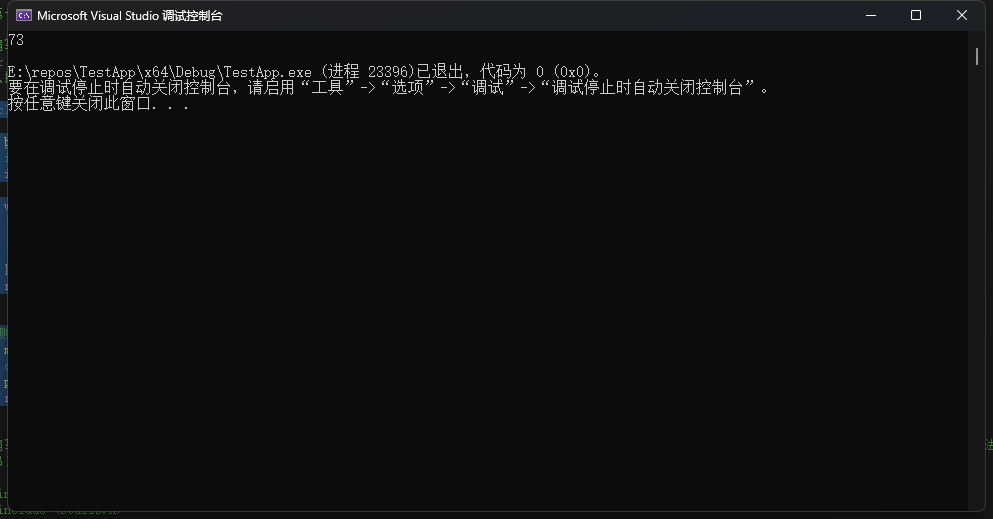
1.编写一个函数,把二进制字符串转换为一个数值。例如,有下面的语句:
char * pbin = "01001001";
那么把pbin作为参数传递给该函数后,它应该返回一个int 类型的值73。
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
int bin_to_int(const char* pbin) {
int result = 0;
if (pbin == NULL) return 0; // 处理空指针
while (*pbin != '\0') {
// 左移当前结果并叠加新位
result = (result << 1) + (*pbin - '0');
pbin++;
}
return result;
}
// 测试示例
int main() {
const char* pbin = "01001001";
printf("%d\n", bin_to_int(pbin)); // 输出:73
return 0;
}
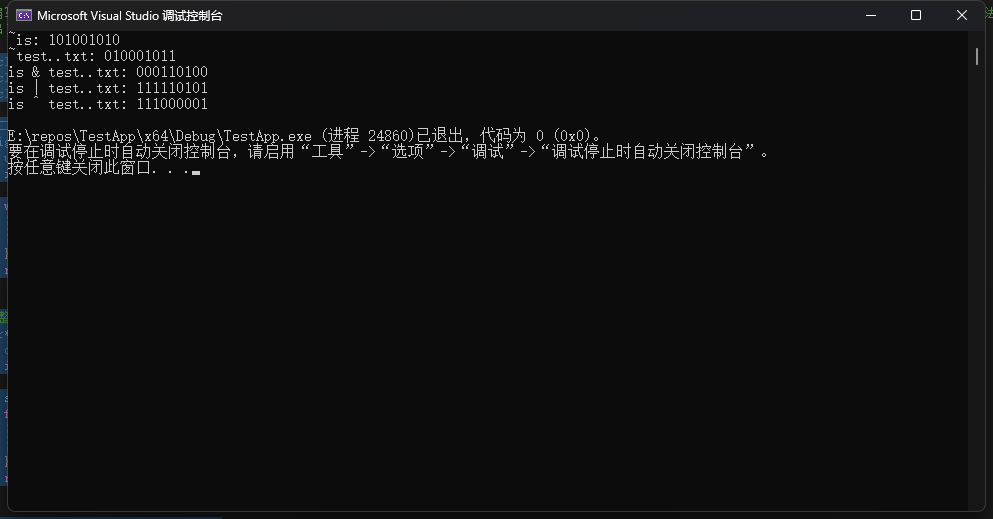
2.编写一个程序,通过命令行参数读取两个二进制字符串,对这两个二进州数使用~运算你、&运算徐、|运算符和^运算行,并以二进制字符串形式打印结果(如果无法使用命令行环境,可以通过交互式让程序读取字符串)。
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
// 二进制字符串转整数
unsigned int bin_to_int(const char* pbin) {
unsigned int result = 0;
if (pbin == NULL) return 0;
while (*pbin != '\0') {
result = (result << 1) + (*pbin - '0');
pbin++;
}
return result;
}
// 整数转二进制字符串
char* int_to_bin(unsigned int num, int bits) {
char* str = (char*)malloc(bits + 1);
if (str == NULL) return NULL;
str[bits] = '\0';
for (int i = bits - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
str[i] = (num & 1) ? '1' : '0';
num >>= 1;
}
return str;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
if (argc != 3) {
printf("Usage: %s <binary_str1> <binary_str2>\n", argv[0]);
printf("Example: %s 01001001 00101110\n", argv[0]);
return 1;
}
char* bin_str1 = argv[1];
char* bin_str2 = argv[2];
// 确定最大位数
size_t len1 = strlen(bin_str1);
size_t len2 = strlen(bin_str2);
int max_bits = (len1 > len2) ? (int)len1 : (int)len2;
// 转换为整数
unsigned int num1 = bin_to_int(bin_str1);
unsigned int num2 = bin_to_int(bin_str2);
// 执行位运算
unsigned int not1 = ~num1;
unsigned int not2 = ~num2;
unsigned int and_result = num1 & num2;
unsigned int or_result = num1 | num2;
unsigned int xor_result = num1 ^ num2;
