文章目录
- 四、创建方式
-
- [4.1 Mono创建](#4.1 Mono创建)
- [4.2 Flux创建](#4.2 Flux创建)
- 五、操作符
-
- [5.1 转换操作符](#5.1 转换操作符)
-
- [5.1.1 map-同步转换](#5.1.1 map-同步转换)
- [5.1.2 flatMap-异步转换(一对多、无序合并)](#5.1.2 flatMap-异步转换(一对多、无序合并))
- [5.1.3 concatMap-保持顺序的flatMap(有序合并)](#5.1.3 concatMap-保持顺序的flatMap(有序合并))
- [5.1.4 switchMap](#5.1.4 switchMap)
- [5.1.5 flatMapSequential()](#5.1.5 flatMapSequential())
- [5.1.6 handle()](#5.1.6 handle())
- [5.1.7 cost](#5.1.7 cost)
- [5.1.8 cast、ofType](#5.1.8 cast、ofType)
- [5.2 过滤操作符](#5.2 过滤操作符)
-
- [5.2.1 filter-基于条件过滤](#5.2.1 filter-基于条件过滤)
- [5.2.2 take-取前N个元素](#5.2.2 take-取前N个元素)
- [5.2.3 takeLast-取最后N个元素](#5.2.3 takeLast-取最后N个元素)
- [5.2.4 takeWhile -当条件为真的时候取元素](#5.2.4 takeWhile -当条件为真的时候取元素)
- 5.2.5-takeUntil-取元素直到条件为真
- [5.2.6 skip-跳过前N个元素](#5.2.6 skip-跳过前N个元素)
- [5.2.7 skipLast-跳过后N个元素](#5.2.7 skipLast-跳过后N个元素)
- [5.2.8 distinct-去重](#5.2.8 distinct-去重)
- [5.2.9 distinctUntilChanged - 去除连续重复](#5.2.9 distinctUntilChanged - 去除连续重复)
- [5.2.10 elementAt()](#5.2.10 elementAt())
- [5.2.11 ignoreElements()](#5.2.11 ignoreElements())
- [5.3 组合操作符](#5.3 组合操作符)
-
- [5.3.1 merge-按时间顺序合并多个流](#5.3.1 merge-按时间顺序合并多个流)
- [5.3.2 mergeWith](#5.3.2 mergeWith)
- [5.3.3 mergedSequential](#5.3.3 mergedSequential)
- [5.3.4 zip-将多个流的元素配对](#5.3.4 zip-将多个流的元素配对)
- [5.3.5 zipWith](#5.3.5 zipWith)
- [5.3.6 combineLatest](#5.3.6 combineLatest)
- [5.3.7 concat-顺序连接流](#5.3.7 concat-顺序连接流)
- [5.3.8 concatWith](#5.3.8 concatWith)
- [5.3.9 startWith-在流开始前添加元素](#5.3.9 startWith-在流开始前添加元素)
- [5.3.10 when-组合多个Mono](#5.3.10 when-组合多个Mono)
四、创建方式
4.1 Mono创建
java
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
public class MonoExamples {
// 创建空的 Mono
Mono<String> emptyMono = Mono.empty();
// 创建包含单个值的 Mono
Mono<String> monoWithValue = Mono.just("Hello Reactor");
// 从可能为 null 的值创建 Mono
String possiblyNull = Math.random() > 0.5 ? "Value" : null;
Mono<String> monoFromNullable = Mono.justOrEmpty(possiblyNull);
// 从 Callable 创建 Mono
Mono<String> monoFromCallable = Mono.fromCallable(() -> {
// 模拟耗时操作
Thread.sleep(100);
return "Result from callable";
});
// 从 Future 创建 Mono
Mono<String> monoFromFuture = Mono.fromFuture(() ->
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Result from future")
);
// 创建错误的 Mono
Mono<String> errorMono = Mono.error(new RuntimeException("Something went wrong"));
}4.2 Flux创建
java
import reactor.core.publisher.Flux;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class FluxExamples {
// 从多个值创建 Flux
Flux<String> fluxFromValues = Flux.just("Apple", "Banana", "Cherry");
// 从数组创建 Flux
String[] fruitsArray = {"Apple", "Banana", "Cherry"};
Flux<String> fluxFromArray = Flux.fromArray(fruitsArray);
