以 IntStream 为例,浅析 Java 中 Stream 的实现
我们在使用 Stream 时,典型的步骤是
- 创建
Stream - 执行若干(可以是
0个)中间操作 - 执行终止操作
下面举一个具体的例子。 假设现在需要计算小于 10 的所有正偶数的立方和,即
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 2 3 + 4 3 + 6 3 + 8 3 2^3 + 4^3 + 6^3 + 8^3 </math>23+43+63+83
可以用如下的代码来计算。⬇️
java
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
public class SimpleIntStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Suppose that we need to calculate the cubic sum of positive even numbers that are less than 10
int result = IntStream.range(1, 10) // Step 1
.filter(n -> (n & 1) == 0) // Step 2
.map(n -> n * n * n) // Step 3
.sum(); // Step 4
System.out.println("The result of 2**3 + 4**3 + 6**3 + 8**3 is: " + result);
}
}上面的代码中和 Stream 有直接关系的代码共有 4 步,我在注释中标出来了。
Step 1: 创建IntStreamStep 2: 调用IntStream.filter(...)方法,生成一个新的IntStreamStep 3: 调用IntStream.map(...)方法,生成一个新的IntStreamStep 4: 调用IntStream.sum()方法,得到结果。
其中 Step 2 和 Step 3 都是中间操作。 Step 4 是终止操作。
我们来看看这 4 个 step 的背后发生了什么。
Step 1: 创建 IntStream
分析
Step 1 就是 IntStream.range(1, 10)。 它创建了 IntStream 的一个实例。 为便于叙述,我们把这个实例称为 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 1 stage_1 </math>stage1。
因为 IntStream 是接口,所以其背后必定有某个实现类。
借助 Intellij IDEA,可以看到对应的实现类是 IntPipeline.Head (全限定类名是 java.util.stream.IntPipeline.Head)⬇️

我画了一张图来表示 Step 1 背后的逻辑 ⬇️

这张图中,灰色背景的节点表示 Step 1 的代码, 蓝色背景的节点表示 IntPipeline.Head 的实例,即 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 1 stage_1 </math>stage1(完整的类名太长了,在图中就简称为 Head 了)。
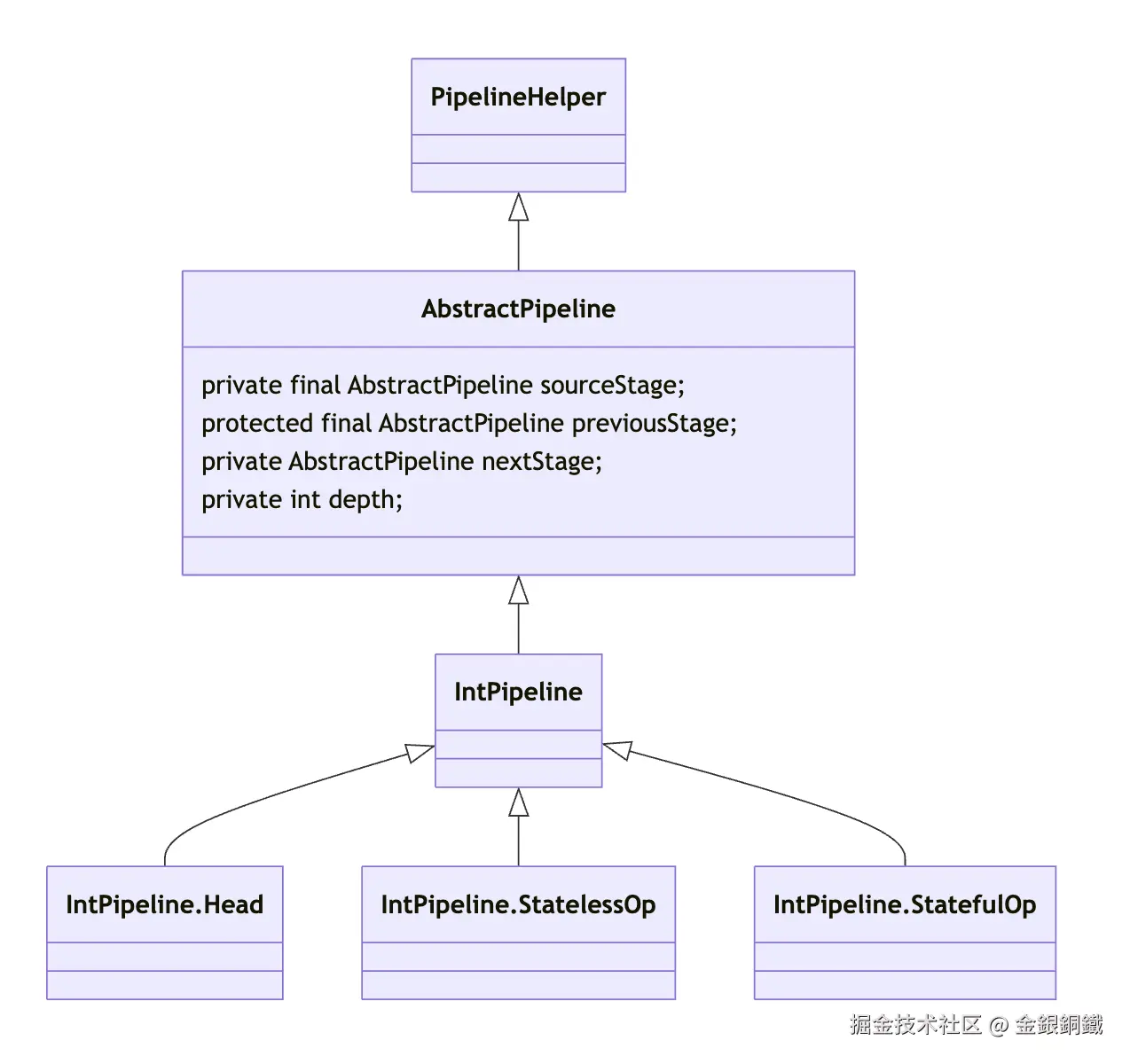
图中有一条名为 sourceStage 的绿色边,这个 sourceStage 字段来自 AbstractPipeline 类。 Head 类和 AbstractPipeline 和之间的关系如下图所示 ⬇️
总结
Step 1 创建了 IntPipeline.Head 类的实例 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 1 stage_1 </math>stage1。
Step 2: 执行 filter 操作得到新的 IntStream
分析
Step 1 创建了 IntStream 的一个实例 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 1 stage_1 </math>stage1, Step 2 通过 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 1 stage_1 </math>stage1 调用 IntStream.filter(...) 方法,并生成 IntStream 的又一个实例。我们称这个新实例为 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 2 stage_2 </math>stage2。
借助 Intellij IDEA,可以看到 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 2 stage_2 </math>stage2 是 java.util.stream.IntPipeline.StatelessOp 的一个 子类 的实例 ⬇️ 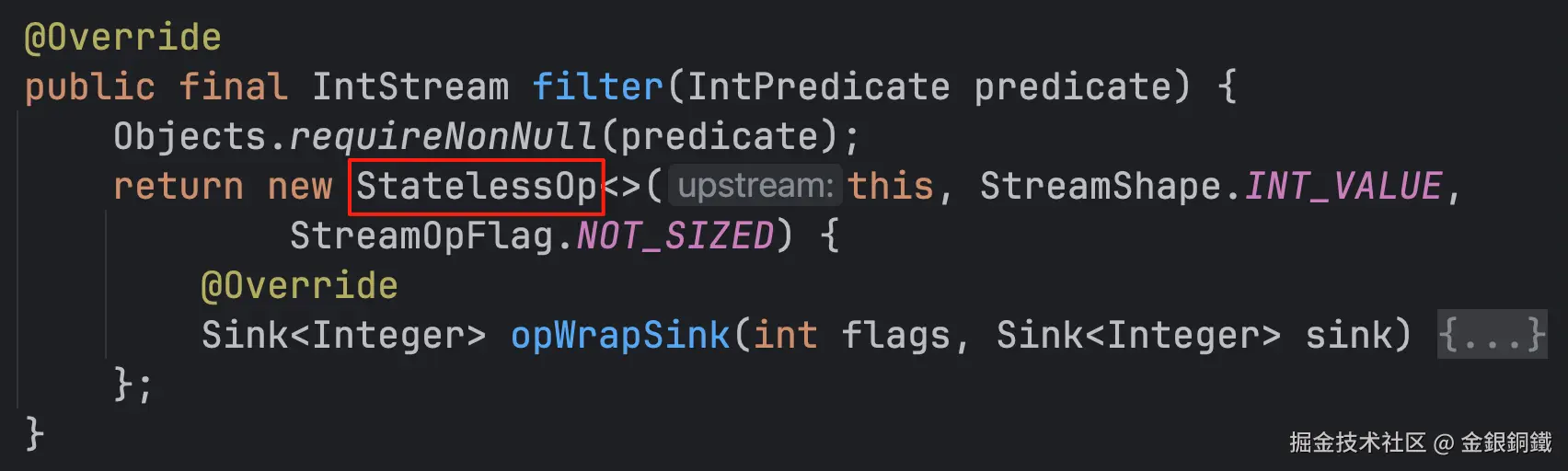 注意: <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 2 stage_2 </math>stage2 的精确类型是
注意: <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 2 stage_2 </math>stage2 的精确类型是 java.util.stream.IntPipeline$10,由于这是一个匿名内部类,我们不必关心这个类的具体名称。
我画了一张图来表示 Step 2 背后的逻辑 ⬇️

