本项目将采用PyTorch深度学习方法搭建一个垃圾分类识别的训练和测试系统,以实现智能化垃圾分类。
一、获取垃圾分类数据集
数据集获取的途径大概有三种:第一种是将需求提交给数据标注团队,花钱标注数据;第二种是爬取各大网站的图片数据,然后使用自己的接口清洗或者人工标注;第三种是翻论文,找公开数据集,到AI比赛网站或者AI开放平台碰碰运气,看看是否有公开垃圾图片数据集。
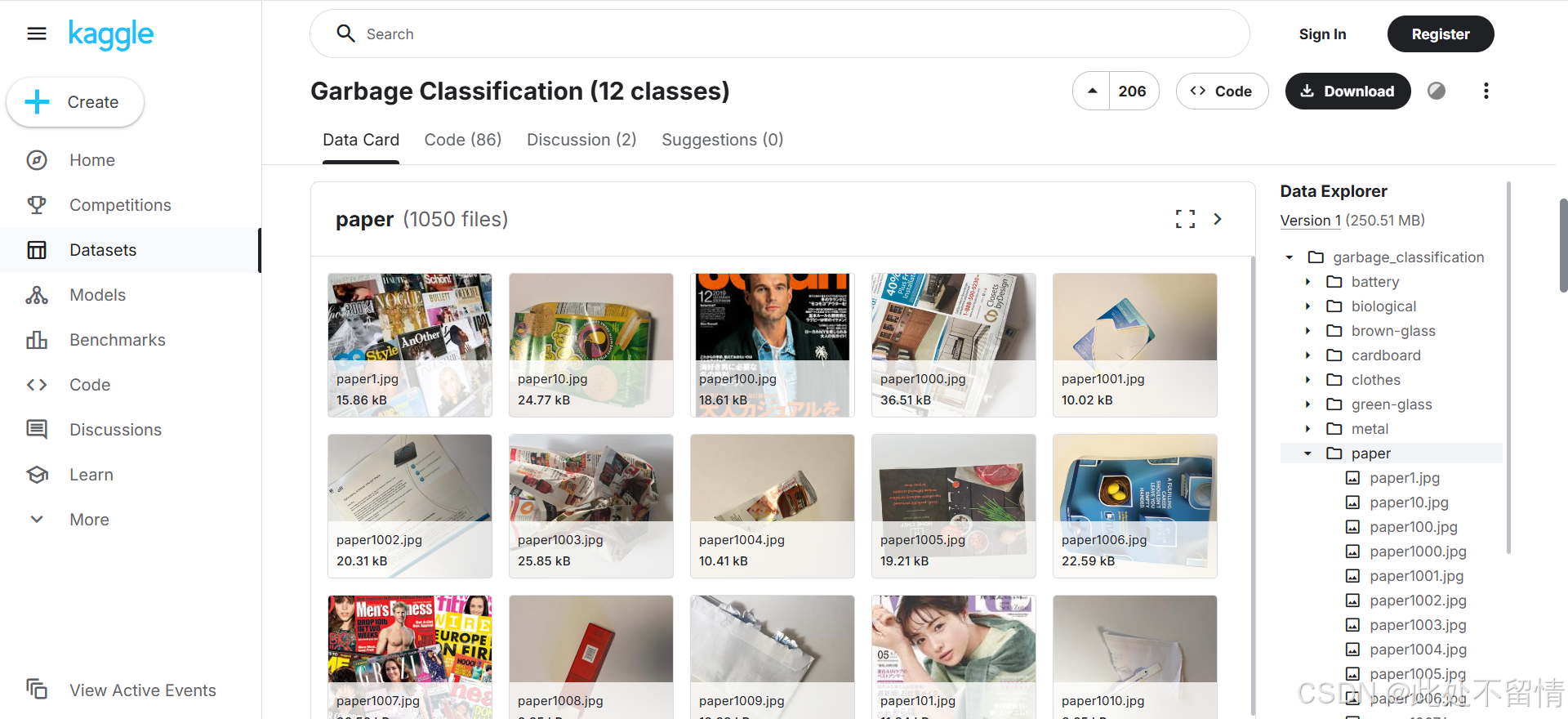
本项目采用的数据集是:Garbage Classification (12 classes)
这个数据集有15 150幅图片,来自12种不同类别的家庭垃圾:纸张、纸板、生物、金属、塑料、绿色玻璃、棕色玻璃、白色玻璃、衣服、鞋子、电池和垃圾。
二、使用的模型介绍
MnasNet模型:MnasNet(Mobile Neural Architecture Search Network)是一种通过搜索得到的高效卷积神经网络,最早由Google提出。MnasNet的主要特点是在保证模型的高性能的同时,尽量降低计算复杂度和参数数量,适用于移动设备等资源有限的场景。
三、分类模型训练代码
python
import numpy as np # 数值计算库
import os # 操作系统接口
import pickle # Python对象序列化
import torch # PyTorch深度学习框架
import torch.optim as optim # 优化算法模块
import torch.nn as nn # 神经网络模块
import torch.nn.functional as F # 神经网络函数模块
from torchvision import transforms, datasets # 计算机视觉工具包
import torchvision # PyTorch视觉库
from tqdm import tqdm # 进度条显示
# 定义超参数和路径
epochs = 10 # 训练轮数
lr = 0.03 # 学习率
batch_size = 32 # 批处理大小
image_path = './garbage_data/data' # 图像数据路径
save_path = './garbage_chk/best_model.pkl' # 模型保存路径
# 设置设备(GPU或CPU)
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
# 1. 数据转换
data_transform = {
# 训练中的数据增强和归一化
'train': transforms.Compose([ # 组合多种图像变换
transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224), # 随机裁剪并调整到224x224
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), # 随机水平翻转
transforms.ToTensor(), # 转换为Tensor格式
transforms.Normalize((0.485, 0.456, 0.406), (0.229, 0.224, 0.225)), # 归一化
]),
}
# 2. 加载数据
# 创建图像数据集,指定根目录和数据变换
train_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=os.path.join(image_path), transform=data_transform['train'])
# 3. 形成迭代器
# 创建数据加载器,用于批量处理数据
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=32, shuffle=True)
print('using{}images to train'.format(len(train_dataset))) # 打印训练图像数量
# 4. 建立分类标签与索引的关系
cloth_list = train_dataset.class_to_idx # 获取类别到索引的映射
class_dict = {} # 创建反向映射字典
for key, val in cloth_list.items(): # 遍历映射关系
class_dict[val] = key # 索引作为键,类别名作为值
# 将类别字典保存到文件
with open('class_dict.pk', 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(class_dict, f)
