目录
[1.1 设计理念与定位](#1.1 设计理念与定位)
[1.2 责任链模式架构](#1.2 责任链模式架构)
[2.1 滑动窗口算法实现](#2.1 滑动窗口算法实现)
[2.2 熔断器状态机与算法](#2.2 熔断器状态机与算法)
[三、Spring Cloud 集成实战](#三、Spring Cloud 集成实战)
[3.1 自动配置机制](#3.1 自动配置机制)
[3.2 Web MVC 深度集成](#3.2 Web MVC 深度集成)
[3.3 OpenFeign 高级集成](#3.3 OpenFeign 高级集成)
[4.1 动态规则配置与持久化](#4.1 动态规则配置与持久化)
[4.2 集群流控架构设计](#4.2 集群流控架构设计)
[4.3 性能优化与监控体系](#4.3 性能优化与监控体系)
[5.1 热点参数限流实现](#5.1 热点参数限流实现)
[5.2 自适应系统保护](#5.2 自适应系统保护)
[5.3 网关层限流集成](#5.3 网关层限流集成)
一、核心架构解析
1.1 设计理念与定位
Spring Cloud Alibaba Sentinel 是一个全方位的分布式系统流量控制与容错组件 ,其核心设计理念是保障微服务架构的稳定性、可靠性和自愈能力。与传统的 Hystrix 相比,Sentinel 在设计理念上有着根本性的创新:
- 资源为中心:将所有需要保护的对象(如方法、接口、服务)抽象为资源,提供统一保护策略
- 多维度控制:支持 QPS、线程数、系统负载、CPU 使用率等多种控制维度
- 实时统计 :基于滑动窗口算法,实现毫秒级实时统计与决策
- 生态丰富:提供对 Dubbo、Spring Cloud Gateway、gRPC 等框架的原生支持
1.2 责任链模式架构
Sentinel 的核心架构基于责任链模式,通过一系列的 Slot 组成处理链条,每个 Slot 承担特定职责:
java
// 责任链执行流程伪代码
public class DefaultSlotChain implements SlotChain {
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper) {
nodeSelectorSlot.entry(context, resourceWrapper); // 收集调用路径和节点关系
clusterBuilderSlot.entry(context, resourceWrapper); // 构建集群统计节点
statisticSlot.entry(context, resourceWrapper); // 实时统计指标收集
authoritySlot.entry(context, resourceWrapper); // 黑白名单授权控制
systemSlot.entry(context, resourceWrapper); // 系统保护规则检查
flowSlot.entry(context, resourceWrapper); // 流量控制规则检查
degradeSlot.entry(context, resourceWrapper); // 熔断降级规则检查
}
}责任链中各个 Slot 的顺序和分工明确,确保流量控制的精确性和高效性。
二、核心技术深度剖析
2.1 滑动窗口算法实现
Sentinel 的流量控制基于高效的滑动窗口算法,解决了固定窗口算法的"边界问题"。
java
public class LeapArray<T> {
private final AtomicReferenceArray<WindowWrap<T>> array;
private final int windowLengthInMs; // 单个窗口长度(毫秒)
private final int sampleCount; // 窗口总数
private final int intervalInMs; // 整个时间区间长度
public WindowWrap<T> currentWindow(long timeMillis) {
// 计算当前时间窗口索引和起始时间
int idx = calculateTimeIdx(timeMillis);
long windowStart = calculateWindowStart(timeMillis);
while (true) {
WindowWrap<T> old = array.get(idx);
if (old == null) {
// 创建新窗口 - CAS保证线程安全
WindowWrap<T> window = new WindowWrap<T>(windowLengthInMs, windowStart, newEmptyBucket(timeMillis));
if (array.compareAndSet(idx, null, window)) {
return window;
} else {
// CAS失败则重试
Thread.yield();
}
}
if (windowStart == old.windowStart()) {
return old;
}
// 处理时间窗口冲突(时钟回拨或窗口过期)
if (windowStart > old.windowStart()) {
if (updateLock.tryLock()) {
try {
return resetWindowTo(old, windowStart);
} finally {
updateLock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
}
// 计算总窗口统计值
public T getValues(long timeMillis) {