灰色背景的节点表示 Step 2 的代码, 蓝色背景的两个节点表示 IntStream 的两个实例,即 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 1 stage_1 </math>stage1 和 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 2 stage_2 </math>stage2。
- 图中有名为
previousStage的黄色边,这个previousStage字段来自AbstractPipeline类。 - 图中有名为
nextStage的蓝色边,这个nextStage字段来自AbstractPipeline类。
总结
Step 2 创建了 IntPipeline.StatelessOp 类的(子类的)实例 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 2 stage_2 </math>stage2,而 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 1 stage_1 </math>stage1, <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 2 stage_2 </math>stage2 通过 previousStage 字段和 nextStage 字段组成了一个双向链表。
Step 3: 执行 map 操作得到新的 IntStream
分析
Step 2 创建了 IntStream 的实例 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 2 stage_2 </math>stage2, Step 3 通过 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 2 stage_2 </math>stage2 调用 IntStream.map(...) 方法,生成 IntStream 的一个实例。我们称这个新实例为 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 3 stage_3 </math>stage3。
借助 Intellij IDEA,可以看到 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 3 stage_3 </math>stage3 是 java.util.stream.IntPipeline.StatelessOp 的一个 子类 的实例 ⬇️

注意: <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 3 stage_3 </math>stage3 的精确类型是 java.util.stream.IntPipeline$4,由于这是一个匿名内部类,我们不必关心这个类的具体名称。
下图展示了 Step 3 背后的逻辑 ⬇️

灰色背景的节点表示 Step 3 的代码, 蓝色背景的三个节点表示 IntStream 的三个实例,即 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 1 stage_1 </math>stage1, <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 2 stage_2 </math>stage2, <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 3 stage_3 </math>stage3。
总结
Step 3 创建了 IntPipeline.StatelessOp 类的(子类的)实例 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 3 stage_3 </math>stage3,而 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 1 stage_1 </math>stage1, <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 2 stage_2 </math>stage2, <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 3 stage_3 </math>stage3 组成了一个双向链表。
nextStage用于指向链表中的下一个节点。如果用 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> → \rightarrow </math>→ 来表示nextStage的话,那么这三个节点的关系可以表示为 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 1 stage_1 </math>stage1 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> → \rightarrow </math>→ <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 2 stage_2 </math>stage2 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> → \rightarrow </math>→ <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 3 stage_3 </math>stage3previousStage用于指向链表中的上一个节点。如果用 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> ← \leftarrow </math>← 来表示previousStage的话,那么这三个节点的关系可以表示为 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 1 stage_1 </math>stage1 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> ← \leftarrow </math>← <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 2 stage_2 </math>stage2 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> ← \leftarrow </math>← <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 3 stage_3 </math>stage3
我把 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 1 stage_1 </math>stage1, <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 2 stage_2 </math>stage2, <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 3 stage_3 </math>stage3 中几个重要字段的值列在下方的表格中(其中 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> d e p t h depth </math>depth 字段上文没有提到,不过它的含义比较直观)。
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s o u r c e S t a g e sourceStage </math>sourceStage | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> n e x t S t a g e nextStage </math>nextStage | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> p r e v i o u s S t a g e previousStage </math>previousStage | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> d e p t h depth </math>depth | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 1 stage_1 </math>stage1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 1 stage_1 </math>stage1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 2 stage_2 </math>stage2 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> n u l l null </math>null | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 |
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 2 stage_2 </math>stage2 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 1 stage_1 </math>stage1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 3 stage_3 </math>stage3 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 1 stage_1 </math>stage1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 |
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 3 stage_3 </math>stage3 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 1 stage_1 </math>stage1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> n u l l null </math>null | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 2 stage_2 </math>stage2 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 2 2 </math>2 |
现在我们只关心 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> n e x t S t a g e nextStage </math>nextStage 和 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> p r e v i o u s S t a g e previousStage </math>previousStage 这两个字段,我把 Step 3 的图简化一下,得到如下的结果 ⬇️

Step 4: 调用 sum() 方法
Step 1 到 Step 3 都是在创建 IntStream 的实例,而真正的计算逻辑是在 Step 4 完成的。
借助 Intellij IDEA,可以看到 sum() 方法的逻辑如下
java
@Override
public final int sum() {
return reduce(0, Integer::sum);
}我们再去查看 reduce(...) 方法 ⬇️
java
@Override
public final int reduce(int identity, IntBinaryOperator op) {
return evaluate(ReduceOps.makeInt(identity, op));
}evaluate(...) 方法的代码如下 ⬇️

通过打断点可以确认,我们的代码对应的 isParallel() 值为 false。
所以会运行到下面这一行。
java
terminalOp.evaluateSequential(this, sourceSpliterator(terminalOp.getOpFlags()))这个 evaluateSequential(...) 方法定义在 java.util.Spliterator.TerminalOp 接口中。
我们需要去 TerminalOp 接口的实现类中查看实际运行的逻辑。
TerminalOp 接口中的 evaluateSequential(...) 方法
TerminalOp 接口的实现类是在下图红框位置生成的 ⬇️ 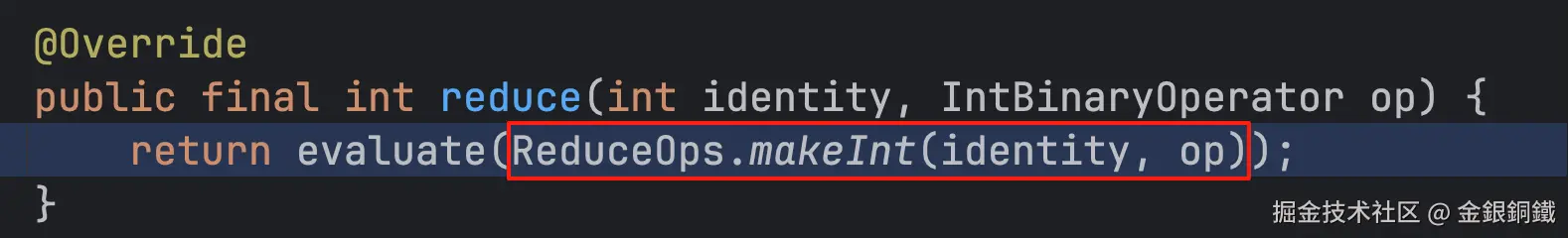
我们再去看 ReduceOps 类中的 makeInt(...) 方法的逻辑 ⬇️
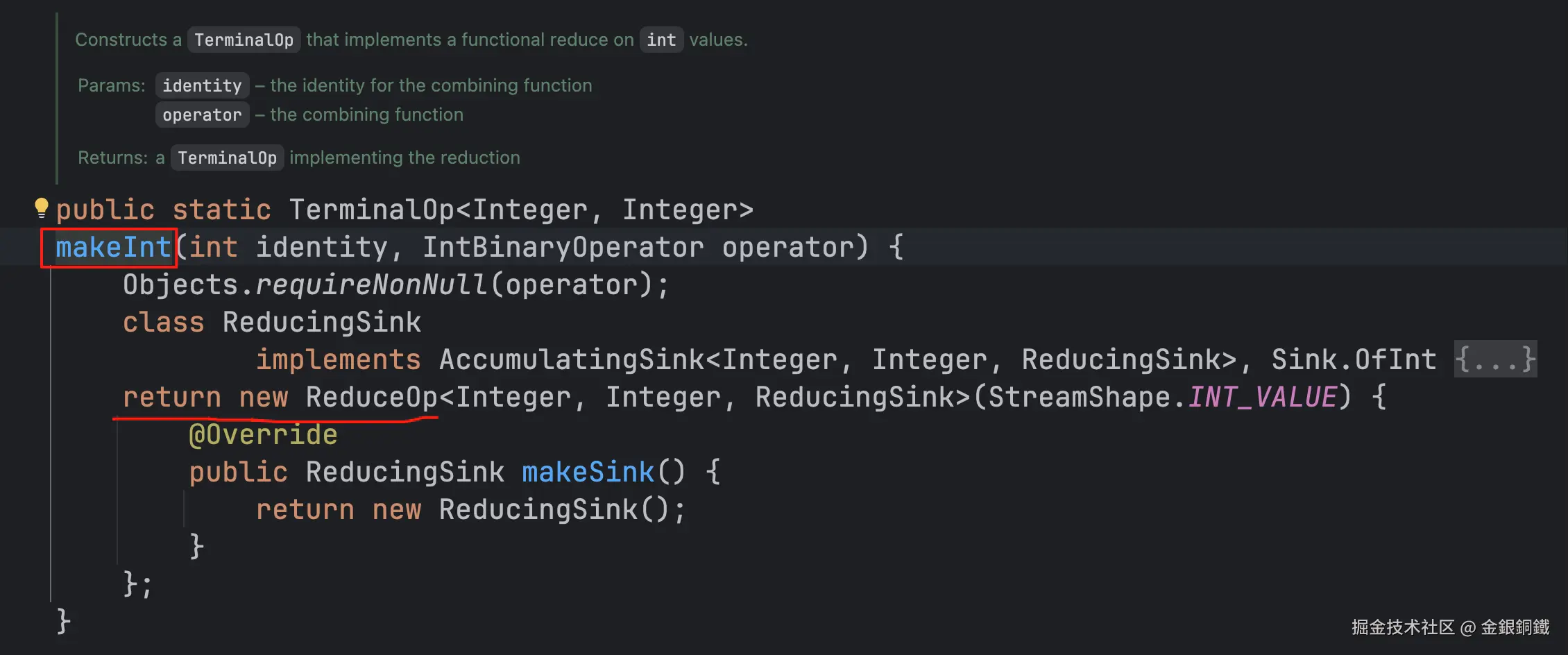
看来 ReduceOps 类中的 makeInt(...) 方法会返回一个匿名内部类,且这个匿名内部类是 ReduceOp 类的子类。
这里啰嗦一句,在打断点时,可以看到这个匿名内部类的全限定类名是 java.util.stream.ReduceOps$6,不过既然是匿名内部类,那么它的名称也就不重要了。这有点像做了好事而不愿留名的人,对这样的人来说,只要好事做完了就可以了,别人不必知道自己的名字。
我画了类图来表示这几个类的继承关系 ⬇️

