背景
本文分析kafka客户端如何发送消息。
注:基于kafka2.6的java客户端。
一、使用案例
Topic1和Topic2都是3分区2副本。
生产者代码:
java
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put("bootstrap.servers", "localhost:9092");
props.put("key.serializer", IntegerSerializer.class.getName());
props.put("value.serializer", StringSerializer.class.getName());
// 压缩策略,默认none不压缩
props.put("compression.type", "zstd");
// ack策略,默认1,0-不等待;1-等待leader落库;all(-1)-等待所有ISR落库
props.put("acks", "all");
// 消息批次 延迟时间 默认0ms
props.put("linger.ms", "1000");
KafkaProducer<Integer, String> producer = new KafkaProducer<>(props);
for (int i = 0; i < 40000; i++) {
producer.send(new ProducerRecord<>("Topic1", i, "Hello World"));
producer.send(new ProducerRecord<>("Topic2", i, "Hello World"));
}
producer.close();
}抓包:生产者发送ProduceRequest包含n个分区的消息。
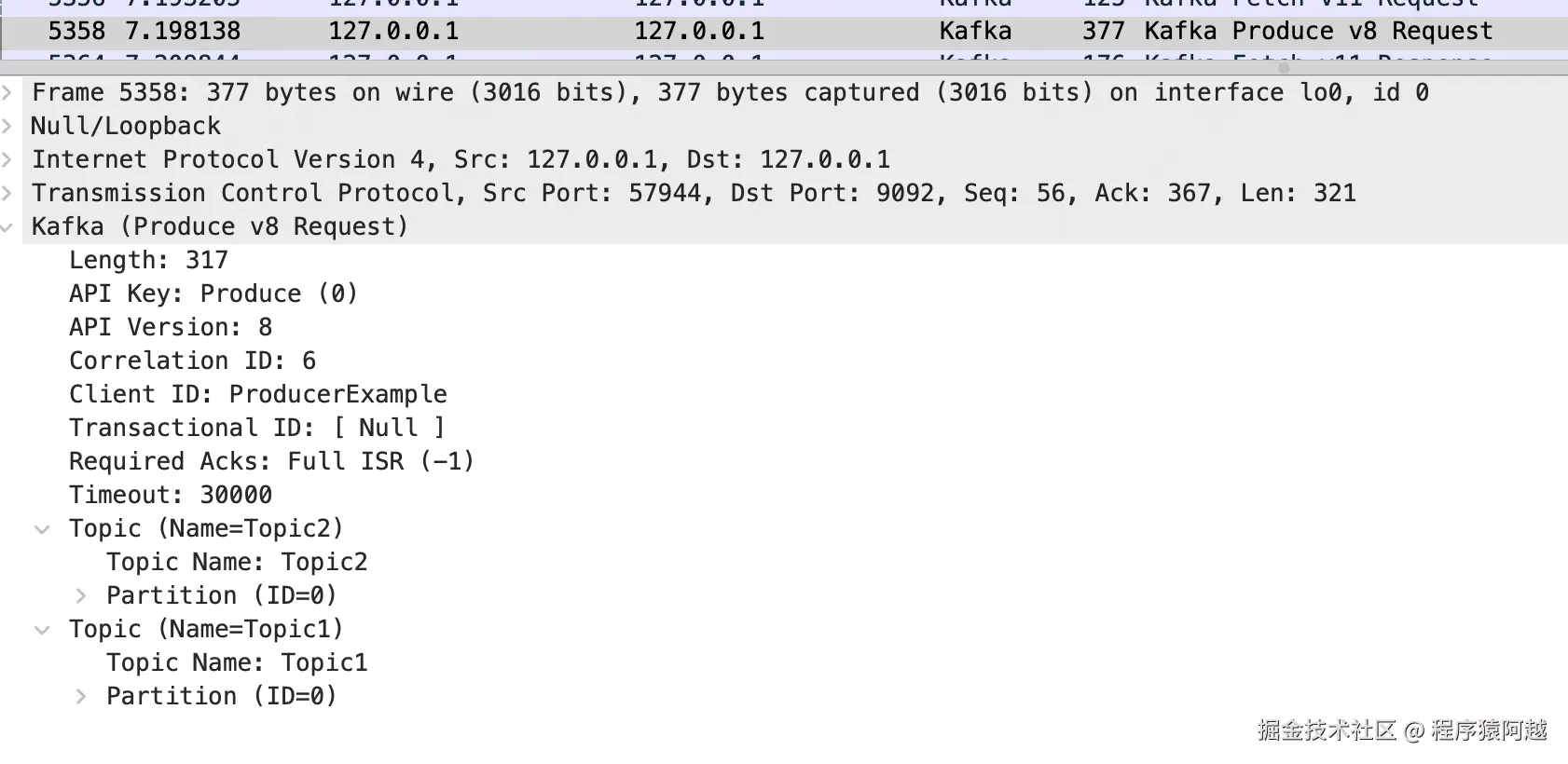
每个分区包含一个批次(RecordBatch),一个批次包含多条消息(Record)。
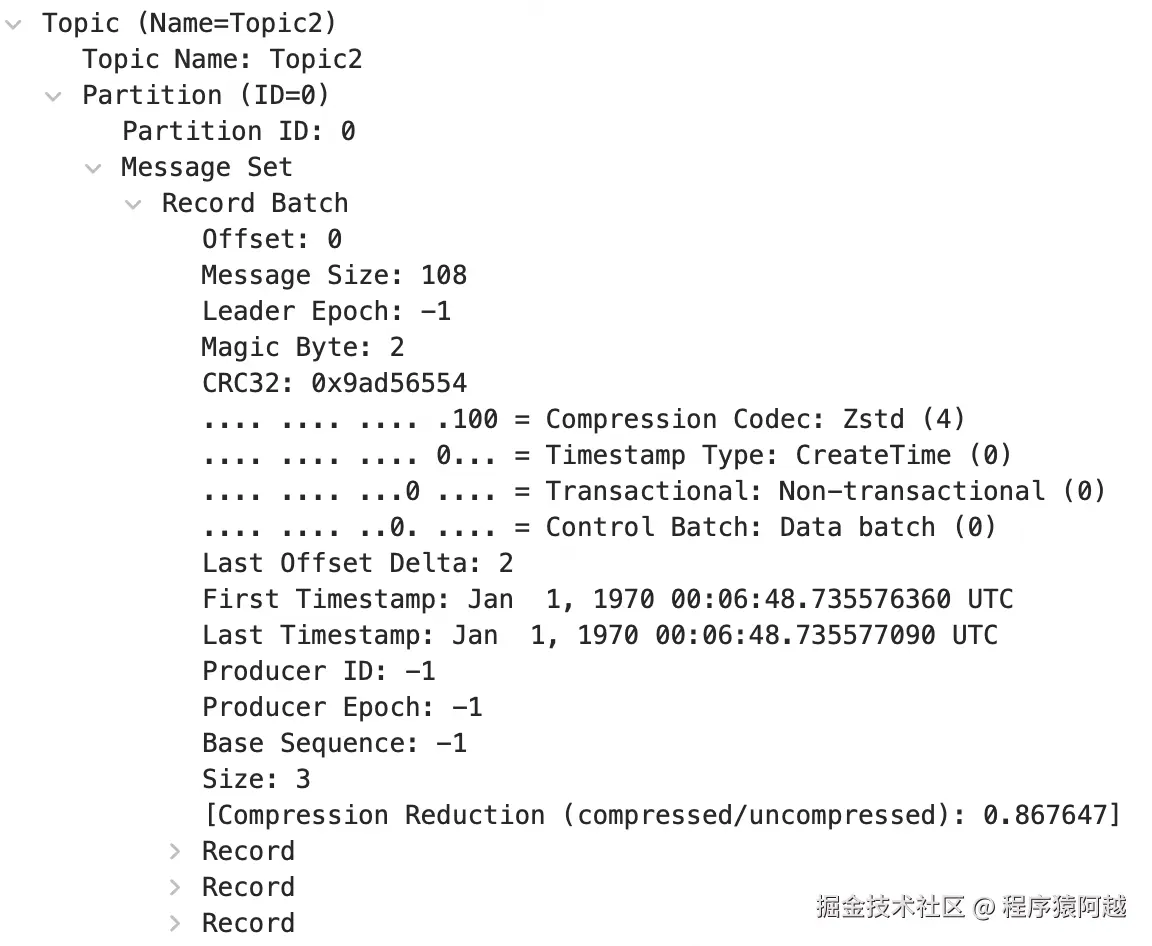
broker侧查看Topic1的p0分区目录如下。
这里将broker的log.segment.bytes调整为32768(32KB),默认为1G。
bash
Topic1-0 % ls -lh
40B 00000000000000000000.index
30K 00000000000000000000.log
72B 00000000000000000000.timeindex
10M 00000000000000011208.index
5.8K 00000000000000011208.log
10B 00000000000000011208.snapshot
10M 00000000000000011208.timeindex
8B leader-epoch-checkpoint使用kafka-dump-log.sh可以查看log的数据信息,第一个log的最后一条记录的lastOffset+1,正是第二个log的文件名。
shell
./kafka-dump-log.sh --files ../config/server1/Topic1-0/00000000000000000000.log
Dumping ../config/server1/Topic1-0/00000000000000000000.log
Starting offset: 0
baseOffset: 0 lastOffset: 668 count: 669 baseSequence: -1 lastSequence: -1 producerId: -1 producerEpoch: -1 partitionLeaderEpoch: 0 isTransactional: false isControl: false position: 0 CreateTime: 1753496555870 size: 1977 magic: 2 compresscodec: ZSTD crc: 273196058 isvalid: true
baseOffset: 669 lastOffset: 1344 count: 676 baseSequence: -1 lastSequence: -1 producerId: -1 producerEpoch: -1 partitionLeaderEpoch: 0 isTransactional: false isControl: false position: 1977 CreateTime: 1753496555939 size: 1933 magic: 2 compresscodec: ZSTD crc: 196171263 isvalid: true
// ...
baseOffset: 10361 lastOffset: 11207 count: 847 baseSequence: -1 lastSequence: -1 producerId: -1 producerEpoch: -1 partitionLeaderEpoch: 0 isTransactional: false isControl: false position: 28449 CreateTime: 1753496556585 size: 2235 magic: 2 compresscodec: ZSTD crc: 2388557788 isvalid: true二、客户端组件介绍
java
public class KafkaProducer<K, V> implements Producer<K, V> {
private final String clientId;
// 分区器
private final Partitioner partitioner;
// max.request.size = 1024 * 1024 = 1MB
private final int maxRequestSize;
// buffer.memory = 32 * 1024 * 1024 = 32MB
private final long totalMemorySize;
// 元数据缓存
private final ProducerMetadata metadata;
// 消息累加器
private final RecordAccumulator accumulator;
// 消息发送IO线程
private final Sender sender;
private final Thread ioThread;
// compression.type=none 压缩实现方式,默认不压缩
private final CompressionType compressionType;
// 序列化器
private final Serializer<K> keySerializer;
private final Serializer<V> valueSerializer;
// producer的配置
private final ProducerConfig producerConfig;
// max.block.ms=60000 send最多block时长(获取元数据+写累积器),默认60s
private final long maxBlockTimeMs;
// 拦截器(扩展点)
private final ProducerInterceptors<K, V> interceptors;
// 事务管理器 IGNORE
private final TransactionManager transactionManager;
}Partitioner
Partitioner:分区器,计算消息发送到哪个分区。
默认partitioner.class=org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.DefaultPartitioner。
java
public interface Partitioner {
public int partition(String topic, Object key,
byte[] keyBytes, Object value,
byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster);
}ProducerMetadata
ProducerMetadata:生产者元数据缓存。
java
public class ProducerMetadata extends Metadata {
// metadata.max.idle.ms=5 * 60 * 1000 5分钟
private final long metadataIdleMs;
// topic -> 元数据过期时间
private final Map<String, Long> topics = new HashMap<>();
// 还未发现元数据的topics
private final Set<String> newTopics = new HashSet<>();
}Metadata:生产者和消费者的元数据基类。
通过元数据缓存MetadataCache可以找到partition leader对应broker的连接信息,用于发送消息。
java
public class Metadata implements Closeable {
// broker集群元数据
private MetadataCache cache = MetadataCache.empty();
}
/**
* An internal mutable cache of nodes, topics, and partitions in the Kafka cluster. This keeps an up-to-date Cluster
* instance which is optimized for read access.
