Q1:模块的例化,只讨论方法,不讨论代码功能。
在 Verilog 中,模块实例化是将一个模块作为组件使用在另一个模块中。这类似于在编程中调用一个函数或在硬件设计中使用一个子电路。通过实例化,可以将复杂的设计分解为更小的、可复用的模块[1]。
模块的定义
cpp
module add32(
input wire [31:0] in1,
input wire [31:0] in2,
output wire [31:0] out
);
// 直接使用运算符,综合工具自动优化
assign out = in1 + in2;
endmodule顶层模块top_module
cpp
module top_module(
input wire [31:0] a,
input wire [31:0] b,
output wire [31:0] sum
);
// 实例化 add32 模块
add32 u_add32 (
.in1(a), // 将顶层模块的输入 a 连接到子模块 add32 的 in1 端口
.in2(b), // 将顶层模块的输入 b 连接到子模块 add32 的 in2 端口
.out(sum) // 将子模块 add32 的输出 out 连接到顶层模块的输出 sum
);
endmoduleYou are given a module my_dff with two inputs and one output (that implements a D flip-flop). Instantiate three of them, then chain them together to make a shift register of length 3. The clk port needs to be connected to all instances.
The moduleprovided to you is:module my_dff (input clk, input d, output q ):
Note that to make the internal connections, you will need to declare some wires. Be careful about naming your wires and module instances: the names must be unique[2].
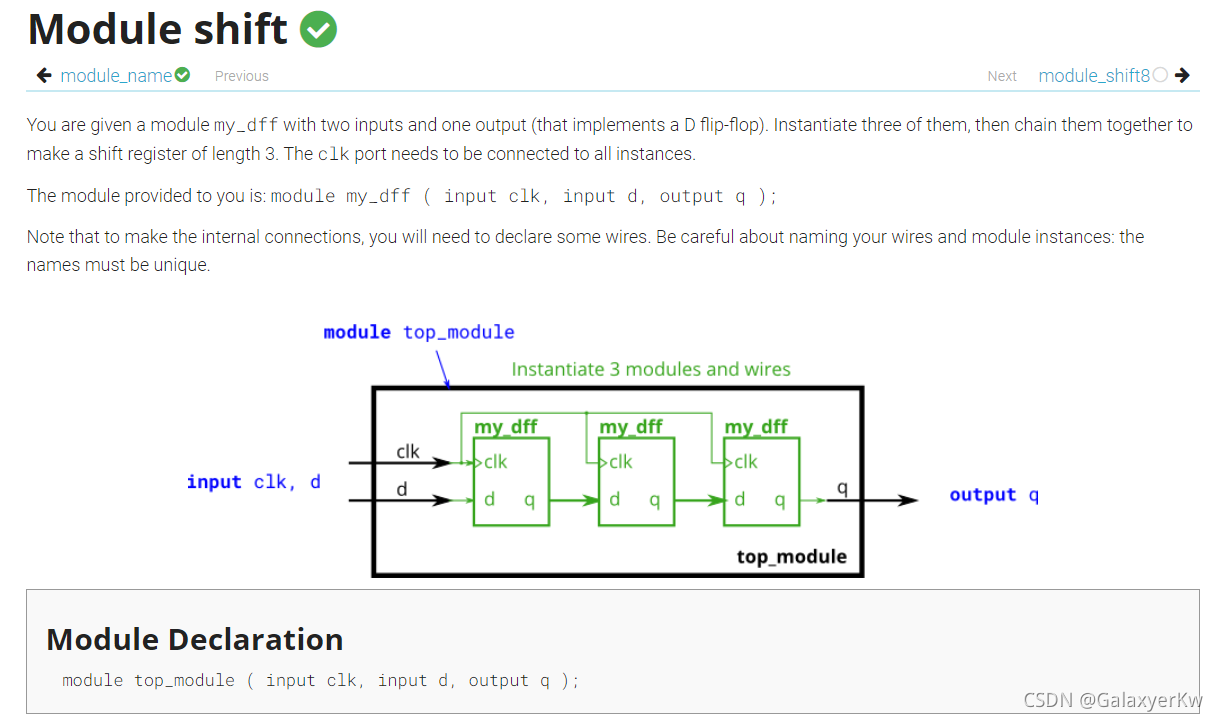
模块定义
cpp
// 带流水线寄存器的加法器
module pipelined_add32(
input wire clk,
input wire rst_n,
input wire [31:0] in1,
input wire [31:0] in2,
output reg [31:0] out
);
reg [31:0] sum_pre;
always @(*) begin
sum_pre = in1 + in2;
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) out <= 0;
else out <= sum_pre;
end
endmodule顶层模块
多个模块的定义
cpp
// 级联加法模块
module multi_add_chain(
input wire clk,
input wire rst_n,
input wire [31:0] a, b, c, d, e,
output wire [31:0] result
);
wire [31:0] sum1, sum2, sum3;
//第一级级联
pipelined_add32 add1 (
.clk(clk),
.rst_n(rst_n),
.in1(a),
.in2(b),
.out(sum1)
);
// 第二级级联
pipelined_add32 add2 (
.clk(clk),
.rst_n(rst_n),
.in1(sum1),
.in2(c),
.out(sum2)