// 转换为二进制字符串
char* not1_str = int_to_bin(not1, max_bits);
char* not2_str = int_to_bin(not2, max_bits);
char* and_str = int_to_bin(and_result, max_bits);
char* or_str = int_to_bin(or_result, max_bits);
char* xor_str = int_to_bin(xor_result, max_bits);
// 打印结果(只显示有效位)
printf("~%s: %s\n", bin_str1, not1_str + (strlen(not1_str) - max_bits));
printf("~%s: %s\n", bin_str2, not2_str + (strlen(not2_str) - max_bits));
printf("%s & %s: %s\n", bin_str1, bin_str2, and_str);
printf("%s | %s: %s\n", bin_str1, bin_str2, or_str);
printf("%s ^ %s: %s\n", bin_str1, bin_str2, xor_str);
// 清理内存
free(not1_str);
free(not2_str);
free(and_str);
free(or_str);
free(xor_str);
return 0;
}
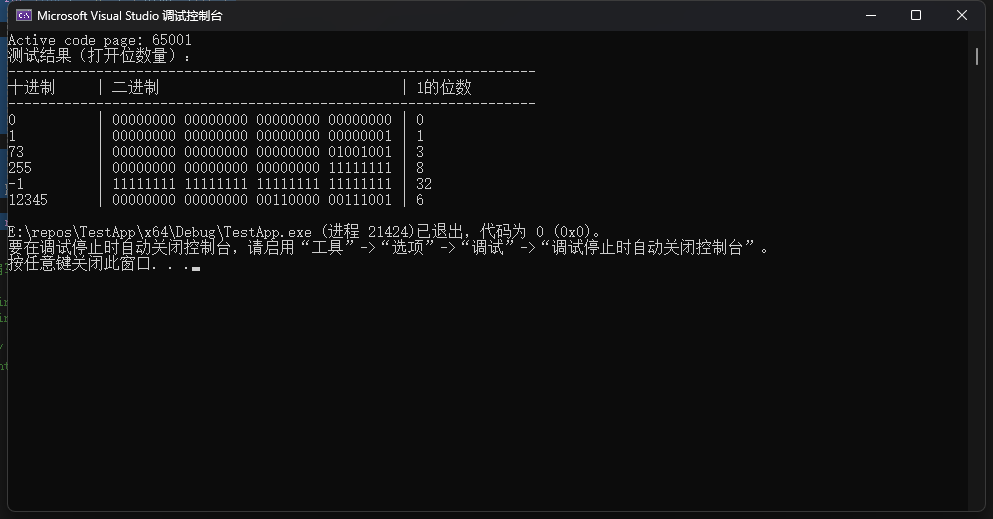
3.编写一个函数,接受一个 int 类型的参数,并返回该参数中打开位的数量。在一个程序中测试该函数。
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
// 计算整数中1的位数(打开位数量)
int count_bits(int num) {
int count = 0;
unsigned int unum = (unsigned int)num;
while (unum) {
count++;
unum &= (unum - 1); // 清除最低位的1
}
return count;
}
int main() {
system("chcp 65001");
int test_numbers[] = { 0, 1, 73, 255, -1, 12345 };
int size = sizeof(test_numbers) / sizeof(test_numbers[0]);
printf("测试结果(打开位数量):\n");
printf("------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
printf("%-13s | %-38s | %s\n", "十进制", "二进制", "1的位数");
printf("------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int num = test_numbers[i];
// 打印二进制表示(简单实现)
printf("%-10d | ", num);
for (int j = sizeof(int) * 8 - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
putchar((num >> j) & 1 ? '1' : '0');
if (j % 8 == 0 && j > 0) putchar(' ');
}
// 使用优化版本计算结果
printf(" | %d\n", count_bits(num));
}
return 0;
}
4.编写一个程序,按受两个 int 类型的参数:一个是值:一个是位的位置。如果指定位的位置为1,该函数返回1;否则返回0。在一个程序中测试该函数。
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <limits.h>
