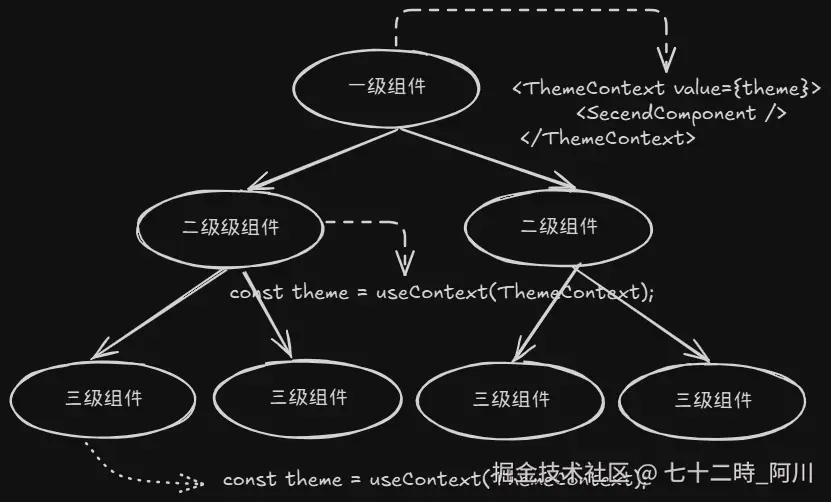
useContext 使用场景
. 组件的嵌套层级很深,当父组件想把数据共享给最深层的子组件时向组件树深层传递数据
. 图示:
useContext 语法格式
tsx
import React, { useContext } from 'react'
const [theme, setTheme] = useState(null);
//1. 在全局创建 Context 对象
const ThemeContext = React.createContext(theme)
//2. 在父组件中使用 Context 提供数据
const App = () => {
return <ThemeContext value={theme}> ...
</ThemeContext>
}
//3. 在子组件中使用 useContext 使用数据
const Son = () => {
const myCtx = useContext(ThemeContext)
return <div></div>
}Context 基础用法
- 在父组件中,调用 React.createContext 向下共享数据;在子组件中调用 useContext() 获取数据。
tsx
import React, { useState, useContext } from 'react'
// 声明 TS 类型
type ContextType = { count: number; setCount: React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<number>> }
// 1. 创建 Context 对象
const AppContext = React.createContext<ContextType>({} as ContextType)
export const LevelA: React.FC = () => {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
return (
<div style={{ padding: 30, backgroundColor: 'lightblue', width: '50vw' }}>
<p>count:{count}</p>
<button onClick={() => setCount((prev) => prev + 1)}>+1</button>
<AppContext.Provider value={{ count, setCount }}>
<LevelB />
</AppContext.Provider>
</div>
)
}
export const LevelB: React.FC = () => {
return (
<div style={{ padding: 30, backgroundColor: 'lightgreen' }}>
<LevelC />
</div>
)
}
export const LevelC: React.FC = () => {
const ctx = useContext(AppContext)
return (
<div style={{ padding: 30, backgroundColor: 'lightsalmon' }}>
<p>count值是:{ctx.count}</p>
<button onClick={() => ctx.setCount((prev) => prev + 1)}>+1</button>
<button onClick={() => ctx.setCount(0)}>重置</button>
</div>
)
}非侵入式 Context
- 把 Context 封装到独立的 Wrapper 函数式组件中- 非侵入式 Context 不会影响组件的结构,只会在组件树中创建一个共享的 Context 对象。
tsx
// 声明 TS 类型
type ContextType = { count: number; setCount: React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<number>> }
// 创建 Context 对象
const AppContext = React.createContext<ContextType>({} as ContextType)
// 定义独立的 Wrapper 组件,被 Wrapper 嵌套的子组件会被 Provider 注入数据
export const AppContextWrapper: React.FC<React.PropsWithChildren> = (props) => {
// 1. 定义要共享的数据
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
// 2. 使用 AppContext.Provider 向下共享数据
return <AppContext value={{ count, setCount }}>{props.children}</AppContext>
}- 在 App.tsx 中使用 AppContextWrapper 包裹
tsx
import React from 'react'
import { AppContextWrapper } from '@/xxx.tsx'
const App: React.FC = () => {
return (
<AppContextWrapper>
<!-- AppContextWrapper 中嵌套使用了 LevelA 组件,形成了父子关系 -->
<!-- LevelA 组件会被当做 children 渲染到 Wrapper 预留的插槽中 -->
<LevelA />
</AppContextWrapper>
)
}
export default App- LevelC 组件中使用 useContext 获取数据
tsx
export const LevelC: React.FC = () => {
// 使用 useContext 接收数据
const ctx = useContext(AppContext)
return (
<div style={{ padding: 30, backgroundColor: 'lightsalmon' }}>
<p>count值是:{ctx.count}</p>
<button onClick={() => ctx.setCount((prev) => prev + 1)}>+1</button>
<button onClick={() => ctx.setCount(0)}>重置</button>
</div>
)
}进阶 useContext 结合 useReducer 使用场景
- 定义 reducer 函数
tsx
function tasksReducer(tasks, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'added': {
return [...tasks, {
id: action.id,
text: action.text,
done: false
}];
}
case 'changed': {
return tasks.map(t => {
if (t.id === action.task.id) {
return action.task;
} else {
return t;
}
});
}
case 'deleted': {
return tasks.filter(t => t.id !== action.id);
}
default: {
throw Error('Unknown action: ' + action.type);
}
}
}
const initialTasks = [
{ id: 0, text: 'Philosopher's Path', done: true },
{ id: 1, text: 'Visit the temple', done: false },
{ id: 2, text: 'Drink matcha', done: false }
];- 在根组件中创建 Context 对象 并抽离成独立组件
tsx
import { createContext, useContext, useReducer } from 'react';
export const TasksContext = createContext(null);
export function TasksProvider({ children }) {
const [tasks, dispatch] = useReducer(
tasksReducer,
initialTasks
);
return (
<TasksContext value={{ tasks , dispatch }}>
{children}
</TasksContext>
);
}- 在根组件中使用 TasksProvider 包裹子组件
tsx
export default function TaskApp() {
return (
<TasksProvider>
<AddTask />
<TaskList />
</TasksProvider>
);
}- 在子组件中使用 useContext 获取数据
tsx
import { useState, useContext } from 'react';
import { TasksContext } from './TasksContext.js';
export default function AddTask() {
const [text, setText] = useState('');
const { dispatch } = useContext(TasksContext);
function handleAdd() {
setText('');
dispatch({
type: 'added',
id: nextId++,
text: text,
});
}
return (
<>
<input
placeholder="Add task"
value={text}
onChange={e => setText(e.target.value)}
/>
<button onClick={() => handleAdd()}>Add</button>
</>
);
}