背景
目前有两个微服务 A 和 B,微服务 A 访问微服务 B 之前需要从授权服务器中获取 Access Token,才能携带 Access Token 访问微服务 B 中的 Restful API,如图 1 所示。微服务 A 使用客户端模式(Client Credentials Grant)的方式,从授权服务器获取 Access Token。目前微服务 A 通过 RestTemplate,从授权服务器获取 Access Token,并通过 Ehcache 来缓存 Access Token。
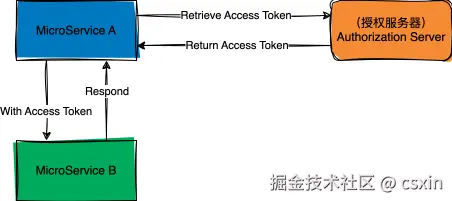 图 1 现状
图 1 现状
但在目前的架构中,我们遇到了一个这样的问题,如图 2 所示。微服务 A 从授权服务器获取的 Access Token,它是具有失效的,比如它的 expires_in 值为 86400 秒(约 24 小时),表示 24 小时之后,该 Access Token 就会过期。微服务 A 在 Ehcache 中通过 Hard Code 的方式配置了缓存 Access Token 为 24 小时。这本来没有啥问题,但是有一天授权服务器侧将 Access Token 的过期时间从 24 小时调整至 1 小时,但此时微服务 A 没有收到这边变动的通知,当然也没有在微服务 A 侧进行同步的调整。这就导致微服务 A 中可能会缓存已经过期的 Access Token,从而导致微服务 A 调用微服务 B 失败。这样的事故固然有沟通的问题,但是我们也尝试是否有其他的解决方案。
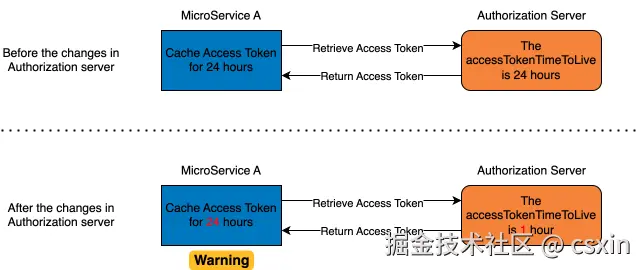
解决方案
曾考虑过动态根据从授权服务器获取的 Access Token 的过期时间,动态调整微服务 A 缓存 Access Token 的时间。这里仅仅需要保证微服务 A 缓存 Access Token 的时间小于 Access Token 的过期时间即可。但这需要手动完成这样的逻辑。幸运的是,我们发现了 Spring Security 中的 OAuth 2.0 Client,使用它可以自动完成对 Access Token 的管理(实现了上述逻辑,缓存 Access Token 和过期处理)。因此我们可以开箱即用,避免重复造轮子。
OAuth 2.0 Client 是如何管理 Access Token
OAuth 2.0 Client 是什么?
OAuth 2.0 Client 是 Spring Security 中为了支持 OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework 中定义的 Client Role 开发的一个特性。主要用于通过 OAuth 2.0 Client 从 OAuth 2.0 Authorization Server 获取 Access Token。
OAuth 2.0 Client 的核心功能支持多种客户端的授权模式,包括授权码模式(authorization code)和客户端模式(client credentials)以及密码模式(resource owner password credentials)等。
OAuth 2.0 Client 对 Access Token 的管理
OAuth 2.0 Client 主要表 1 中的接口来对 Access Token 进行管理。对与这些接口或实现类的详细说明可以参考官方Core Interfaces and Classes
| 接口 | 说明 | 实现类举例 |
|---|---|---|
| OAuth2AuthorizedClientManager | 用来管理获取 Access Token 的整个流程。通过 OAuth2AuthorizedClientProvider 获取 Access Token。通过 OAuth2AuthorizedClientRepository 缓存或持久化 Access Token。唯一的方法为 authorize,用来获取授权。 | DefaultOAuth2AuthorizedClientManager,用于 HttpServletRequest 上下文中的默认 OAuth2AuthorizedClientManager 实现。 AuthorizedClientServiceOAuth2AuthorizedClientManager 一个 OAuth2AuthorizedClientManager 的实现,能够在 HttpServletRequest 的上下文之外运行,例如在计划任务/后台线程中和/或在服务层中。 |
| OAuth2AuthorizedClientRepository | 用来缓存 Access Token。 loadAuthorizedClient 方法用来从缓存中获取 Access Token;saveAuthorizedClient 方法用户在得到新的 Access Token 之后,将其缓存或持久化;removeAuthorizedClient 方法用来移除缓存中的 Access Token。 | HttpSessionOAuth2AuthorizedClientRepository,用于将 Access Token 缓存在 HttpSession 会话中。 |
| OAuth2AuthorizedClientProvider | 用来获取 Access Token。 authorize 方法先从入参中获取 Access Token,如果没有过期,则返回该 Access Token;如果过期,则重新从 Authorization Server 获取新的 Access Token。 | ClientCredentialsOAuth2AuthorizedClientProvider,用于以客户端模式的方式从 Authorization Server 中获取 Access Token(如果缓存中 Access Token 以及过期的情况下)。 |
| OAuth2AuthorizationSuccessHandler | 从 Authorization Server 成功获取 Access Token (授权成功)之后的处理器。比如将 Access Token 缓存到 OAuth2AuthorizedClientRepository 中或其他后续操作。 | |
| OAuth2AuthorizedClient | 代表一个 OAuth 2.0 "Authorized Client"。通常其中包含 Client 信息和后续获取到的 Access Token。 | |
| OAuth2AuthorizationFailureHandler | 用来处理授权失败之后的处理器。比如从 Access Token 从 OAuth2AuthorizedClientRepository 中或其他后续操作。 |
