《Java零基础教学》是一套深入浅出的 Java 编程入门教程。全套教程从Java基础语法开始,适合初学者快速入门,同时也从实例的角度进行了深入浅出的讲解,让初学者能够更好地理解Java编程思想和应用。
本教程内容包括数据类型与运算、流程控制、数组、函数、面向对象基础、字符串、集合、异常处理、IO 流及多线程等 Java 编程基础知识,并提供丰富的实例和练习,帮助读者巩固所学知识。本教程不仅适合初学者学习,也适合已经掌握一定 Java 基础的读者进行查漏补缺。
前言
在当今实战Java开发中,输入输出(I/O)操作 是非常常见的开发需求。无论是读取文件、写入文件,还是与用户交互,I/O操作都扮演着至关重要的角色。理解Java中I/O操作的基本概念和使用方法,不仅能够帮助你高效地处理文件,还能提升代码的可读性和性能。
在这篇文章中,我将带大家一起深入学习Java中的基本输入输出(I/O)操作,特别是如何处理文件的读写操作,并结合实际开发中的常见场景,帮助大家掌握文件处理的最佳实践,我相信,屏幕前的你读了本期内容,一定会学到点东西。
1. Java I/O概述
首先,我们都知道,Java它本身就提供了一套强大的I/O系统,支持多种数据输入和输出的操作。Java的I/O操作主要通过两大类来实现:
- 字节流(Byte Stream):用于处理原始二进制数据,适合处理所有类型的I/O,包括图像、音频等。
- 字符流(Character Stream):用于处理文本数据,适合处理字符和字符串。
Java的I/O操作主要通过java.io包中的各种类来实现。常用的类包括File、InputStream、OutputStream、Reader、Writer等。
1.1 字节流和字符流的区别
- 字节流 :处理8位字节数据,适用于所有I/O类型(包括文本和二进制数据)。
InputStream和OutputStream是字节流的基类。 - 字符流 :处理16位Unicode字符,专门用于处理文本文件。
Reader和Writer是字符流的基类。