由于匿名内部类(即 ReduceOps$6)中没有 override evaluateSequential(...) 方法, 所以最终调用的是 ReduceOp 类里的 evaluateSequential(...) 方法。
ReduceOp 类里的 evaluateSequential(...) 方法是这样的 ⬇️
java
@Override
public <P_IN> R evaluateSequential(PipelineHelper<T> helper,
Spliterator<P_IN> spliterator) {
return helper.wrapAndCopyInto(makeSink(), spliterator).get();
}所以要看以下两处逻辑
-
makeSink() -
helper.wrapAndCopyInto(...)
先看 makeSink()。
makeSink() 方法
makeSink() 的字面意思是制作 sink。怎么理解呢?
从 Step 1 到 Step 3,我们生成了 3 个 IntStream 的实例。我们可以把这些实例想象成水流, 那么水流要流到哪里去呢?要流到 sink 去。我去 Google 了一下 ⬇️

看来厨房和卫生间的水槽都可以称为 sink。水从 sink 流走, stream 也从 sink 流走。

通过打断点可以看到 makeSink() 中只有以下一句代码
java
return new ReducingSink();这句代码返回了 ReducingSink 类的实例,我们称这个实例为 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 1 sink_1 </math>sink1。 注意:ReducingSink 类是局部内部类,它的全限定类名是 java.util.stream.ReduceOps$5ReducingSink(我们不用关心它的具体名称)。
makeSink() 我们已经看完了,更新一下任务列表 ⬇️
-
makeSink() -
helper.wrapAndCopyInto(...)
然后再看 helper.wrapAndCopyInto(...)。
helper.wrapAndCopyInto(...) 方法
wrapAndCopyInto(...) 方法定义在 PipelineHelper 这个抽象类中 ⬇️

AbstractPipeline 类中 override 了这个方法 ⬇️
java
// 以下代码是从 AbstractPipeline.java 里 copy 过来的
@Override
final <P_IN, S extends Sink<E_OUT>> S wrapAndCopyInto(S sink, Spliterator<P_IN> spliterator) {
copyInto(wrapSink(Objects.requireNonNull(sink)), spliterator);
return sink;
}其中的主要逻辑是 wrapSink(...) 和 copyInto(...),我们将任务列表更新如下 ⬇️
-
makeSink() -
helper.wrapAndCopyInto(...)-
wrapSink(...) -
copyInto(...)
-
先看 wrapSink(...),从名字来看,似乎是要对 Sink 做一些包装的工作。 它的 javadoc 如下 ⬇️ 看来确实如此 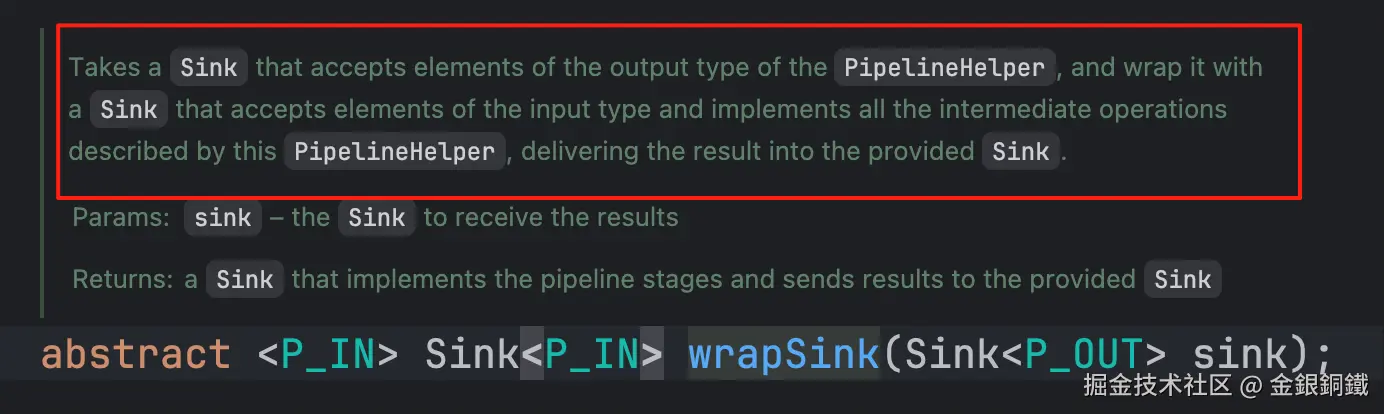
其代码如下
java
// 以下代码是从 AbstractPipeline.java 里 copy 过来的
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
final <P_IN> Sink<P_IN> wrapSink(Sink<E_OUT> sink) {
Objects.requireNonNull(sink);
for ( @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") AbstractPipeline p=AbstractPipeline.this; p.depth > 0; p=p.previousStage) {
sink = p.opWrapSink(p.previousStage.combinedFlags, sink);
}
return (Sink<P_IN>) sink;
}通过阅读代码和打断点,会发现这段代码的作用是将所有的非 Head 节点包装成 sink。 从 Step 1 到 Step 3,我们得到了 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 1 stage_1 </math>stage1, <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 2 stage_2 </math>stage2, <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 3 stage_3 </math>stage3。其中只有 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 1 stage_1 </math>stage1 是 Head 节点。 包装后会变成这样 ⬇️

请注意
3个stage节点是从Head的实例算起的,所以 从上到下 依次是 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 1 stage_1 </math>stage1, <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 2 stage_2 </math>stage2, <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 3 stage_3 </math>stage3 (Head实例是 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s t a g e 1 stage_1 </math>stage1)3个sink节点是从ReducingSink的实例算起的,所以 从下到上 依次是 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 1 sink_1 </math>sink1, <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 2 sink_2 </math>sink2, <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 3 sink_3 </math>sink3(ReducingSink实例是 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 1 sink_1 </math>sink1),这3个sink节点通过downstream字段构成了一个单链表 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 3 sink_3 </math>sink3 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> → \rightarrow </math>→ <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 2 sink_2 </math>sink2 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> → \rightarrow </math>→ <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 1 sink_1 </math>sink1
wrapSink(...) 方法的返回值就是上图的 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 3 sink_3 </math>sink3
wrapSink(...) 方法看完了,更新后的任务列表如下 ⬇️
-
makeSink() -
helper.wrapAndCopyInto(...)-
wrapSink(...) -
copyInto(...)
-
然后我们再去看 copyInto(...) 方法。从名称来看,这个方法的作用应该是把 stream 中的元素 copy 到 sink 里去。
这个方法的 javadoc 如下 ⬇️

