一、概述
本文将深入剖析SpringBoot启动原理,揭示ServletContainerInitializer如何配合@HandlesTypes及SpringBootServletInitializer,实现应用启动。从SPI机制到容器初始化,全面解读。
二、初始化流程
2.1初始化容器
当SpringBoot项目启动以后,启动类型为web Application类型并引入相关web模块后。会启动一个Servlet容器,容器启动以后将去扫描每个jar包的ServletContainerInitializer的实现。
根据servlet开发规范,ServletContainerInitializer接口的实现类,必须在META-INF/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer文件里面进行声明,声明的内容就是实现ServletContainerInitializer接口的全类名。(该声明使用的)
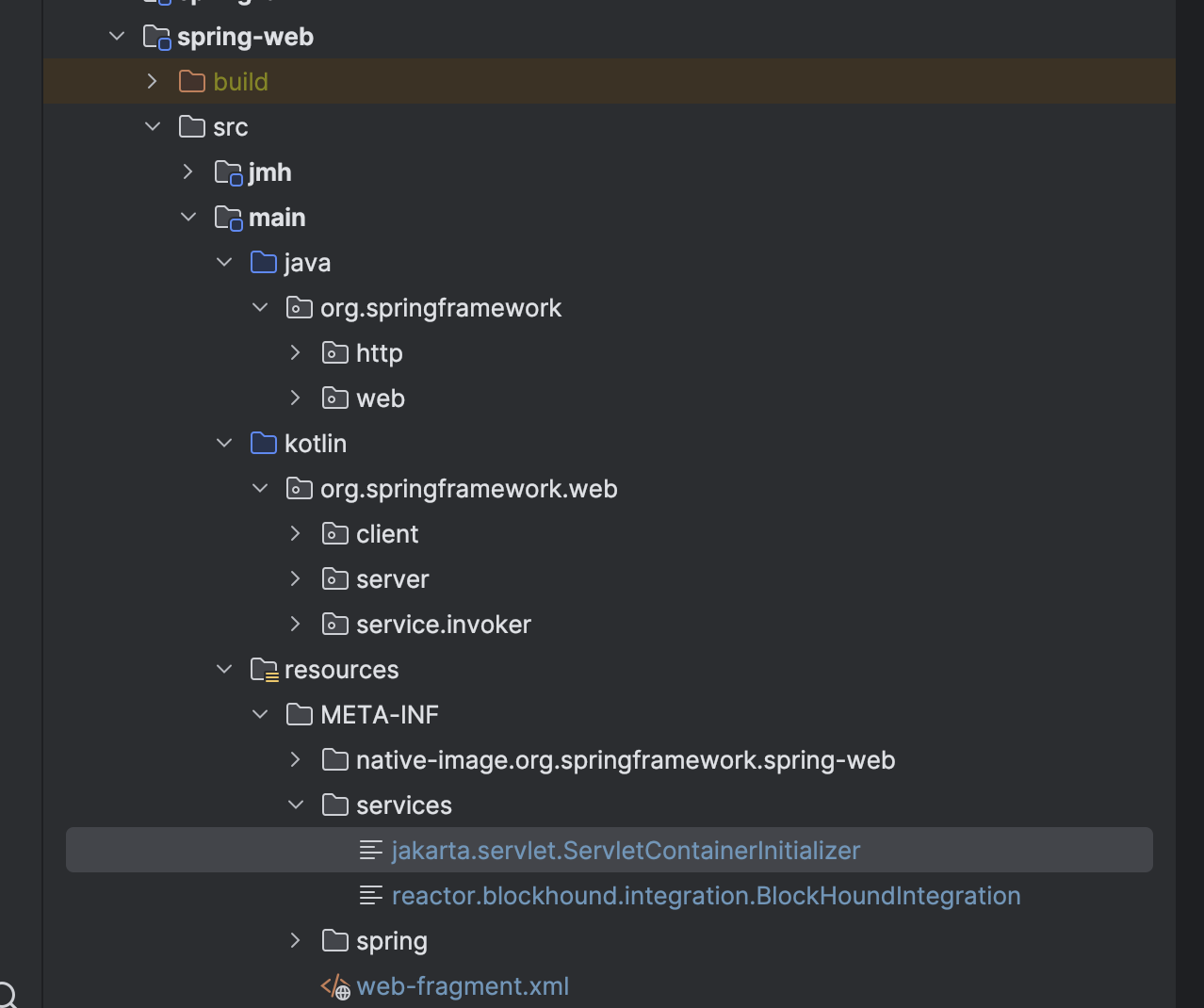
如上图,Spring 6.0x 的声明是在spring-web模块下。其ServletContainerInitializer的实现类为org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer。
java
@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)
public class SpringServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(@Nullable Set<Class<?>> webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext)
throws ServletException {
List<WebApplicationInitializer> initializers = Collections.emptyList();
if (webAppInitializerClasses != null) {
initializers = new ArrayList<>(webAppInitializerClasses.size());
for (Class<?> waiClass : webAppInitializerClasses) {
// Be defensive: Some servlet containers provide us with invalid classes,
// no matter what @HandlesTypes says...
