
}
}7. 部署与运维
7.1 生产环境部署
python
// MCP工具服务器部署配置
class MCPToolServerDeployment {
private server: MCPServer;
private config: DeploymentConfig;
private healthChecker: HealthChecker;
constructor(config: DeploymentConfig) {
this.config = config;
this.server = new MCPServer(config.serverConfig);
this.healthChecker = new HealthChecker();
this.setupDeployment();
}
private setupDeployment() {
// 注册工具
this.registerTools();
// 设置健康检查
this.setupHealthCheck();
// 配置监控
this.setupMonitoring();
// 设置日志
this.setupLogging();
}
private registerTools() {
const tools = [
new DataProcessingTool(),
new DataFetcherTool(),
new DataCleanerTool(),
new DataAnalyzerTool(),
new DataVisualizerTool()
];
tools.forEach(tool => {
this.server.registerTool(tool);
});
}
private setupHealthCheck() {
this.server.addHealthCheck('tools', async () => {
const toolCount = this.server.getRegisteredToolCount();
return {
status: toolCount > 0 ? 'healthy' : 'unhealthy',
details: { registeredTools: toolCount }
};
});
this.server.addHealthCheck('database', async () => {
try {
await this.testDatabaseConnection();
return { status: 'healthy' };
} catch (error) {
return {
status: 'unhealthy',
error: error.message
};
}
});
}
async start(): Promise<void> {
try {
await this.server.start();
console.log(`MCP工具服务器已启动,端口: ${this.config.port}`);
// 启动健康检查
this.healthChecker.start();
} catch (error) {
console.error('服务器启动失败:', error);
throw error;
}
}
async stop(): Promise<void> {
await this.healthChecker.stop();
await this.server.stop();
console.log('MCP工具服务器已停止');
}
}7.2 监控与告警
python
// 监控告警系统
class MonitoringAlertSystem {
private metrics: MetricsCollector;
private alertManager: AlertManager;
private dashboard: MonitoringDashboard;
constructor() {
this.metrics = new MetricsCollector();
this.alertManager = new AlertManager();
this.dashboard = new MonitoringDashboard();
this.setupAlerts();
}
private setupAlerts() {
// 响应时间告警
this.alertManager.addRule({
name: 'high_response_time',
condition: (metrics) => metrics.avgResponseTime > 1000,
severity: 'warning',
message: '工具响应时间过高',
actions: ['email', 'slack']
});
// 错误率告警
this.alertManager.addRule({
name: 'high_error_rate',
condition: (metrics) => metrics.errorRate > 0.05,
severity: 'critical',
message: '工具错误率过高',
actions: ['email', 'slack', 'pagerduty']
});
// 资源使用告警
this.alertManager.addRule({
name: 'high_memory_usage',
condition: (metrics) => metrics.memoryUsage > 0.85,
severity: 'warning',
message: '内存使用率过高',
actions: ['email']
});
}
async collectAndAnalyze(): Promise<void> {
const metrics = await this.metrics.collect();
// 检查告警条件
await this.alertManager.checkRules(metrics);
// 更新仪表板
await this.dashboard.update(metrics);
}
}总结
经过这篇深入的MCP工具开发实战指南,我作为博主摘星想要与读者分享一些重要的思考和经验总结。MCP工具开发绝不仅仅是简单的编程实现,它代表了AI应用架构设计的一次重要革新,体现了从单体应用向模块化、可组合系统的演进趋势。通过本文的详细阐述,我们可以看到MCP工具开发涉及多个技术层面的深度整合:从基础的参数验证和错误处理,到复杂的异步调用优化和性能监控,再到高级的工具组合和链式调用实现,每一个环节都需要开发者具备扎实的技术功底和系统性思维。在实际项目实践中,我发现最关键的成功因素不是单个工具的功能强大程度,而是整个工具生态系统的协调性和可扩展性。优秀的MCP工具应该具备良好的单一职责设计、健壮的错误处理机制、高效的性能表现,以及与其他工具无缝协作的能力。特别值得强调的是,随着AI技术的快速发展和应用场景的不断扩展,MCP工具开发正在成为AI工程师必备的核心技能之一。掌握这项技术不仅能够帮助开发者构建更加智能、灵活的AI应用,更重要的是能够为AI系统注入真正的"超能力",让智能体能够与现实世界进行更加深入、有效的交互。我相信,通过持续的学习和实践,每一位开发者都能够在MCP工具开发领域找到属于自己的技术突破点,为推动AI技术的普及和应用贡献自己的力量。
参考资源
本文由博主摘星原创,专注于AI技术前沿探索。如需转载请注明出处,技术交流欢迎关注我的技术博客。
🌈我是摘星!如果这篇文章在你的技术成长路上留下了印记:
👁️*【关注】与我一起探索技术的无限可能,见证每一次突破*
👍*【点赞】为优质技术内容点亮明灯,传递知识的力量*
🔖*【收藏】将精华内容珍藏,随时回顾技术要点*
💬*【评论】分享你的独特见解,让思维碰撞出智慧火花*
🗳️*【投票】用你的选择为技术社区贡献一份力量*
技术路漫漫,让我们携手前行,在代码的世界里摘取属于程序员的那片星辰大海!