2. 文件处理:如何读取和写入文件?
2.1 使用File类操作文件
File类是Java中用于表示文件和目录的类。它允许我们检查文件的属性、创建文件、删除文件、重命名文件等操作。File类并不用于文件的内容操作,而是用于文件的管理。
常见操作:
- 创建文件或目录
- 删除文件或目录
- 获取文件属性(如大小、路径等)
示例:使用File类操作文件
接着,我给大家展示下,结合理论与实战给大家把知识点讲透,案例代码如下:
java
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个File对象,表示一个文件
File file = new File("example.txt");
try {
// 创建文件
if (file.createNewFile()) {
System.out.println("File created: " + file.getName());
} else {
System.out.println("File already exists.");
}
// 获取文件的路径和大小
System.out.println("File path: " + file.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("File size: " + file.length() + " bytes");
// 删除文件
if (file.delete()) {
System.out.println("File deleted: " + file.getName());
} else {
System.out.println("Failed to delete the file.");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("An error occurred.");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}根据如上案例,本地实际结果运行展示如下,仅供参考:
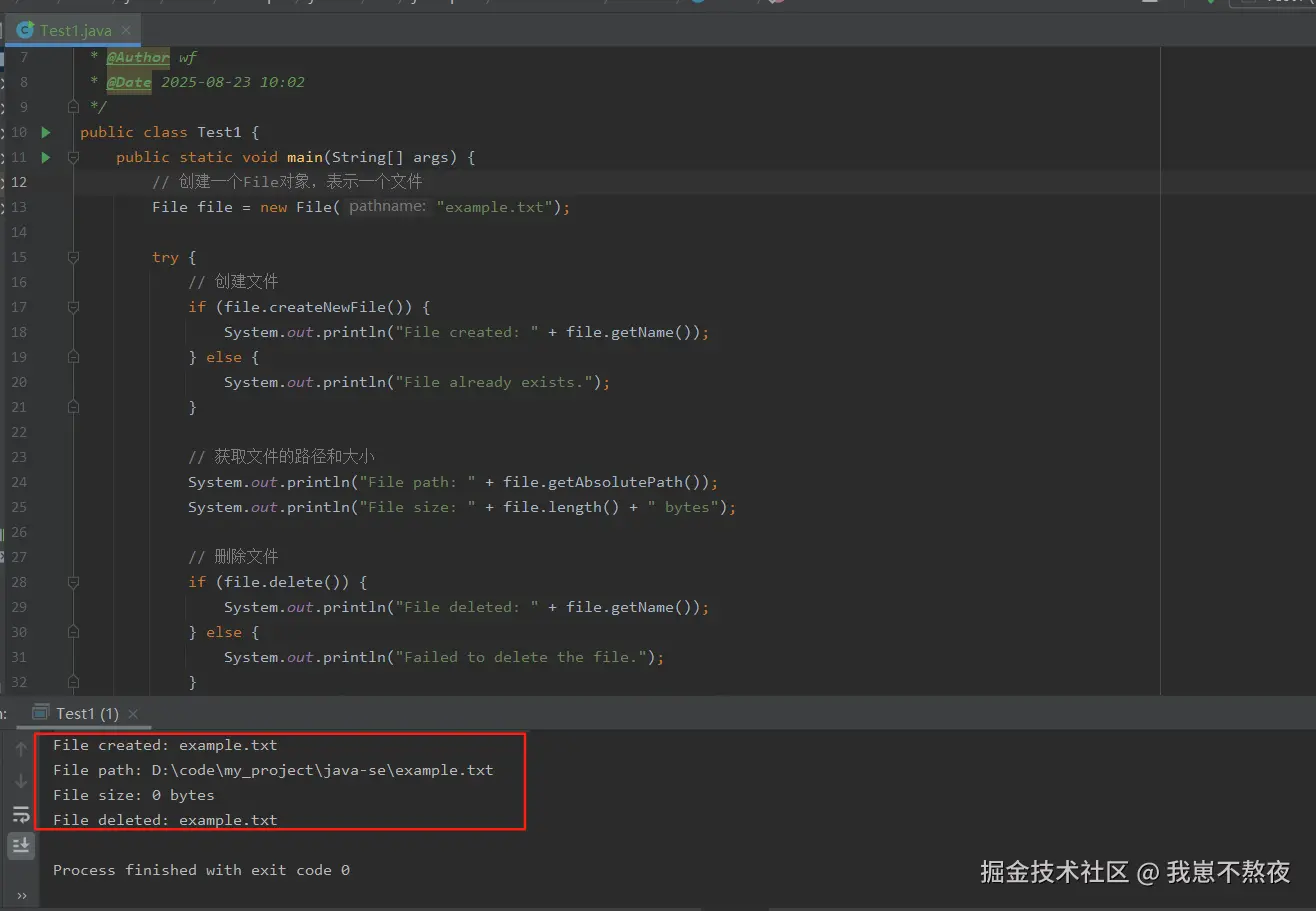
解释:
createNewFile():尝试创建一个新文件,如果文件已经存在,则返回false。getAbsolutePath():返回文件的绝对路径。length():返回文件的大小,以字节为单位。delete():删除文件,如果文件删除成功返回true。
2.2 字节流处理文件(InputStream 和 OutputStream)
读取文件:FileInputStream
FileInputStream是字节流类,用于读取文件中的字节。它适合用于读取二进制数据,或处理文本文件时按字节读取。
接着,我给大家展示下,结合理论与实战给大家把知识点讲透,案例代码如下:
java
/**
* @Author wf
* @Date 2025-08-23 10:02
*/
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("example.txt")) {
int byteData;
while ((byteData = fileInputStream.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) byteData); // 将字节转换为字符并输出
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("An error occurred while reading the file.");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}根据如上案例,本地实际结果运行展示如下,仅供参考:
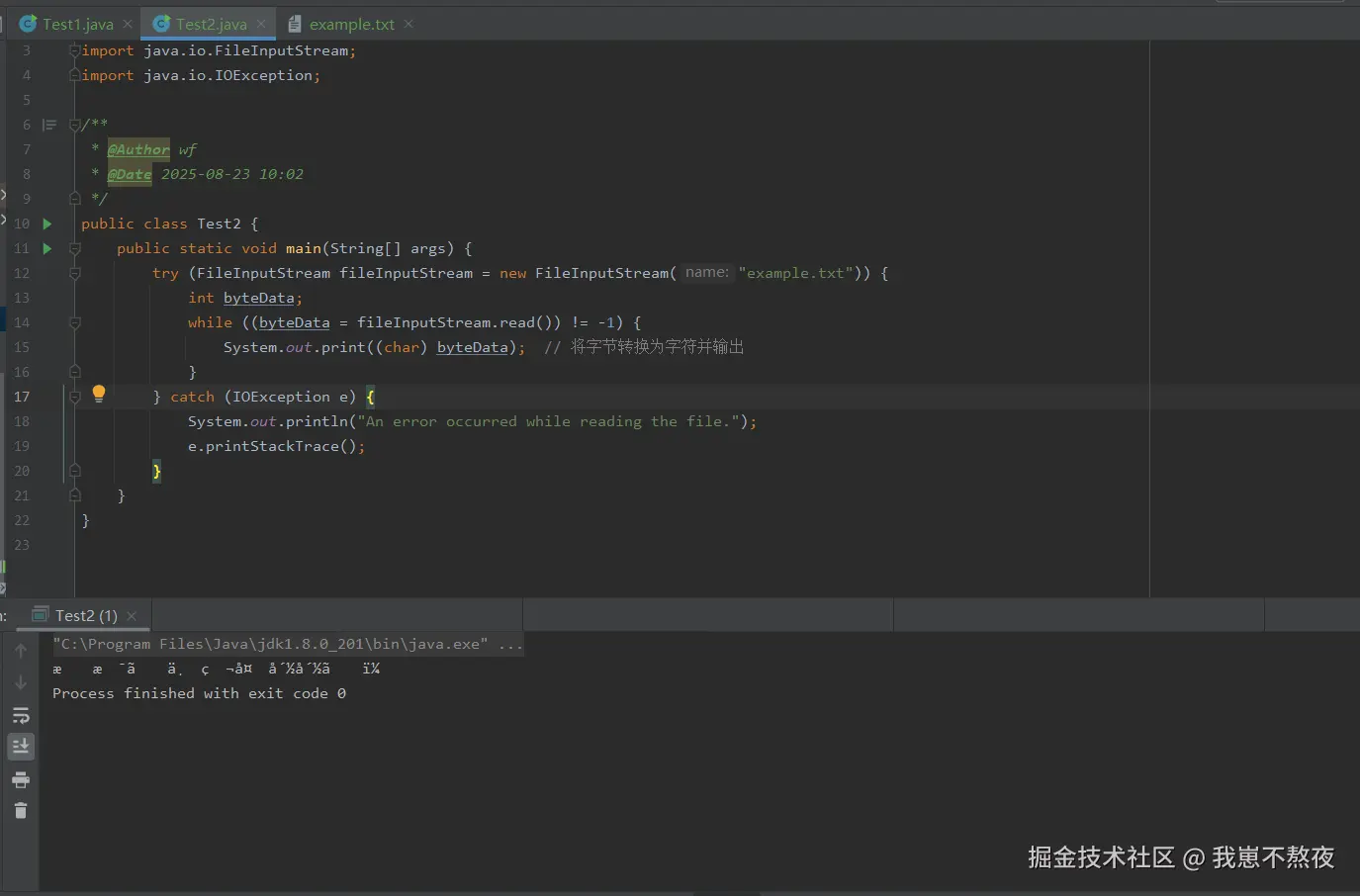
写入文件:FileOutputStream
FileOutputStream是字节流类,用于写入文件中的字节。它适合用于写入二进制数据或文本数据。