*/
public class MetadataCache {
private final String clusterId;
// brokerId -> broker连接信息 ip port
private final Map<Integer, Node> nodes;
private final Set<String> unauthorizedTopics;
private final Set<String> invalidTopics;
private final Set<String> internalTopics;
// controller连接信息
private final Node controller;
// 分区元数据
private final Map<TopicPartition, PartitionMetadata> metadataByPartition;
// 由上述信息构成的不可变视图对象
private Cluster clusterInstance;
}
public static class PartitionMetadata {
public final TopicPartition topicPartition;
public final Errors error;
// leader(brokerId)
public final Optional<Integer> leaderId;
// leader任期
public final Optional<Integer> leaderEpoch;
// 副本id(brokerIds)
public final List<Integer> replicaIds;
// ISR副本id(brokerIds)
public final List<Integer> inSyncReplicaIds;
public final List<Integer> offlineReplicaIds;
}客户端侧,一般使用MetadataCache构建的Cluster只读视图。
java
public final class Cluster {
private final boolean isBootstrapConfigured;
private final List<Node> nodes;
private final Set<String> unauthorizedTopics;
private final Set<String> invalidTopics;
private final Set<String> internalTopics;
// controller节点
private final Node controller;
// 分区 -> 分区信息
private final Map<TopicPartition, PartitionInfo> partitionsByTopicPartition;
// topic -> topic所有分区
private final Map<String, List<PartitionInfo>> partitionsByTopic;
// topic -> leader存活的所有分区
private final Map<String, List<PartitionInfo>> availablePartitionsByTopic;
// brokerId -> 分区
private final Map<Integer, List<PartitionInfo>> partitionsByNode;
// brokerId -> broker
private final Map<Integer, Node> nodesById;
}RecordAccumulator
RecordAccumulator:消息累积器。
kafka生产者支持通过ProducerBatch合并多个消息为一个批次发送到Broker,提升吞吐量。
批处理主要取决于两个配置:
1)batch.size:一批消息的大小,默认16384=16KB,如果单条消息超出该容量,按照消息实际大小分配;
2)linger.ms:未达到batch.size,一批消息最多延迟多久发送,默认0,即未开启批消息;
java
public final class RecordAccumulator {
private final AtomicInteger flushesInProgress;
private final AtomicInteger appendsInProgress;
// 批消息 内存分配大小 默认batch.size=16384=16KB
private final int batchSize;
// 压缩方式
private final CompressionType compression;
// 批消息 延迟时间 默认linger.ms=0ms
private final int lingerMs;
private final long retryBackoffMs;
private final int deliveryTimeoutMs;
// buffer池 容量 = buffer.memory = 32 * 1024 * 1024 = 32MB
private final BufferPool free;
// partition -> 批次队列
private final ConcurrentMap<TopicPartition, Deque<ProducerBatch>> batches;
private final IncompleteBatches incomplete;
private final Set<TopicPartition> muted;
private int drainIndex;
private final TransactionManager transactionManager;
private long nextBatchExpiryTimeMs = Long.MAX_VALUE;
}Sender
业务线程使用KafkaProducer实例发送消息,将数据写入RecordAccumulator累积器。
Sender线程(kafka-producer-network-thread)读取累积器中的数据,实际执行IO读写操作。
java
public class Sender implements Runnable {
// 网络客户端
private final KafkaClient client;
// 累积器
private final RecordAccumulator accumulator;
}KafkaClient底层使用NIO的Selector,处理多个Broker连接通道(SocketChannel)上的IO事件。
客户端与Broker建立的连接会被封装为KafkaChannel。
java
public class NetworkClient implements KafkaClient {
private final Selectable selector;
}
public class Selector implements Selectable, AutoCloseable {
// nio Selector
private final java.nio.channels.Selector nioSelector;
// brokerId -> 连接
private final Map<String, KafkaChannel> channels;
}
public class KafkaChannel implements AutoCloseable {
// brokerId
private final String id;
// 通过TransportLayer收发数据
private final TransportLayer transportLayer;
// 收到的buffer
private NetworkReceive receive;
// 发出的buffer
private Send send;
}
public class PlaintextTransportLayer implements TransportLayer {
// 通过SelectionKey设置nio关心的读写连接事件
private final java.nio.channels.SelectionKey key;
// nio底层通讯通道,可以读写数据
private final java.nio.channels.SocketChannel socketChannel;
}Serializer
Serializer:序列化器。
通过key.serializer和value.serializer指定消息Record的key和value如何序列化。
java
public class IntegerSerializer implements Serializer<Integer> {
public byte[] serialize(String topic, Integer data) {
if (data == null)
return null;
return new byte[] {
(byte) (data >>> 24),
(byte) (data >>> 16),
(byte) (data >>> 8),
data.byteValue()
};
}
}
public class StringSerializer implements Serializer<String> {
private String encoding = "UTF8";
@Override
public byte[] serialize(String topic, String data) {
try {
if (data == null)
return null;
else
return data.getBytes(encoding);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
throw new SerializationException("Error when serializing string to byte[] due to unsupported encoding " + encoding);
}
}
}三、生产者主流程
KafkaProducer#send:发送消息的入口,执行所有ProducerInterceptor钩子,可以改变ProducerRecord。
java
@Override
public Future<RecordMetadata> send(ProducerRecord<K, V> record) {
return send(record, null);
}
@Override
public Future<RecordMetadata> send(ProducerRecord<K, V> record, Callback callback) {
ProducerRecord<K, V> interceptedRecord = this.interceptors.onSend(record);
return doSend(interceptedRecord, callback);
}ProducerInterceptors#onSend:循环执行所有ProducerInterceptor,所有异常会被try-catch不影响消息发送。
java
public ProducerRecord<K, V> onSend(ProducerRecord<K, V> record) {
ProducerRecord<K, V> interceptRecord = record;
for (ProducerInterceptor<K, V> interceptor : this.interceptors) {
try {
interceptRecord = interceptor.onSend(interceptRecord);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn()
}
}
return interceptRecord;
}KafkaProducer#doSend:发送消息主流程
【1】获取topic元数据,如果缓存未命中,需要唤醒IO线程(Sender)发送MetadataRequest;
【2】key/value序列化;(忽略)
【3】计算消息分区;
【4】预计消息大小,校验消息不超过max.request.size,默认1MB;(忽略)
【5】将消息写入累积器;
【6】唤醒IO线程(Sender),IO线程会拉取累积器中的消息发送,返回Future;
java
private Future<RecordMetadata> doSend(ProducerRecord<K, V> record, Callback callback) {
TopicPartition tp = null;
try {
throwIfProducerClosed();
long nowMs = time.milliseconds();
ClusterAndWaitTime clusterAndWaitTime;
try {
//【1】获取元数据,包括集群broker信息,topic-partition信息
clusterAndWaitTime = waitOnMetadata(record.topic(), record.partition(), nowMs, maxBlockTimeMs);
} catch (KafkaException e) {
if (metadata.isClosed())
throw new KafkaException();
throw e;
}
nowMs += clusterAndWaitTime.waitedOnMetadataMs;
long remainingWaitMs = Math.max(0, maxBlockTimeMs - clusterAndWaitTime.waitedOnMetadataMs);
Cluster cluster = clusterAndWaitTime.cluster;
// 【2】key/value序列化
byte[] serializedKey;
try {
serializedKey = keySerializer.serialize(record.topic(), record.headers(), record.key());
} catch (ClassCastException cce) {
throw new SerializationException();
}
byte[] serializedValue;
try {
serializedValue = valueSerializer.serialize(record.topic(), record.headers(), record.value());
} catch (ClassCastException cce) {
throw new SerializationException();
}
// 【3】计算partition,如果ProducerRecord没显示指定分区,DefaultPartitioner
int partition = partition(record, serializedKey, serializedValue, cluster);
tp = new TopicPartition(record.topic(), partition);
setReadOnly(record.headers());
Header[] headers = record.headers().toArray();
// 【4】校验消息大小不能超过max.request.size = 1024 * 1024 = 1MB
int serializedSize = AbstractRecords.estimateSizeInBytesUpperBound(apiVersions.maxUsableProduceMagic(),
compressionType, serializedKey, serializedValue, headers);
ensureValidRecordSize(serializedSize);
long timestamp = record.timestamp() == null ? nowMs : record.timestamp();
Callback interceptCallback = new InterceptorCallback<>(callback, this.interceptors, tp);
if (transactionManager != null && transactionManager.isTransactional()) {
transactionManager.failIfNotReadyForSend();
}
// 【5】将消息加入累积器
RecordAccumulator.RecordAppendResult result = accumulator.append(tp, timestamp, serializedKey,
serializedValue, headers, interceptCallback, remainingWaitMs, true, nowMs);
// KIP-480 开启新批次,重新执行partitioner
if (result.abortForNewBatch) {
int prevPartition = partition;
partitioner.onNewBatch(record.topic(), cluster, prevPartition);
partition = partition(record, serializedKey, serializedValue, cluster);
tp = new TopicPartition(record.topic(), partition);
interceptCallback = new InterceptorCallback<>(callback, this.interceptors, tp);
result = accumulator.append(tp, timestamp, serializedKey,
serializedValue, headers, interceptCallback, remainingWaitMs, false, nowMs);
}
if (transactionManager != null && transactionManager.isTransactional())
transactionManager.maybeAddPartitionToTransaction(tp);
// 【6】唤醒io线程发送消息
if (result.batchIsFull || result.newBatchCreated) {
this.sender.wakeup();
}
return result.future;
}
}四、获取生产者元数据
producer并不需要全量的元数据,不需要未send过的topic的元数据。
java
public class ProducerMetadata extends Metadata {
// metadata.max.idle.ms=5 * 60 * 1000 5分钟
private final long metadataIdleMs;
// topic -> 元数据过期时间,这些topic是producer关心的
private final Map<String, Long> topics = new HashMap<>();
// 还未发现元数据的topics
private final Set<String> newTopics = new HashSet<>();
}所以producer需要告知sender线程需要更新哪些topic的元数据。
对于producer来说,先从缓存获取元数据,如果获取不到,需要等待sender线程获取。
而sender可能阻塞在IO上,比如Selector#select,所以需要producer唤醒sender。
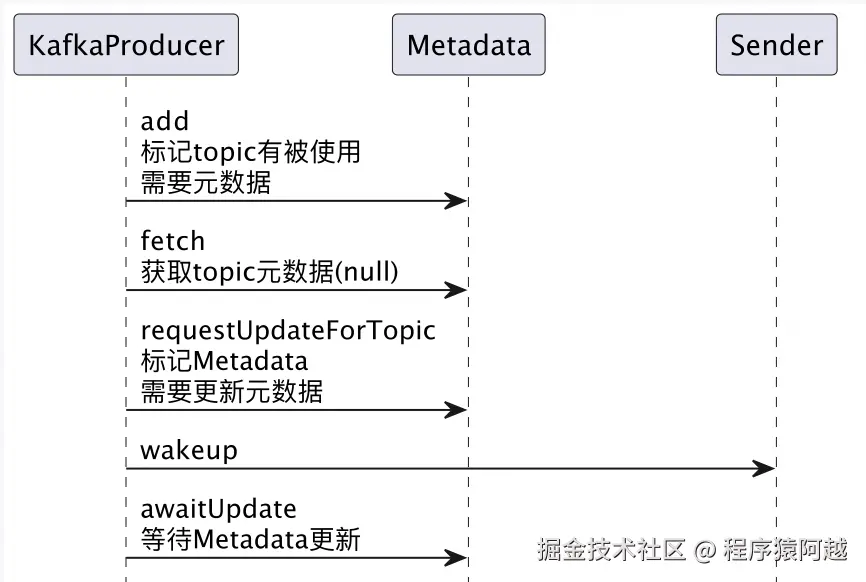
sender被唤醒后反查Metadata是否需要更新,由Metadata构建MetadataRequest(包含必要topic),sender调用broker查询元数据,broker返回后,sender更新Metadata,唤醒producer。
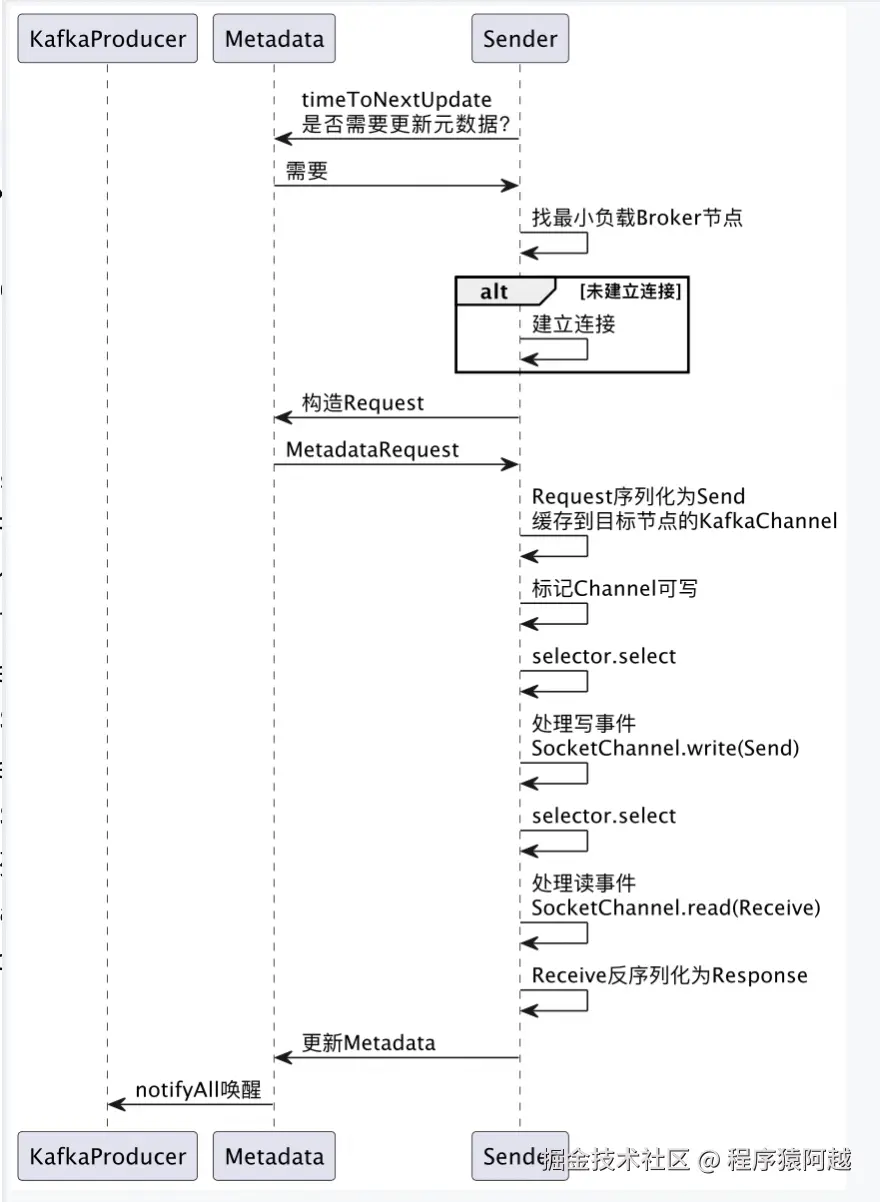
Producer线程
KafkaProducer#waitOnMetadata:producer线程获取元数据的流程
【1】metadata.add,标记topic需要元数据;
【2】cluster.partitionCountForTopic,从缓存中获取topic元数据,如果缓存命中,结束流程;
【3】缓存未命中,sender.wakeup唤醒Sender线程;
【4】metadata.awaitUpdate,等待Sender线程更新缓存;
java
private final ProducerMetadata metadata;
private final Sender sender;
private ClusterAndWaitTime waitOnMetadata(String topic, Integer partition, long nowMs, long maxWaitMs)
throws InterruptedException {
Cluster cluster = metadata.fetch();
// 标记生产者需要该topic的元数据,刷新缓存时效,不要让其被移除
metadata.add(topic, nowMs);
// 通过Cluster视图获取topic对应partition数量
Integer partitionsCount = cluster.partitionCountForTopic(topic);
// topic元数据缓存命中,直接返回
if (partitionsCount != null && (partition == null || partition < partitionsCount))
return new ClusterAndWaitTime(cluster, 0);
// topic元数据缓存未命中,需要io线程发送MetadataRequest
long remainingWaitMs = maxWaitMs;
long elapsed = 0;
do {
metadata.add(topic, nowMs + elapsed);
// 标记元数据需要部分或全量更新
int version = metadata.requestUpdateForTopic(topic);
// 唤醒sender的nioSelector
sender.wakeup();
try {
// 等待sender更新metadata
metadata.awaitUpdate(version, remainingWaitMs);
} catch (TimeoutException ex) {
throw new TimeoutException();
}
cluster = metadata.fetch();
elapsed = time.milliseconds() - nowMs;
if (elapsed >= maxWaitMs) {
throw new TimeoutException();
}
metadata.maybeThrowExceptionForTopic(topic);
remainingWaitMs = maxWaitMs - elapsed;
// 通过Cluster视图获取topic对应partition数量
partitionsCount = cluster.partitionCountForTopic(topic);
} while (partitionsCount == null || (partition != null && partition >= partitionsCount));
return new ClusterAndWaitTime(cluster, elapsed);
}ProducerMetadata#add:
【1】producer线程发送消息,将目标topic写入ProducerMetadata,标记这个topic需要元数据。
java
public class ProducerMetadata extends Metadata {
public synchronized void add(String topic, long nowMs) {
if (topics.put(topic, nowMs + metadataIdleMs) == null) {
// 还未发现该topic的元数据,加入newTopics
newTopics.add(topic);
// 标记Metadata需要部分更新
requestUpdateForNewTopics();
}
}
public synchronized int requestUpdateForTopic(String topic) {
if (newTopics.contains(topic)) {
// 如果还未发现该topic的元数据,标记部分更新
return requestUpdateForNewTopics();
} else {
// 否则标记为全量更新
return requestUpdate();
}
}
// Sender线程调用,仅获取新增topic的元数据
@Override
public synchronized MetadataRequest.Builder newMetadataRequestBuilderForNewTopics() {
return new MetadataRequest.Builder(new ArrayList<>(newTopics), true);
}
// Sender线程调用,获取缓存topics的全量元数据
@Override
public synchronized MetadataRequest.Builder newMetadataRequestBuilder() {
return new MetadataRequest.Builder(new ArrayList<>(topics.keySet()), true);
}
}ProducerMetadata#awaitUpdate:
【4】缓存未命中,producer线程等待Sender线程更新缓存。
java
private final Time time; // SystemTime
public synchronized void awaitUpdate(final int lastVersion, final long timeoutMs) throws InterruptedException {
long currentTimeMs = time.milliseconds();
long deadlineMs = currentTimeMs + timeoutMs < 0 ? Long.MAX_VALUE : currentTimeMs + timeoutMs;
time.waitObject(this, () -> {
maybeThrowFatalException();
// 等待MetadataResponse返回,更新缓存后,version++
return updateVersion() > lastVersion || isClosed();
}, deadlineMs);
if (isClosed())
throw new KafkaException("Requested metadata update after close");
}
// SystemTime
@Override
public void waitObject(Object obj, Supplier<Boolean> condition, long deadlineMs) throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (obj) {
while (true) {
if (condition.get())
return;
long currentTimeMs = milliseconds();
if (currentTimeMs >= deadlineMs)
throw new TimeoutException();
obj.wait(deadlineMs - currentTimeMs);
}
}
}Sender线程
Sender线程如下。
java
@Override
public void run() {
while (running) {
runOnce();
}
}
void runOnce() {
long currentTimeMs = time.milliseconds();
// 将累积器中的消息转换为Send缓存到KafkaChannel
long pollTimeout = sendProducerData(currentTimeMs);
// 执行IO
client.poll(pollTimeout, currentTimeMs);
}NetworkClient#poll:poll是Sender的主要逻辑。
java
// NetworkClient#poll
private final Selectable selector;
private final MetadataUpdater metadataUpdater;
@Override
public List<ClientResponse> poll(long timeout, long now) {
// 【1】可能构造MetadataRequest缓存到channel
long metadataTimeout = metadataUpdater.maybeUpdate(now);
// 【2】执行io操作 读 写 ...
