这个网站创建了一个简易版本的React,来让我们明白React的基本原理
在这里,对这篇文章内的代码做一个解读
HTML的大体构成
在下面的代码中,我们可以大体看到html展示页面内容的一个构成
也就是说,如果我们需要展示一些东西(文字、图片等内容),我们可以在body标签内通过不同的标签来写明,并且加上样式
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=<device-width>, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.base {
color: palevioletred;
font-size: medium;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>title</h1>
<div class="base">show something</div>
</body>
</html>通过JS来操作
这里就直接拿网站上的模版来当作示例了
没有写其他的标签,只有一个div标签,这里也是可以直接运行的
- 通过
document.getElementById('root')来获取容器container - 创建了一个
h1标签,并设置属性title = "foo" - 通过
document.createTextNode('')创建了一个文本节点,并且把文本节点的nodeValue设置成了Hello - 最后就是把文本节点
text放入到了node里面,然后将node放入到了container中
html
<div id="root"></div>
<script>
const element = {
type: 'h1',
props: {
title: 'foo',
children: 'Hello',
}
}
const container = document.getElementById('root')
const node = document.createElement(element.type)
node['title'] = element.props.title
const text = document.createTextNode('')
text['nodeValue'] = element.props.children
node.appendChild(text)
container.appendChild(node)
</script>我们可以在开发者工具中看到最后的html代码是这样的 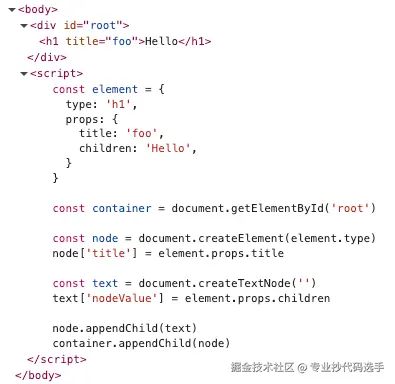
在react以及vue中,都是通过js来操作,将一些需要展示的内容,通过js的操作来逐步放入到容器内,最后进行渲染。
React实现原理
React 的核心工作原理可以分为三步:
- 创建虚拟节点(element) :通过
createElement把 JSX 转换成一个普通的 JS 对象。 - 构建 Fiber 树 :利用
performUnitOfWork一步步生成 Fiber 节点,并打上「更新」「新增」「删除」等标记。 - 提交 DOM:在空闲时间统一把 Fiber 树的变更提交到真实 DOM。
js
function createElement(type, props, ...children) {
return {
type,
props: {
...props,
children: children.map(child =>
typeof child === "object" ? child : createTextElement(child)
)
}
};
}
function createTextElement(text) {
return {
type: "TEXT_ELEMENT",
props: {
nodeValue: text,
children: []
}
};
}
function createDom(fiber) {
const dom =
fiber.type == "TEXT_ELEMENT"
? document.createTextNode("")
: document.createElement(fiber.type);
updateDom(dom, {}, fiber.props);
return dom;
}
const isEvent = key => key.startsWith("on");
const isProperty = key => key !== "children" && !isEvent(key);
const isNew = (prev, next) => key => prev[key] !== next[key];
const isGone = (prev, next) => key => !(key in next);
function updateDom(dom, prevProps, nextProps) {
//Remove old or changed event listeners
Object.keys(prevProps)
.filter(isEvent)
.filter(key => !(key in nextProps) || isNew(prevProps, nextProps)(key))
.forEach(name => {
const eventType = name.toLowerCase().substring(2);
dom.removeEventListener(eventType, prevProps[name]);
});
// Remove old properties
Object.keys(prevProps)
.filter(isProperty)
.filter(isGone(prevProps, nextProps))
.forEach(name => {
dom[name] = "";
});
// Set new or changed properties
Object.keys(nextProps)
.filter(isProperty)
.filter(isNew(prevProps, nextProps))
.forEach(name => {
dom[name] = nextProps[name];
});
// Add event listeners
Object.keys(nextProps)
.filter(isEvent)
.filter(isNew(prevProps, nextProps))
.forEach(name => {
const eventType = name.toLowerCase().substring(2);
dom.addEventListener(eventType, nextProps[name]);
});
}
function commitRoot() {
deletions.forEach(commitWork);
commitWork(wipRoot.child);
currentRoot = wipRoot;
wipRoot = null;
}
function commitWork(fiber) {
if (!fiber) {
return;
}