接着,我给大家展示下,结合理论与实战给大家把知识点讲透,案例代码如下:
java
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @Author wf
* @Date 2025-08-23 10:02
*/
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("output.txt")) {
String content = "Hello, this is a test file.";
byte[] contentBytes = content.getBytes(); // 将字符串转换为字节数组
fileOutputStream.write(contentBytes);
System.out.println("File written successfully.");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("An error occurred while writing the file.");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}根据如上案例,本地实际结果运行展示如下,仅供参考:
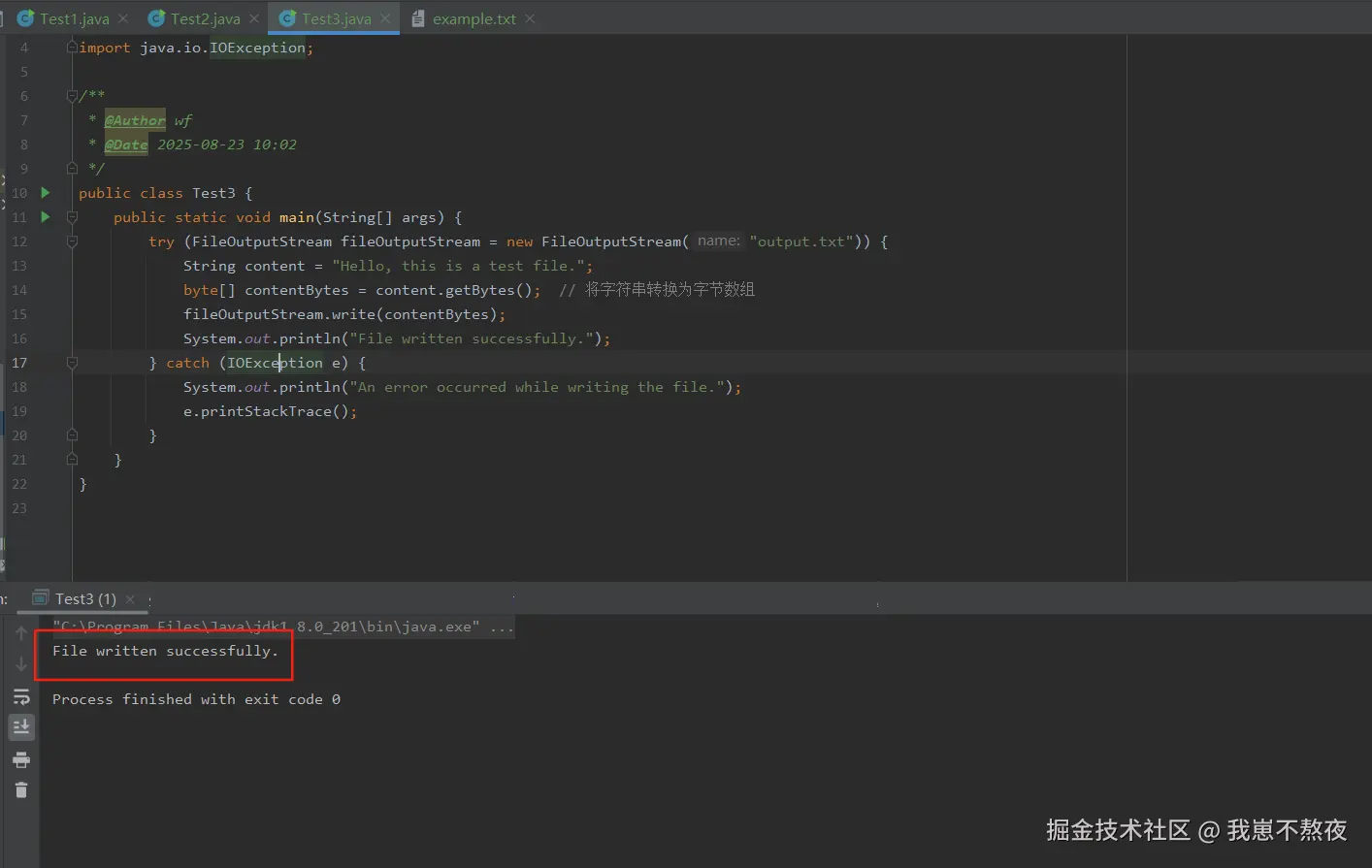
解释:
FileInputStream和FileOutputStream是用于处理字节数据的流类,适合于处理二进制数据或文本数据的原始字节表示。read()方法:按字节读取数据,直到文件结束(-1)。write()方法:将字节数据写入文件。
2.3 字符流处理文件(Reader 和 Writer)
读取文件:FileReader
FileReader是字符流类,用于读取文件中的字符数据。它适合用于读取文本文件,自动进行字符编码的转换。
接着,我给大家展示下,结合理论与实战给大家把知识点讲透,案例代码如下:
java
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileReaderExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (FileReader fileReader = new FileReader("example.txt")) {
int charData;
while ((charData = fileReader.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) charData); // 输出字符
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("An error occurred while reading the file.");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}写入文件:FileWriter
FileWriter是字符流类,用于将字符数据写入文件。它适合用于处理文本文件,自动进行字符编码转换。
接着,我给大家展示下,结合理论与实战给大家把知识点讲透,案例代码如下:
java
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileWriterExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter("output.txt")) {
String content = "Hello, this is a text file using FileWriter.";
fileWriter.write(content);
System.out.println("File written successfully.");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("An error occurred while writing the file.");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}解释:
FileReader和FileWriter是字符流类,适合于处理文本数据。read()方法:按字符读取数据。write()方法:将字符数据写入文件。
3. 高级文件操作:缓冲流与文件拷贝
3.1 缓冲流(BufferedReader 和 BufferedWriter)
缓冲流可以提高I/O操作的效率。它通过缓冲区缓存数据,减少了与硬盘的交互次数,从而提高了读写效率。
使用BufferedReader读取文本文件
接着,我给大家展示下,结合理论与实战给大家把知识点讲透,案例代码如下:
java
/**
* @Author wf
* @Date 2025-08-23 10:02
*/
public class Test6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("example.txt"))) {
String line;
while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("An error occurred while reading the file.");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}根据如上案例,本地实际结果运行展示如下,仅供参考:
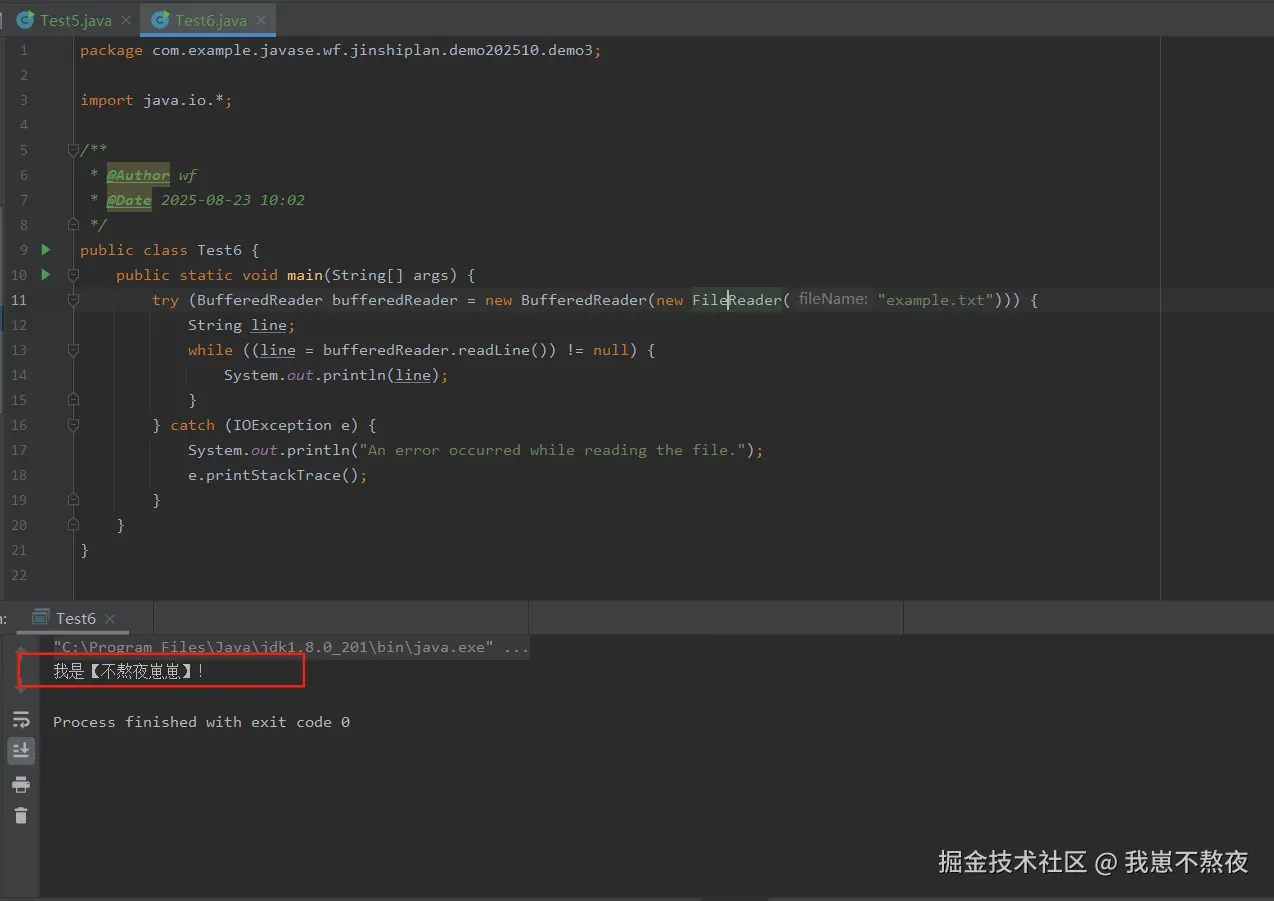
使用BufferedWriter写入文本文件
接着,我给大家展示下,结合理论与实战给大家把知识点讲透,案例代码如下:
java
/**
* @Author wf
* @Date 2025-08-23 10:02
*/
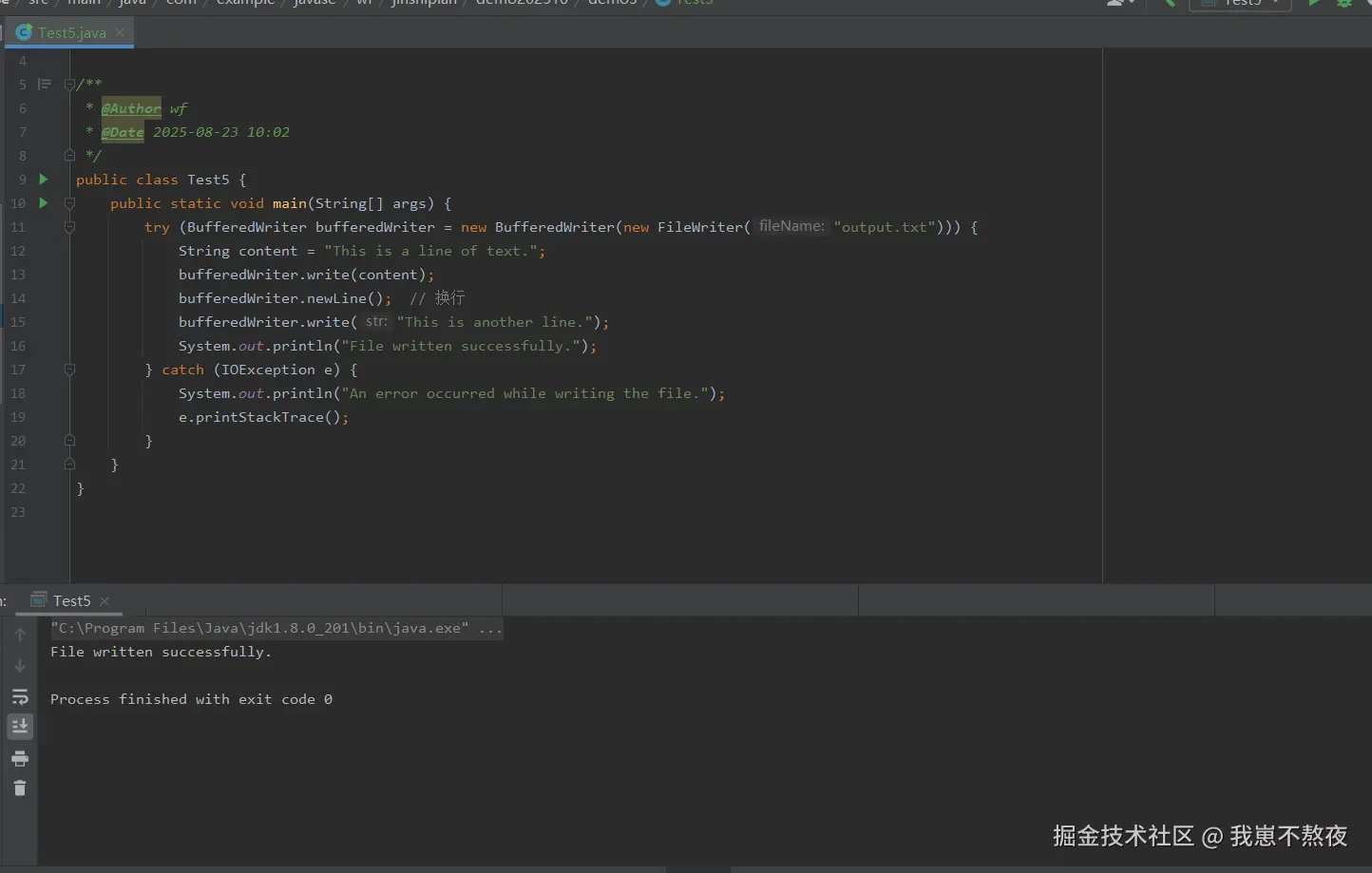