// 检查指定位是否为1
int check_bit(int value, int position) {
// 验证位置有效性
if (position < 0 || position >= (int)(sizeof(int) * CHAR_BIT)) {
printf("错误:位位置 %d 超出范围 (0-%d)\n", position, (int)(sizeof(int) * CHAR_BIT - 1));
return 0;
}
// 创建掩码并检查位状态
return (value & (1 << position)) ? 1 : 0;
}
// 打印整数的二进制表示
void print_binary(int num) {
for (int i = sizeof(int) * CHAR_BIT - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
putchar((num >> i) & 1 ? '1' : '0');
if (i > 0 && i % 8 == 0) putchar(' ');
}
}
int main() {
system("chcp 65001");
// 测试用例数组:{测试值, 测试位位置}
int tests[][2] = {
{0b10101010, 0}, // 位0:0
{0b10101010, 1}, // 位1:1
{0b10101010, 3}, // 位3:0
{0b10101010, 7}, // 位7:1
{255, 0}, // 最低位:1
{255, 7}, // 最高位(8位):1
{12345, 0}, // 12345的最低位
{12345, 13}, // 12345的第13位
{-1, 0}, // 负数测试:最低位
{-1, 31} // 负数测试:最高位(32位系统)
};
int num_tests = sizeof(tests) / sizeof(tests[0]);
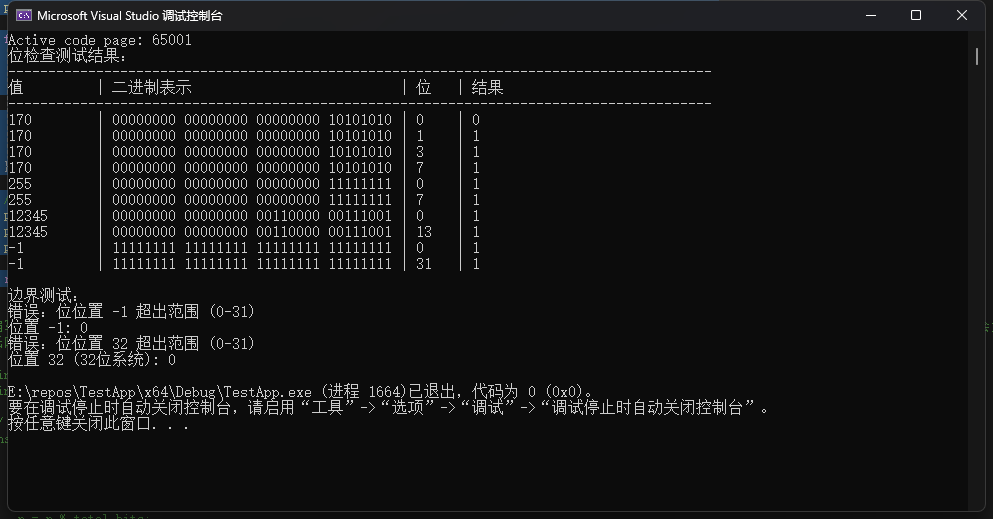
printf("位检查测试结果:\n");
printf("----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
printf("%-11s | %-40s | %-5s | %s\n", "值", "二进制表示", "位", "结果");
printf("----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
for (int i = 0; i < num_tests; i++) {
int value = tests[i][0];
int position = tests[i][1];
int result = check_bit(value, position);
printf("%-10d | ", value);
print_binary(value);
printf(" | %-4d | %d\n", position, result);
}
// 边界测试
printf("\n边界测试:\n");
printf("位置 -1: %d\n", check_bit(255, -1));
printf("位置 32 (32位系统): %d\n", check_bit(255, sizeof(int) * CHAR_BIT));
return 0;
}
5.编写一个函数,把一个 unsigned int 类型值中的所有位向左旋转指定数量的位。例如,rotate_1(x,4)把×中所有位向左移动4个位置,而且从最左端移出的位会重新出现在右端。也就是说,把高阶位移出的位放入低阶位。在一个程序中测试该函数。
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <limits.h>
// 循环左移函数
unsigned int rotate_left(unsigned int value, int n) {
// 获取总位数