this.selector.poll(Utils.min(timeout, metadataTimeout, defaultRequestTimeoutMs));
long updatedNow = this.time.milliseconds();
List<ClientResponse> responses = new ArrayList<>();
// 【3】处理收到的响应
handleCompletedReceives(responses, updatedNow);
// ..
return responses;
}DefaultMetadataUpdater#maybeUpdate:Sender需要根据Metadata判断是否需要刷新元数据。
java
// NetworkClient的内部类DefaultMetadataUpdater#maybeUpdate
private final Metadata metadata;
@Override
public long maybeUpdate(long now) {
// 元数据判断是否需要刷新
long timeToNextMetadataUpdate = metadata.timeToNextUpdate(now);
// IO线程还有元数据刷新请求没处理,不刷新
long waitForMetadataFetch = hasFetchInProgress() ?
defaultRequestTimeoutMs : 0;
long metadataTimeout = Math.max(timeToNextMetadataUpdate, waitForMetadataFetch);
if (metadataTimeout > 0) {
return metadataTimeout;
}
// 找到最小负载节点
Node node = leastLoadedNode(now);
if (node == null) {
return reconnectBackoffMs;
}
return maybeUpdate(now, node);
}
// NetworkClient的内部类DefaultMetadataUpdater#maybeUpdate
private long maybeUpdate(long now, Node node) {
String nodeConnectionId = node.idString();
// 未建立连接 这里为false 不能发请求 先要走initiateConnect
if (canSendRequest(nodeConnectionId, now)) {
Metadata.MetadataRequestAndVersion requestAndVersion = metadata.newMetadataRequestAndVersion(now);
MetadataRequest.Builder metadataRequest = requestAndVersion.requestBuilder;
// NetworkClient将Request缓存到Channel
sendInternalMetadataRequest(metadataRequest, nodeConnectionId, now);
inProgress = new InProgressData(requestAndVersion.requestVersion, requestAndVersion.isPartialUpdate);
return defaultRequestTimeoutMs;
}
// 还未与node建立连接,先建立连接,下次poll才能发送请求
if (connectionStates.canConnect(nodeConnectionId, now)) {
initiateConnect(node, now);
return reconnectBackoffMs;
}
// ...
}
// NetworkClient#sendInternalMetadataRequest
void sendInternalMetadataRequest(MetadataRequest.Builder builder, String nodeConnectionId, long now) {
ClientRequest clientRequest = newClientRequest(nodeConnectionId, builder, now, true);
doSend(clientRequest, true, now);
}Metadata#timeToNextUpdate:元数据自身判断是否需要更新有几个条件
1)retry.backoff.ms=100内发生过更新,不需要更新;
2)满足以下一个条件,允许更新:
2-1)producer请求更新,比如新发送一个topic不存在元数据需要增量更新;
2-2)距离上次Metadata更新超过metadata.max.age.ms=5分钟,需要刷新;
java
public synchronized long timeToNextUpdate(long nowMs) {
long timeToExpire =
// producer请求更新,部分或全量
updateRequested() ? 0 :
// 到达metadata.max.age.ms=5分钟 需要刷新
Math.max(this.lastSuccessfulRefreshMs + this.metadataExpireMs - nowMs, 0);
return Math.max(timeToExpire,
// 如果retry.backoff.ms=100内发生过更新,不更新
timeToAllowUpdate(nowMs));
}Sender请求响应的主要工作方式是:
【1】先把Request序列化为Send放到目标Channel,标记Channel可写;
java
// NetworkClient#doSend
private final Selectable selector;
private void doSend(ClientRequest clientRequest, boolean isInternalRequest, long now, AbstractRequest request) {
String destination = clientRequest.destination(); // brokerId
RequestHeader header = clientRequest.makeHeader(request.version());
// request序列化为bytebuffer,转换为Send对象
Send send = request.toSend(destination, header);
// 正在发送的请求
InFlightRequest inFlightRequest = new InFlightRequest(
clientRequest, header,
isInternalRequest, request,
send, now);
this.inFlightRequests.add(inFlightRequest);
// 将Send缓存到目标连接KafkaChannel
selector.send(send);
}
// org.apache.kafka.common.network.Selector#send
private final Map<String, KafkaChannel> channels;
public void send(Send send) {
String connectionId = send.destination();
// KafkaChannel channel = channels.get(connectionId);
KafkaChannel channel = openOrClosingChannelOrFail(connectionId);
channel.setSend(send);
}
// org.apache.kafka.common.network.KafkaChannel#setSend
private final TransportLayer transportLayer;
private Send send;
public void setSend(Send send) {
// 单channel只能有一个Send被缓存
// 发消息和获取元数据不能并发,上层做了校验
if (this.send != null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
this.send = send;
this.transportLayer.addInterestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
// PlaintextTransportLayer#addInterestOps
private final SelectionKey key;
public void addInterestOps(int ops) {
key.interestOps(key.interestOps() | ops);
}【2】selector.select发现Channel可写,将Channel中的Send写到对端;
java
private final java.nio.channels.Selector nioSelector;
@Override
public void poll(long timeout) throws IOException {
int numReadyKeys = select(timeout);
long endSelect = time.nanoseconds();
if (numReadyKeys > 0) {
Set<SelectionKey> readyKeys = this.nioSelector.selectedKeys();
// ...
pollSelectionKeys(readyKeys, false, endSelect);
// ...
}
// ...
}
private int select(long timeoutMs) throws IOException {
if (timeoutMs == 0L)
return this.nioSelector.selectNow();
else
return this.nioSelector.select(timeoutMs);
}
void pollSelectionKeys(Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys,
boolean isImmediatelyConnected,
long currentTimeNanos) {
for (SelectionKey key : selectionKeys) {
KafkaChannel channel = channel(key);
try {
// ...
// 处理读事件
if (channel.ready() && (key.isReadable() || ...)) {
attemptRead(channel);
}
// 处理写事件(发送消息、发送MetadataRequest)
attemptWrite(key, channel, nowNanos);
}
}
}
// 连接建立时,通过attachment绑定netty通道->业务KafkaChannel通道
private KafkaChannel channel(SelectionKey key) {
return (KafkaChannel) key.attachment();
}Selector#attemptWrite:将缓存在KafkaChannel的Send对象写到SocketChannel。
java
// org.apache.kafka.common.network.Selector#attemptWrite
private void attemptWrite(SelectionKey key, KafkaChannel channel, long nowNanos) throws IOException {
if (channel.hasSend() && channel.ready() && key.isWritable()) {
write(channel);
}
}
// org.apache.kafka.common.network.Selector#write
void write(KafkaChannel channel) throws IOException {
String nodeId = channel.id();
long bytesSent = channel.write(); // 将Send写入channel
}
// org.apache.kafka.common.network.KafkaChannel#write
private Send send; // 【1】缓存的Send对象,待发送的请求
public long write() throws IOException {
return send.writeTo(transportLayer);
}
// ByteBufferSend#writeTo
public long writeTo(GatheringByteChannel channel) throws IOException {
long written = channel.write(buffers);
return written;
}
// PlaintextTransportLayer#write
private final SocketChannel socketChannel;
public long write(ByteBuffer[] srcs) throws IOException {
return socketChannel.write(srcs);
}【3】对端处理完成,selector.select发现Channel可读,读到Receive里,反序列化为Response,执行回调;
java
// Selector#attemptRead
private final LinkedHashMap<String, NetworkReceive> completedReceives;
private void attemptRead(KafkaChannel channel) throws IOException {
String nodeId = channel.id();
long bytesReceived = channel.read();
if (bytesReceived != 0) {
NetworkReceive receive = channel.maybeCompleteReceive();
if (receive != null) {
// 读到的数据缓存下来
addToCompletedReceives(channel, receive, currentTimeMs);
}
}
}
private void addToCompletedReceives(KafkaChannel channel, NetworkReceive networkReceive, long currentTimeMs) {
this.completedReceives.put(channel.id(), networkReceive);
}
// KafkaChannel#read
private NetworkReceive receive; // 收到的响应
public long read() throws IOException {
long bytesReceived = receive(this.receive);
return bytesReceived;
}
private long receive(NetworkReceive receive) throws IOException {
return receive.readFrom(transportLayer);
}
// NetworkReceive#readFrom
private final ByteBuffer size = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);
private int requestedBufferSize = -1;
private ByteBuffer buffer;
public long readFrom(ScatteringByteChannel channel) throws IOException {
int read = 0;
// 先读4个byte得到响应大小
if (size.hasRemaining()) {
int bytesRead = channel.read(size);
if (bytesRead < 0)
throw new EOFException();
read += bytesRead;
if (!size.hasRemaining()) {
size.rewind();
int receiveSize = size.getInt();
requestedBufferSize = receiveSize;
if (receiveSize == 0) {
buffer = EMPTY_BUFFER;
}
}
}
if (buffer == null && requestedBufferSize != -1) {
// 按照上面读到的size,分配内存
buffer = memoryPool.tryAllocate(requestedBufferSize);
}
if (buffer != null) {
// 从socketChannel读数据到buffer
int bytesRead = channel.read(buffer);
read += bytesRead;
}
return read;
}NetworkClient#poll:此时可以从Selector的缓存Receives拿到需要处理的响应。
java
public List<ClientResponse> poll(long timeout, long now) {
// 可能构造MetadataRequest缓存到channel
long metadataTimeout = metadataUpdater.maybeUpdate(now);
// 执行io操作 读 写 ...
this.selector.poll(Utils.min(timeout, metadataTimeout, defaultRequestTimeoutMs));
long updatedNow = this.time.milliseconds();
List<ClientResponse> responses = new ArrayList<>();
// 处理收到的响应【此处从selector的completedReceives中拿到需要处理的响应】
handleCompletedReceives(responses, updatedNow);
return responses;
}
private void handleCompletedReceives(List<ClientResponse> responses, long now) {
for (NetworkReceive receive : this.selector.completedReceives()) {
String source = receive.source(); // KafkaChannel.id即brokerId
InFlightRequest req = inFlightRequests.completeNext(source);
// 反序列化为Response
Struct responseStruct = parseStructMaybeUpdateThrottleTimeMetrics(receive.payload(), req.header,
throttleTimeSensor, now);
AbstractResponse response = AbstractResponse.