打断点后,会看到我们的代码将运行到 copyInto(...) 方法里的 if 分支 ⬇️

上图中的 wrappedSink 就是上文刚刚提到的 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 3 sink_3 </math>sink3
java
wrappedSink.begin(spliterator.getExactSizeIfKnown());
spliterator.forEachRemaining(wrappedSink);
wrappedSink.end();看来又有新的代码要看了,更新后的任务列表如下 ⬇️
-
makeSink() -
helper.wrapAndCopyInto(...)-
wrapSink(...) -
copyInto(...)-
begin(long)method inSinkinterface -
forEachRemaining(Consumer)method inSpliteratorinterface -
end()method inSinkinterface
-
-
先猜测一下 ⬇️
begin(long)听起来像是在真正的处理前,做准备工作的步骤forEachRemaining(Consumer)听起来像是真正干活的步骤end()听起来像是干完活后,处理善后事宜的步骤
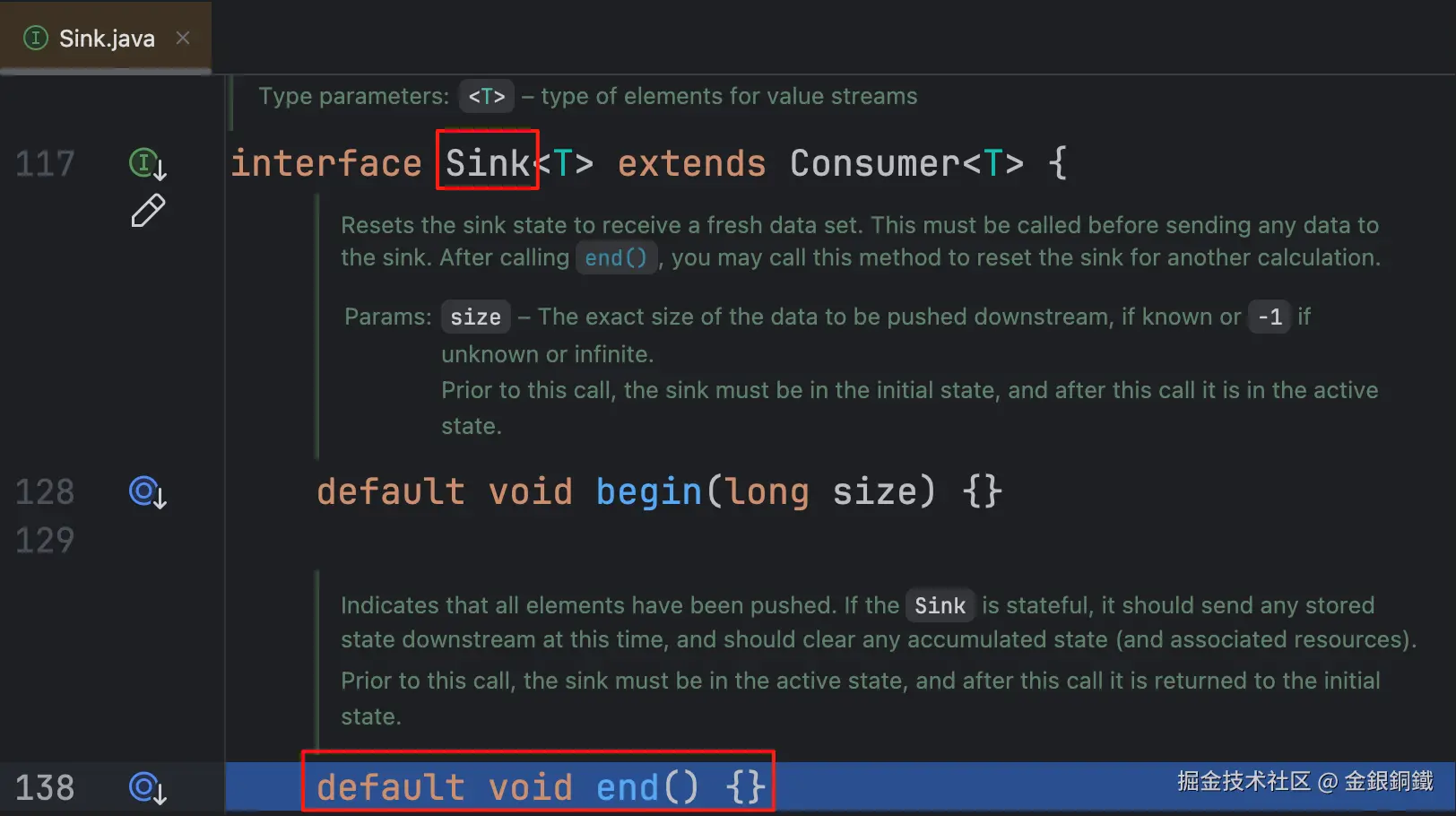
begin(long) 和 end() 都是 Sink 接口中定义的方法,我把这两个方法的 javadoc 复制到下方 ⬇️
java
// 下方的代码是从 Sink.java 中 copy 的
/**
* Resets the sink state to receive a fresh data set. This must be called
* before sending any data to the sink. After calling {@link #end()},
* you may call this method to reset the sink for another calculation.
* @param size The exact size of the data to be pushed downstream, if
* known or {@code -1} if unknown or infinite.
*
* <p>Prior to this call, the sink must be in the initial state, and after
* this call it is in the active state.
*/
default void begin(long size) {}
/**
* Indicates that all elements have been pushed. If the {@code Sink} is
* stateful, it should send any stored state downstream at this time, and
* should clear any accumulated state (and associated resources).
*
* <p>Prior to this call, the sink must be in the active state, and after
* this call it is returned to the initial state.
*/
default void end() {}forEachRemaining(Consumer) 来自 Spliterator 接口,它的 javadoc 如下 ⬇️
java
// 下方的代码是从 Spliterator.java 中 copy 的
/**
* Performs the given action for each remaining element, sequentially in
* the current thread, until all elements have been processed or the action
* throws an exception. If this Spliterator is {@link #ORDERED}, actions
* are performed in encounter order. Exceptions thrown by the action
* are relayed to the caller.
* <p>
* Subsequent behavior of a spliterator is unspecified if the action throws
* an exception.
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation repeatedly invokes {@link #tryAdvance} until
* it returns {@code false}. It should be overridden whenever possible.
*
* @param action The action
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified action is null
*/
default void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super T> action) {
do { } while (tryAdvance(action));
}但通过打断点,可以看到,我们的代码实际上执行的并不是上面这个方法,Spliterator.OfInt 这个嵌套类(其实它是个接口,但是如果叫"嵌套接口"的话,感觉有点拗口)中 override 了 forEachRemaining(Consumer) 方法。我们的代码会执行这个 override 的方法 ⬇️

通过打断点,我们会发现,上图的 if 分支成立。 这个 if 分支里只有下面一行代码
java
forEachRemaining((IntConsumer) action);上面的这个 forEachRemaining(IntConsumer) 方法在 Spliterator.OfInt 类中。 打断点后,会发现 java.util.stream.Streams.RangeIntSpliterator 类中 override 了 forEachRemaining(IntConsumer) 方法。
这里有一点绕,我们可以参考下方的类图来辅助理解。
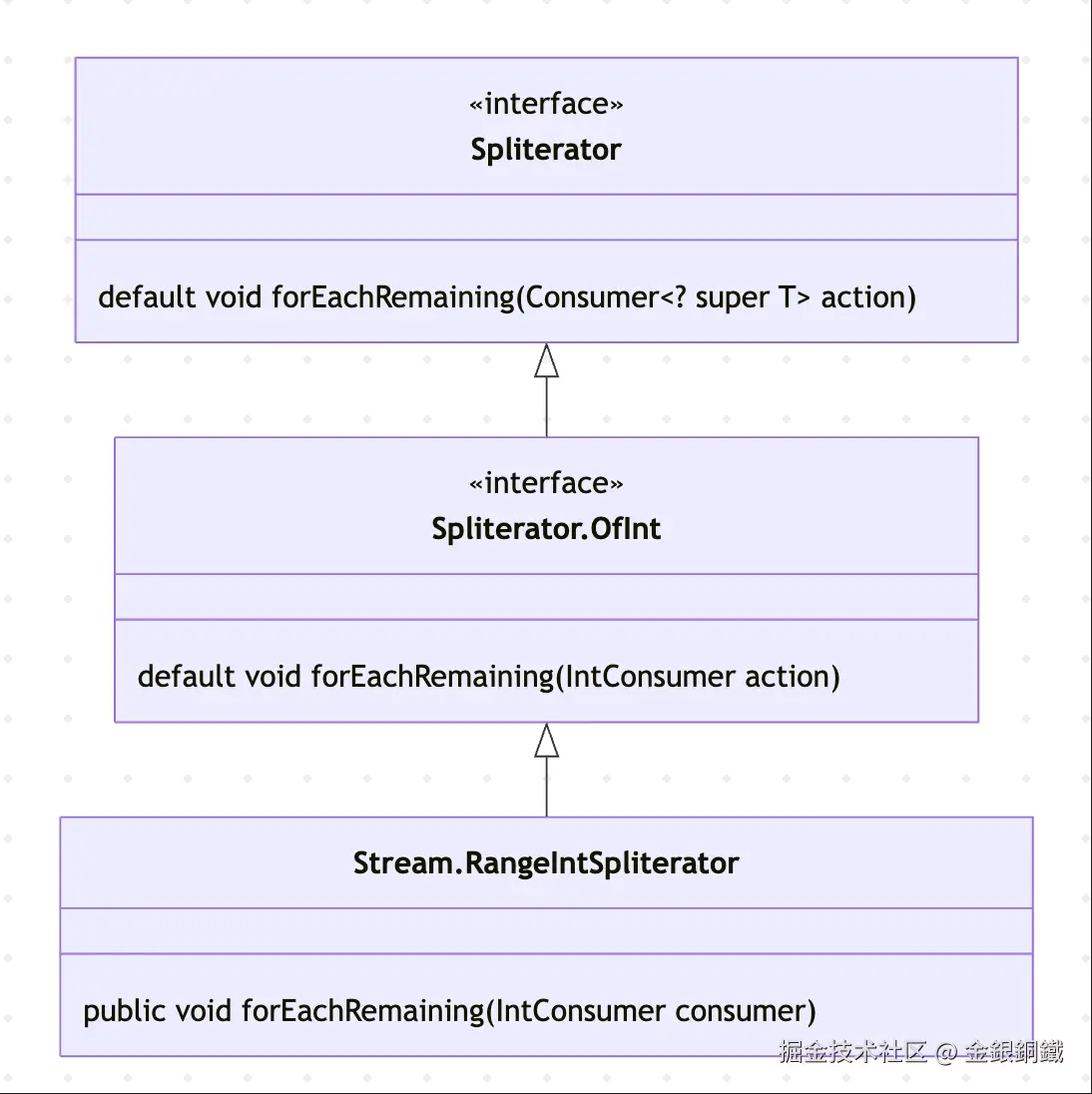
打断点后,可以看到 i 会从 1 遍历到 10 (不包含 10)⬇️