);
// 第三级级联
pipelined_add32 add3 (
.clk(clk),
.rst_n(rst_n),
.in1(sum2),
.in2(d),
.out(sum3)
);
// 第四级级联
pipelined_add32 add4 (
.clk(clk),
.rst_n(rst_n),
.in1(sum3),
.in2(e),
.out(result)
);
endmodule多个模块的例化,还有一种比较有效的方法:
generate for
cpp
generate
for (genvar i=0; i<4; i++) begin : gen_block //块名"gen_block"
add32 u_add32 (
.din(din[i]),
.dout(dout[i])
);
end
endgenerate
cpp
module generate_for_example (
input wire [7:0] a,
output wire [7:0] b
);
genvar i;
generate
for (i = 0; i < 8; i = i + 1) begin : gen_block
assign b[i] = a[i];
end
endgenerate
endmodule生成的实例路径为top.gen_block[0].u_add32、top.gen_block[1].u_add32等。
Q2: 使用参数
参数化模块可以提高模块的灵活性,允许在实例化时指定参数值。
《韩非子·卷十五·难一》:兵不厌诈。
下面的代码会直观的告诉你答案:
adder模块中自带参数,这个参数可以接受top层下达的旨意。喵喵。
cpp
module adder #(parameter WIDTH = 4) (
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] a,
input wire [WIDTH-1:0] b,
output wire [WIDTH-1:0] sum
);
assign sum = a + b;
endmodule
// 实例化带参数的模块
module top;
wire [7:0] sum;
adder #(8) my_adder (
.a(8'b00001111),
.b(8'b00000001),
.sum(sum)
);
endmodule参数可分为两大类:局部参数和普通参数,分别由关键词local_parameter和parameter声明。它们俩的区别在于,局部参数不允许使用defparam语句或在模块实例化时(在elaboration阶段)进行参数覆盖,普通参数在满足一定条件时允许参数覆盖。需要注意的是参数代表常量,在运行时修改它们的值是非法的[4]。
local_parameter可以在下面这些位置声明:
cpp
module example_module (
input wire clk,
input wire rst,
output wire [3:0] out
);
localparam integer WIDTH = 4; // 在模块中声明localparam
localparam [WIDTH-1:0] MAX_VALUE = 15;
reg [WIDTH-1:0] counter;
always @(posedge clk or posedge rst) begin
if (rst) begin
counter <= 0;
end else if (counter < MAX_VALUE) begin
counter <= counter + 1;
end else begin
counter <= 0;
end
end
assign out = counter;
endmodule参考文献:
【1】【Verilog入门】模块的实例化(巨巨巨巨详细讲解)_verilog实例化-CSDN博客
【2】【Verilog】子模块连接相关问题(加法器及其优化)_verilog怎么把两个模块连接-CSDN博客