parseResponse(req.header.apiKey(), responseStruct, req.header.apiVersion());
if (req.isInternalRequest && response instanceof MetadataResponse)
// 元数据响应
metadataUpdater.handleSuccessfulResponse(req.header, now, (MetadataResponse) response);
else
// ... 其他响应,比如发送消息响应
responses.add(req.completed(response, now));
}
}ProducerMetadata#update:最终Sender线程收到MetadataResponse,调用Metadata更新缓存,唤醒等待元数据的producer线程。
java
public class ProducerMetadata extends Metadata {
// Sender线程收到MetadataResponse,调用Metadata更新缓存
@Override
public synchronized void update(int requestVersion, MetadataResponse response, boolean isPartialUpdate, long nowMs) {
// 生产消费Metadata统一逻辑,更新Metadata缓存,会回调retainTopic
super.update(requestVersion, response, isPartialUpdate, nowMs);
if (!newTopics.isEmpty()) {
for (MetadataResponse.TopicMetadata metadata : response.topicMetadata()) {
// 新发现的topic元数据,从newTopics标记中移除
newTopics.remove(metadata.topic());
}
}
// 唤醒等待元数据的producer线程
notifyAll();
}
/**
* super.update判断是否需要保留该主题的元数据
* @param topic 主题
* @param isInternal 内部请求
* @param nowMs 当前时间
* @return true-需要保留该topic的元数据 false-该topic的元数据可以清理
*/
@Override
public synchronized boolean retainTopic(String topic, boolean isInternal, long nowMs) {
Long expireMs = topics.get(topic);
if (expireMs == null) {
return false;
} else if (newTopics.contains(topic)) {
// 新发现的topic,需要保留
return true;
} else if (expireMs <= nowMs) {
// topic长时间没有发消息,移除topic的元数据
topics.remove(topic);
return false;
} else {
// topic最近有发消息,需要保留topic的元数据
return true;
}
}
}五、计算分区
KafkaProducer#partition:如果用户未主动指定Record的partition属性,由分区器计算Record发往哪个分区。
java
private int partition(ProducerRecord<K, V> record, byte[] serializedKey, byte[] serializedValue, Cluster cluster) {
Integer partition = record.partition(); // 用户指定分区
return partition != null ?
partition :
partitioner.partition(...);
}默认分区器为DefaultPartitioner,可以通过partitioner.class=完全限定类名,定义分区器。
case1,如果用户消息指定了key,通过hash(key)%分区数得到分区。
注意这里cluster.partitionsForTopic(topic).size()得到的分区数,是topic下所有分区,无论这个分区是否可用(leader是否存在,即LeaderAndIsr中的leader=-1也会被选中)。
java
public class DefaultPartitioner implements Partitioner {
private final StickyPartitionCache stickyPartitionCache = new StickyPartitionCache();
public int partition(String topic, Object key,
byte[] keyBytes, Object value,
byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster) {
return partition(topic, key, keyBytes, value, valueBytes,
cluster,
cluster.partitionsForTopic(topic).size());
}
public int partition(String topic, Object key,
byte[] keyBytes, Object value,
byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster,
int numPartitions) {
if (keyBytes == null) {
// KIP-480 Sticky Partitioner 没有指定key,采取一个批次一个partition
return stickyPartitionCache.partition(topic, cluster);
}
// hash(key)%分区数量
return Utils.toPositive(Utils.murmur2(keyBytes)) % numPartitions;
}
}case2,KIP-480引入,如果用户未指定key,采取Sticky粘滞分区策略。(原来是round-robin)
Sticky策略将没有key的消息,合并到一个分区批次中发送,降低无key消息的发送延迟。
StickyPartitionCache缓存了每个topic的粘滞分区,如果topic还未发送过无key消息,需要选择分区。
这里选择分区的逻辑中,优先从可用分区(leader存在)随机选择,降级从所有分区随机选择。
有key消息不会受分区leader下线而hash到另一个分区。
java
public class StickyPartitionCache {
// topic -> 当前stiky的分区
private final ConcurrentMap<String, Integer> indexCache;
public StickyPartitionCache() {
this.indexCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
}
public int partition(String topic, Cluster cluster) {
Integer part = indexCache.get(topic);
if (part == null) {
// 还没有stiky分区,选一个缓存下来
return nextPartition(topic, cluster, -1);
}
// 优先用stiky分区
return part;
}
public int nextPartition(String topic,
Cluster cluster, int prevPartition) {
// 所有分区
List<PartitionInfo> partitions = cluster.partitionsForTopic(topic);
Integer oldPart = indexCache.get(topic);
Integer newPart = oldPart;
if (oldPart == null || oldPart == prevPartition) {
// 有leader的分区
List<PartitionInfo> availablePartitions = cluster.availablePartitionsForTopic(topic);
if (availablePartitions.size() < 1) {
// 所有分区都没有leader,从所有分区中任意选择一个
Integer random = Utils.toPositive(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt());
newPart = random % partitions.size();
} else if (availablePartitions.size() == 1) {
// 只有一个分区有leader,选择这个
newPart = availablePartitions.get(0).partition();
} else {
// 从有leader的分区中随机选择一个
// 不能是老分区,保证整体负载均衡
while (newPart == null || newPart.equals(oldPart)) {
Integer random = Utils.toPositive(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt());
newPart = availablePartitions.get(random % availablePartitions.size()).partition();
}
}
if (oldPart == null) {
indexCache.putIfAbsent(topic, newPart);
} else {
indexCache.replace(topic, prevPartition, newPart);
}
return indexCache.get(topic);
}
return indexCache.get(topic);
}
}KafkaProducer#doSend:如果累积器写入返回abortForNewBatch,代表当前分区批次已满,该分区需要开启新批次。因为引入了Stiky分区策略,需要StickyPartitionCache在批次满了之后,重新分配一个新的黏滞分区,来整体保证无key消息的负载均衡。
java
private Future<RecordMetadata> doSend(ProducerRecord<K, V> record, Callback callback) {
// 【3】计算partition,如果ProducerRecord没显示指定分区,DefaultPartitioner
int partition = partition(...);
// 【5】将消息加入累积器
RecordAccumulator.RecordAppendResult result = accumulator.append(...);
if (result.abortForNewBatch) { // KIP-480
// 开启新批次
int prevPartition = partition;
// 再来一次sticky策略
partitioner.onNewBatch(record.topic(), cluster, prevPartition);
// 重新分区
partition = partition(...);
// 再写入累积器
result = accumulator.append(...);
}
}
// DefaultPartitioner
public void onNewBatch(String topic, Cluster cluster, int prevPartition) {
stickyPartitionCache.nextPartition(topic, cluster, prevPartition);
}六、写累积器
1、重要模型
RecordAccumulator
java
public final class RecordAccumulator {
// 正在写累加器的线程数量
private final AtomicInteger appendsInProgress;
// 消息批次分配内存大小 默认batch.size=16KB
private final int batchSize;
// 压缩方式
private final CompressionType compression;
// 消息批次 延迟时间 默认linger.ms=0ms
private final int lingerMs;
// 重试间隔 retry.backoff.ms=100ms
private final long retryBackoffMs;
// send方法发送超时时间,用来控制重试次数(retries默认Integer.MAX_VALUE)
// 默认delivery.timeout.ms=2分钟
private final int deliveryTimeoutMs;
// buffer池 容量=buffer.memory=32MB
private final BufferPool free;
private final Time time;
private final ApiVersions apiVersions;
// partition -> 批次队列
private final ConcurrentMap<TopicPartition, Deque<ProducerBatch>> batches;
// 已经发送但还未收到响应的ProducerBatch
private final IncompleteBatches incomplete;
// 下面是提供给sender用的
private final Set<TopicPartition> muted;
private int drainIndex;
private final TransactionManager transactionManager;
private long nextBatchExpiryTimeMs = Long.MAX_VALUE;
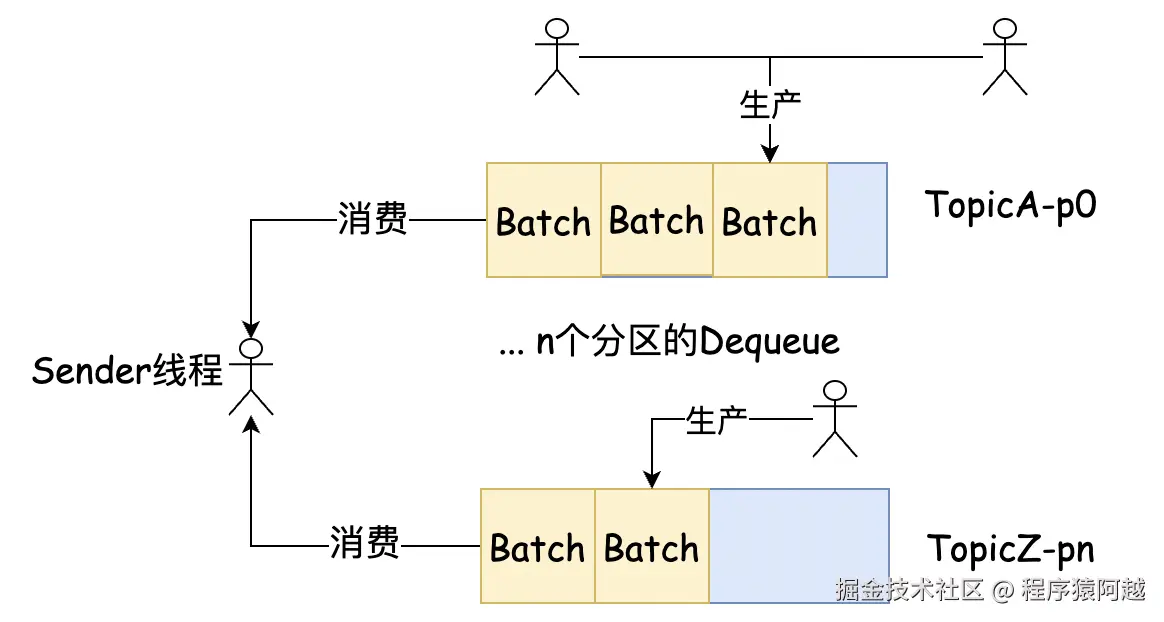
}batches 为每个分区维护了一个Deque 双端队列,队列中的元素即为消息批次ProducerBatch。
n个生产者线程将消息写入各分区队尾的批次,sender线程从各分区队首拉取批次发送。
ProducerBatch
ProducerBatch属于一个分区,代表了一个消息批次。
java
// 批次创建时间
final long createdMs;
// 分区
final TopicPartition topicPartition;
// 发送future
final ProduceRequestResult produceFuture;
// Thunk=(回调方法,发送结果),批次发送响应后
// 循环thunks回调InterceptorCallback和用户callback
private final List<Thunk> thunks = new ArrayList<>();
// 【重点】消息写入MemoryRecordsBuilder
private final MemoryRecordsBuilder recordsBuilder;
// 重试次数
private final AtomicInteger attempts = new AtomicInteger(0);
// 消息数量
int recordCount;
// 最大消息大小
int maxRecordSize;
// 最后一次尝试时间,初始等于createdMs
private long lastAttemptMs;
// 最后一次追加时间(批次被append新消息)
private long lastAppendTime;每个ProducerBatch用MemoryRecordsBuilder维护底层消息buffer。
对于producer,用ByteBufferOutputStream包装ByteBuffer,用于写数据。
对于sender,用MemoryRecords包装同一个ByteBuffer,用于读数据。
java
public class MemoryRecordsBuilder {
// producer 消息写入buffer
private final ByteBufferOutputStream bufferStream;
// sender 消息读取,底层与bufferStream使用同一个buffer
private MemoryRecords builtRecords;
}
public class ByteBufferOutputStream extends OutputStream {
private ByteBuffer buffer;
}BufferPool
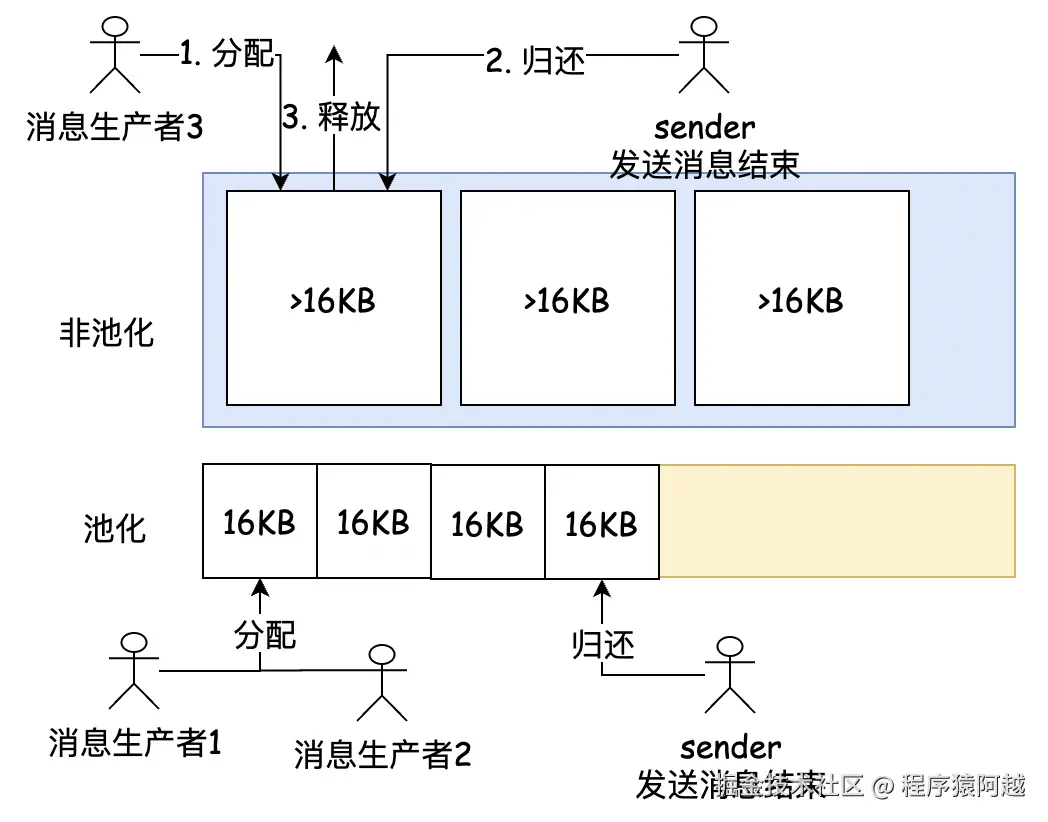
BufferPool,为ProducerBatch(MemoryRecordsBuilder)分配buffer,默认buffer池大小为32MB。(buffer.memory)
java
public class BufferPool {
// 池容量=buffer.memory=32MB
private final long totalMemory;
// 池化buffer的大小=buffer.size=16KB
private final int poolableSize;
private final ReentrantLock lock;
// 池化buffer归还到这里,后续可直接分配出去
private final Deque<ByteBuffer> free;
// 等待获取buffer的conditions
private final Deque<Condition> waiters;
// 非池化的buffer大小,初始=池容量=32MB
private long nonPooledAvailableMemory;
}默认消息批次大小poolableSize=buffer.size=16KB,只要单条消息不大于16KB,都可以正常使用池化能力。消息生产者,触发批次创建,由BufferPool分配buffer,BufferPool优先使用free队列中已经池化的buffer,否则新创建buffer返回;Sender,发送消息结束,将buffer归还到BufferPool,BufferPooll用free队列池化buffer,供后续生产者使用。
如果单条消息大小超过16KB,则无法使用池化能力。消息生产者,BufferPool直接分配内存;Sender发送消息结束,BufferPool直接释放内存。
2、出入参
RecordAccumulator.append是生产者写入累积器的api。
入参如下:
java
public RecordAppendResult append(
// 目标分区
TopicPartition tp,
// 消息时间(如果用户未设置,则为当前时间)
long timestamp,
// 消息key
byte[] key,
// 消息value
byte[] value,
// 消息header
Header[] headers,
// interceptors和用户callback
Callback callback,
// max.block.ms(60s)-先前等待元数据花费的时间
long maxTimeToBlock,
// 如果要创建新批次,是否直接返回,上面KIP-480的sticky分区策略需要更换新分区
boolean abortOnNewBatch,
// 当前时间
long nowMs) throws InterruptedException {
}出参如下:
java
public final static class RecordAppendResult {
// 如果写入累积器成功,返回这个future,
// sender会完成这个future,生产者线程通过这个future获取消息发送结果
public final FutureRecordMetadata future;
// dequeue中是否有批次已经满了,需要通知sender线程来消费
public final boolean batchIsFull;
// 是否创建了一个新的批次
public final boolean newBatchCreated;
// KIP-480 为stiky分区策略轮转分区
// 如果入参abortOnNewBatch=true,且需要创建新批次,返回true
public final boolean abortForNewBatch;
}最终结果有三种:
case1:出参newBatchCreated=false,abortForNewBatch=false,加入现有批次成功;
case2:出参newBatchCreated=false,abortForNewBatch=true,当入参abortForNewBatch=true,且无法加入最近的一个批次,目的是让上层执行KIP-480stiky分区策略轮转分区;
case3:出参newBatchCreated=true,abortForNewBatch=false,创建新批次并加入成功;
3、主流程
RecordAccumulator#append:主流程。
java
public RecordAppendResult append(TopicPartition tp,
long timestamp,
byte[] key,
byte[] value,
Header[] headers,
Callback callback,
long maxTimeToBlock,
boolean abortOnNewBatch,
long nowMs) throws InterruptedException {
appendsInProgress.incrementAndGet();
ByteBuffer buffer = null;
if (headers == null) headers = Record.EMPTY_HEADERS;
try {
// 每个partition对应一个Deque,Deque里是n个批次
Deque<ProducerBatch> dq = getOrCreateDeque(tp);
synchronized (dq) {
// Step1,尝试将消息添加到批次中
RecordAppendResult appendResult = tryAppend(timestamp, key, value, headers, callback, dq, nowMs);
if (appendResult != null)
// case1 加入现有批次成功
return appendResult;
}
// case2 加入现有批次失败,入参abortOnNewBatch=true,KIP-480
if (abortOnNewBatch) {
return new RecordAppendResult(null, false, false, true);
}
// case3 加入现有批次失败,创建新批次
// size=Math.max(batch.size=16384=16k, 预估消息大小)
byte maxUsableMagic = apiVersions.maxUsableProduceMagic();
int size = Math.max(this.batchSize, AbstractRecords.estimateSizeInBytesUpperBound(maxUsableMagic, compression, key, value, headers));
// Step2,分配内存大小size,如果没有可用内存,则阻塞
// maxTimeToBlock=max.block.ms(60s)-先前等待元数据花费的时间
buffer = free.allocate(size, maxTimeToBlock);
nowMs = time.milliseconds();
synchronized (dq) {
// Step3,再次尝试加入现有批次