T result = newEmptyBucket(timeMillis);
for (WindowWrap<T> window : array) {
if (window != null && !window.isTimeInWindow(timeMillis)) {
continue;
}
result.add(window.value());
}
return result;
}
}滑动窗口算法将固定时间区间划分为多个更细粒度的子窗口,随时间推移滑动更新,实现更精确的流量统计。
2.2 熔断器状态机与算法
Sentinel 的熔断降级基于状态机模式,支持三种熔断策略:慢调用比例、异常比例和异常数。
java
public class CircuitBreaker {
// 熔断器三种状态
enum State { CLOSED, OPEN, HALF_OPEN }
private volatile State state = State.CLOSED;
private final Metric metric;
private final double failureThreshold; // 失败阈值(比例或数量)
private final long retryTimeoutMs; // 重试超时时间
private volatile long nextRetryTime; // 下次重试时间
public void onRequestComplete(long rt, Throwable error) {
metric.addRt(rt);
if (error != null) metric.addError();
switch (state) {
case CLOSED:
// 检查是否需要熔断
if (metric.exceedsThreshold(failureThreshold)) {
transitionToOpen();
}
break;
case OPEN:
// 检查是否应该尝试恢复
if (System.currentTimeMillis() >= nextRetryTime) {
transitionToHalfOpen();
}
break;
case HALF_OPEN:
// 半开状态下允许少量请求通过
if (probeRequestArrived()) {
if (probeRequestSucceeded()) {
transitionToClosed(); // 探针请求成功,恢复服务
} else {
transitionToOpen(); // 探针请求失败,继续保持熔断
}
}
break;
}
}
private void transitionToOpen() {
state = State.OPEN;
nextRetryTime = System.currentTimeMillis() + retryTimeoutMs;
// 发布状态变更事件
eventPublisher.publish(new CircuitBreakerStateEvent(this, State.OPEN));
}
}熔断器状态机确保系统在故障时快速失败,同时通过半开状态智能检测服务恢复情况。
三、与Spring Cloud 集成实战
3.1 自动配置机制
Spring Cloud Alibaba Sentinel 通过自动配置机制实现无缝集成:
java
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(SentinelProperties.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "spring.cloud.sentinel.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
public class SentinelAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SentinelResourceAspect sentinelResourceAspect() {
return new SentinelResourceAspect();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
public FilterRegistrationBean<CommonFilter> sentinelFilterRegistration() {
FilterRegistrationBean<CommonFilter> registration = new FilterRegistrationBean<>();
registration.setFilter(new CommonFilter());
registration.addUrlPatterns("/*");
registration.setOrder(FilterRegistrationBean.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
registration.addInitParameter("HTTP_METHOD_SPECIFY", "true");
return registration;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public UrlCleaner urlCleaner() {
return new DefaultUrlCleaner();
}
}3.2 Web MVC 深度集成
自定义资源名称解析器实现精细化流量控制:
java
@Component