// 从集合创建 Flux
List<String> fruitsList = Arrays.asList("Apple", "Banana", "Cherry");
Flux<String> fluxFromIterable = Flux.fromIterable(fruitsList);
// 创建数值范围的 Flux
Flux<Integer> numberRange = Flux.range(1, 10); // 1 到 10
// 创建间隔发布的 Flux
Flux<Long> intervalFlux = Flux.interval(Duration.ofSeconds(1))
.take(5); // 每秒发射一个值,最多5个
// 创建空的 Flux
Flux<String> emptyFlux = Flux.empty();
// 创建错误的 Flux
Flux<String> errorFlux = Flux.error(new RuntimeException("Flux error"));
// 使用 generate 创建 Flux(有状态)
Flux<Integer> generatedFlux = Flux.generate(
() -> 0, // 初始状态
(state, sink) -> {
if (state < 5) {
sink.next(state); // 发射状态值
return state + 1; // 新状态
} else {
sink.complete(); // 完成序列
return state; // 最终状态
}
}
);
// 使用 create 创建 Flux(更灵活)
Flux<String> createdFlux = Flux.create(sink -> {
// 模拟异步事件源
new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
sink.next("Event " + i);
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
sink.error(e);
}
}
sink.complete();
}).start();
});
}just()
just Apple Banana Cherry subscribe
fromArray
java
String[] array = {"A", "B", "C"};
Flux<String> flux = Flux.fromArray(array);fromArray A B C subscribe
fromIterable()
java
List<String> list = List.of("Red", "Green", "Blue");
Flux<String> flux = Flux.fromIterable(list);fromIterable Red Green Blue subscribe
range
java
Flux<Integer> flux = Flux.range(1, 5); // Emits 1, 2, 3, 4, 5range(1,5) 1 2 3 4 5 subscribe
empty()
java
Flux<String> flux = Flux.empty();complete empty subscribe
error
java
Flux<String> flux = Flux.error(new RuntimeException("Oops!"));error X onError subscribe
defer
- 为每个订阅者延迟创建
Flux。当订阅发生时,才会调用提供的Supplier来生成实际的Flux。
java
Flux<Long> flux = Flux.defer(() -> Flux.just(System.currentTimeMillis()));subscribe1 invokes subscribe2 invokes defer Supplier Flux1 subscribe1 Supplier Flux2 subscribe2
interval
- 描述: 创建一个按固定时间间隔发出递增
Long值的Flux(从 0 开始)。
java
Flux<Long> flux = Flux.interval(Duration.ofSeconds(1)); // Emits 0, 1, 2... every second1s 1s 1s ... interval 0 1 2 subscribe
五、操作符
5.1 转换操作符
5.1.1 map-同步转换
map是 "转换 "(将元素 T 变为 R),结果是Stream<R>,元素数量不变;
java
// map - 同步转换
Flux<Integer> squared = numbers.map(n -> n * n);
squared.subscribe(System.out::println); // 1, 4, 9, 16, 25
Flux<String> flux = Flux.just(1, 2, 3).map(i -> "Number: " + i);1 Number: 1 2 Number: 2 3 Number: 3 source map subscribe
5.1.2 flatMap-异步转换(一对多、无序合并)
flatMap是 "先转换后扁平化 "(将元素 T 变为Stream<R>,再合并所有子流),结果是Stream<R>,元素数量可能增加。- 描述: 将
Flux中的每个元素异步转换为一个新的Flux(或Mono),然后将这些内部Flux合并成一个单一的Flux。元素的顺序可能不被保留。
java
Flux.just(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
.flatMap(i -> Flux.just(i, i * 2))
.subscribe(System.out::println); // 1 1 2 4 3 6 ...