表 1 OAuth 2.0 Client 的主要接口
下面以客户端模式(client credentials grant)授权模式下的 OAuth 2.0 Client 为例,来具体说明 Access Token 的整个管理过程。通过 OAuth 2.0 Client 以客户端模式(client credentials grant)授权模式获取 Access Token 时,通常有两种使用场景。第一种的 Access Token 的 scope 是用户,每一个用户一个 Access Token。第二种的 Access Token 的 scope 是应用,每一个应用一个 Access Token。这两种的使用场景如图 3 所示。
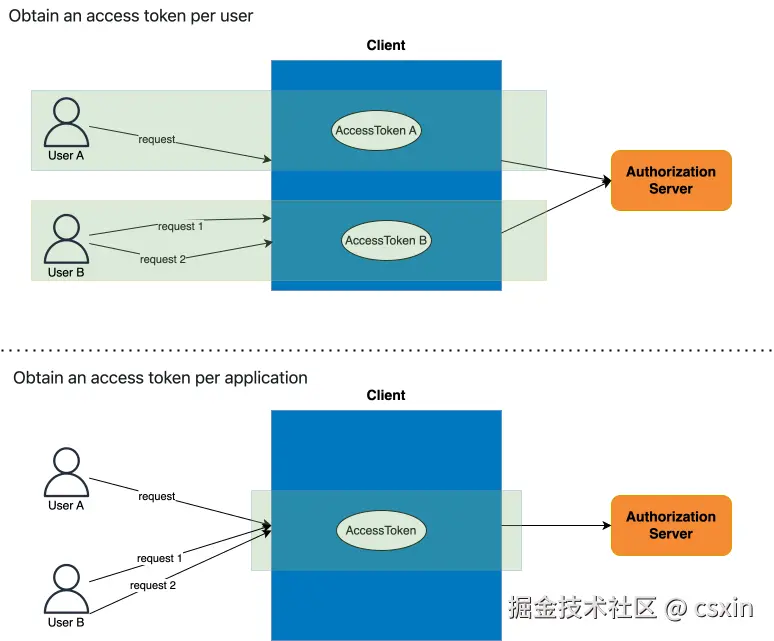 图 3 一个用户一个 Access Token VS 一个用户一个 Access Token
图 3 一个用户一个 Access Token VS 一个用户一个 Access Token
在 Spring Security OAuth2 client 中通过不同的 OAuth2AuthorizedClientManager 实现类来完成相应的工作。第一种是通过 DefaultOAuth2AuthorizedClientManager,其工作原理时序图如图4 所示。第二种是通过 AuthorizedClientServiceOAuth2AuthorizedClientManager,其工作原理时序图如图 5 所示。
下面以第一种为示例,来详细说明其过程。
- 我们的组件通过 DefaultOAuth2AuthorizedClientManager(OAuth2AuthorizedClientManager) 的 authorize 方法来尝试获取授权。
- DefaultOAuth2AuthorizedClientManager(OAuth2AuthorizedClientManager)尝试通过 HttpSessionOAuth2AuthorizedClientRepository(OAuth2AuthorizedClientRepository)的 loadAuthorizedClient 方法,从缓存(HttpSession)中获取 OAuth2AuthorizedClient 对象(如果缓存中有 Access Token, 那么该对象中就会包含旧的 Access Token)。
- DefaultOAuth2AuthorizedClientManager(OAuth2AuthorizedClientManager)通过 ClientCredentialsOAuth2AuthorizedClientProvider(OAuth2AuthorizedClientProvider)的 authorize 方法,判断 Access Token 是否过期。如何没有过期,则返回携带旧 Access Token 的 OAuth2AuthorizedClient 对象;如果以及过期,则从 Authorization Server 中重新获取新的 Access Token。
- 如果授权失败,DefaultOAuth2AuthorizedClientManager(OAuth2AuthorizedClientManager)通过 OAuth2AuthorizationFailureHandler 移除 HttpSessionOAuth2AuthorizedClientRepository(OAuth2AuthorizedClientRepository)中缓存的 Access Token。
- 如果授权成功,DefaultOAuth2AuthorizedClientManager(OAuth2AuthorizedClientManager)通过 OAuth2AuthorizationSuccessHandler 将新的 Access Token 重新缓存到 HttpSessionOAuth2AuthorizedClientRepository(OAuth2AuthorizedClientRepository)中。
 图 4 对于每一个用户一个 Access Token 的情况,OAuth 2.0 Client 通过 DefaultOAuth2AuthorizedClientManager 管理 Access Token 的时序图
图 4 对于每一个用户一个 Access Token 的情况,OAuth 2.0 Client 通过 DefaultOAuth2AuthorizedClientManager 管理 Access Token 的时序图
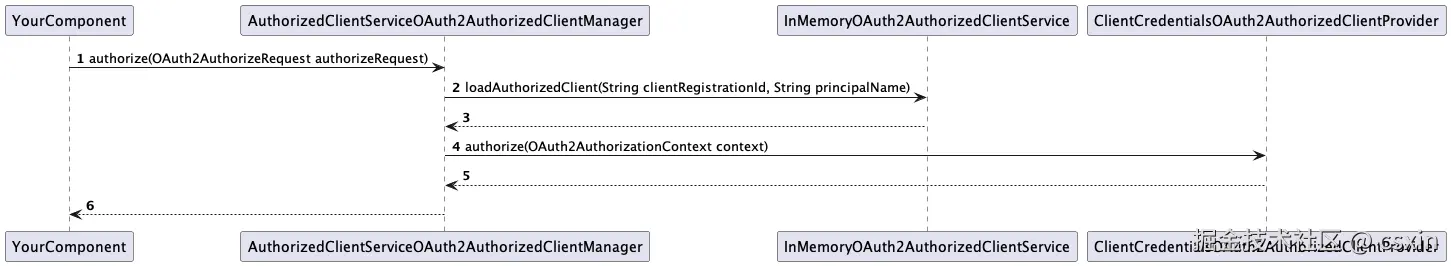
图 5 对于每一个应用一个 Access Token 的情况,OAuth 2.0 Client 通过 AuthorizedClientServiceOAuth2AuthorizedClientManager 管理 Access Token 的时序图
对于背景中描述的场景,我们符合第二种(每一个应用一个 Access Token)。
OAuth 2.0 Client 的使用
下面以客户端授权模式为 client_credentials__grant 并且客户端认证方式为 client_secret_post 的情况为例,来说明如何使用 OAuth 2.0 Client。使用 OAuth 2.0 Client 时,需要在 application.yaml 中配置 client 信息和指定 OAuth2AuthorizedClientProvider 采用的客户端授权模式。
引入依赖
如代码清单 1 所示,除了其他依赖外我们重点要引入 spring-security-oauth2-client 依赖项。
代码清单 1:引入依赖 pom.xml
xml
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.boot/spring-boot-starter-web -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.security/spring-security-oauth2-client -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-oauth2-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.squareup.okhttp3/mockwebserver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.squareup.okhttp3</groupId>
<artifactId>mockwebserver</artifactId>