const int total_bits = sizeof(unsigned int) * CHAR_BIT;
// 处理n为负数或超过总位数的情况
n = n % total_bits;
if (n < 0) n += total_bits; // 将负位移转换为正位移
// 执行循环左移
return (value << n) | (value >> (total_bits - n));
}
// 打印无符号整数的二进制表示
void print_binary(unsigned int num) {
for (int i = sizeof(unsigned int) * CHAR_BIT - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
putchar((num >> i) & 1 ? '1' : '0');
if (i > 0 && i % 8 == 0) putchar(' ');
}
}
int main() {
system("chcp 65001");
// 测试用例数组:{测试值, 位移数}
struct TestCase {
unsigned int value;
int shift;
} tests[] = {
{0x00000001, 1}, // 1左移1位 → 2
{0x00000001, 31}, // 1左移31位 → 0x80000000
{0x80000000, 1}, // 0x80000000左移1位 → 1
{0x12345678, 4}, // 0x12345678左移4位 → 0x23456781
{0xAAAAAAAA, 1}, // 1010...左移1位 → 0101...
{0x55555555, 31}, // 0101...左移31位 → 1010...
{0x00FF0000, 8}, // 0x00FF0000左移8位 → 0xFF000000
{0x0000FFFF, 16} // 0x0000FFFF左移16位 → 0xFFFF0000
};
int num_tests = sizeof(tests) / sizeof(tests[0]);
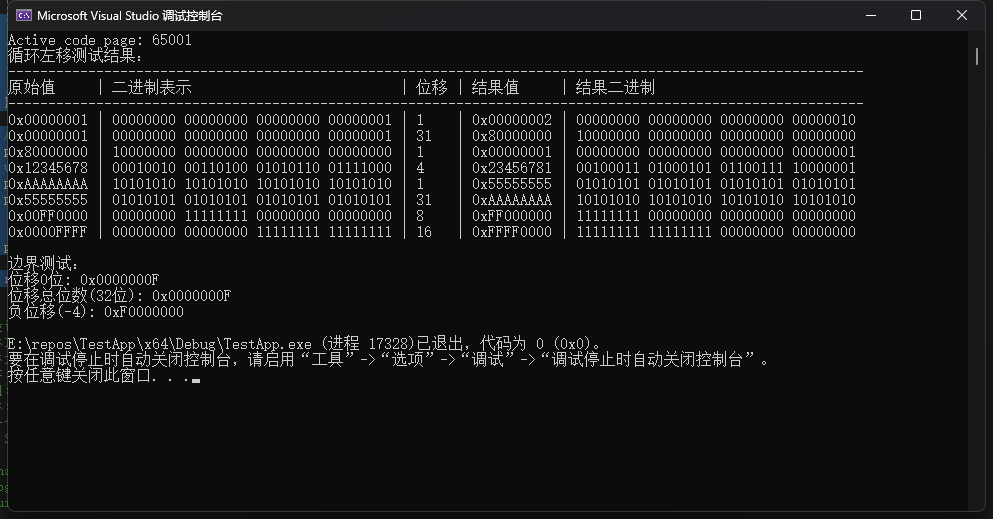
printf("循环左移测试结果:\n");
printf("-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
printf("%-13s | %-40s | %-6s | %-13s | %s\n",
"原始值", "二进制表示", "位移", "结果值", "结果二进制");
printf("-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n");
for (int i = 0; i < num_tests; i++) {
unsigned int value = tests[i].value;
int shift = tests[i].shift;
unsigned int result = rotate_left(value, shift);
printf("0x%08X | ", value);
print_binary(value);
printf(" | %-4d | 0x%08X | ", shift, result);
print_binary(result);
printf("\n");
}
// 边界测试
printf("\n边界测试:\n");
unsigned int test_val = 0x0000000F;
printf("位移0位: 0x%08X\n", rotate_left(test_val, 0));
printf("位移总位数(%d位): 0x%08X\n",
(int)(sizeof(unsigned int) * CHAR_BIT),
rotate_left(test_val, sizeof(unsigned int) * CHAR_BIT));
printf("负位移(-4): 0x%08X\n", rotate_left(test_val, -4));
return 0;
}