java
// 原始流:1, 2, 3(每个元素代表一个任务ID)
Flux<Integer> taskIds = Flux.range(1, 3);
// 使用flatMap:每个任务ID转换为一个子流(模拟异步处理,延迟随ID递增)
Flux<String> results = taskIds
.flatMap(taskId -> {
// 模拟异步处理:任务ID越大,处理时间越长(100ms, 200ms, 300ms)
return Flux.just("任务" + taskId + "结果")
.delayElements(Duration.ofMillis(taskId * 100)) // 异步延迟
.doOnNext(result -> System.out.println("子流处理完成: " + result));
});
// 订阅并输出结果
results.subscribe(
result -> System.out.println("最终接收: " + result),
error -> System.err.println("错误: " + error.getMessage()),
() -> System.out.println("所有处理完成")
);
// 等待所有异步任务完成
Thread.sleep(1000);
java
子流处理完成: 任务1结果
最终接收: 任务1结果
子流处理完成: 任务2结果
最终接收: 任务2结果
子流处理完成: 任务3结果
最终接收: 任务3结果
所有处理完成- 子流并发执行(任务 1、2、3 同时开始处理);
- 先完成的子流元素先输出(任务 1 最快,最先输出);
- 适合对顺序无要求的场景(如并行查询多个独立资源)。
java
Flux<String> flux = Flux.just("a", "b")
.flatMap(s -> Flux.just(s.toUpperCase(), s + s));
// Emits "A", "aa", "B", "bb" (顺序可能变化)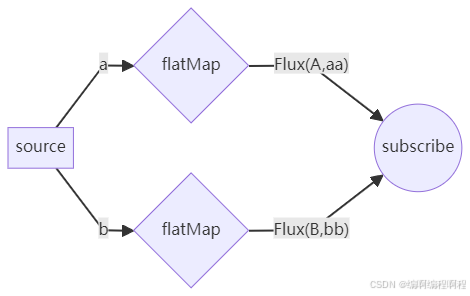
5.1.3 concatMap-保持顺序的flatMap(有序合并)
concatMap与flatMap的转换逻辑相同(将元素转为子流),但按输入顺序串行处理子流 :必须等前一个子流完全处理完成,才会开始处理下一个子流。因此,输出结果的顺序与输入顺序严格一致,但处理效率可能较低(无法并发)。
java
// 原始流:1, 2, 3(与flatMap示例相同)
Flux<Integer> taskIds = Flux.range(1, 3);
// 使用concatMap:按顺序处理子流(前一个完成才开始下一个)
Flux<String> results = taskIds
.concatMap(taskId -> {
// 同样模拟异步处理(延迟随ID递增)
return Flux.just("任务" + taskId + "结果")
.delayElements(Duration.ofMillis(taskId * 100))
.doOnNext(result -> System.out.println("子流处理完成: " + result));
});
// 订阅并输出结果
results.subscribe(
result -> System.out.println("最终接收: " + result),
error -> System.err.println("错误: " + error.getMessage()),
() -> System.out.println("所有处理完成")
);
// 等待所有任务完成
Thread.sleep(1000);
java
子流处理完成: 任务1结果
最终接收: 任务1结果
子流处理完成: 任务2结果
最终接收: 任务2结果
子流处理完成: 任务3结果
最终接收: 任务3结果
所有处理完成- 子流串行执行(任务 1 完成后才开始任务 2,任务 2 完成后才开始任务 3);
- 输出顺序与输入顺序完全一致;
- 适合对顺序有严格要求的场景(如按序处理消息队列中的消息)
描述: 类似于 flatMap,但它会按照原始元素的顺序连接内部 Flux。前一个内部 Flux 完成后,才会订阅下一个。
java
Flux<String> flux = Flux.just("a", "b")
.concatMap(s -> Flux.just(s.toUpperCase(), s + s)
.delayElements(Duration.ofMillis(100)));
// Emits "A", "aa", "B", "bb" (按顺序)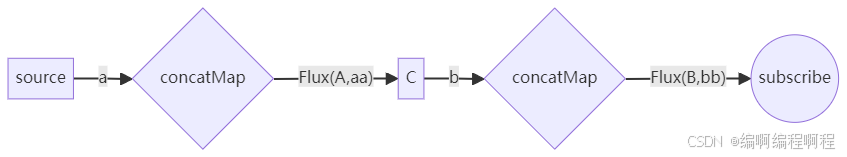
5.1.4 switchMap
在 Reactor 中,switchMap是一个强大的转换操作符,它的核心特性是在新元素到达时取消前一个未完成的子流,只保留最新的子流结果。这种 "切换" 特性使其在处理动态变化的数据源(如用户输入、状态更新)时特别有用。
| 关键特性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 转换逻辑 | 将元素T转换为子流Publisher<R>,与flatMap类似 |
| 子流处理 | 当新元素到达时,立即取消当前正在处理的子流,只处理最新的子流 |
| 输出顺序 | 只输出最新子流的结果,旧子流的结果会被丢弃 |
| 适用场景 | 处理动态更新的数据源(如搜索输入、实时状态刷新) |