// 小概率成功,其他线程先进入了synchronized代码块创建了新批次
RecordAppendResult appendResult = tryAppend(timestamp, key, value, headers, callback, dq, nowMs);
if (appendResult != null) {
return appendResult;
}
// Step4,创建新批次,并写入消息
MemoryRecordsBuilder recordsBuilder = recordsBuilder(buffer, maxUsableMagic);
ProducerBatch batch = new ProducerBatch(tp, recordsBuilder, nowMs);
FutureRecordMetadata future = Objects.requireNonNull(batch.tryAppend(timestamp, key, value, headers,
callback, nowMs));
dq.addLast(batch);
incomplete.add(batch);
buffer = null;
return new RecordAppendResult(future, dq.size() > 1 || batch.isFull(), true, false);
}
} finally {
if (buffer != null)
// Step3的case
// 其他线程创建了批次,但是当前线程已分配了buffer,需要归还
free.deallocate(buffer);
appendsInProgress.decrementAndGet();
}
}RecordAccumulator#tryAppend:尝试写入dequeue的尾部最后一个批次。
java
private RecordAppendResult tryAppend(long timestamp,
byte[] key, byte[] value,
Header[] headers, Callback callback,
Deque<ProducerBatch> deque, long nowMs) {
ProducerBatch last = deque.peekLast();
if (last != null) {
// 消息写入批次
FutureRecordMetadata future = last.tryAppend(timestamp, key, value, headers, callback, nowMs);
if (future == null)
// case1 这个批次满了
last.closeForRecordAppends();
else
// case2 放到这个批次里了
return new RecordAppendResult(future, deque.size() > 1 || last.isFull(), false, false);
}
// case1+3 批次满了 or 还没创建过批次
return null;
}总体来说累积器分为两步:1-如果要创建新批次,申请buffer;2-写入批次。
4、申请buffer
BufferPool#allocate:申请buffer
1)申请大小为buffer.size=16k,优先从free链表分配;
2)池化失败,可用内存足够(buffer.memory=32MB),直接分配buffer;
3)池化失败,可用内存不足,加入waiters等待队列,最多等待maxTimeToBlockMs,sender线程发送消息完成后,归还内存,唤醒allocate等待线程;
java
// 池容量=buffer.memory=32MB
private final long totalMemory;
// 池化buffer的大小=buffer.size=16KB
private final int poolableSize;
private final ReentrantLock lock;
// 池化buffer归还到这里,后续可直接分配出去
private final Deque<ByteBuffer> free;
// 等待获取buffer的conditions
private final Deque<Condition> waiters;
// 非池化的buffer大小,初始=池容量=32MB
private long nonPooledAvailableMemory;
public ByteBuffer allocate(int size, long maxTimeToBlockMs) throws InterruptedException {
// totalMemory=buffer.memory=32MB
if (size > this.totalMemory)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
ByteBuffer buffer = null;
this.lock.lock();
try {
// Step1,申请大小=poolableSize=batch.size=16k,先从free池中获取
if (size == poolableSize && !this.free.isEmpty())
return this.free.pollFirst();
int freeListSize = freeSize() * this.poolableSize;
// 剩余可分配内存 = nonPooledAvailableMemory + free链表 >= 目标内存
if (this.nonPooledAvailableMemory + freeListSize >= size) {
// Step2,如果池化失败,但剩余内存足够,按照请求大小分配内存
// 如果池非空,可分配内存不足size,释放free池
freeUp(size);
this.nonPooledAvailableMemory -= size;
} else {
// Step3,剩余内存不足,需要等待sender发送消息后释放
int accumulated = 0;
Condition moreMemory = this.lock.newCondition();
try {
long remainingTimeToBlockNs = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.toNanos(maxTimeToBlockMs);
this.waiters.addLast(moreMemory);
while (accumulated < size) {
long startWaitNs = time.nanoseconds();
long timeNs;
boolean waitingTimeElapsed;
try {
// 等待sender释放
waitingTimeElapsed = !moreMemory.await(remainingTimeToBlockNs, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);
} finally {
long endWaitNs = time.nanoseconds();
timeNs = Math.max(0L, endWaitNs - startWaitNs);
recordWaitTime(timeNs);
}
// moreMemory等待可用内存超时
if (waitingTimeElapsed) {
throw new BufferExhaustedException("Failed to allocate memory within the configured max blocking time " + maxTimeToBlockMs + " ms.");
}
// moreMemory被唤醒,计算accumulated可累计分配的内存,达到size后可退出
remainingTimeToBlockNs -= timeNs;
if (accumulated == 0 && size == this.poolableSize && !this.free.isEmpty()) {
// 如果申请大小为16k,还是优先走池化分配
buffer = this.free.pollFirst();
accumulated = size;
} else {
// 否则,走非池化分配
freeUp(size - accumulated);
int got = (int) Math.min(size - accumulated, this.nonPooledAvailableMemory);
this.nonPooledAvailableMemory -= got;
accumulated += got;
}
}
accumulated = 0;
} finally {
this.nonPooledAvailableMemory += accumulated;
this.waiters.remove(moreMemory);
}
}
} finally {
try {
// 如果有内存可用,由当前线程唤醒后一个等待内存的线程
if (!(this.nonPooledAvailableMemory == 0 && this.free.isEmpty()) && !this.waiters.isEmpty())
this.waiters.peekFirst().signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
if (buffer == null)
// 池化失败,分配内存
return safeAllocateByteBuffer(size);
else
return buffer;
}
private void freeUp(int size) {
while (!this.free.isEmpty() && this.nonPooledAvailableMemory < size)
this.nonPooledAvailableMemory += this.free.pollLast().capacity();
}BufferPool#deallocate:sender线程发送消息后,调用BufferPool归还内存。
java
public void deallocate(ByteBuffer buffer, int size) {
lock.lock();
try {
if (size == this.poolableSize && size == buffer.capacity()) {
// 是池化的buffer大小,加入free链表
buffer.clear();
this.free.add(buffer);
} else {
// 非池化的buffer大小(单条消息超过16k),仅仅修改可用非池化大小
this.nonPooledAvailableMemory += size;
}
// 唤醒等待内存的生产者线程
Condition moreMem = this.waiters.peekFirst();
if (moreMem != null)
moreMem.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}5、写入批次
5-1、创建批次
RecordAccumulator#append:如果批次不存在,需要先创建批次,批次的底层buffer由MemoryRecordsBuilder维护。
java
// MemoryRecordsBuilder
MemoryRecordsBuilder recordsBuilder = recordsBuilder(buffer, maxUsableMagic);
// ProducerBatch
ProducerBatch batch = new ProducerBatch(tp, recordsBuilder, nowMs);
// 写批次
FutureRecordMetadata future = Objects.requireNonNull(batch.tryAppend(timestamp, key, value, headers,
callback, nowMs));
// 批次放到dequeue里,下次可以继续写
dq.addLast(batch);
incomplete.add(batch);RecordAccumulator#recordsBuilder:MemoryRecordsBuilder构建入参只有几个
1)buffer:从BufferPool申请的内存;
2)maxUsableMagic:魔数2;
3)compression:压缩类型,默认NONE;
4)timestampType:logAppendTime的类型,CREATE_TIME;
5)baseOffset:0,代表这个批次的第一条消息;
java
// RecordAccumulator
private MemoryRecordsBuilder recordsBuilder(ByteBuffer buffer, byte maxUsableMagic) {
return MemoryRecords.builder(buffer, maxUsableMagic, compression, TimestampType.CREATE_TIME, 0L);
}
public static MemoryRecordsBuilder builder(ByteBuffer buffer,
byte magic,
CompressionType compressionType,
TimestampType timestampType,
long baseOffset) {
long logAppendTime = RecordBatch.NO_TIMESTAMP;
if (timestampType == TimestampType.LOG_APPEND_TIME)
logAppendTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
return builder(buffer, magic, compressionType, timestampType, baseOffset, logAppendTime,
RecordBatch.NO_PRODUCER_ID, RecordBatch.NO_PRODUCER_EPOCH, RecordBatch.NO_SEQUENCE, false,
RecordBatch.NO_PARTITION_LEADER_EPOCH);
}MemoryRecordsBuilder:最终构建的时候,buffer被包装为bufferStream,如果有压缩类型,在bufferStream会再包装一个压缩Stream,最终写入的stream为appendStream。
java
public MemoryRecordsBuilder(ByteBuffer buffer,...) {
this(new ByteBufferOutputStream(buffer), ...);
}
public MemoryRecordsBuilder(ByteBufferOutputStream bufferStream,
...) {
this.magic = magic;
this.timestampType = timestampType;
this.compressionType = compressionType;
this.baseOffset = baseOffset; // 0
this.logAppendTime = logAppendTime; // -1
this.numRecords = 0;
this.maxTimestamp = RecordBatch.NO_TIMESTAMP; // -1
this.writeLimit = writeLimit; // buffer可用大小
// 初始位置0
this.initialPosition = bufferStream.position();
// 批次头大小
this.batchHeaderSizeInBytes = AbstractRecords.recordBatchHeaderSizeInBytes(magic, compressionType);
// 写入位置从头之后开始
bufferStream.position(initialPosition + batchHeaderSizeInBytes);
this.bufferStream = bufferStream;
// 在ByteBufferOutputStream(buffer)外面再包一层,是可以压缩的
this.appendStream = new DataOutputStream(compressionType.wrapForOutput(this.bufferStream, magic));
}
// 比如压缩类型为lz4,在原始在ByteBufferOutputStream(buffer)外面再包一层
LZ4(3, "lz4", 1.0f) {
@Override
public OutputStream wrapForOutput(ByteBufferOutputStream buffer, byte messageVersion) {
return new KafkaLZ4BlockOutputStream(buffer,...);
}
}5-2、tryAppend
ProducerBatch#tryAppend:
java
// 【重点】消息写入MemoryRecordsBuilder
private final MemoryRecordsBuilder recordsBuilder;
// 批次发送future,sender来完成
final ProduceRequestResult produceFuture;
// Thunk=(回调方法,发送结果),批次发送响应后
// 循环thunks回调InterceptorCallback和用户callback
private final List<Thunk> thunks = new ArrayList<>();
public FutureRecordMetadata tryAppend(long timestamp, byte[] key, byte[] value,
Header[] headers, Callback callback, long now) {
if (!recordsBuilder.hasRoomFor(timestamp, key, value, headers)) {
// 如果底层buffer写满了,返回null,外面就要创建新批次了
return null;
} else {
// 写入appendStream,可能包含压缩
Long checksum =
this.recordsBuilder.append(timestamp, key, value, headers);
this.lastAppendTime = now;
// producerFuture一个批次一个,如果sender完成了会完成这个future
// 一个producerFuture对应n次send的FutureRecordMetadata(future)
// 如果发送完成,sender完成producerFuture,producerFuture完成FutureRecordMetadata
FutureRecordMetadata future = new FutureRecordMetadata(
this.produceFuture, this.recordCount,
timestamp, checksum,
key == null ? -1 : key.length,
value == null ? -1 : value.length,
Time.SYSTEM);
// 将所有future加入链表
thunks.add(new Thunk(callback, future));
this.recordCount++;
return future;
}
}每条消息Record包含如下属性:
1)Length:Varint编码,1-5字节,消息大小,压缩前的;
2)Attributes:1字节,未使用;
3)TimestampDelta:Varlong编码,1-10字节,消息相对于第一个消息的偏移创建时间;
4)OffsetDelta:Varint编码,1-5字节,消息在批次中的下标,从0开始;
5)key/value/headers:消息key/value/headers;
MemoryRecordsBuilder#appendDefaultRecord:
消息写入appendStream完成压缩逻辑,实际是否写入底层buffer,和压缩实现有关。
如果这里没有写入底层buffer,sender从累积器拉数据时会flush到底层buffer。
java
// 底层BufferPool分配的bytebuffer
private final ByteBufferOutputStream bufferStream;
// 包装压缩算法
private DataOutputStream appendStream =
new DataOutputStream(
compressionType.wrapForOutput(this.bufferStream, magic));
private void appendDefaultRecord(long offset,
long timestamp,
ByteBuffer key, ByteBuffer value,
Header[] headers) throws IOException {
ensureOpenForRecordAppend();
// 批次中的消息下标,从0开始
int offsetDelta = (int) (offset - baseOffset);
// 批次里的第n条消息 - 第1条消息的创建时间
long timestampDelta = timestamp - firstTimestamp;
// 写入appendStream,可能压缩
int sizeInBytes = DefaultRecord.writeTo(appendStream, offsetDelta, timestampDelta, key, value, headers);
// 记录写入大小,后面可以判断是否写满了
recordWritten(offset, timestamp, sizeInBytes);
}如zstd压缩,ZstdOutputStream里面还有一个dst的buffer,压缩数据会先写入dst,在适当时机再写入BufferPool分配的最底层buffer。
java
public ZstdOutputStream(OutputStream outStream/*BufferPool分配的底层buffer*/) throws IOException {
super(outStream);
// create compression context
this.stream = createCStream();
this.closeFrameOnFlush = false;
this.dst = new byte[(int) dstSize];
}5-3、返回future
每次生产者调用send写buffer成功后,返回给生产者一个future(FutureRecordMetadata),生产者可以等待这个future完成或注册Callback,拿到发布响应RecordMetadata。
java
public final class FutureRecordMetadata implements Future<RecordMetadata> {
// 批次future
private final ProduceRequestResult result;
@Override
public RecordMetadata get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
this.result.await();
if (nextRecordMetadata != null)
return nextRecordMetadata.get();
return valueOrError();
}
@Override
public RecordMetadata get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
long now = time.milliseconds();
long timeoutMillis = unit.toMillis(timeout);