<version>4.12.0</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>配置 application.yaml 中配置 client 信息
如代码清单 2 所示,在 application.yaml 中需要配置 registration 和 provider。
- registration
- registration 中注册一个名为
some-client的 client。- provider: 该 client 下面包含了
provider需要与spring.security.oauth2.client.provider下的某个 provider 一致。如代码清单 2 中的spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.some-client.provider的值与spring.security.oauth2.client.provider.some-provider一致。 - client-id: client 的 id
- client-secret: client secret
- authorization-grant-type: 用来表示客户端授权的模式。可选择值有 authorization_code_grant,client_credentials__grant,implicit_grant,resource_owner_password_credentials_grant。
- client-authentication-method:用来表示认证的方式。可选值有 client_secret_basic,client_secret_post,client_secret_jwt,private_key_jwt,tls_client_auth,self_signed_tls_client_auth。
- provider: 该 client 下面包含了
- registration 中注册一个名为
- provider
- some-provider: provider 的名字。可以自定义。
- token-uri: 获取授权的地址。
代码清单 2:Oauth 2.0 Client 的配置 application.yaml
yaml
spring:
security:
oauth2:
client:
registration:
some-client:
provider: some-provider
client-id: custom-client-id
client-secret: custom-client-secret
authorization-grant-type: client_credentials
client-authentication-method: client_secret_post
scope:
- "read"
provider:
some-provider:
token-uri: http://localhost:9000/oauth2/token指定 OAuth2AuthorizedClientProvider 的授权模式
如代码清单 3 所示,配置和指定 OAuth2AuthorizedClientProvider 的客户端授权模式。
代码清单 3:用来指定 OAuth2AuthorizedClientProvider 的客户端授权模式 Oauth2ClientConfig.java
java
package com.mervyn.springboot.learn.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.AuthorizedClientServiceOAuth2AuthorizedClientManager;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.OAuth2AuthorizedClientManager;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.OAuth2AuthorizedClientProvider;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.OAuth2AuthorizedClientProviderBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.OAuth2AuthorizedClientService;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.registration.ClientRegistrationRepository;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.web.client.OAuth2ClientHttpRequestInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestClient;
@Configuration
public class RestClientConfig {
@Bean
public OAuth2AuthorizedClientManager authorizedClientManager(
ClientRegistrationRepository clientRegistrationRepository,
OAuth2AuthorizedClientService OAuth2AuthorizedClientService) {
OAuth2AuthorizedClientProvider authorizedClientProvider =
OAuth2AuthorizedClientProviderBuilder.builder()
.clientCredentials()
.build();
AuthorizedClientServiceOAuth2AuthorizedClientManager authorizedClientManager =
new AuthorizedClientServiceOAuth2AuthorizedClientManager(clientRegistrationRepository, OAuth2AuthorizedClientService);
authorizedClientManager.setAuthorizedClientProvider(authorizedClientProvider);
return authorizedClientManager;
}
@Bean