let domParentFiber = fiber.parent;
while (!domParentFiber.dom) {
domParentFiber = domParentFiber.parent;
}
const domParent = domParentFiber.dom;
if (fiber.effectTag === "PLACEMENT" && fiber.dom != null) {
domParent.appendChild(fiber.dom);
} else if (fiber.effectTag === "UPDATE" && fiber.dom != null) {
updateDom(fiber.dom, fiber.alternate.props, fiber.props);
} else if (fiber.effectTag === "DELETION") {
commitDeletion(fiber, domParent);
}
commitWork(fiber.child);
commitWork(fiber.sibling);
}
function commitDeletion(fiber, domParent) {
if (fiber.dom) {
domParent.removeChild(fiber.dom);
} else {
commitDeletion(fiber.child, domParent);
}
}
function render(element, container) {
wipRoot = {
dom: container,
props: {
children: [element]
},
alternate: currentRoot
};
deletions = [];
nextUnitOfWork = wipRoot;
}
let nextUnitOfWork = null;
let currentRoot = null;
let wipRoot = null;
let deletions = null;
function workLoop(deadline) {
let shouldYield = false;
while (nextUnitOfWork && !shouldYield) {
nextUnitOfWork = performUnitOfWork(nextUnitOfWork);
shouldYield = deadline.timeRemaining() < 1;
}
if (!nextUnitOfWork && wipRoot) {
commitRoot();
}
requestIdleCallback(workLoop);
}
requestIdleCallback(workLoop);
function performUnitOfWork(fiber) {
const isFunctionComponent = fiber.type instanceof Function;
if (isFunctionComponent) {
updateFunctionComponent(fiber);
} else {
updateHostComponent(fiber);
}
if (fiber.child) {
return fiber.child;
}
let nextFiber = fiber;
while (nextFiber) {
if (nextFiber.sibling) {
return nextFiber.sibling;
}
nextFiber = nextFiber.parent;
}
}
let wipFiber = null;
let hookIndex = null;
function updateFunctionComponent(fiber) {
wipFiber = fiber;
hookIndex = 0;
wipFiber.hooks = [];
const children = [fiber.type(fiber.props)];
reconcileChildren(fiber, children);
}
function useState(initial) {
const oldHook =
wipFiber.alternate &&
wipFiber.alternate.hooks &&
wipFiber.alternate.hooks[hookIndex];
const hook = {
state: oldHook ? oldHook.state : initial,
queue: []
};
const actions = oldHook ? oldHook.queue : [];
actions.forEach(action => {
hook.state = action(hook.state);
});
const setState = action => {
hook.queue.push(action);
wipRoot = {
dom: currentRoot.dom,
props: currentRoot.props,
alternate: currentRoot
};
nextUnitOfWork = wipRoot;
deletions = [];
};
wipFiber.hooks.push(hook);
hookIndex++;
return [hook.state, setState];
}
function updateHostComponent(fiber) {
if (!fiber.dom) {
fiber.dom = createDom(fiber);
}
reconcileChildren(fiber, fiber.props.children);
}
function reconcileChildren(wipFiber, elements) {
let index = 0;
let oldFiber = wipFiber.alternate && wipFiber.alternate.child;
let prevSibling = null;
while (index < elements.length || oldFiber != null) {
const element = elements[index];
let newFiber = null;
const sameType = oldFiber && element && element.type == oldFiber.type;
if (sameType) {
newFiber = {
type: oldFiber.type,
props: element.props,
dom: oldFiber.dom,
parent: wipFiber,
alternate: oldFiber,
effectTag: "UPDATE"
};
}
if (element && !sameType) {
newFiber = {
type: element.type,
props: element.props,
dom: null,
parent: wipFiber,
alternate: null,
effectTag: "PLACEMENT"
};
}
if (oldFiber && !sameType) {