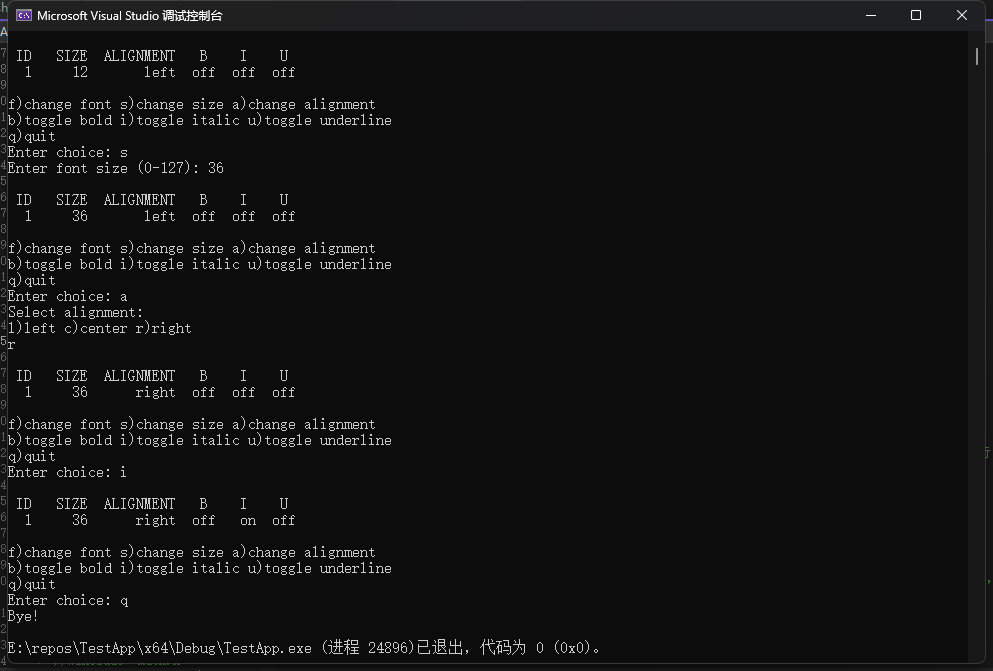
6.设计一个位字段结构以存储下面的信息。
字体ID:0~255之间的一个数;
字体大小:0~127之间的一个数;
对齐:0~2之间的一个数,表示左对齐、居中、右对齐;
加粗:开(1)或闭(0);
斜体:开(1)或闭(0);
在一个程序中使用该结构来打印字体参数,并使用循环菜单来让用户改变参数。例如,该程序的一个运行示例如下:
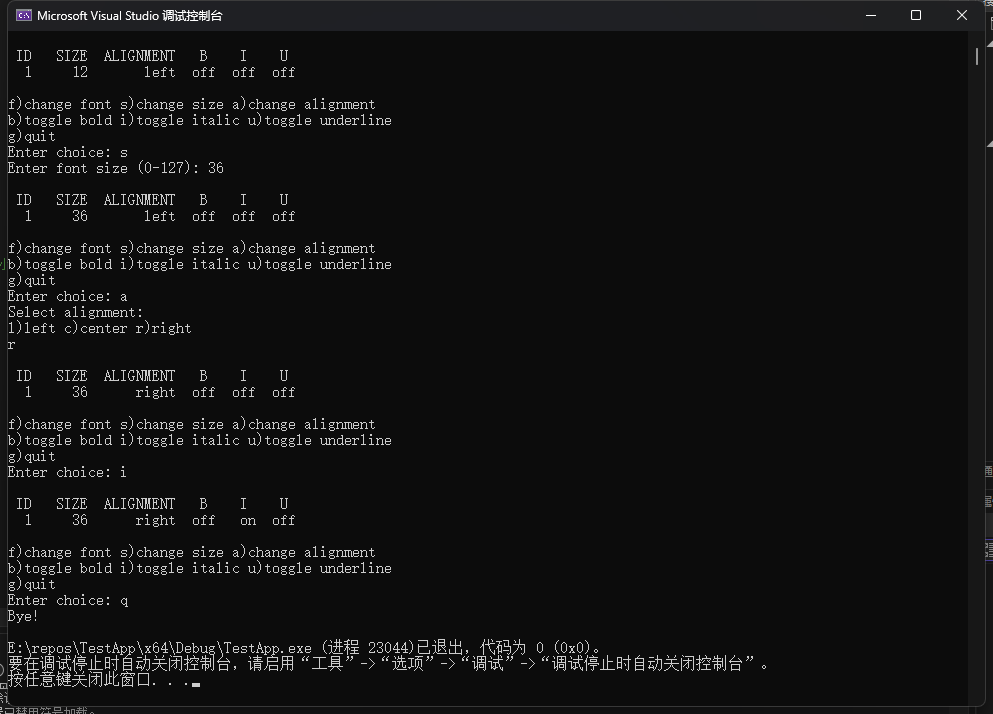
ID SIZE ALIGNMENT B I U
1 12 left off off off
f)change font s)change size a)change alignment
b)toggle bold i)toggle italic u)toggle underline
q)quit
s
Enter font size (0-127):36
ID SIZE ALIGNMENT B I U
1 36 left off off off
f)change font s)change size a)change alignment
b)toggle bold i)toggle italic u)toggle underline
q)quit
a
Select alignment:
l)left c) center r) right
r
ID SIZE ALIGNMENT B I U
1 36 right off off off
f)change font s)change size a)change alignment
b)toggle bold i)toggle italic u)toggle underline
q)quit
i
ID SIZE ALIGNMENT B I U
1 36 left off on off
f)change font s)change size a)change alignment
b)toggle bold i)toggle italic u)toggle underline
q)quit
q
Byte!
该程序要使用按位与运算符(&)和合适的掩码来把字体ID和字体大小信息转换到指定范围内。
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 位字段结构定义
typedef struct {
unsigned int font_id : 8; // 0-255 (8位)
unsigned int font_size : 7; // 0-127 (7位)
unsigned int alignment : 2; // 0-2 (2位)
unsigned int bold : 1; // 0-1 (1位)
unsigned int italic : 1; // 1位
unsigned int underline : 1; // 1位 (根据示例添加)
} Font;
// 对齐方式文本映射
const char* alignments[] = { "left", "center", "right" };
// 打印当前字体设置
void show_settings(const Font* f) {
printf("\n ID SIZE ALIGNMENT B I U\n");
printf("%3d %6d %10s %4s %4s %4s\n",
f->font_id,
f->font_size,
alignments[f->alignment],
f->bold ? "on" : "off",
f->italic ? "on" : "off",
f->underline ? "on" : "off"
);
}
// 菜单显示
void show_menu() {
printf("\nf)change font s)change size a)change alignment\n");
printf("b)toggle bold i)toggle italic u)toggle underline\n");
printf("g)quit\n");
}