long deadline = Long.MAX_VALUE - timeoutMillis < now ? Long.MAX_VALUE : now + timeoutMillis;
boolean occurred = this.result.await(timeout, unit);
if (!occurred)
throw new TimeoutException();
if (nextRecordMetadata != null)
return nextRecordMetadata.get(deadline - time.milliseconds(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
return valueOrError();
}
RecordMetadata valueOrError() throws ExecutionException {
if (this.result.error() != null)
throw new ExecutionException(this.result.error());
else
return value();
}
// producer.send可以拿到RecordMetadata
RecordMetadata value() {
if (nextRecordMetadata != null)
return nextRecordMetadata.value();
return new RecordMetadata(
result.topicPartition(), this.result.baseOffset(),
this.relativeOffset, timestamp(), this.checksum,
this.serializedKeySize, this.serializedValueSize);
}
}底层FutureRecordMetadata 需要等待批次future(ProduceRequestResult)完成。
当sender发送批次成功后,完成批次future。
java
public class ProduceRequestResult {
private final CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
// sender来完成
public void done() {
this.latch.countDown();
}
// 批次对应n次send
// n个FutureRecordMetadata可以通过ProduceRequestResult等待该批次发送完成
public void await() throws InterruptedException {
latch.await();
}
public boolean await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
return latch.await(timeout, unit);
}
}七、Sender发送消息
Sender#runOnce:sender线程while-true逻辑。
在上面分析获取元数据的时候已经分析过sender线程的工作逻辑,即client.poll。这里主要分析sendProducerData中的逻辑,包含如何与服务端建立连接,如何消费累积器中的消息。
java
void runOnce() {
if (transactionManager != null) {
//...
}
long currentTimeMs = time.milliseconds();
// 从累积器拉取消息,转换为Send,缓存到每个broker对应的KafkaChannel
long pollTimeout = sendProducerData(currentTimeMs);
// 真实发送Send
client.poll(pollTimeout, currentTimeMs);
}Sender#sendProducerData:将消息缓存到每个broker节点对应的KafkaChannel中,分为5步。
注意这里不会发送ProduceRequest,所有IO都在poll里。
java
private long sendProducerData(long now) {
Cluster cluster = metadata.fetch();
// Step1, 从累积器获取,有消息的分区对应的node
RecordAccumulator.ReadyCheckResult result = this.accumulator.ready(cluster, now);
// 未知leader的分区topic,标记为需要元数据
if (!result.unknownLeaderTopics.isEmpty()) {
for (String topic : result.unknownLeaderTopics)
this.metadata.add(topic, now);
this.metadata.requestUpdate();
}
// Step2,对有消息的node,判断是否允许发送消息,如果不允许,从readyNodes中移除
// 1. 如果还未建立连接,则触发建立连接,但不可用,不能发送消息
// 2. 如果节点超出阈值的请求还未响应,max.in.flight.requests.per.connection=5,不能发送消息
// 3. 如果需要发送MetadataRequest,不能发送消息
Iterator<Node> iter = result.readyNodes.iterator();
long notReadyTimeout = Long.MAX_VALUE;
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Node node = iter.next();
if (!this.client.ready(node, now)) {
iter.remove();
notReadyTimeout = Math.min(notReadyTimeout, this.client.pollDelayMs(node, now));
}
}
// Step3,从累积器中获取每个broker需要发送的批次,每个分区最多发一个批次
Map<Integer/*brokerId*/, List<ProducerBatch>> batches = this.accumulator.drain(cluster, result.readyNodes, this.maxRequestSize, now);
// 将批次加入inflight列表
addToInflightBatches(batches);
// max.in.flight.requests.per.connection=1 为true 默认为5
if (guaranteeMessageOrder) { // 是否保证顺序
for (List<ProducerBatch> batchList : batches.values()) {
for (ProducerBatch batch : batchList)
// 标记分区mut,在请求处理完前不会再次发送消息
this.accumulator.mutePartition(batch.topicPartition);
}
}
accumulator.resetNextBatchExpiryTime();
// delivery.timeout.ms=2分钟
// Step4,获取 inflight的超时批次 + 累积器中的超时批次,完成future为TimeoutException,归还buffer到BufferPool
List<ProducerBatch> expiredInflightBatches = getExpiredInflightBatches(now);
List<ProducerBatch> expiredBatches = this.accumulator.expiredBatches(now);
expiredBatches.addAll(expiredInflightBatches);
for (ProducerBatch expiredBatch : expiredBatches) {
failBatch(expiredBatch, -1, NO_TIMESTAMP, new TimeoutException(), false);
}
long pollTimeout = Math.min(result.nextReadyCheckDelayMs, notReadyTimeout);
pollTimeout = Math.min(pollTimeout, this.accumulator.nextExpiryTimeMs() - now);
pollTimeout = Math.max(pollTimeout, 0);
if (!result.readyNodes.isEmpty()) {
pollTimeout = 0;
}
// Step5,将每个节点的批次,缓存到KafkaChannel
sendProduceRequests(batches, now);
return pollTimeout;
}7-1、获取需要发送消息的Node
RecordAccumulator#ready:从累积器获取需要发送消息的Broker节点。
循环每个分区的批次队列,判断分区对应节点是否需要发送消息,满足以下几个条件之一,则节点需要发送消息:
1)full:有分区批次满了;2)expired:超过linger.ms(默认0);3)exhausted:BufferPool内存不足了,有生产者线程在等待分配内存;4)closed:生产者关闭;5)flushInProgress:生产者主动调用flush;
java
private final BufferPool free;
private final ConcurrentMap<TopicPartition, Deque<ProducerBatch>> batches;
public ReadyCheckResult ready(Cluster cluster, long nowMs) {
Set<Node> readyNodes = new HashSet<>();
long nextReadyCheckDelayMs = Long.MAX_VALUE;
Set<String> unknownLeaderTopics = new HashSet<>();
// 等待BufferPool分配内存的生产者线程 > 0
boolean exhausted = this.free.queued() > 0;
for (Map.Entry<TopicPartition, Deque<ProducerBatch>> entry : this.batches.entrySet()) {
Deque<ProducerBatch> deque = entry.getValue();
synchronized (deque) {
ProducerBatch batch = deque.peekFirst();
if (batch != null) {
TopicPartition part = entry.getKey();
Node leader = cluster.leaderFor(part);
if (leader == null) {
unknownLeaderTopics.add(part.topic());
} else if (!readyNodes.contains(leader) && !isMuted(part)) {
// Math.max(0, nowMs - 创建时间/上次重试时间)
long waitedTimeMs = batch.waitedTimeMs(nowMs);
// 正在重试,但是还没到retryBackoffMs
boolean backingOff = batch.attempts() > 0 && waitedTimeMs < retryBackoffMs;
// 需要等待的时长lingerMs
long timeToWaitMs = backingOff ? retryBackoffMs : lingerMs;
// 是否有批次是否满
boolean full = deque.size() > 1 || batch.isFull();
// 等待时间到lingerMs
boolean expired = waitedTimeMs >= timeToWaitMs;
boolean sendable = full || /*有批次满了*/
expired || /*超过lingerMs*/
exhausted || /*BufferPool内存不足了,有生产者在等待*/
closed || /*生产者关闭了*/
flushInProgress(); /*生产者调用flush*/
if (sendable && !backingOff) {
readyNodes.add(leader);
} else {
long timeLeftMs = Math.max(timeToWaitMs - waitedTimeMs, 0);
nextReadyCheckDelayMs = Math.min(timeLeftMs, nextReadyCheckDelayMs);
}
}
}
}
}
return new ReadyCheckResult(readyNodes, nextReadyCheckDelayMs, unknownLeaderTopics);
}7-2、移除非ready的Node&建立连接
NetworkClient#ready:对于需要发送消息的节点,验证是否ready,此外这里会真正触发与broker建立连接。
java
public boolean ready(Node node, long now) {
if (isReady(node, now))
return true;
if (connectionStates.canConnect(node.idString(), now))
// if we are interested in sending to a node and we don't have a connection to it, initiate one
initiateConnect(node, now);
return false;
}
private void initiateConnect(Node node, long now) {
String nodeConnectionId = node.idString();
connectionStates.connecting(nodeConnectionId, now, node.host(), clientDnsLookup);
InetAddress address = connectionStates.currentAddress(nodeConnectionId);
selector.connect(nodeConnectionId,
new InetSocketAddress(address, node.port()),
this.socketSendBuffer,
this.socketReceiveBuffer);
}NetworkClient#isReady:节点ready条件
1)需要更新元数据,这个是全局限制,和节点无关,只要需要更新元数据,所有节点都不能发送消息;
2)已经建立连接;(未建立连接需要等待下一次sender循环再判断)
3)节点未响应的请求≤并发请求数量,默认max.in.flight.requests.per.connection=5;
java
public boolean isReady(Node node, long now) {
return !metadataUpdater.isUpdateDue(now) // 不需要更新元数据
&& canSendRequest(node.idString(), now);
}
private boolean canSendRequest(String node, long now) {
return connectionStates.isReady(node, now) // 已经建立连接
&& selector.isChannelReady(node)
&& inFlightRequests.canSendMore(node); // 节点未响应的请求>并发请求数量
}
// InFlightRequests#canSendMore
public boolean canSendMore(String node) {
Deque<NetworkClient.InFlightRequest> queue = requests.get(node);
return queue == null || queue.isEmpty()
|| (queue.peekFirst().send.completed()
&& queue.size() < this.maxInFlightRequestsPerConnection);
}
// Metadata#timeToNextUpdate
public synchronized long timeToNextUpdate(long nowMs) {
long timeToExpire = updateRequested() ? // producer请求更新
0 :
// 到达metadata.max.age.ms=5分钟 需要刷新
Math.max(this.lastSuccessfulRefreshMs + this.metadataExpireMs - nowMs, 0);
return Math.max(timeToExpire,
// 如果retry.backoff.ms=100内发生过更新,不更新
timeToAllowUpdate(nowMs));
}Selector#connect:与broker建立连接。
java
public void connect(String id, InetSocketAddress address, int sendBufferSize, int receiveBufferSize) throws IOException {
ensureNotRegistered(id);
// 创建一个socketChannel
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
SelectionKey key = null;
try {
// 配置socket
// send.buffer.bytes=128 * 1024 -- SocketOptions.SO_SNDBUF
// receive.buffer.bytes=32 * 1024 -- SocketOptions.SO_RCVBUF
configureSocketChannel(socketChannel, sendBufferSize, receiveBufferSize);
// 与broker建立连接socketChannel.connect(address)
boolean connected = doConnect(socketChannel, address);
// 注册socketChannel到selector,注册CONNECT事件
key = registerChannel(id, socketChannel, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
if (connected) {
immediatelyConnectedKeys.add(key);
key.interestOps(0);
}
} catch (IOException | RuntimeException e) {
if (key != null)
immediatelyConnectedKeys.remove(key);
channels.remove(id);
socketChannel.close();
throw e;
}
}Selector#registerChannel:KafkaChannel=socketChannel+SelectionKey。
java
private final Map<String, KafkaChannel> channels;
protected SelectionKey registerChannel(String id, SocketChannel socketChannel, int interestedOps) throws IOException {
SelectionKey key = socketChannel.register(nioSelector, interestedOps);
KafkaChannel channel = buildAndAttachKafkaChannel(socketChannel, id, key);
this.channels.put(id, channel);
if (idleExpiryManager != null)
idleExpiryManager.update(channel.id(), time.nanoseconds());
return key;
}
private KafkaChannel buildAndAttachKafkaChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel, String id, SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
KafkaChannel channel = channelBuilder.buildChannel(...);
// SelectionKey->KafkaChannel,
// 发生io事件key.attachment()可以拿到KafkaChannel
key.attach(channel);
return channel;
}7-3、从Accumulator拉消息批次
RecordAccumulator#drain:循环每个ready节点,sender从Accumulator拉取消息批次,maxSize=单个请求大小上限=1MB。
java
public Map<Integer, List<ProducerBatch>> drain(Cluster cluster, Set<Node> nodes, int maxSize, long now) {
Map<Integer, List<ProducerBatch>> batches = new HashMap<>();
for (Node node : nodes) {
// maxSize=max.request.size=1MB 一个broker的消息大小上限
List<ProducerBatch> ready = drainBatchesForOneNode(cluster, node, maxSize, now);
batches.put(node.id(), ready);
}
return batches;
}RecordAccumulator#drainBatchesForOneNode:
遍历broker的所有分区,在maxSize内,对于每个分区拿一个批次。
注意,累积器通过full/expired等方式判断分区所在节点是否需要发送,只要一个分区满足条件,这个节点下所有分区都会触发消息发送,即使单个分区未满足full/expired。
java
private List<ProducerBatch> drainBatchesForOneNode(Cluster cluster, Node node, int maxSize, long now) {
int size = 0;
// 遍历broker下的所有partition
List<PartitionInfo> parts = cluster.partitionsForNode(node.id());
List<ProducerBatch> ready = new ArrayList<>();
int start = drainIndex = drainIndex % parts.size();
do {
PartitionInfo part = parts.get(drainIndex);
TopicPartition tp = new TopicPartition(part.topic(), part.partition());
this.drainIndex = (this.drainIndex + 1) % parts.size();
// Only proceed if the partition has no in-flight batches.