java
package cn.tcmeta;
import reactor.core.publisher.Flux;
import java.time.Duration;
/**
* switchMap示例
*/
public class SwitchMapExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 模拟用户输入的搜索关键词流(3个关键词,间隔300ms)
Flux<String> searchQueries = Flux.just("java", "reactor", "switchMap")
.delayElements(Duration.ofMillis(300)); // 模拟用户输入间隔
// 使用switchMap处理搜索:每次输入触发查询,只保留最新结果
Flux<String> searchResults = searchQueries
.doOnNext(query -> System.out.println("收到搜索关键词: " + query))
.switchMap(query -> {
// 模拟异步查询(查询耗时随关键词长度递增)
int delay = query.length() * 100; // java(400ms), reactor(700ms), switchMap(900ms)
return Flux.just("查询结果: " + query.toUpperCase())
.delayElements(Duration.ofMillis(delay))
.doOnSubscribe(sub -> System.out.println("开始查询: " + query + " (耗时" + delay + "ms)"))
.doOnCancel(() -> System.out.println("取消查询: " + query)); // 监控取消行为
});
// 订阅并输出结果
searchResults.subscribe(
result -> System.out.println("收到结果: " + result),
error -> System.err.println("错误: " + error.getMessage()),
() -> System.out.println("所有查询完成")
);
// 等待所有操作完成
Thread.sleep(3000);
}
}
java
收到搜索关键词: java
开始查询: java (耗时400ms)
收到搜索关键词: reactor
取消查询: java
开始查询: reactor (耗时700ms)
收到搜索关键词: switchMap
取消查询: reactor
开始查询: switchMap (耗时900ms)
收到结果: 查询结果: SWITCHMAP
所有查询完成5.1.5 flatMapSequential()
描述: 类似于 flatMap,但会保留原始元素的顺序,同时并发地订阅和处理内部 Flux。内部 Flux 的结果会按原始顺序缓存和发出。
java
Flux<String> flux = Flux.just("a", "b")
.flatMapSequential(s -> Flux.just(s.toUpperCase(), s + s)
.delayElements(Duration.ofMillis(100)));
// Emits "A", "aa", "B", "bb" (按顺序, 但内部并发)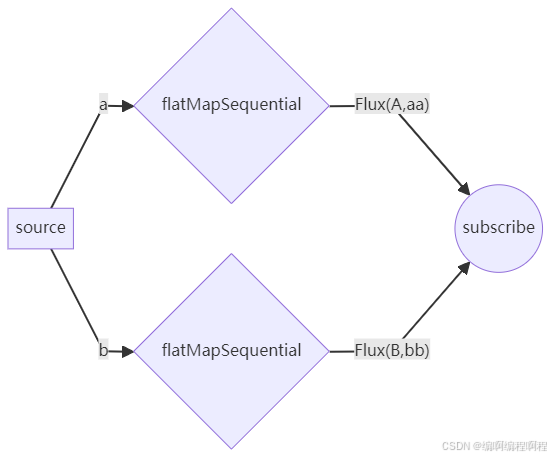
5.1.6 handle()
描述: 更通用的转换操作,允许基于每个元素发出零个、一个或多个元素,或者发出错误或完成信号。
java
Flux<String> flux = Flux.just(1, 2, 3, -1, 4)
.handle((i, sink) -> {
if (i > 0) {
sink.next("Val: " + i);
} else if (i == -1) {
sink.complete(); // 或者 sink.error(new RuntimeException("Negative one"));
}
// 如果 i <= 0 且不为 -1, 则不发出任何东西 (过滤)
});
// Emits "Val: 1", "Val: 2", "Val: 3", then completes1 Val: 1 2 Val: 2 3 Val: 3 -1 complete source handle subscribe
5.1.7 cost
描述: 将 Flux 中的所有元素转换为指定的类型。如果转换失败则发出 onError
java
Flux<Number> numbers = Flux.just(1, 2, 3);
Flux<Integer> integers = numbers.cast(Integer.class);5.1.8 cast、ofType
java
@Test
public void castTest(){
Flux<? extends Serializable> mixedFlux = Flux.just("Hello", 1223, "World", 3.14);
// cast强制类型转换
mixedFlux.filter(o -> o instanceof String)
.cast(String.class)
.subscribe(System.out::println);