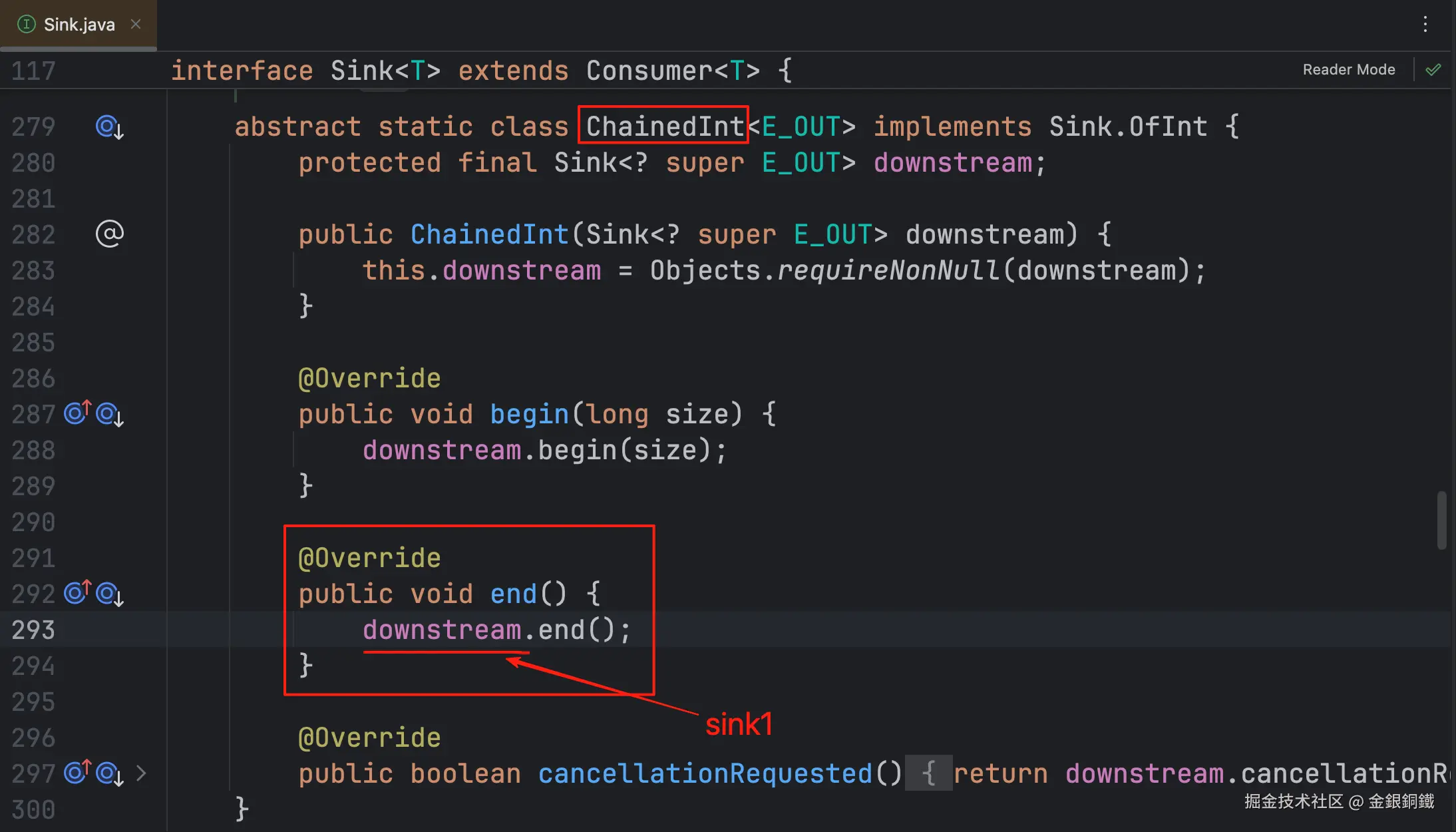
图中的 consumer 就是上文提到的 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 3 sink_3 </math>sink3。 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 3 sink_3 </math>sink3 和 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 2 sink_2 </math>sink2 都是 Sink.ChainedInt 的子类的实例。
下方的表格展示了 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 3 sink_3 </math>sink3, <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 2 sink_2 </math>sink2, <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 1 sink_1 </math>sink1 是如何通过 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> d o w n s t r e a m downstream </math>downstream 字段连接起来的 ⬇️
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c l a s s class </math>class | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> d o w n s t r e a m downstream </math>downstream | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c o d e code </math>code | |