if (isMuted(tp))
continue;
Deque<ProducerBatch> deque = getDeque(tp);
if (deque == null)
continue;
synchronized (deque) {
ProducerBatch first = deque.peekFirst();
if (first == null)
continue;
boolean backoff = first.attempts() > 0 && first.waitedTimeMs(now) < retryBackoffMs;
if (backoff)
// 批次重试中,且小于retry.backoff.ms=100ms
continue;
if (size + first.estimatedSizeInBytes() > maxSize && !ready.isEmpty()) {
// 遍历到一个partition的批次导致超出maxSize,退出
break;
} else {
// ... 省略事务消息
// 关闭批次
batch.close();
size += batch.records().sizeInBytes();
ready.add(batch);
batch.drained(now);
}
}
} while (start != drainIndex);
return ready;
}ProducerBatch#close:关闭消息批次。关闭底层appendStream写入流,writeDefaultBatchHeader写入批次头,构造MemoryRecords用于sender自己读取buffer。
java
// ProducerBatch#close
private final MemoryRecordsBuilder recordsBuilder;
public void close() {
recordsBuilder.close();
reopened = false;
}
// MemoryRecordsBuilder#close
// producer写入
private DataOutputStream appendStream;
// sender读取
private MemoryRecords builtRecords;
public void close() {
if (builtRecords != null)
return;
validateProducerState();
closeForRecordAppends();
if (numRecords == 0L) {
buffer().position(initialPosition);
builtRecords = MemoryRecords.EMPTY;
} else {
// 写批次头
this.actualCompressionRatio = (float) writeDefaultBatchHeader() / this.uncompressedRecordsSizeInBytes;
ByteBuffer buffer = buffer().duplicate();
buffer.flip();
buffer.position(initialPosition);
// 构造builtRecords=MemoryRecords
builtRecords = MemoryRecords.readableRecords(buffer.slice());
}
}
public void closeForRecordAppends() {
if (appendStream != CLOSED_STREAM) {
try {
// 如果有压缩,这里确保压缩的内置buffer刷到底层buffer(BufferPool分配的)
appendStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new KafkaException(e);
} finally {
appendStream = CLOSED_STREAM;
}
}
}DefaultRecordBatch#writeHeader:每个消息批次头包含如下属性,由sender写入底层buffer。
java
static void writeHeader(ByteBuffer buffer, ...) {
// 16bit attributes:Unused (6-15) | Control (5) | Transactional (4) | Timestamp Type (3) | Compression Type (0-2)
short attributes = computeAttributes(compressionType, timestampType, isTransactional, isControlBatch);
int position = buffer.position();
buffer.putLong(position + BASE_OFFSET_OFFSET, baseOffset); // 0
buffer.putInt(position + LENGTH_OFFSET, sizeInBytes - LOG_OVERHEAD); // 批次里的n个消息的大小总和
buffer.putInt(position + PARTITION_LEADER_EPOCH_OFFSET, partitionLeaderEpoch); // -1
buffer.put(position + MAGIC_OFFSET, magic); // 魔数2
buffer.putShort(position + ATTRIBUTES_OFFSET, attributes); // 压缩类型 时间类型 是否事务...
buffer.putLong(position + FIRST_TIMESTAMP_OFFSET, firstTimestamp); // 第一条消息的创建时间
buffer.putLong(position + MAX_TIMESTAMP_OFFSET, maxTimestamp); // 最大的消息创建时间
buffer.putInt(position + LAST_OFFSET_DELTA_OFFSET, lastOffsetDelta); // 最后一条消息的偏移量(一般就是消息数量)
buffer.putLong(position + PRODUCER_ID_OFFSET, producerId); // 生产者id -1
buffer.putShort(position + PRODUCER_EPOCH_OFFSET, epoch); // 生产者epoch -1
buffer.putInt(position + BASE_SEQUENCE_OFFSET, sequence); // -1
buffer.putInt(position + RECORDS_COUNT_OFFSET, numRecords); // 消息数量
long crc = Crc32C.compute(buffer, ATTRIBUTES_OFFSET, sizeInBytes - ATTRIBUTES_OFFSET);
buffer.putInt(position + CRC_OFFSET, (int) crc); // crc
buffer.position(position + RECORD_BATCH_OVERHEAD);
}ProducerBatch→MemoryRecordsBuilder→MemoryRecords,最终消息批次构造为MemoryRecords供sender后续读取。
java
public class MemoryRecords extends AbstractRecords {
// 消息批次头 + n条消息
private final ByteBuffer buffer;
private final Iterable<MutableRecordBatch> batches = this::batchIterator;
private MemoryRecords(ByteBuffer buffer) {
this.buffer = buffer;
}
}7-4、超时批次处理
Sender#sendProducerData:处理超时批次,设置future为Timeout。
生产者默认重试次数retris=Integer.MAX_VALUE,无限重试,一般通过配置delivery.timeout.ms超时时间来控制重试次数,默认超时时间为2分钟。
java
// Step4,处理 inflight的超时批次 + 累积器中的超时批次
// 已经发送给broker,但是超时未收到响应
List<ProducerBatch> expiredInflightBatches = getExpiredInflightBatches(now);
// 在累积器中,还没拿出来,超时
List<ProducerBatch> expiredBatches = this.accumulator.expiredBatches(now);
expiredBatches.addAll(expiredInflightBatches);
if (!expiredBatches.isEmpty())
for (ProducerBatch expiredBatch : expiredBatches) {
// 完成future为TimeoutException,归还buffer到BufferPool
failBatch(expiredBatch, -1, NO_TIMESTAMP, new TimeoutException(errorMessage), false);
}7-5、将ProducerRequest放到KafkaChannel
Sender#sendProduceRequest:构造ProduceRequest,包括acks响应策略、produceRecordsByPartition每个分区对应的MemoryRecords批次数据。
java
private void sendProduceRequest(long now, int destination, short acks, int timeout, List<ProducerBatch> batches) {
// 每个partition一个批次
// 用于构造请求
Map<TopicPartition, MemoryRecords> produceRecordsByPartition = new HashMap<>(batches.size());
// 用于处理响应
final Map<TopicPartition, ProducerBatch> recordsByPartition = new HashMap<>(batches.size());
byte minUsedMagic = apiVersions.maxUsableProduceMagic();
for (ProducerBatch batch : batches) {
if (batch.magic() < minUsedMagic)
minUsedMagic = batch.magic();
}
for (ProducerBatch batch : batches) {
TopicPartition tp = batch.topicPartition;
MemoryRecords records = batch.records(); // builtRecords
produceRecordsByPartition.put(tp, records);
recordsByPartition.put(tp, batch);
}
// 构建请求,在每个分区的消息批次
ProduceRequest.Builder requestBuilder = ProduceRequest.Builder.forMagic(minUsedMagic, acks, timeout,
produceRecordsByPartition, transactionalId);
// 响应处理
RequestCompletionHandler callback = response -> handleProduceResponse(response, recordsByPartition, time.milliseconds());
String nodeId = Integer.toString(destination);
ClientRequest clientRequest = client.newClientRequest(nodeId, requestBuilder, now, acks != 0,
requestTimeoutMs, callback);
// 缓存到KafkaChannel的Send
client.send(clientRequest, now);
}NetworkClient#send:将ProduceRequest序列化为Send,放到KafkaChannel。
java
public void send(ClientRequest request, long now) {
doSend(request, false, now);
}
private void doSend(ClientRequest clientRequest, boolean isInternalRequest, long now) {
AbstractRequest.Builder<?> builder = clientRequest.requestBuilder();
try {
doSend(clientRequest, isInternalRequest, now, builder.build(version));
}
}
private void doSend(ClientRequest clientRequest, boolean isInternalRequest, long now, AbstractRequest request) {
String destination = clientRequest.destination();
// 创建请求头
RequestHeader header = clientRequest.makeHeader(request.version());
// request序列化为bytebuffer
Send send = request.toSend(destination, header);
InFlightRequest inFlightRequest = new InFlightRequest(...);
this.inFlightRequests.add(inFlightRequest);
// 将Send缓存到目标连接KafkaChannel
selector.send(send);
}
// Selector#send->KafkaChannel#setSend
// 发出的buffer
private Send send;
public void setSend(Send send) {
if (this.send != null)
// 一个channel在一轮sender循环中,只能发送一个请求
throw new IllegalStateException();
this.send = send;
// 标记nioSelector关心write事件
this.transportLayer.addInterestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}ClientRequest#makeHeader:创建请求头,注意这里的correlationId。
每个客户端和服务端的连接下,一个请求都对应一个唯一id,由sender每次创建请求时分配,顺序递增,在rpc请求响应模型下,响应中也会携带这个唯一id,找到对应请求。
java
public RequestHeader makeHeader(short version) {
short requestApiKey = requestBuilder.apiKey().id;
return new RequestHeader(
new RequestHeaderData().
// 是哪个api方法,比如ProducerRequest
setRequestApiKey(requestApiKey).
// api版本
setRequestApiVersion(version).
// clientId
setClientId(clientId).
// 请求id
setCorrelationId(correlationId),
ApiKeys.forId(requestApiKey).requestHeaderVersion(version));
}
// NetworkClient.java
private int correlation;
int nextCorrelationId() {
return correlation++;
}AbstractRequest#toSend:请求转Send。
java
public Send toSend(String destination, RequestHeader header) {
return new NetworkSend(destination, serialize(header));
}
public ByteBuffer serialize(RequestHeader header) {
// 先转Struct,再转ByteBuffer
return RequestUtils.serialize(header.toStruct(), toStruct());
}所有api对象会定义各自的Schema,每个Schema包含多个按照顺序编排的Field字段,每个Field字段有自己的Type数据类型,不同的Type使用不同的序列化方式。
java
// ProduceRequestData
public static final Schema SCHEMA_3 =
new Schema(new Field("transactional_id", Type.NULLABLE_STRING),
new Field("acks", Type.INT16),
new Field("timeout_ms", Type.INT32),
new Field("topics", new ArrayOf(TopicProduceData.SCHEMA_0)));ProduceRequest#toStruct:请求对象转Struct后才能序列化。(同理响应对象,需要先反序列化为Struct,才能转换为响应对象,byte-Struct-对象)
ProducerRequest重新按照topic分组,每个topic下挂n个分区。
java
public Struct toStruct() {
Map<TopicPartition, MemoryRecords> partitionRecords = partitionRecordsOrFail();
short version = version();
Struct struct = new Struct(ApiKeys.PRODUCE.requestSchema(version));
Map<String, Map<Integer, MemoryRecords>> recordsByTopic = CollectionUtils.groupPartitionDataByTopic(partitionRecords);
struct.set(ACKS_KEY_NAME, acks);
struct.set(TIMEOUT_KEY_NAME, timeout);
struct.setIfExists(NULLABLE_TRANSACTIONAL_ID, transactionalId);
List<Struct> topicDatas = new ArrayList<>(recordsByTopic.size());
for (Map.Entry<String, Map<Integer, MemoryRecords>> topicEntry : recordsByTopic.entrySet()) {
Struct topicData = struct.instance(TOPIC_DATA_KEY_NAME);
topicData.set(TOPIC_NAME, topicEntry.getKey());
List<Struct> partitionArray = new ArrayList<>();
for (Map.Entry<Integer, MemoryRecords> partitionEntry : topicEntry.getValue().entrySet()) {
MemoryRecords records = partitionEntry.getValue();
Struct part = topicData.instance(PARTITION_DATA_KEY_NAME)
.set(PARTITION_ID, partitionEntry.getKey())
.set(RECORD_SET_KEY_NAME, records);
partitionArray.add(part);
}
topicData.set(PARTITION_DATA_KEY_NAME, partitionArray.toArray());
topicDatas.add(topicData);
}
struct.set(TOPIC_DATA_KEY_NAME, topicDatas.toArray());
return struct;
}RequestUtils#serialize:序列化。
java
public static ByteBuffer serialize(Struct headerStruct, Struct bodyStruct) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(headerStruct.sizeOf() + bodyStruct.sizeOf());
headerStruct.writeTo(buffer);
bodyStruct.writeTo(buffer);
buffer.rewind();
return buffer;
}Type#write:Struct中的所有数据类型都有自己的序列化方式。
比如MemoryRecords的序列化方式如下,4字节buffer大小+实际buffer,这里需要将MemoryRecords中原始的buffer拷贝到NetworkSend中的目标buffer。
java
public static final DocumentedType RECORDS = new DocumentedType() {
public void write(ByteBuffer buffer, Object o) {
MemoryRecords records = (MemoryRecords) o;
// MemoryRecords中的buffer拷贝到刚才分配的buffer
NULLABLE_BYTES.write(buffer, records.buffer().duplicate());
}
}
public static final DocumentedType NULLABLE_BYTES = new DocumentedType() {
public void write(ByteBuffer buffer, Object o) {
if (o == null) {
buffer.putInt(-1);
return;
}
ByteBuffer arg = (ByteBuffer) o;
int pos = arg.position();
// 写入MemoryRecords中的buffer大小
buffer.putInt(arg.remaining());
// 写入MemoryRecords中的buffer
buffer.put(arg);
arg.position(pos);
}
}7-6、poll
NetworkClient#poll:最终通过nioSelector监听socket上的IO事件,发送请求接收响应。
java
public List<ClientResponse> poll(long timeout, long now) {
ensureActive();
// 可能构造MetadataRequest缓存到channel
long metadataTimeout = metadataUpdater.maybeUpdate(now);
try {
// 执行io操作 读 写 ...