public class Test5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("output.txt"))) {
String content = "This is a line of text.";
bufferedWriter.write(content);
bufferedWriter.newLine(); // 换行
bufferedWriter.write("This is another line.");
System.out.println("File written successfully.");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("An error occurred while writing the file.");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}根据如上案例,本地实际结果运行展示如下,仅供参考:
3.2 文件拷贝
通过缓冲流可以实现高效的文件拷贝操作。接着,我给大家展示下,结合理论与实战给大家把知识点讲透,案例代码如下:
java
/**
* @Author wf
* @Date 2025-08-23 10:02
*/
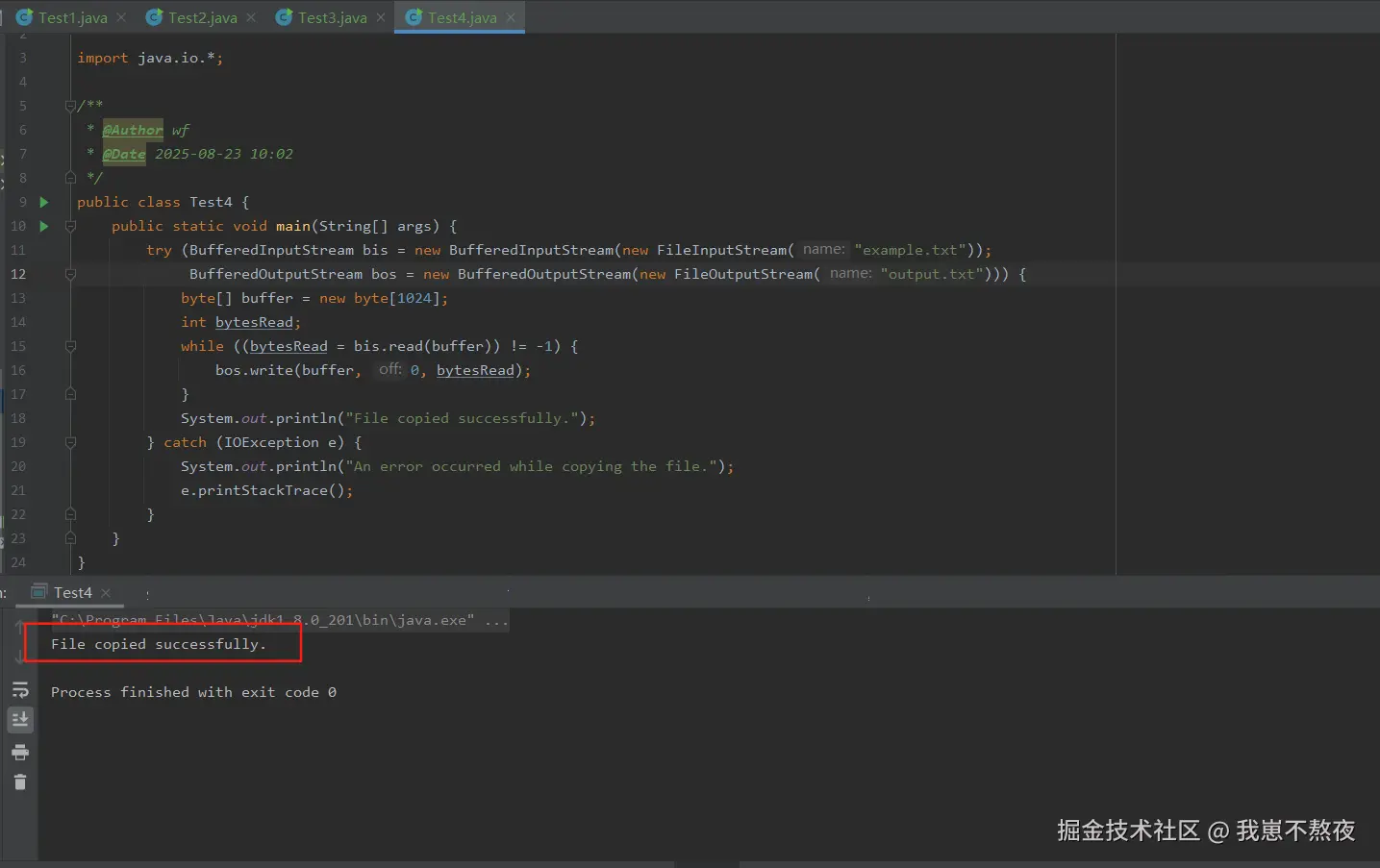
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("example.txt"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("output.txt"))) {
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int bytesRead;
while ((bytesRead = bis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