if (!waiClass.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(waiClass.getModifiers()) &&
WebApplicationInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(waiClass)) {
try {
initializers.add((WebApplicationInitializer)
ReflectionUtils.accessibleConstructor(waiClass).newInstance());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate WebApplicationInitializer class", ex);
}
}
}
}
if (initializers.isEmpty()) {
servletContext.log("No Spring WebApplicationInitializer types detected on classpath");
return;
}
servletContext.log(initializers.size() + " Spring WebApplicationInitializers detected on classpath");
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(initializers);
for (WebApplicationInitializer initializer : initializers) {
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
}可以看到 SpringServletContainerInitializer 重写了,onStartup()方法。其中第一个参数传入的是 类上@HandlesTypes 注解的值即 WebApplicationInitializer.class。
拿到WebApplicationInitializer 之后 获取到其实现类并始终反射原理对实现类进行初始化。
根据源码,我们找到了其实现类 有四个。我们重点查看AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer 它是用来初始化 DispatcherServlet的。
看到onStartup()-> registerDispatcherServlet()方法,
java
protected void registerDispatcherServlet(ServletContext servletContext) {
String servletName = getServletName();
Assert.state(StringUtils.hasLength(servletName), "getServletName() must not return null or empty");
WebApplicationContext servletAppContext = createServletApplicationContext();
Assert.state(servletAppContext != null, "createServletApplicationContext() must not return null");
FrameworkServlet dispatcherServlet = createDispatcherServlet(servletAppContext);
Assert.state(dispatcherServlet != null, "createDispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext) must not return null");
dispatcherServlet.setContextInitializers(getServletApplicationContextInitializers());
ServletRegistration.Dynamic registration = servletContext.addServlet(servletName, dispatcherServlet);
if (registration == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to register servlet with name '" + servletName + "'. " +
"Check if there is another servlet registered under the same name.");
}
registration.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registration.addMapping(getServletMappings());
registration.setAsyncSupported(isAsyncSupported());
Filter[] filters = getServletFilters();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(filters)) {
for (Filter filter : filters) {
registerServletFilter(servletContext, filter);
}
}
customizeRegistration(registration);
}该方法创建了dispatcherServlet,并将其注册到容器中。
2.2 dispatcherServlet的初始化
由于 DispatcherServlet继承 FrameworkServlet,FrameworkServlet继承HttpServletBean,而 HttpServletBean 实际是一个 HttpServlet 对象。所以在DispatcherServlet对象被创建时,实际上是创建了一个 HttpServlet 对象。
我们在 AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer类的createDispatcherServlet()中看到其创建了一个 DispatcherServlet对象。
java
protected FrameworkServlet createDispatcherServlet(WebApplicationContext servletAppContext) {
return new DispatcherServlet(servletAppContext);
}当HttpServlet对象被容器创建是,就会执行 init()方法,如源码中 HttpServletBean 的init()方法。
java
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
initServletBean();
}该方法初始化配置了servlet参数,而其中initServletBean() 方法则由其子类FrameworkServlet实现。
java
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Initializing Servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String value = this.enableLoggingRequestDetails ?
"shown which may lead to unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data" :
"masked to prevent unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data";
logger.debug("enableLoggingRequestDetails='" + this.enableLoggingRequestDetails +
"': request parameters and headers will be " + value);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Completed initialization in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + " ms");
}
}该方法中的 this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext(); 作用为初始化上下文,
java
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac && !cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}根据业务逻辑代码将进入 configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac)方法。
java
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
if (this.contextId != null) {
wac.setId(this.contextId);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(getServletContext().getContextPath()) + '/' + getServletName());
}
}
wac.setServletContext(getServletContext());
wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
wac.setNamespace(getNamespace());
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment cwe) {
cwe.initPropertySources(getServletContext(), getServletConfig());
}
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);
applyInitializers(wac);
wac.refresh();
}该方法除了设置setServletConfig之外,还注册了一个 事件监听器,wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
java
/**
* ApplicationListener endpoint that receives events from this servlet's WebApplicationContext
* only, delegating to {@code onApplicationEvent} on the FrameworkServlet instance.
*/
private class ContextRefreshListener implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
FrameworkServlet.this.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
}该监听器用于监听spring上下文刷新时间,等SpringIoc容器初始化完成,发送上下文刷新事件后。对应的Listener方法接收到以后,就会执行onRefresh()方法。
java
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
this.refreshEventReceived = true;
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
onRefresh(event.getApplicationContext());
}
}onRefresh(ApplicationContext context)的具体实现在DispatcherServlet 类中,
java
/**
* This implementation calls {@link #initStrategies}.
*/
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
/**
* Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses.
* <p>May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects.
*/
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}这时将开始对DispatcherServlet的初始化,
initMultipartResolver(context); // 初始化文件上传解析器
initLocaleResolver(context); // 初始化国际化解析器
initThemeResolver(context); // 初始化主题解析器
initHandlerMappings(context); // 初始化处理器映射器
initHandlerAdapters(context); // 初始化处理器适配器
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); // 初始化异常解析器
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context); // 初始化视图名称翻译器
initViewResolvers(context); // 初始化视图解析器
initFlashMapManager(context); // 初始化FlashMap管理器
initStrategies()里面的初始化流程比较长,将再下一章节再详细讲解。
三、结尾
本文只是对SpringMVC在SpringBoot的注解模式下如何整合初始化的流程作讲解,如有不对的地方,欢迎指正相互学习。