public class CustomUrlCleaner implements UrlCleaner {
private static final Pattern USER_ID_PATTERN = Pattern.compile("/users/(\\d+)");
private static final Pattern ORDER_ID_PATTERN = Pattern.compile("/orders/(\\d+/items/\\d+)");
@Override
public String clean(String originUrl) {
if (originUrl == null) return originUrl;
// RESTful URL 参数化 - 提高规则复用性
Matcher userIdMatcher = USER_ID_PATTERN.matcher(originUrl);
if (userIdMatcher.find()) {
return userIdMatcher.replaceAll("/users/{id}");
}
Matcher orderMatcher = ORDER_ID_PATTERN.matcher(originUrl);
if (orderMatcher.find()) {
return orderMatcher.replaceAll("/orders/{orderId}/items/{itemId}");
}
return originUrl;
}
}
// 全局异常处理增强
@ControllerAdvice
public class SentinelGlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(BlockException.class)
@ResponseBody
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> handleBlockException(BlockException ex,
HttpServletRequest request) {
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
result.put("code", 429);
result.put("message", "请求过于频繁,请稍后重试");
result.put("timestamp", System.currentTimeMillis());
result.put("path", request.getRequestURI());
// 区分不同类型的BlockException
if (ex instanceof FlowException) {
result.put("type", "flow_control");
} else if (ex instanceof DegradeException) {
result.put("type", "circuit_breaker");
} else if (ex instanceof ParamFlowException) {
result.put("type", "param_flow_control");
}
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.TOO_MANY_REQUESTS).body(result);
}
}3.3 OpenFeign 高级集成
FallbackFactory 实现提供精细化降级策略:
java
@Component
@Slf4j
public class UserServiceFallbackFactory implements FallbackFactory<UserService> {
private final MetricRegistry metricRegistry;
public UserServiceFallbackFactory(MetricRegistry metricRegistry) {
this.metricRegistry = metricRegistry;
}
@Override
public UserService create(Throwable cause) {
return new UserServiceFallback(cause, metricRegistry);
}
static class UserServiceFallback implements UserService {
private final Throwable cause;
private final MetricRegistry metricRegistry;
public UserServiceFallback(Throwable cause, MetricRegistry metricRegistry) {
this.cause = cause;
this.metricRegistry = metricRegistry;
logError(cause);
}
private void logError(Throwable cause) {
// 记录降级指标
metricRegistry.counter("feign.circuit_breaker").inc();
if (cause instanceof DegradeException) {
log.warn("服务熔断降级: {}", cause.getMessage());
metricRegistry.counter("feign.circuit_breaker.degrade").inc();
