最近在尝试使用springsecurity新版本做一个授权服务器的功能,在使用过程中结合查资料发现springsecurity的认证管理器有局部和全局的概念,这里通过进行源码的分析,找到相关证明。
从 Spring Security 5.7 开始 ,WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 被标记为 @Deprecated (不推荐使用),并在 Spring Security 6 中被移除 推荐我们使用如下方式直接构建过滤器链
less
@Bean
@Order(2)
public SecurityFilterChain defaultSecurityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http)
throws Exception {
// 框架会先获取一个新的 HttpSecurity 实例
// 相当于:http = applicationContext.getBean(HttpSecurity.class);
http
.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize
.anyRequest().authenticated()
)
// Form login handles the redirect to the login page from the
// authorization server filter chain
.formLogin(new FormLoginConfigurerCustomer());
return http.build();
}1. HttpSecurity http 参数从哪来?
Spring 容器会自动为这个 @Bean 方法注入一个全新的 HttpSecurity 实例。
👉 每次创建 SecurityFilterChain Bean 时,都会传入一个"干净的、新创建的" HttpSecurity 实例。
之所以每次都是一个全新的实例 是因为HttpSecurityConfiguration类中有如下配置
scss
@Bean(HTTPSECURITY_BEAN_NAME)
@Scope("prototype")
HttpSecurity httpSecurity() throws Exception {
LazyPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder = new LazyPasswordEncoder(this.context);
AuthenticationManagerBuilder authenticationBuilder = new DefaultPasswordEncoderAuthenticationManagerBuilder(
this.objectPostProcessor, passwordEncoder);
authenticationBuilder.parentAuthenticationManager(authenticationManager());
authenticationBuilder.authenticationEventPublisher(getAuthenticationEventPublisher());
HttpSecurity http = new HttpSecurity(this.objectPostProcessor, authenticationBuilder, createSharedObjects());
WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter webAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter = new WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter();
webAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter.setSecurityContextHolderStrategy(this.securityContextHolderStrategy);
// @formatter:off
http
.csrf(withDefaults())
.addFilter(webAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter)
.exceptionHandling(withDefaults())
.headers(withDefaults())
.sessionManagement(withDefaults())
.securityContext(withDefaults())
.requestCache(withDefaults())
.anonymous(withDefaults())
.servletApi(withDefaults())
.apply(new DefaultLoginPageConfigurer<>());
http.logout(withDefaults());
// @formatter:on
applyCorsIfAvailable(http);
applyDefaultConfigurers(http);
return http;
}@Scope("prototype") 确保了每次都能是独立的实例
@Scope("prototype") → 每次 getBean("httpSecurity") 都会重新执行 httpSecurity() 方法,创建新对象
HttpSecurity的创建
java
// 1 创建一个AuthenticationManagerBuilder
AuthenticationManagerBuilder authenticationBuilder = new DefaultPasswordEncoderAuthenticationManagerBuilder(
this.objectPostProcessor, passwordEncoder);
// 2设置父级认证管理器
authenticationBuilder.parentAuthenticationManager(authenticationManager());
authenticationBuilder.authenticationEventPublisher(getAuthenticationEventPublisher());
//3 创建HttpSecurity
HttpSecurity http = new HttpSecurity(this.objectPostProcessor, authenticationBuilder, createSharedObjects());构造器如下图:
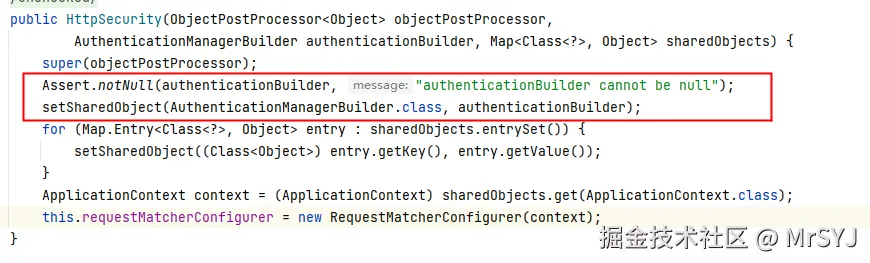
所以每个httpScurity内部都有一个独立的AuthenticationManagerBuilder 保存在sharedObjects属性中 这个是共享属性,确保后续使用的时候可以从共享属性中再次获取到
AuthenticationManagerBuilder
AuthenticationManagerBuilder是用来构建AuthenticationManager认证管理器的,每个HttpSecurity都持有一个自己的AuthenticationManagerBuilder。
AuthenticationManager是认证管理器,并在身份认证成功后返回一个经过认证的 Authentication 对象。AuthenticationManager 是一个接口,ProviderManager实现了这个接口
ProviderManager 维护了一个 AuthenticationProvider 列表,每个 AuthenticationProvider 都是一个认证器,不同的 AuthenticationProvider 用来处理不同的 Authentication 对象的认证。一次完整的身份认证流程可能会经过多个 AuthenticationProvider。
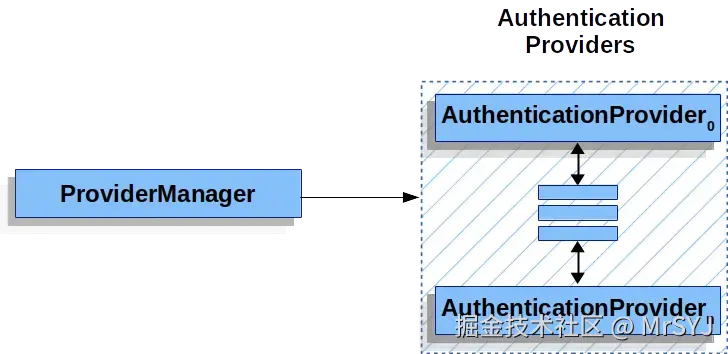
每一个 ProviderManager 管理多个 AuthenticationProvider,同时每一个 ProviderManager 都可以配置一个 parent,如果当前的 ProviderManager 中认证失败了,还可以去它的 parent 中继续执行认证
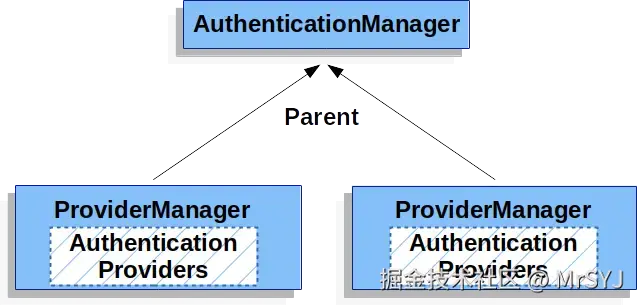
根据配置方式和作用范围,我们可以将 AuthenticationManager 分为:
- "全局" :指被注册为 Spring Bean 的、可被整个应用共享的
AuthenticationManager - "局部" :指仅在某个
SecurityFilterChain内部创建并使用的AuthenticationManager,作用范围有限
全局认证管理器
scss
DefaultPasswordEncoderAuthenticationManagerBuilder(
this.objectPostProcessor, passwordEncoder);
authenticationBuilder.parentAuthenticationManager(authenticationManager());前面我们了解到构建httpsecurity的时候需要创建authenticationBuilder,authenticationBuilder会通过调用authenticationManager()方法来设置全局认证管理器
csharp
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager() throws Exception {
return this.authenticationConfiguration.getAuthenticationManager();
}底层调用的是AuthenticationConfiguration中的方法
kotlin
public AuthenticationManager getAuthenticationManager() throws Exception {
if (this.authenticationManagerInitialized) {
return this.authenticationManager;
}
AuthenticationManagerBuilder authBuilder = this.applicationContext.getBean(AuthenticationManagerBuilder.class);
if (this.buildingAuthenticationManager.getAndSet(true)) {
return new AuthenticationManagerDelegator(authBuilder);
}
for (GlobalAuthenticationConfigurerAdapter config : this.globalAuthConfigurers) {
authBuilder.apply(config);
}
this.authenticationManager = authBuilder.build();
if (this.authenticationManager == null) {
this.authenticationManager = getAuthenticationManagerBean();
}
this.authenticationManagerInitialized = true;
return this.authenticationManager;
}上面这段方法确保了全局认证管理器只能被初始化一次,调用多次返回的是已经构建好的,基本原理还是从容器中获取到AuthenticationManagerBuilder,调用这个builder的build方法来构建。下面的代码展示了builder是如何放进容器的
java
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Import(ObjectPostProcessorConfiguration.class)
public class AuthenticationConfiguration {
// 在容器中放了一个AuthenticationManagerBuilder 将来用来构建全局认证管理器
@Bean
public AuthenticationManagerBuilder authenticationManagerBuilder(ObjectPostProcessor<Object> objectPostProcessor,
ApplicationContext context) {
LazyPasswordEncoder defaultPasswordEncoder = new LazyPasswordEncoder(context);
AuthenticationEventPublisher authenticationEventPublisher = getAuthenticationEventPublisher(context);
DefaultPasswordEncoderAuthenticationManagerBuilder result = new DefaultPasswordEncoderAuthenticationManagerBuilder(
objectPostProcessor, defaultPasswordEncoder);
if (authenticationEventPublisher != null) {
result.authenticationEventPublisher(authenticationEventPublisher);
}
return result;
}局部认证管理器
根据前面的介绍,HttpSecurity 在构建的时候就会传入 AuthenticationManagerBuilder,传入进来的 AuthenticationManagerBuilder ,被保存到SharedObject 里边去了缓存了起来
最终httpsecurity在build的过程中 会先执行beforeConfigure方法,用来构建局部认证管理器
scss
@Override
protected void beforeConfigure() throws Exception {
if (this.authenticationManager != null) {
setSharedObject(AuthenticationManager.class, this.authenticationManager);
}
else {
ObservationRegistry registry = getObservationRegistry();
AuthenticationManager manager = getAuthenticationRegistry().build();
if (!registry.isNoop() && manager != null) {
setSharedObject(AuthenticationManager.class, new ObservationAuthenticationManager(registry, manager));
}
else {
setSharedObject(AuthenticationManager.class, manager);
}
}
}你会发现getAuthenticationRegistry中返回的就是提前缓存好的authenticationManagerBuilder,最终构建出来的认证管理器是局部管理器
kotlin
@Override
public HttpSecurity authenticationProvider(AuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider) {
getAuthenticationRegistry().authenticationProvider(authenticationProvider);
return this;
}
@Override
public HttpSecurity userDetailsService(UserDetailsService userDetailsService) throws Exception {
getAuthenticationRegistry().userDetailsService(userDetailsService);
return this;
}
private AuthenticationManagerBuilder getAuthenticationRegistry() {
return getSharedObject(AuthenticationManagerBuilder.class);
}总结
总结下 本文主要讲解了 1.httpsecurity采用了多实例的方式,作者这么设计的原因是因为一个应用可以配置多条过滤器链,每个过滤器链需要单独的进行配置,httpSecurity就是过滤器链的配置类,所以需要多实例。
2.有全局认证管理器和局部认证管理器,全局认证管理器使用容器中的builder进行构建的,整个应用共享 局部认证管理器是和每个过滤器链,也就是每个HttpSecurity实例绑定的。