oldFiber.effectTag = "DELETION";
deletions.push(oldFiber);
}
if (oldFiber) {
oldFiber = oldFiber.sibling;
}
if (index === 0) {
wipFiber.child = newFiber;
} else if (element) {
prevSibling.sibling = newFiber;
}
prevSibling = newFiber;
index++;
}
}
const Didact = {
createElement,
render,
useState
};
/** @jsx Didact.createElement */
function Counter() {
const [state, setState] = Didact.useState(1);
return (
<h1 onClick={() => setState(c => c + 1)} style="user-select: none">
Count: {state}
</h1>
);
}
const element = <Counter />;
const container = document.getElementById("root");
Didact.render(element, container);render
这里函数执行的入口就是Didact.render
- 创建一个wipRoot Fiber节点
- wipRoot.child = null,准备为其创建子树
- nextUnitOfWork = wipRoot,为后续做准备
js
function render(element, container) {
wipRoot = {
dom: container,
props: {
children: [element]
},
alternate: currentRoot
};
deletions = [];
nextUnitOfWork = wipRoot;
}执行入口
这里利用requestIdleCallback来利用浏览器的空闲时间来执行
js
requestIdleCallback(workLoop);workLoop
调用workLoop函数来开始
- 利用
performUnitOfWork构建整个fiber树 - 构建完之后就把fiber树提交给
commitRoot
js
function workLoop(deadline) {
let shouldYield = false;
while (nextUnitOfWork && !shouldYield) {
nextUnitOfWork = performUnitOfWork(nextUnitOfWork);
shouldYield = deadline.timeRemaining() < 1; // 空闲时间不足就让出
}
if (!nextUnitOfWork && wipRoot) {
// 整个 fiber 树构建完成后,统一提交到 DOM
commitRoot();
}
requestIdleCallback(workLoop);
}performUnitOfWork
这里首先判断是函数组件还是普通的元素
- 函数组件:调用
updateFunctionComponent,执行函数、生成子元素 - 普通元素:调用
updateHostComponent,创建DOM节点、生成子元素
这里殊路同归,都是调用reconcileChildren函数,来对节点进行标记
- UPDATE:需要更新的元素
- PLACEMENT:插入新节点
- DELETION:需要删除的旧节点
最后都是构建完fiber树
js
function performUnitOfWork(fiber) {
const isFunctionComponent = fiber.type instanceof Function;
if (isFunctionComponent) {
updateFunctionComponent(fiber);
} else {
updateHostComponent(fiber);
}
// 深度优先遍历
if (fiber.child) return fiber.child;
let nextFiber = fiber;
while (nextFiber) {
if (nextFiber.sibling) return nextFiber.sibling;
nextFiber = nextFiber.parent;
}
}commitRoot
上面构建完fiber树之后,然后通过commitRoot函数来提交,构成真实的DOM
通过上面的标记
- 首先来进行删除操作
- 再来从fiber的child开始,递归的进行替换
PLACEMENT还有更新UPDATE操作 - 保存fiber树到currentRoot,以便下一次使用
- 清空wipRoot
deletions.forEach(commitWork)是先执行删除,再执行添加/更新,这样保证不会出现「残留旧节点」的问题
js
function commitRoot() {
deletions.forEach(commitWork);
commitWork(wipRoot.child);
currentRoot = wipRoot;
wipRoot = null;
}commitWork
- 从根 fiber 的第一个 child 开始,把 fiber 树一层一层地提交到真实 DOM。
commitWork会检查 fiber 的effectTag:PLACEMENT→ 插入新节点UPDATE→ 更新已有节点DELETION→ 删除节点
这一步才是真正的「渲染到页面」,也是 React 的 commit 阶段。
js
function commitWork(fiber) {
if (!fiber) {
return;
}
let domParentFiber = fiber.parent;
while (!domParentFiber.dom) {
domParentFiber = domParentFiber.parent;
}
const domParent = domParentFiber.dom;
if (fiber.effectTag === "PLACEMENT" && fiber.dom != null) {
domParent.appendChild(fiber.dom);
} else if (fiber.effectTag === "UPDATE" && fiber.dom != null) {
updateDom(fiber.dom, fiber.alternate.props, fiber.props);
} else if (fiber.effectTag === "DELETION") {
commitDeletion(fiber, domParent);
}
commitWork(fiber.child);
commitWork(fiber.sibling);
}总结
以上就是整个React的执行原理了
JSX 会先被转换成 JS 对象(element),再一步步构建 Fiber 树。在浏览器空闲时,React 调和 Fiber 节点并打上标记,最后统一提交到真实 DOM。