bos.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
System.out.println("File copied successfully.");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("An error occurred while copying the file.");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}根据如上案例,本地实际结果运行展示如下,仅供参考:
解释:
- 缓冲流 :通过
BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream对数据进行缓冲,提高文件读写的效率。 - 文件拷贝:通过缓冲区读取源文件并写入目标文件,减少了直接读写硬盘的次数,从而提高了性能。
4. 总结:如何处理文件?
总言之,Java它本身的文件处理提供了丰富的API,包括字节流、字符流、缓冲流等。合理选择和使用这些工具能够让你高效地进行文件的读取、写入和管理。
- 字节流(
InputStream和OutputStream):适用于二进制数据的读取和写入,适合处理图像、音频等文件。 - 字符流(
Reader和Writer):适用于文本数据的读取和写入,处理字符和字符串时使用。 - 缓冲流(
BufferedReader和BufferedWriter):提高读写效率,减少I/O操作的次数。 File类:用于文件的创建、删除、路径操作等管理工作。
最后,我想说,通过合理的I/O操作,你可以轻松处理文件的输入输出任务,并在开发中优化性能和资源使用,这点对于初学者而已,是非常重要的,在日常开发中,是非常有帮助的。
最后
大家如果觉得看了本文有帮助的话,麻烦给不熬夜崽崽点个三连(点赞、收藏、关注)支持一下哈,大家的支持就是我写作的无限动力。