} else if (cause instanceof FlowException) {
log.warn("流量控制限制: {}", cause.getMessage());
metricRegistry.counter("feign.circuit_breaker.flow").inc();
} else if (cause instanceof SocketTimeoutException) {
log.warn("服务调用超时: {}", cause.getMessage());
metricRegistry.counter("feign.circuit_breaker.timeout").inc();
} else {
log.warn("服务调用异常: {}", cause.getMessage());
metricRegistry.counter("feign.circuit_breaker.other").inc();
}
}
@Override
public User getUserById(Long id) {
// 多级降级策略
if (id == null || id <= 0) {
return User.unknownUser();
}
// 从本地缓存获取降级数据
User cachedUser = LocalCache.getUser(id);
if (cachedUser != null) {
return cachedUser;
}
// 返回基本降级数据
return User.fallbackUser(id);
}
@Override
public List<User> getUsersByIds(List<Long> ids) {
// 批量查询降级策略
return ids.stream()
.map(this::getUserById)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}
}四、生产环境最佳实践
4.1 动态规则配置与持久化
Sentinel 支持多种动态规则数据源,实现规则的热更新:
XML
spring:
cloud:
sentinel:
enabled: true
eager: true
transport:
dashboard: localhost:8080
port: 8719
datasource:
# Flow规则数据源 - Nacos
flow:
nacos:
server-addr: ${spring.cloud.nacos.config.server-addr}
dataId: ${spring.application.name}-flow-rules
groupId: SENTINEL_GROUP
namespace: ${spring.cloud.nacos.config.namespace}
data-type: json
rule-type: flow
# 降级规则数据源 - ZooKeeper
degrade:
zk:
server-addr: ${zookeeper.server-addr}
path: /sentinel/rules/${spring.application.name}/degrade
data-type: json
rule-type: degrade
# 系统规则数据源 - Apollo
system:
apollo:
namespace: application
flow-rules-key: sentinel.system.rules
rule-type: system
# 热点参数规则 - Redis
param-flow:
redis:
host: ${redis.host}
port: ${redis.port}
database: 0
key: sentinel:param-flow:${spring.application.name}
data-type: json
rule-type: param-flow多数据源支持确保规则的高可用性和一致性,避免单点故障。
4.2 集群流控架构设计
对于大规模分布式系统,集群流控是必不可少的特性:
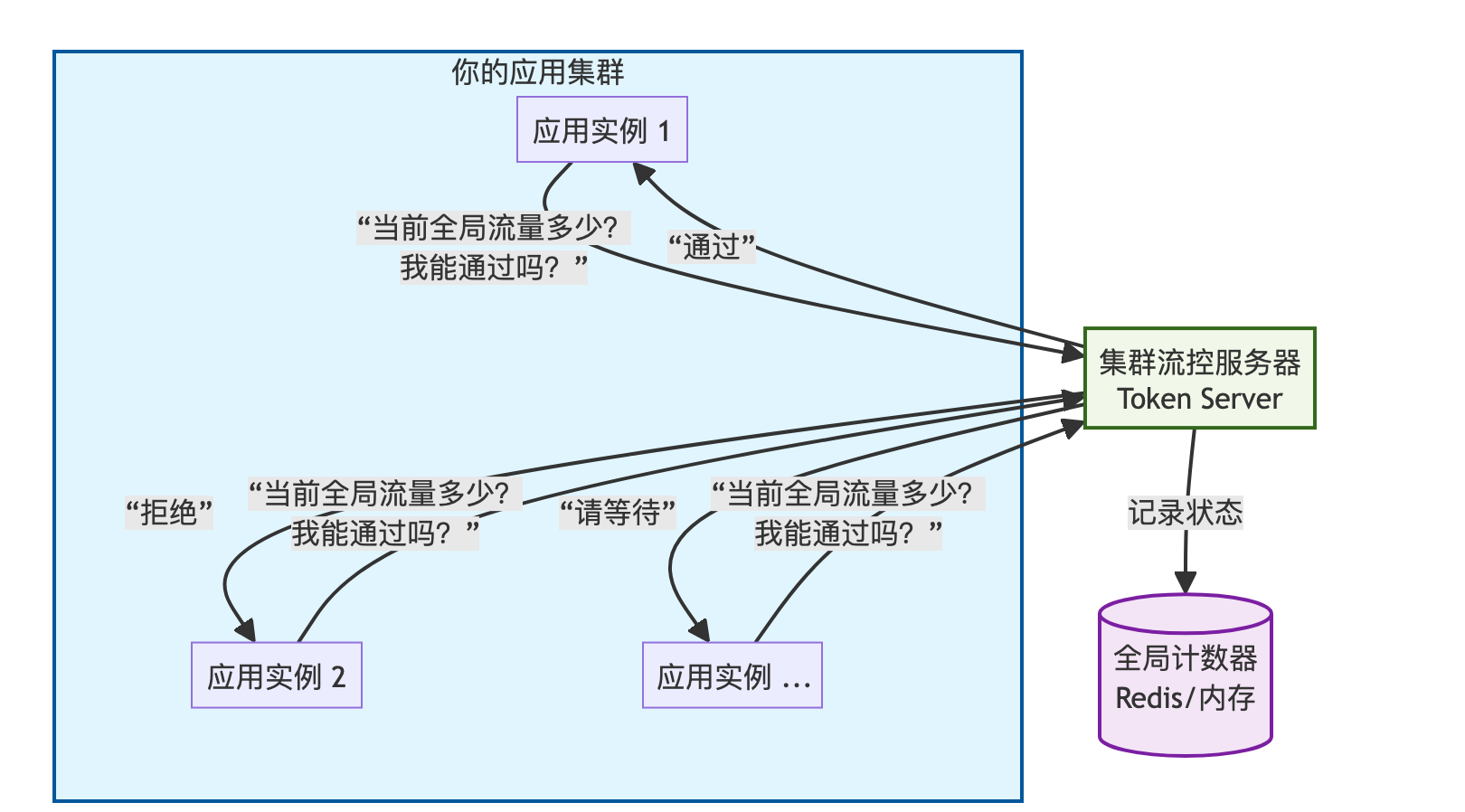
如何理解这张图?
三要素:
- 你的应用集群 (Your Application Cluster): 分散在不同机器上的多个服务实例。
- 集群流控服务器 (Token Server): 唯一的"大脑"或"交通警察"。它知道整个集群的总流量情况。
- 全局计数器 (Global Counter): Token Server 用来快速查询和更新当前全局流量(如QPS)的存储。它可以是一个Redis数据库,也可以是Token Server自己内存中的一个计数器。两个核心动作:
两个核心动作:
- 询问 (Ask): 应用集群中的每个实例,在处理每个请求时,都会向Token Server发出灵魂拷问:"当前全局流量多少?这个请求能通过吗?"
- 决策与响应 (Decide & Respond): Token Server 检查全局计数器,并立即做出决策,返回三种响应之一:
-
- 通过 (Pass): 流量未超限,请求可以继续处理。
- 拒绝 (Block): 流量已超限,这个请求应该被立即拒绝(快速失败)。
- 等待 (Wait): 一种复杂响应,让客户端等待一小段时间后再重试。
最重要的隐含特性 (降级):
- 如果应用实例 和Token Server 之间的网络出现问题,客户端会自动降级到本地限流模式,使用一个保守的阈值,保证系统不会因为流控组件本身故障而彻底瘫痪。这是生产环境中必须具备的能力。
这个图剥离了所有实现细节(如配置中心、控制台、主备切换),只保留了最核心的思想,希望它足够简洁和清晰!