System.out.println("------------------------------");
// 类型安全的过滤
Flux<String> stringFlux = mixedFlux.ofType(String.class);
stringFlux.subscribe(System.out::println);
}- 强制类型转换
- cast: 失败会报错
- 类型安全过滤
- ofType
5.2 过滤操作符
5.2.1 filter-基于条件过滤
java
Flux<Integer> numbers = Flux.range(1, 10);
// filter - 基于条件过滤
Flux<Integer> evens = numbers.filter(n -> n % 2 == 0);1 2 2 3 4 4 source filter (i % 2 == 0) subscribe
5.2.2 take-取前N个元素
java
// take - 取前N个元素
Flux<Integer> firstThree = Flux.range(1, 10).take(3);1 1 2 2 3 3 complete source take 3 C subscribe
5.2.3 takeLast-取最后N个元素
java
Flux<Integer> firstThree = Flux.range(1, 10).takeLast(3);1..3 4 4 5 5 source takeLast 2 subscribe
5.2.4 takeWhile -当条件为真的时候取元素
java
Flux<Integer> takeWhile = Flux.range(1, 10).takeWhile(n -> n < 5);5.2.5-takeUntil-取元素直到条件为真
java
// takeUntil - 取元素直到条件为真
Flux<Integer> takeUntil = Flux.range(1, 10).takeUntil(n -> n > 7);5.2.6 skip-跳过前N个元素
java
// skip - 跳过前N个元素
Flux<Integer> skipThree = Flux.range(1, 10).skip(3);1..3 4 4 5 5 source skip 3 subscribe
5.2.7 skipLast-跳过后N个元素
java
Flux<Integer> skipLastThree = Flux.range(1, 10).skipLast(3);1 1 2 2 3 3 4..5 source skipLast 2 subscribe
5.2.8 distinct-去重
java
Flux<Integer> withDuplicates = Flux.just(1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3);
Flux<Integer> distinct = withDuplicates.distinct();a a b b a c c source distinct subscribe
5.2.9 distinctUntilChanged - 去除连续重复
java
Flux<Integer> consecutiveDuplicates = Flux.just(1, 1, 2, 2, 1, 1);
Flux<Integer> distinctConsecutive = consecutiveDuplicates.distinctUntilChanged();5.2.10 elementAt()
描述: 只发出 Flux 中指定索引位置的元素,返回 Mono。
java
Mono<String> mono = Flux.just("A", "B", "C").elementAt(1); // Emits "B"A B B C source elementAt(1) subscribe
5.2.11 ignoreElements()
描述: 忽略所有元素,只传递完成或错误信号,返回 Mono<Void>。
java
Mono<Void> mono = Flux.just(1, 2, 3).ignoreElements();1,2,3 complete source ignoreElements subscribe
5.3 组合操作符
java
Flux<String> fruits = Flux.just("Apple", "Banana", "Cherry");
Flux<String> vegetables = Flux.just("Carrot", "Potato", "Tomato");5.3.1 merge-按时间顺序合并多个流
java
// merge - 合并多个流,按时间顺序
Flux<String> merged = Flux.merge(fruits, vegetables);描述: 将多个 Flux (作为源 Flux 的元素或者直接传入) 合并为一个 Flux,元素交错发出,不保证顺序。
java
Flux<Integer> flux1 = Flux.just(1, 2).delayElements(Duration.ofMillis(10));
Flux<Integer> flux2 = Flux.just(3, 4).delayElements(Duration.ofMillis(5));
Flux<Integer> merged = Flux.merge(flux1, flux2);