|---|---|---|---|
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 3 sink_3 </math>sink3 | Sink.ChainedInt 的一个匿名子类 |
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 2 sink_2 </math>sink2 | 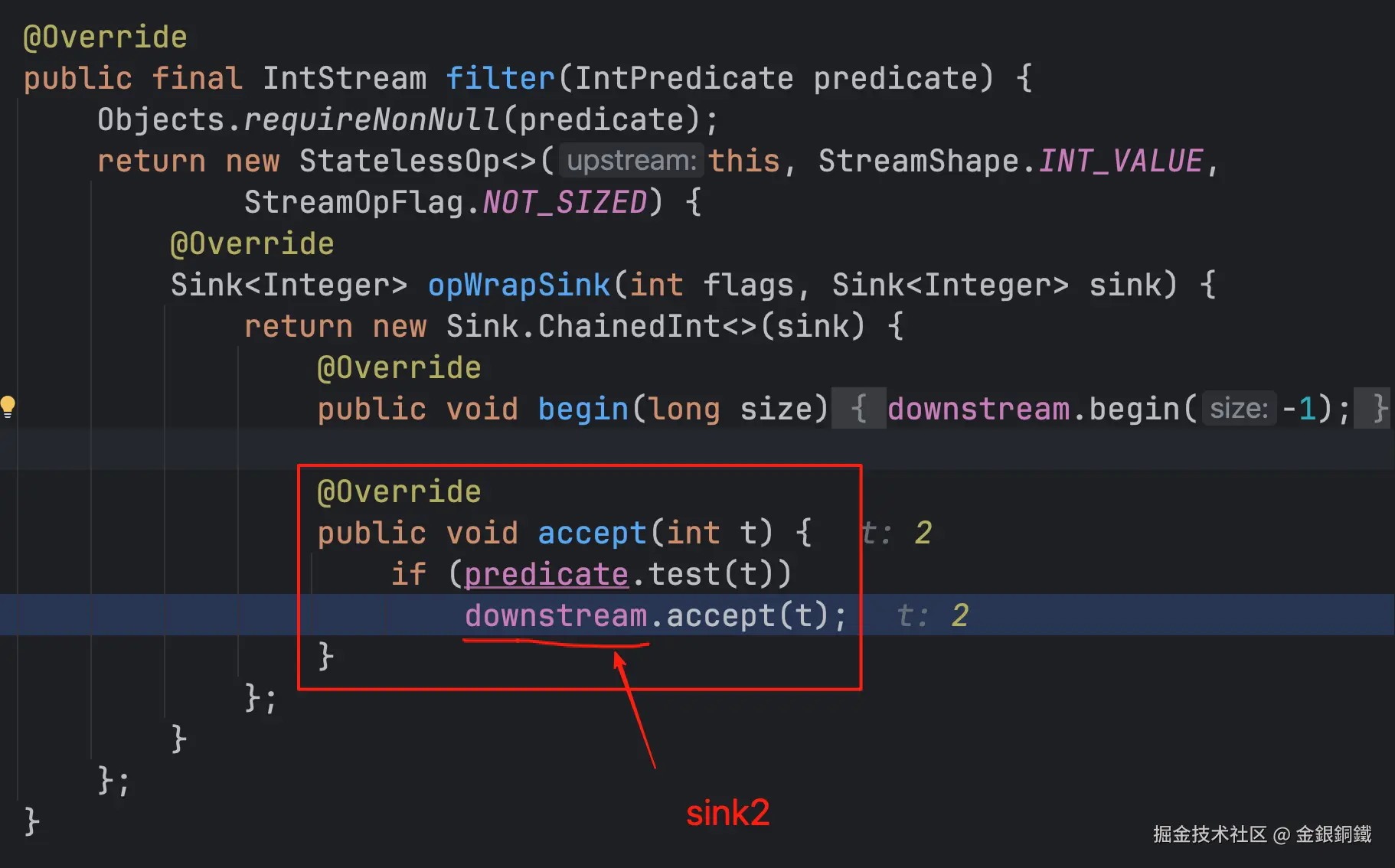 |
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 2 sink_2 </math>sink2 | Sink.ChainedInt 的一个匿名子类 |
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 1 sink_1 </math>sink1 | 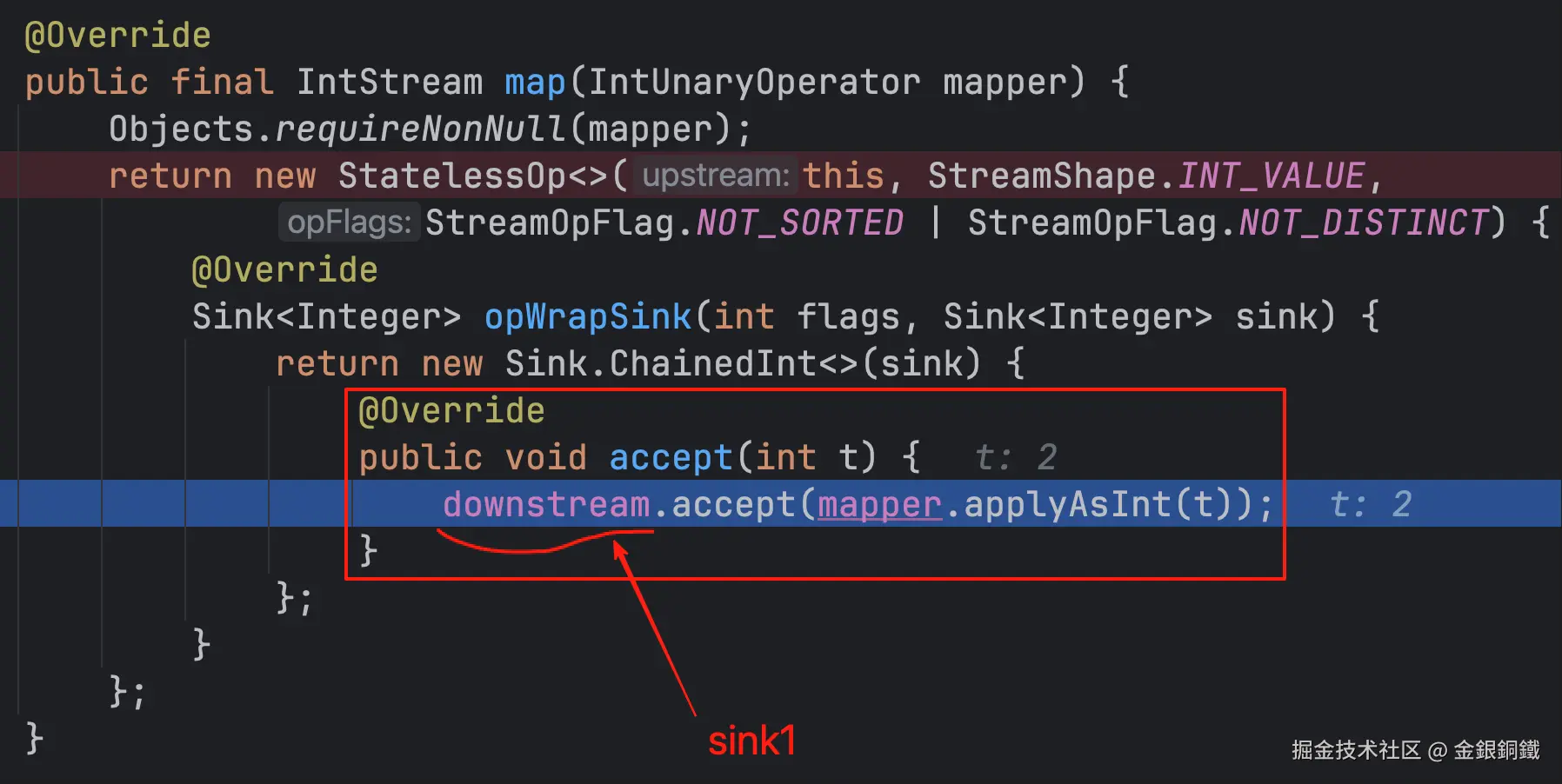 |
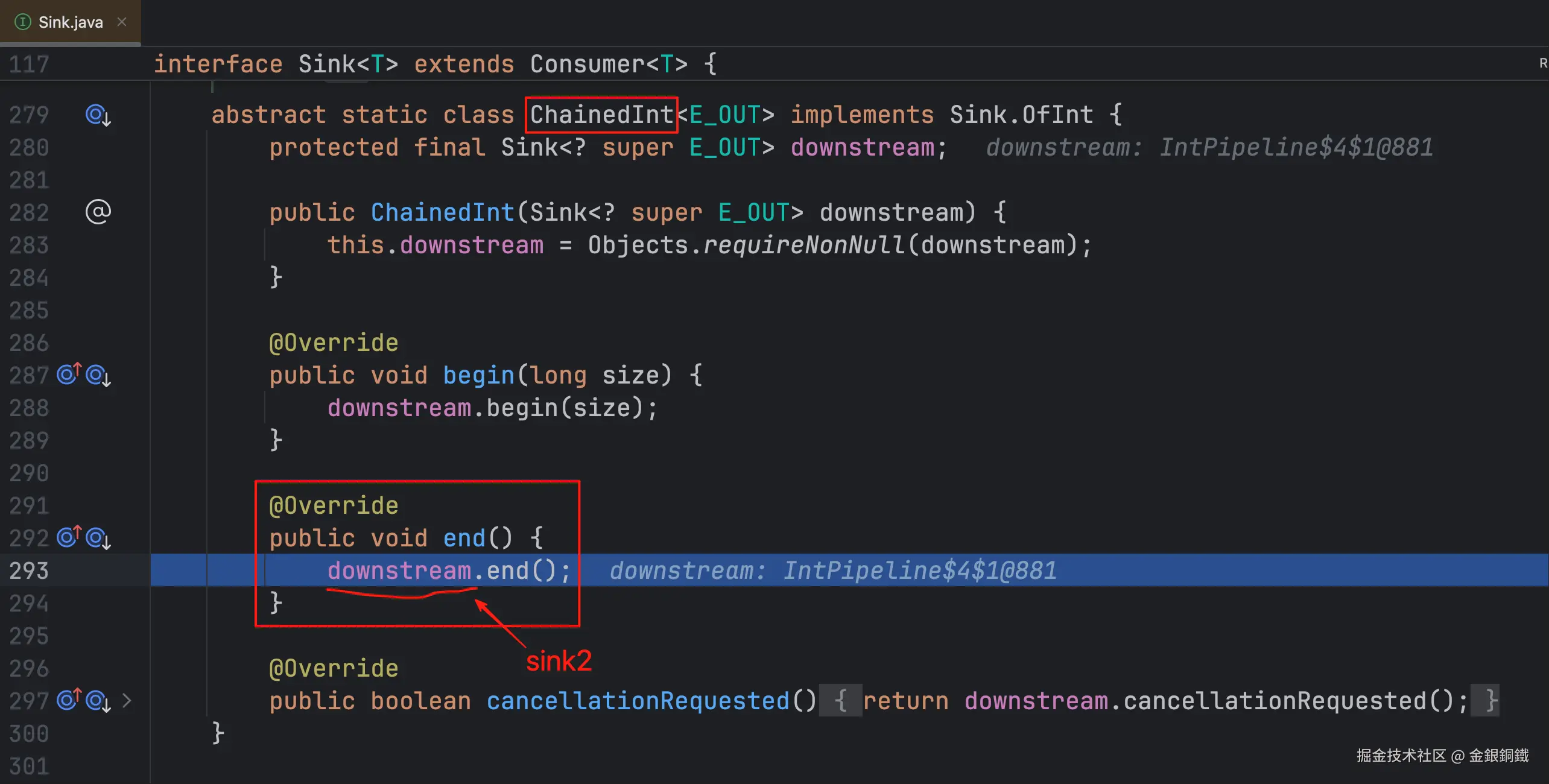
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 1 sink_1 </math>sink1 | ReducingSink ⬅️ 它是一个局部内部类 |
没有 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> d o w n s t r e a m downstream </math>downstream 字段 | 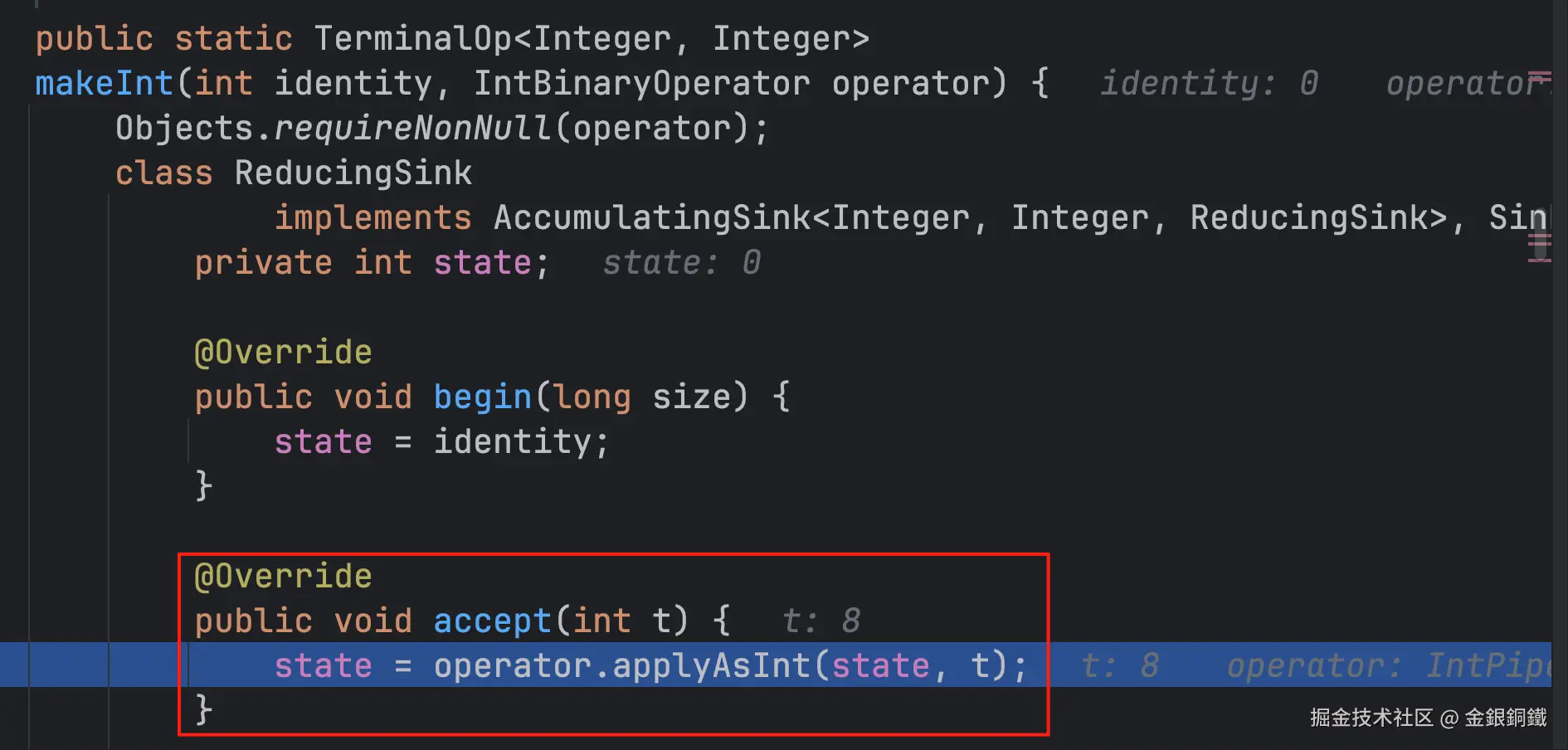 |