int main() {
Font font = { 1, 12, 0, 0, 0, 0 }; // 初始值
char choice;
while (1) {
show_settings(&font);
show_menu();
printf("Enter choice: ");
scanf_s(" %c", &choice, 1); // 注意空格跳过空白字符
choice = tolower(choice);
switch (choice) {
case 'f': {
unsigned int id;
printf("Enter font ID (0-255): ");
scanf_s("%u", &id);
font.font_id = id & 0xFF; // 确保0-255范围
break;
}
case 's': {
unsigned int size;
printf("Enter font size (0-127): ");
scanf_s("%u", &size);
font.font_size = size & 0x7F; // 确保0-127范围
break;
}
case 'a': {
char align_choice;
printf("Select alignment:\nl)left c)center r)right\n");
scanf_s(" %c", &align_choice, 1);
switch (tolower(align_choice)) {
case 'l': font.alignment = 0; break;
case 'c': font.alignment = 1; break;
case 'r': font.alignment = 2; break;
default: printf("Invalid choice!\n");
}
break;
}
case 'b': font.bold ^= 1; break; // 切换加粗
case 'i': font.italic ^= 1; break; // 切换斜体
case 'u': font.underline ^= 1; break; // 切换下划线
case 'q':
printf("Bye!\n");
exit(0);
default:
printf("Invalid choice!\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
7.编写一个与编程练习6功能相同的程序,使用unsigned long类型的变量存储字体信息,并且使用按位运算符而不是成员位来管理这些信息。
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 位掩码和偏移量定义
#define FONT_ID_MASK 0xFF000u // 字体ID掩码(位12-19)
#define FONT_ID_SHIFT 12
#define FONT_SIZE_MASK 0xFE0u // 字体大小掩码(位5-11)
#define FONT_SIZE_SHIFT 5
#define ALIGNMENT_MASK 0x18u // 对齐方式掩码(位3-4)
#define ALIGNMENT_SHIFT 3
#define BOLD_MASK 0x1u // 加粗掩码(位0)
#define ITALIC_MASK 0x2u // 斜体掩码(位1)
#define UNDERLINE_MASK 0x4u // 下划线掩码(位2)
// 对齐方式文本映射
const char* alignments[] = { "left", "center", "right" };
// 打印当前字体设置
void show_settings(unsigned long font_info) {
// 提取各个字段
unsigned int id = (font_info & FONT_ID_MASK) >> FONT_ID_SHIFT;
unsigned int size = (font_info & FONT_SIZE_MASK) >> FONT_SIZE_SHIFT;