// 可能是 3, 1, 4, 2 或其他交错顺序1 2 3 4 Flux1 merge Flux2 subscribe
5.3.2 mergeWith
描述: 将当前 Flux 与另一个 Publisher 合并,元素交错发出,不保证顺序。
java
Flux<Integer> flux1 = Flux.just(1, 2).delayElements(Duration.ofMillis(10));
Flux<Integer> merged = flux1.mergeWith(Flux.just(3, 4).delayElements(Duration.ofMillis(5)));1 2 3 4 flux1 mergeWith otherFlux subscribe
5.3.3 mergedSequential
- 按顺序合并(先完成第一个流的所有元素)
java
// mergeSequential - 按顺序合并(先完成第一个流的所有元素)
Flux<String> mergedSequential = Flux.mergeSequential(fruits, vegetables);5.3.4 zip-将多个流的元素配对
java
// zip - 将多个流的元素配对
Flux<String> zipped = Flux.zip(fruits, vegetables,
(f, v) -> f + " with " + v);
// 输出: "Apple with Carrot", "Banana with Potato", "Cherry with Tomato"zip处理多个Mono
java
// 使用 zip 处理多个 Mono
Mono<String> result = Mono.zip(mono1, mono2, (s1, s2) -> s1 + " " + s2);描述: 将多个 Flux (或 Iterable) 的元素按照它们在各自序列中的位置进行配对组合,使用提供的 combinator 函数处理每组配对的元素。如果一个源 Flux 完成,则 zip 操作也完成,并且不会再从其他源 Flux 请求更多元素。
5.3.5 zipWith
描述: 将当前 Flux 与另一个 Publisher 的元素进行配对组合。
java
Flux<String> zipped = Flux.just("A", "B")
.zipWith(Flux.just(1, 2, 3), (s, i) -> s + i);
// Emits "A1", "B2"A B 1 2 3 A1 B2 current Flux A,B zipWith other Flux 1,2,3 subscribe
5.3.6 combineLatest
- 每当任何输入流发出值时,组合所有流的最新值
java
Flux<Long> interval1 = Flux.interval(Duration.ofMillis(500));
Flux<Long> interval2 = Flux.interval(Duration.ofMillis(700));
Flux<String> combined = Flux.combineLatest(
interval1, interval2,
(i1, i2) -> "i1: " + i1 + ", i2: " + i2
);5.3.7 concat-顺序连接流
- 顺序连续流
java
Flux<String> concatenated = Flux.concat(fruits, vegetables);描述: 按顺序连接多个 Flux (作为源 Flux 的元素或者直接传入)。只有前一个 Flux 完成后,才会订阅并发出下一个 Flux 的元素。
java
Flux<Integer> flux1 = Flux.just(1, 2).delayElements(Duration.ofMillis(10));
Flux<Integer> flux2 = Flux.just(3, 4);
Flux<Integer> concat = Flux.concat(flux1, flux2); // Emits 1, 2, 3, 41 2 onComplete1 3 4 Flux1 concat Flux2 subscribe
5.3.8 concatWith
描述: 将当前 Flux 与另一个 Publisher 按顺序连接。
java
Flux<Integer> flux1 = Flux.just(1, 2).delayElements(Duration.ofMillis(10));
Flux<Integer> concat = flux1.concatWith(Flux.just(3, 4)); // Emits 1, 2, 3, 41 2 onComplete1 3 4 flux1 concatWith otherFlux subscribe
5.3.9 startWith-在流开始前添加元素
java
// startWith - 在流开始前添加元素
Flux<String> withPrefix = fruits.startWith("Fruits:");5.3.10 when-组合多个Mono
java
// 使用 when 组合多个 Mono
Mono<String> mono1 = Mono.just("Hello");
Mono<String> mono2 = Mono.just("World");
Mono<Void> combined = Mono.when(mono1, mono2);