至于 begin(long) 和 end(),它们也是沿着 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 3 → s i n k 2 → s i n k 1 sink_3 \rightarrow sink_2 \rightarrow sink_1 </math>sink3→sink2→sink1 的方向来处理的。
为了方便理解,我画了对应的表格 ⬇️
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c l a s s class </math>class | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> d o w n s t r e a m downstream </math>downstream | code for <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> b e g i n ( l o n g ) begin(long) </math>begin(long) | code for <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> e n d ( ) end() </math>end() | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 3 sink_3 </math>sink3 | Sink.ChainedInt 的一个匿名子类 |
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 2 sink_2 </math>sink2 | 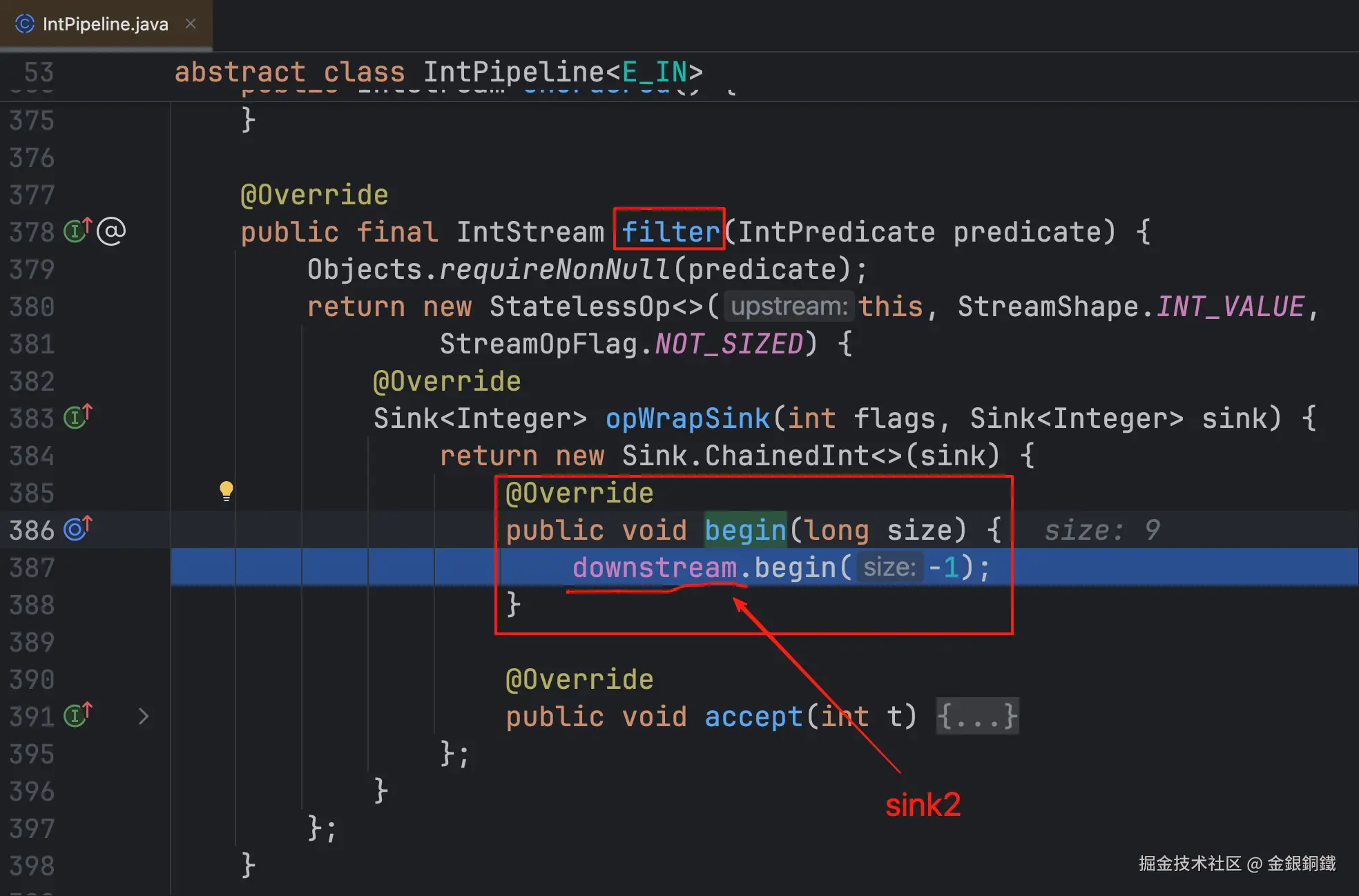 |
 |
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 2 sink_2 </math>sink2 | Sink.ChainedInt 的一个匿名子类 |
