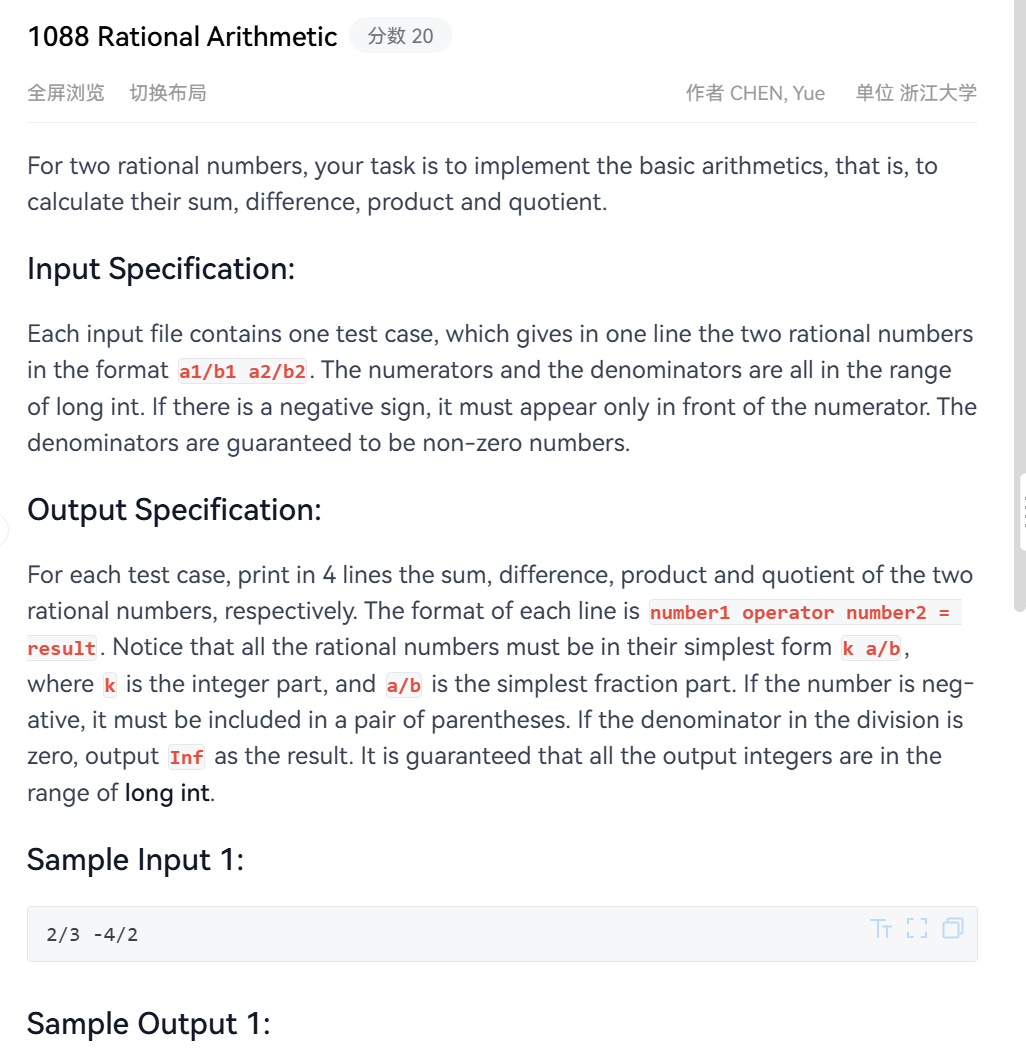

这一题的大意是让模拟两个分数进行加减乘除运算,输出计算后的结果。
看起来比较麻烦,但是认真的拆分成一步一步来做还是比较简单的
要注意负数,0,等特殊情况
在进行分数运算的时候,要注意通分和约分,这里会涉及到最小公倍数和最大公因数的算法的书写。
过程就是模拟分数的运算。
第一次提交的代码如下:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <limits.h>
#include <queue>
#include <string.h>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
// 123456789
int a1;
int b1;
int a2;
int b2;
int gcd(int x,int y)
{
if(y==0)
{
return x;
}
else
{
return gcd(y,x%y);
}
}
int lcm(int x,int y)
{
return x*y/gcd(x,y);
}
void yuefen(int x,int y)
{
if(x==0)
{
cout<<"0";
return;
}
if(y==0)
{
cout<<"Inf";
return;
}
int temp=gcd(abs(x),abs(y));
//要判断能不能化为带分数,或者整数
if(abs(x/temp)<abs(y/temp))
{
if(x/temp<0)
{
cout<<"(";
cout<<x/temp<<"/"<<y/temp;
cout<<")";
}
else
{
cout<<x/temp<<"/"<<y/temp;
}
}
else
{
if(x/temp<0)
{
cout<<"(";
cout<<(x/temp)/(y/temp);
if(abs(x/temp)%abs(y/temp)!=0)
{
cout<<" ";
cout<<abs(x/temp)%abs(y/temp)<<"/"<<y/temp;
}
cout<<")";
}
else
{
cout<<(x/temp)/(y/temp);
if(abs(x/temp)%abs(y/temp)!=0)
{
//5/3比如余2
cout<<" ";
cout<<abs(x/temp)%abs(y/temp)<<"/"<<y/temp;
}
}
}
}
void print_computejia(int a1,int b1,int a2,int b2)
{
//需要通分
int x=lcm(b1,b2);
int newa1=a1*x/b1+a2*x/b2;
//新的分子分母都知道了
yuefen(a1,b1);
cout<<" + ";
yuefen(a2,b2);
cout<<" = ";
yuefen(newa1,x);
cout<<endl;
}
void print_computejian(int a1,int b1,int a2,int b2)
{
//需要通分
int x=lcm(b1,b2);
int newa1=a1*x/b1-a2*x/b2;
//新的分子分母都知道了
yuefen(a1,b1);
cout<<" - ";
yuefen(a2,b2);
cout<<" = ";
yuefen(newa1,x);
cout<<endl;
}
void print_computecheng(int a1,int b1,int a2,int b2)
{
//需要通分
int newa1=a1*a2;
int x=b1*b2;
//新的分子分母都知道了
yuefen(a1,b1);
cout<<" * ";
yuefen(a2,b2);
cout<<" = ";
yuefen(newa1,x);
cout<<endl;
}
void print_computechu(int a1,int b1,int a2,int b2)
{
//需要通分
int newa1=a1*b2;
int x=b1*a2;
if(x<0)
{
x=abs(x);
newa1=newa1*(-1);
}
//新的分子分母都知道了
yuefen(a1,b1);
cout<<" / ";
yuefen(a2,b2);
cout<<" = ";
if(a2==0)
{
cout<<"Inf";
}
else
{
yuefen(newa1,x);
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main()
{
//ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(
scanf("%d/%d %d/%d",&a1,&b1,&a2,&b2);
//将两个分数进行计算
// 加件法需要通分,
// 乘法分子分母直接相乘
//除法等于乘一个数的倒数
print_computejia(a1,b1,a2,b2);
//最后将一个分数化成最简形式
print_computejian(a1,b1,a2,b2);
print_computecheng(a1,b1,a2,b2);
print_computechu(a1,b1,a2,b2);
return 0;
} 只通过了两个测试用例,原因是没有开long long
我实际是想到要开long long的,但是
在输入的时候
cpp
scanf("%ld/%ld %ld/%ld",&a1,&b1,&a2,&b2);这里应该是lld
即:
cpp