unsigned int align = (font_info & ALIGNMENT_MASK) >> ALIGNMENT_SHIFT;
printf("\n ID SIZE ALIGNMENT B I U\n");
printf("%3d %6d %10s %4s %4s %4s\n",
id,
size,
alignments[align],
(font_info & BOLD_MASK) ? "on" : "off",
(font_info & ITALIC_MASK) ? "on" : "off",
(font_info & UNDERLINE_MASK) ? "on" : "off"
);
}
// 菜单显示
void show_menu() {
printf("\nf)change font s)change size a)change alignment\n");
printf("b)toggle bold i)toggle italic u)toggle underline\n");
printf("q)quit\n");
}
int main() {
// 初始化字体信息: ID=1, 大小=12, 左对齐(0), 所有样式关闭
unsigned long font_info = (1u << FONT_ID_SHIFT) | (12u << FONT_SIZE_SHIFT);
char choice;
while (1) {
show_settings(font_info);
show_menu();
printf("Enter choice: ");
scanf_s(" %c", &choice, 1);
choice = tolower(choice);
switch (choice) {
case 'f': {
unsigned int id;
printf("Enter font ID (0-255): ");
scanf_s("%u", &id);
// 清除原ID,设置新ID
font_info &= ~FONT_ID_MASK;
font_info |= (id & 0xFFu) << FONT_ID_SHIFT;
break;
}
case 's': {
unsigned int size;
printf("Enter font size (0-127): ");
scanf_s("%u", &size);
// 清除原大小,设置新大小
font_info &= ~FONT_SIZE_MASK;
font_info |= (size & 0x7Fu) << FONT_SIZE_SHIFT;
break;
}
case 'a': {
char align_choice;
printf("Select alignment:\nl)left c)center r)right\n");
scanf_s(" %c", &align_choice, 1);
// 清除原对齐方式
font_info &= ~ALIGNMENT_MASK;
switch (tolower(align_choice)) {
case 'l': font_info |= (0u << ALIGNMENT_SHIFT); break;
case 'c': font_info |= (1u << ALIGNMENT_SHIFT); break;
case 'r': font_info |= (2u << ALIGNMENT_SHIFT); break;
default: printf("Invalid choice!\n");
}
break;
}
case 'b': font_info ^= BOLD_MASK; break; // 切换加粗
case 'i': font_info ^= ITALIC_MASK; break; // 切换斜体
case 'u': font_info ^= UNDERLINE_MASK; break; // 切换下划线
case 'q':
printf("Bye!\n");
exit(0);
default:
printf("Invalid choice!\n");
}
}
return 0;
}