# 自定义损失函数,需要在forward()方法中定义
class LossWithLogits(nn.Module): # 继承nn.Module类
def __init__(self):
super(LossWithLogits, self).__init__() # 调用父类构造函数
# 参数为传入的预测值和真实值,返回所有样本的损失值
def forward(self, pred, label): # 前向传播函数
exp = torch.exp(pred) # 计算指数
tmp1 = exp.gather(1, label.unsqueeze(-1)).squeeze() # 获取正确类别的指数值
tmp2 = exp.sum(1) # 计算所有类别的指数和
softmax = tmp1 / tmp2 # 计算softmax概率
log = -torch.log(softmax) # 计算负对数似然
return log.mean() # 返回平均损失
# 5. 加载预训练好的MnasNet模型
# 使用预训练的MNASNet模型
model = torchvision.models.mnasnet1_0(weights=torchvision.models.MNASNet1_0_Weights.IMAGENET1K_V1)
# 冻结模型参数(不进行梯度更新)
for param in model.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
# 修改最后一层的全连接层,适应12个分类任务
model.classifier[1] = nn.Linear(model.classifier[1].in_features, 12)
# 将模型加载到CPU中
model = model.to('cpu')
# 使用自定义的损失函数
criterion = LossWithLogits()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.01) # 定义优化器
# 6. 训练模型
best_acc = 0 # 保存最佳准确率
best_model = None # 保存最佳模型
# 开始训练循环
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train() # 设置模型为训练模式
running_loss = 0 # 训练损失累计
epoch_acc = 0 # 训练准确率
epoch_acc_count = 0 # 正确预测计数
train_count = 0 # 训练数据总数
train_bar = tqdm(train_loader) # 创建进度条
# 遍历训练数据
for data in train_bar:
images, labels = data # 获取图像和标签
optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度清零
outputs = model(images.to(device)) # 模型前向传播
loss = criterion(outputs, labels.to(device)) # 计算损失
loss.backward() # 反向传播
optimizer.step() # 更新参数
running_loss += loss.item() # 累计损失
# 更新进度条描述
train_bar.desc = "trian epoch[{}/{}] loss:{:.3f}".format(epoch + 1, epochs, running_loss / train_count)
# 计算每个epoch正确的个数
epoch_acc_count += (outputs.argmax(axis=1) == labels.view(-1)).sum() # 统计正确预测数
train_count += len(images) # 累计训练数据数量
# 每个epoch对应的准确率
epoch_acc = epoch_acc_count / train_count
# 打印训练信息
print("【EPOCH:】%s" % str(epoch + 1))
print("训练损失为%s" % str(running_loss))
print("训练精度为%s" % str(epoch_acc.item() * 100)[:5] + '%')
# 保存最佳模型
if epoch_acc > best_acc:
best_acc = epoch_acc
best_model = model.state_dict()
# 在训练结束保存最优的模型参数
if epoch == epochs - 1: # 最后一次保存模型参数
torch.save(best_model, save_path)