public RestClient restClient(OAuth2AuthorizedClientManager authorizedClientManager) {
OAuth2ClientHttpRequestInterceptor requestInterceptor =
new OAuth2ClientHttpRequestInterceptor(authorizedClientManager);
return RestClient.builder().requestInterceptor(requestInterceptor).build();
}
}测试
为了测试是否能从 Authorization Server 获取到 Access Token。通过 /token-test接口暴露 Access Token 的值,因此这里我们通过 MockMvc 来测试该接口的返回值。在这里我们通过 MockWebServer 来模拟 Authorization Server 的行为,并且通过 takeRequest 方法获取 OAuth2AuthorizedClientProvider 发送的请求是否符合期望。 代码清单 4: 对获取 Access Token 的接口进行集成测试 AuthorizationClientTest.java
java
package com.mervyn.springboot.learn;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.json.JsonMapper;
import okhttp3.mockwebserver.Dispatcher;
import okhttp3.mockwebserver.MockResponse;
import okhttp3.mockwebserver.MockWebServer;
import okhttp3.mockwebserver.RecordedRequest;
import org.hamcrest.core.Is;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.OAuth2AuthorizedClientService;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MvcResult;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.UUID;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.containsString;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.not;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.notNullValue;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.nullValue;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.content;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;
@SpringBootTest
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
public class AuthorizationClientTest {
private static MockWebServer server;
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@Autowired
private OAuth2AuthorizedClientService authorizedClientService;
@BeforeAll
public static void setup() throws IOException {
server = new MockWebServer();
final Dispatcher dispatcher = new Dispatcher() {
@Override
public MockResponse dispatch(RecordedRequest request) throws InterruptedException {
switch (request.getPath()) {
case "/oauth2/token":
Map<String, String> responseMap = new HashMap<>();
responseMap.put("access_token", UUID.randomUUID().toString());
responseMap.put("scope", "read");
responseMap.put("token_type", "Bearer");
responseMap.put("expires_in", "120");
JsonMapper jsonMapper = new JsonMapper();
String response = buildJsonResponse(jsonMapper, responseMap);
return new MockResponse()
.addHeader("Content-Type", "application/json; charset=utf-8")
.setResponseCode(200)
.setBody(response);
}
return new MockResponse().setResponseCode(404);
}
};
server.setDispatcher(dispatcher);
server.start(9000);
}
private static String buildJsonResponse(JsonMapper jsonMapper, Map<String, String> responseMap) {
String response = null;
try {
response = jsonMapper.writeValueAsString(responseMap);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
}
return response;
}
@Test
public void shouldReturnAccessTokenWhenRetrieveAccessToken() throws Exception {
mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/token-test"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string(notNullValue()))
.andExpect(content().string(not("")));
RecordedRequest request = server.takeRequest();
assertThat(request.getHeaders().get("Content-Type"), containsString(MediaType.APPLICATION_FORM_URLENCODED_VALUE));
String bodyContent = request.getBody().readUtf8();
assertThat(bodyContent, containsString("client_id=custom-client-id"));
assertThat(bodyContent, containsString("client_secret=custom-client-secret"));
assertThat(bodyContent, containsString("grant_type=client_credentials"));
assertThat(bodyContent, containsString("scope=read"));
}
@Test
public void shouldReturnSameAccessTokenAndCallAuthorizationServerOnlyOnceWhenAccessTokenIsNotExpired() throws Exception {
MvcResult mvcResult1 = mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/token-test"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string(notNullValue()))
.andExpect(content().string(not("")))
.andReturn();
MvcResult mvcResult2 = mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/token-test"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string(notNullValue()))
.andExpect(content().string(not("")))
.andReturn();
String response1 = mvcResult1.getResponse().getContentAsString();
String response2 = mvcResult2.getResponse().getContentAsString();
assertThat(response1, Is.is(response2));
RecordedRequest request = server.takeRequest(3, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
assertThat(request, notNullValue());
RecordedRequest request1 = server.takeRequest(3, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
assertThat(request1, nullValue());
}
@Test
void shouldReturnDifferentAccessTokenCallAuthorizationServerTwiceWhenAccessTokenIsExpired() throws Exception {
MvcResult mvcResult1 = mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/token-test"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string(notNullValue()))
.andExpect(content().string(not("")))
.andReturn();
RecordedRequest request = server.takeRequest(3, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
assertThat(request, notNullValue());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(140);
MvcResult mvcResult2 = mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/token-test"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string(notNullValue()))
.andExpect(content().string(not("")))
.andReturn();
RecordedRequest request1 = server.takeRequest(3, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
assertThat(request1, notNullValue());
String response1 = mvcResult1.getResponse().getContentAsString();
String response2 = mvcResult2.getResponse().getContentAsString();
assertThat(response1, not(equalTo(response2)));
}
@AfterEach
public void removeAccessTokenFromCache() {
authorizedClientService.removeAuthorizedClient("some-client", "test");
}
@AfterAll
public static void teardown() throws IOException {
server.shutdown();
}
}