this.selector.poll(Utils.min(timeout, metadataTimeout, defaultRequestTimeoutMs));
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("Unexpected error during I/O", e);
}
long updatedNow = this.time.milliseconds();
List<ClientResponse> responses = new ArrayList<>();
// 处理acks=0的请求
handleCompletedSends(responses, updatedNow);
// 处理收到的响应
handleCompletedReceives(responses, updatedNow);
// ...
// 调用callback
completeResponses(responses);
return responses;
}Step1,简单概括一下selector.poll的逻辑。
对于写事件(发送请求),将Send写入底层socketChannel。
java
Selector#poll
// 通道IO事件触发
Selector#pollSelectionKeys
// 有写操作,比如ProduceRequest发送消息
Selector#attemptWrite
// 将socketChannel对应的KafkaChannel的Send写入socketChannel
Selector#write
KafkaChannel#write
ByteBufferSend#writeTo
PlaintextTransportLayer#write
SocketChannel#write
// Selector#write
void write(KafkaChannel channel) throws IOException {
String nodeId = channel.id();
long bytesSent = channel.write(); // 将Send写入channel
Send send = channel.maybeCompleteSend(); // 取消OP_WRITE
}
// KafkaChannel#write
// 发出的buffer
private Send send;
public long write() throws IOException {
midWrite = true;
return send.writeTo(transportLayer);
}对于读事件(接收响应),将数据读入NetworkReceive。
java
Selector#poll
// 通道IO事件触发
Selector#pollSelectionKeys
// 收到服务端响应
Selector#attemptRead
KafkaChannel#read
KafkaChannel#receive
NetworkReceive#readFrom
PlaintextTransportLayer#read
SocketChannel#read
// KafkaChannel#read
// 收到的buffer
private NetworkReceive receive;
public long read() throws IOException {
if (receive == null) {
receive = new NetworkReceive(maxReceiveSize, id, memoryPool);
}
long bytesReceived = receive(this.receive);
return bytesReceived;
}
public class NetworkReceive implements Receive {
// 报文长度
private final ByteBuffer size;
// 报文
private ByteBuffer buffer;
}Step2,处理响应。
NetworkClient#handleCompletedSends:循环所有等待响应的请求(Send),如果ack=0,构建ClientResponse加入responses结果集,用于后续处理。
java
private void handleCompletedSends(List<ClientResponse> responses, long now) {
for (Send send : this.selector.completedSends()) {
// 获取刚发送的请求
InFlightRequest request =
this.inFlightRequests.lastSent(send.destination());
// 对于ack=0,expectResponse=false
if (!request.expectResponse) {
// 弹出刚发送的请求
this.inFlightRequests.completeLastSent(send.destination());
// 构造为ClientResponse,加入结果集
responses.add(request.completed(null, now));
}
}
}NetworkClient#handleCompletedReceives:循环所有收到的响应,反序列化并封装为AbstractResponse。
java
private void handleCompletedReceives(List<ClientResponse> responses, long now) {
for (NetworkReceive receive : this.selector.completedReceives()) {
String source = receive.source(); // brokerId
// 弹出最早的等待响应的请求
InFlightRequest req = inFlightRequests.completeNext(source);
// 反序列化为Struct
// 这里会校验请求响应的correlationId一致,kafka只能按照顺序发送和接收响应
// 和普通rpc不同,通过id找挂起的请求
Struct responseStruct = parseStructMaybeUpdateThrottleTimeMetrics(receive.payload(), req.header,
throttleTimeSensor, now);
// Struct转对象
AbstractResponse response = AbstractResponse.
parseResponse(req.header.apiKey(), responseStruct, req.header.apiVersion());
// ...
// 将响应加入结果集
responses.add(req.completed(response, now));
}
}Step3,回调callback。
NetworkClient#completeResponses:
java
private void completeResponses(List<ClientResponse> responses) {
for (ClientResponse response : responses) {
try {
response.onComplete();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Uncaught error in request completion:", e);
}
}
}
// ClientResponse.java
private final RequestCompletionHandler callback;
public void onComplete() {
if (callback != null)
callback.onComplete(this);
}Sender#sendProduceRequest:回到7-5的callback。
java
private void sendProduceRequest(long now, int destination, short acks, int timeout, List<ProducerBatch> batches) {
// ...
// 构建请求
ProduceRequest.Builder requestBuilder = ProduceRequest.Builder.forMagic(minUsedMagic, acks, timeout,
produceRecordsByPartition, transactionalId);
// 响应处理【focus】
RequestCompletionHandler callback = response -> handleProduceResponse(response, recordsByPartition, time.milliseconds());
String nodeId = Integer.toString(destination);
ClientRequest clientRequest = client.newClientRequest(nodeId, requestBuilder, now, acks != 0,
requestTimeoutMs, callback);
// 缓存到KafkaChannel的Send
client.send(clientRequest, now);
}Sender#handleProduceResponse:一个ProduceResponse对应n个分区批次,循环响应每个分区批次。
java
private void handleProduceResponse(ClientResponse response, Map<TopicPartition, ProducerBatch> batches, long now) {
RequestHeader requestHeader = response.requestHeader();
int correlationId = requestHeader.correlationId();
// ...
if (response.hasResponse()) {
// ack!=0,有server端响应
ProduceResponse produceResponse = (ProduceResponse) response.responseBody();
for (Map.Entry<TopicPartition, ProduceResponse.PartitionResponse> entry : produceResponse.responses().entrySet()) {
TopicPartition tp = entry.getKey();
ProduceResponse.PartitionResponse partResp = entry.getValue();
ProducerBatch batch = batches.get(tp);
completeBatch(batch, partResp, correlationId, now);
}
} else {
// ack=0,无server响应
for (ProducerBatch batch : batches.values()) {
completeBatch(batch, new ProduceResponse.PartitionResponse(Errors.NONE), correlationId, now);
}
}
}ProducerBatch#completeFutureAndFireCallbacks:一个分区批次对应n次send方法调用,循环回调所有send方法的callback(先ProducerInterceptor#onAcknowledgement,后用户自己传入的callback),最终完成produceFuture,唤醒阻塞等待发送结果的生产者线程。
所以生产结果的callback都在io线程里执行。
java
// 批次发送future
final ProduceRequestResult produceFuture;
// Thunk=(回调方法,发送结果)
private final List<Thunk> thunks = new ArrayList<>();
private void completeFutureAndFireCallbacks(long baseOffset, long logAppendTime, RuntimeException exception) {
// 设置批次发送future结果
produceFuture.set(baseOffset, logAppendTime, exception);
// 循环thunks回调InterceptorCallback和用户callback
for (Thunk thunk : thunks) {
try {
if (exception == null) {
RecordMetadata metadata = thunk.future.value();
if (thunk.callback != null)
thunk.callback.onCompletion(metadata, null);
} else {
if (thunk.callback != null)
thunk.callback.onCompletion(null, exception);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(..., e);
}
}
// 完成批次发送future(countdownLatch.countDown)
// 唤醒所有等待发送结果的生产者
produceFuture.done();
}
private static class InterceptorCallback<K, V> implements Callback {
private final Callback userCallback;
private final ProducerInterceptors<K, V> interceptors;
public void onCompletion(RecordMetadata metadata, Exception exception) {
this.interceptors.onAcknowledgement(metadata, exception);
if (this.userCallback != null)
this.userCallback.onCompletion(metadata, exception);
}
}总结
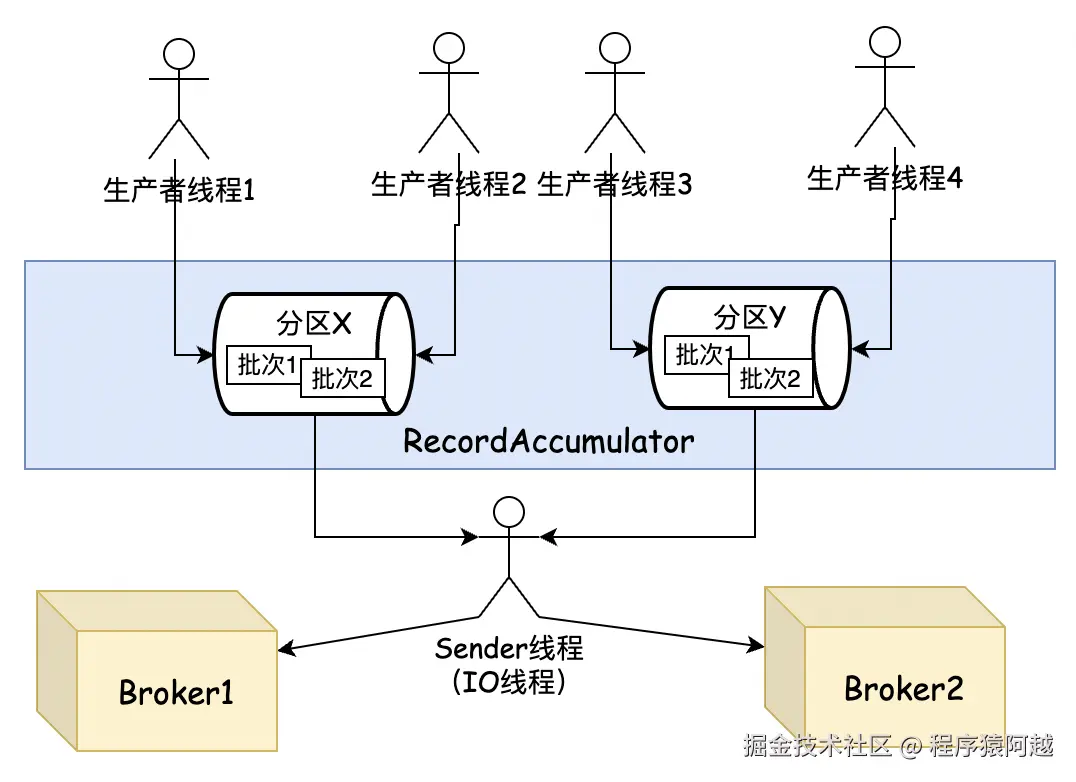
Kafka生产者客户端使用两个线程:
1)生产者线程,调用send方法返回一个Future,可以选择阻塞等待Future完成,也可以选择send方法传入第二个callback方法用于处理回调;send方法底层将消息写入RecordAccumulator累积器,每个分区维护1个消息批次队列Dequeue,1个消息批次ProducerBatch包含n条消息;
2)Sender线程,无限循环从RecordAccumulator中拉取ProducerBatch,发送ProduceRequest,接收ProduceResponse,执行所有callback,完成生产Future;
生产者线程:
1)获取topic元数据:先从cache获取,如果cache miss,需要唤醒Sender获取元数据写入cache,生产者线程等待元数据返回;
2)key/value序列化;
3)计算消息分区:如果消息指定了key,用hash(key)%分区数决定,反之,采用sticky策略,将没有key的消息,合并到一个分区批次中发送,降低无key消息的发送延迟;
4)预计消息大小:校验消息不超过max.request.size,默认1MB;
5)将消息写入累积器:
5-1)优先写入消息对应分区(分区锁)的现有批次,如果加入失败,需要创建新批次;
5-2)创建新批次,需要从内存池BufferPool分配一块内存(全局锁,默认16K),这个内存将在sender发送消息完成后归还并池化,如果内存池可用内存不足(32M),将会阻塞生产者;
5-3)将消息写入批次时,会完成消息压缩;
Sender线程:
1)从累积器筛选需要发送消息的节点,满足下面条件之一的分区对应节点:分区批次满了、在累积器中等待超过linger.ms(默认0)、内存池内存不足,有生产者线程在等待分配内存;
2)过滤未就绪的节点:需要更新元数据(全局限制)、未建立连接(触发建立连接,但是要下一轮循环才能发送消息)、节点未响应的请求数量小于max.in.flight.requests.per.connection=5;
3)循环节点,每个分区从累积器拉取1个消息批次,单节点数据大小不超过max.request.size=1MB,对每个消息批次构造批次头;
4)移除超时批次:通过配置delivery.timeout.ms超时时间来控制重试次数,默认超时时间为2分钟,超时批次包含已经发送给broker的和在累积器中还未发送的,完成生产Future为超时异常;
5)为每个节点构造ProduceRequest,序列化后封装为Send对象,放到KafkaChannel;
6)poll:执行IO操作,包括发送Send和接收Receive并反序列化为ProduceResponse,执行callback方法,完成生产Future;