scanf("%lld/%lld %lld/%lld",&a1,&b1,&a2,&b2);导致溢出
因此最终代码是:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <limits.h>
#include <queue>
#include <string.h>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
// 123456789
long long a1;
long long b1;
long long a2;
long long b2;
long long gcd(long long x,long long y)
{
if(y==0)
{
return x;
}
else
{
return gcd(y,x%y);
}
}
long long lcm(long long x,long long y)
{
return x*y/gcd(x,y);
}
void yuefen(long long x,long long y)
{
if(x==0)
{
cout<<"0";
return;
}
if(y==0)
{
cout<<"Inf";
return;
}
long long temp=gcd(abs(x),abs(y));
//要判断能不能化为带分数,或者整数
if(abs(x/temp)<abs(y/temp))
{
if(x/temp<0)
{
cout<<"(";
cout<<x/temp<<"/"<<y/temp;
cout<<")";
}
else
{
cout<<x/temp<<"/"<<y/temp;
}
}
else
{
if(x/temp<0)
{
cout<<"(";
cout<<(x/temp)/(y/temp);
if(abs(x/temp)%abs(y/temp)!=0)
{
cout<<" ";
cout<<abs(x/temp)%abs(y/temp)<<"/"<<y/temp;
}
cout<<")";
}
else
{
cout<<(x/temp)/(y/temp);
if(abs(x/temp)%abs(y/temp)!=0)
{
//5/3比如余2
cout<<" ";
cout<<abs(x/temp)%abs(y/temp)<<"/"<<y/temp;
}
}
}
}
void print_computejia(long long a1,long long b1,long long a2,long long b2)
{
//需要通分
long long x=lcm(b1,b2);
long long newa1=a1*x/b1+a2*x/b2;
//新的分子分母都知道了
yuefen(a1,b1);
cout<<" + ";
yuefen(a2,b2);
cout<<" = ";
yuefen(newa1,x);
cout<<endl;
}
void print_computejian(long long a1,long long b1,long long a2,long long b2)
{
//需要通分
long long x=lcm(b1,b2);
long long newa1=a1*x/b1-a2*x/b2;
//新的分子分母都知道了
yuefen(a1,b1);
cout<<" - ";
yuefen(a2,b2);
cout<<" = ";
yuefen(newa1,x);
cout<<endl;
}
void print_computecheng(long long a1,long long b1,long long a2,long long b2)
{
//需要通分
long long newa1=a1*a2;
long long x=b1*b2;
//新的分子分母都知道了
yuefen(a1,b1);
cout<<" * ";
yuefen(a2,b2);
cout<<" = ";
yuefen(newa1,x);
cout<<endl;
}
void print_computechu(long long a1,long long b1,long long a2,long long b2)
{
//需要通分
long long newa1=a1*b2;
long long x=b1*a2;
if(x<0)
{
x=abs(x);
newa1=newa1*(-1);
}
//新的分子分母都知道了
yuefen(a1,b1);
cout<<" / ";
yuefen(a2,b2);
cout<<" = ";
if(a2==0)
{
cout<<"Inf";
}
else
{
yuefen(newa1,x);
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main()
{
//ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(
scanf("%lld/%lld %lld/%lld",&a1,&b1,&a2,&b2);
//将两个分数进行计算
// 加件法需要通分,
// 乘法分子分母直接相乘
//除法等于乘一个数的倒数
print_computejia(a1,b1,a2,b2);
//最后将一个分数化成最简形式
print_computejian(a1,b1,a2,b2);
print_computecheng(a1,b1,a2,b2);
print_computechu(a1,b1,a2,b2);
return 0;
} 总结,这一道题是模拟分数的四则运算,注意细节,要记牢最大公因数和最小公倍数的算法。
有一道类似的题:
`