print("训练结束")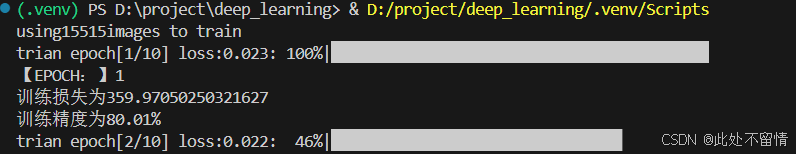
四、模型预测代码
import os
import pickle
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import torch
from torchvision import transforms
from PIL import Image
import torchvision
import torch.nn.functional as F # 神经网络函数模块
def load_model(model_path, class_dict_path):
"""
加载训练好的模型和类别字典
"""
# 创建模型架构
model = torchvision.models.mnasnet1_0()
model.classifier[1] = torch.nn.Linear(model.classifier[1].in_features, 12)
# 加载模型权重
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path, map_location=torch.device('cpu')))
model.eval()
# 加载类别字典
with open(class_dict_path, 'rb') as f:
class_dict = pickle.load(f)
return model, class_dict
def get_transform():
"""
定义测试时的图像预处理流程
"""
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(256), # 调整图像大小
transforms.CenterCrop(224), # 中心裁剪
transforms.ToTensor(), # 转换为Tensor
transforms.Normalize((0.485, 0.456, 0.406), (0.229, 0.224, 0.225)) # 归一化
])
return transform
def predict_image(image_path, model, class_dict, transform):
"""
对单张图像进行预测
参数:
image_path: 图像文件路径
model: 加载的模型
class_dict: 类别索引到名称的映射字典
transform: 图像预处理转换
返回:
predicted_class: 预测的类别名称
confidence: 预测置信度
"""
# 加载并预处理图像
image = Image.open(image_path).convert('RGB')
image_tensor = transform(image).unsqueeze(0) # 添加批次维度
# 执行预测
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(image_tensor)
probabilities = F.softmax(outputs, dim=1)
confidence, predicted_idx = torch.max(probabilities, dim=1)
# 获取类别名称
predicted_class = class_dict[predicted_idx.item()]
confidence = confidence.item()
return predicted_class, confidence
model_path = 'best_model.pkl'
class_dict_path = 'class_dict.pk'
model, class_dict = load_model(model_path, class_dict_path)
transform = get_transform()
# 单张图像预测示例
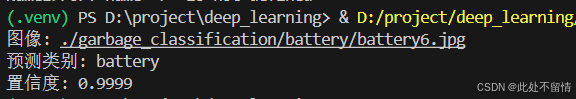
single_image_path = './garbage_classification/battery/battery6.jpg'
if os.path.exists(single_image_path):
predicted_class, confidence = predict_image(single_image_path, model, class_dict, transform)
print(f"图像: {single_image_path}")
print(f"预测类别: {predicted_class}")
print(f"置信度: {confidence:.4f}")