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 1 sink_1 </math>sink1 | 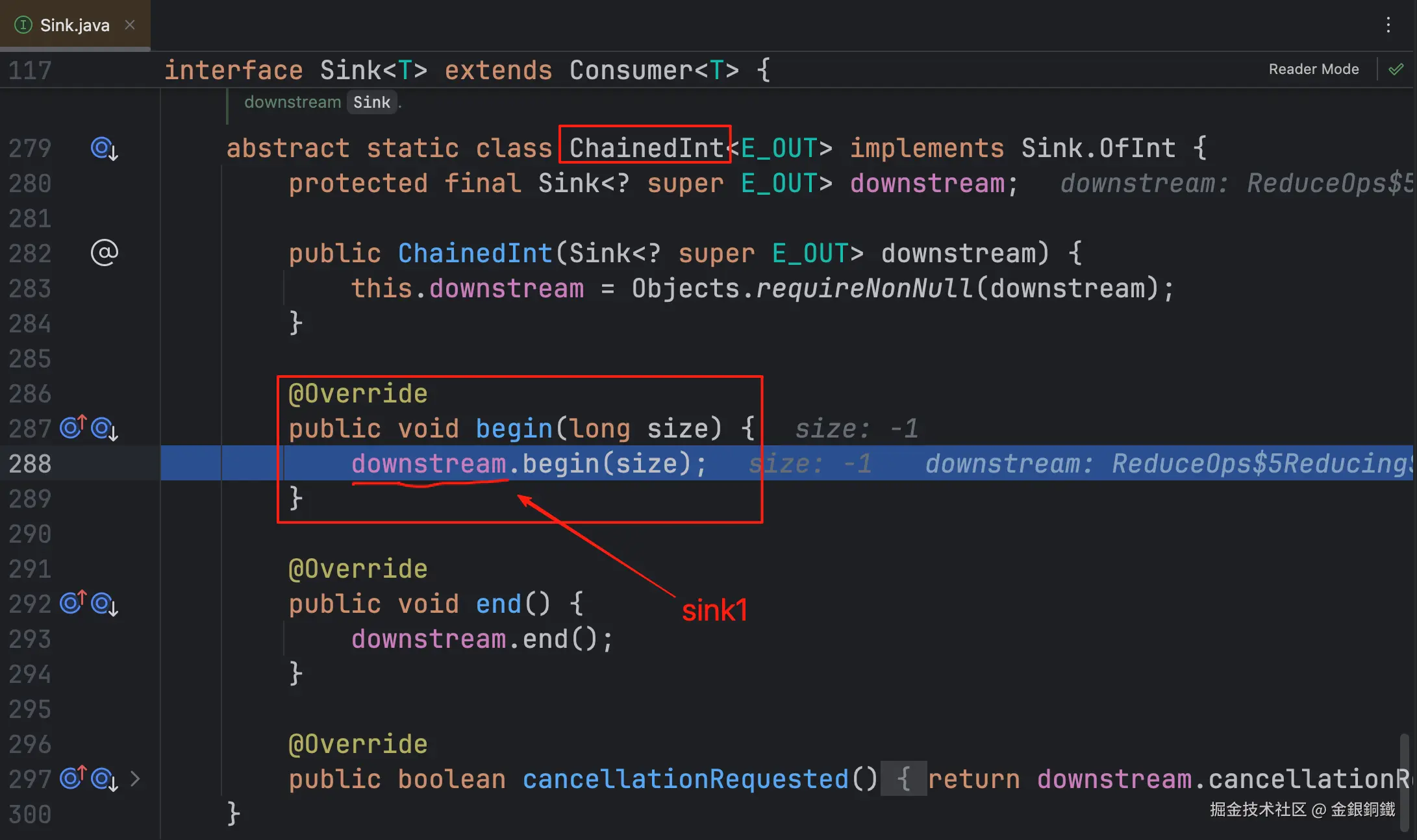 注意:由于匿名子类没有 注意:由于匿名子类没有 override <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> b e g i n ( l o n g ) begin(long) </math>begin(long) 方法,所以这里的 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> b e g i n ( l o n g ) begin(long) </math>begin(long) 方法来自 Sink.ChainedInt |
 注意:其实本图和上一行的图对应的代码在同一个位置 注意:其实本图和上一行的图对应的代码在同一个位置 |
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s i n k 1 sink_1 </math>sink1 | ReducingSink ⬅️ 它是一个局部内部类 |
没有 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> d o w n s t r e a m downstream </math>downstream 字段 | 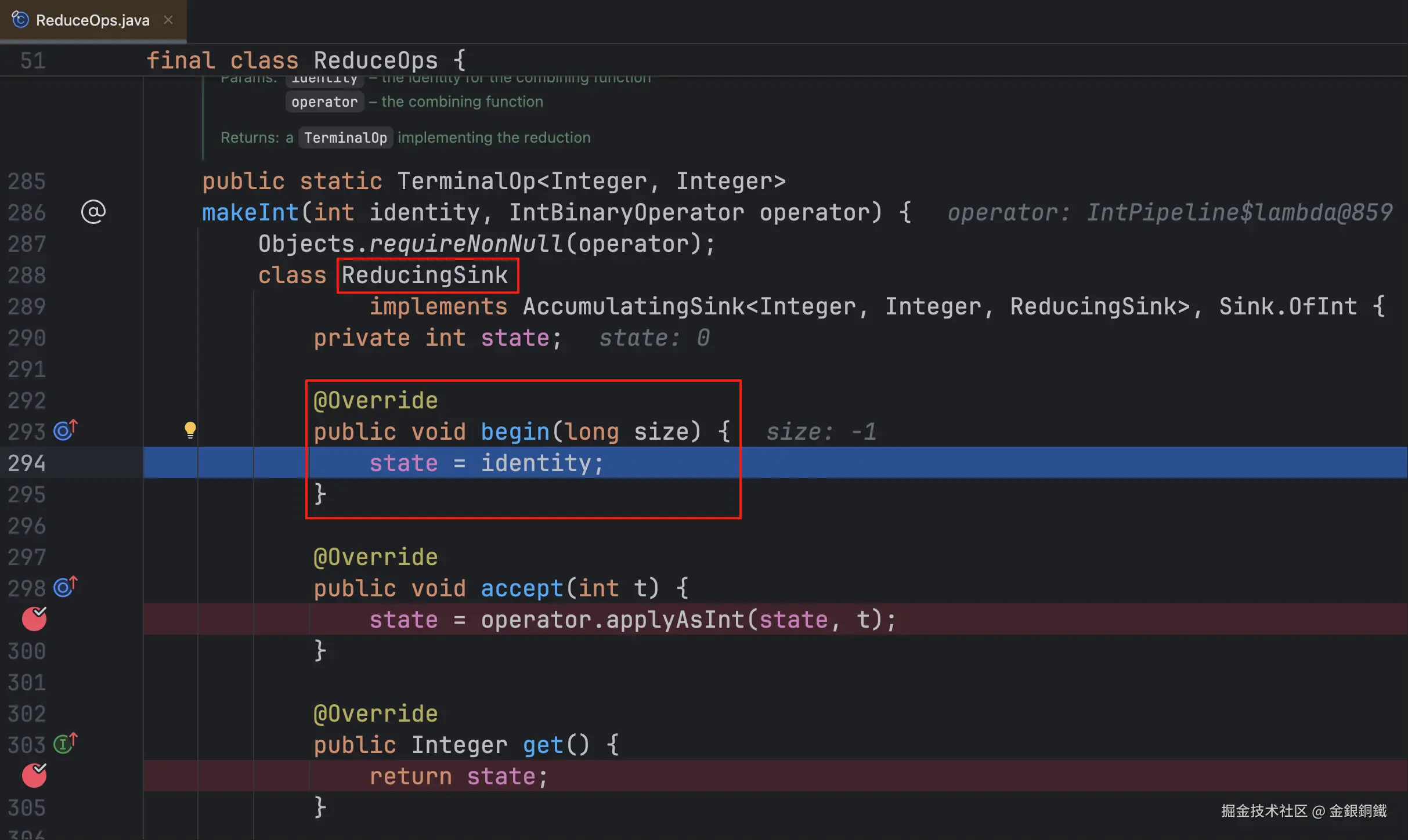 |
 |
再更新一下任务列表,Step 4 我们也看完了。
-
makeSink() -
helper.wrapAndCopyInto(...)-
wrapSink(...) -
copyInto(...)-
begin(long)method inSinkinterface -
forEachRemaining(Consumer)method inSpliteratorinterface -
end()method inSinkinterface
-
-