- Token Server 高可用:通过协调集群(ZooKeeper/ETCD)解决单点故障问题
- 智能容错策略:通过滑动窗口统计节点可用率,自动降级为本地流控
- 多维路由策略:支持系统维度和资源维度路由,实现负载均衡
- 动态阈值分配:支持均值分配和动态权重分配策略
集群流控解决方案关键特性:
- Token Server 高可用:通过协调集群(ZooKeeper/ETCD)解决单点故障问题
- 智能容错策略:通过滑动窗口统计节点可用率,自动降级为本地流控
- 多维路由策略:支持系统维度和资源维度路由,实现负载均衡
- 动态阈值分配:支持均值分配和动态权重分配策略
4.3 性能优化与监控体系
JVM 与系统级优化配置:
spring:
cloud:
sentinel:
# 指标配置
metric:
file-single-size: 104857600 # 100MB
file-total-count: 10 # 最多保留10个日志文件
charset: UTF-8
# 日志配置
log:
dir: ${user.home}/logs/csp/
output-type: file
switch-pid: true
# 传输配置
transport:
port: 8719
heartbeat-interval-ms: 10000
client-ip: ${spring.cloud.client.ip-address}
# 异步配置
async:
core-pool-size: 8
max-pool-size: 16
queue-capacity: 10000
# 高级配置
flow:
cold-factor: 3 # 冷启动因子
stat-interval-ms: 1000 # 统计间隔
degrade:
stat-interval-ms: 1000 # 熔断统计间隔监控指标收集与可视化:
java
@Configuration
public class SentinelMetricsConfiguration {
@Bean
public MeterRegistryCustomizer<MeterRegistry> sentinelMetrics() {
return registry -> {
// 实时QPS监控
Gauge.builder("sentinel.qps",
() -> getCurrentQps("resourceName"))
.description("Current QPS of resource")
.tag("resource", "resourceName")
.register(registry);
// 异常比例监控
Gauge.builder("sentinel.exception.ratio",
() -> getExceptionRatio("resourceName"))
.description("Exception ratio of resource")
.tag("resource", "resourceName")
.register(registry);
// 线程数监控
Gauge.builder("sentinel.thread.count",
() -> getThreadCount("resourceName"))
.description("Thread count of resource")
.tag("resource", "resourceName")
.register(registry);
};
}
// 集成Prometheus监控
@Bean
public CollectorRegistry sentinelCollectorRegistry() {
CollectorRegistry registry = new CollectorRegistry(true);
DefaultExports.register(registry);
// 自定义Sentinel指标收集
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
try {
collectSentinelMetrics(registry);
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Metrics collection error", e);
}
}
}).start();
return registry;
}
}五、高级特性与挑战解决方案
5.1 热点参数限流实现
热点参数限流是对特定参数的精细化流量控制:
java
@GetMapping("/api/products/{productId}")
@SentinelResource(value = "productDetail",
blockHandler = "handleProductBlock",
fallback = "handleProductFallback")
public Product getProductDetail(@PathVariable Long productId,
@RequestParam(required = false) String userId) {
return productService.getProductDetail(productId, userId);
}
// 热点参数限流规则配置
private void initHotParamRules() {
ParamFlowRule rule = new ParamFlowRule("productDetail")
.setParamIdx(0) // 第一个参数(productId)
.setCount(50); // 整体阈值
// 特殊商品限流配置
ParamFlowItem item = new ParamFlowItem()
.setObject("hotProduct123") // 热门商品ID
.setClassType(Long.class.getName())
.setCount(200); // 特殊阈值
rule.setParamFlowItemList(Collections.singletonList(item));
ParamFlowRuleManager.loadRules(Collections.singletonList(rule));
}
// 热点参数限流处理
public Product handleProductBlock(Long productId, String userId, BlockException ex) {
log.warn("商品详情接口限流,productId: {}, userId: {}", productId, userId);
// 返回降级数据
Product product = cacheService.getProductFromCache(productId);
if (product != null) {
return product;
}
return Product.degradedProduct(productId);
}5.2 自适应系统保护
系统自适应保护根据系统指标动态调整流量:
java
@Configuration
public class SystemRuleConfiguration {
@PostConstruct
public void initSystemRules() {
List<SystemRule> rules = new ArrayList<>();
// CPU使用率保护
SystemRule cpuRule = new SystemRule();
cpuRule.setHighestCpuUsage(0.8); // CPU使用率阈值80%
cpuRule.setMetricType(SystemRule.METRIC_CPU_USAGE);
rules.add(cpuRule);
// 平均RT保护
SystemRule rtRule = new SystemRule();
rtRule.setAvgRt(100); // 平均响应时间阈值100ms
rtRule.setMetricType(SystemRule.METRIC_AVG_RT);
rules.add(rtRule);
// 并发线程数保护
SystemRule threadRule = new SystemRule();
threadRule.setMaxThread(1000); // 最大并发线程数1000
threadRule.setMetricType(SystemRule.METRIC_THREAD);
rules.add(threadRule);
// QPS保护
SystemRule qpsRule = new SystemRule();
qpsRule.setQps(5000); // 系统最大QPS5000
qpsRule.setMetricType(SystemRule.METRIC_QPS);
rules.add(qpsRule);
SystemRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
}
// 动态调整系统规则
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 60000) // 每分钟调整一次
public void adjustSystemRules() {
double currentCpuUsage = getCurrentCpuUsage();
double currentLoad = getSystemLoadAverage();
List<SystemRule> rules = SystemRuleManager.getRules();
if (rules.isEmpty()) return;
// 根据系统负载动态调整规则
for (SystemRule rule : rules) {
switch (rule.getMetricType()) {
case SystemRule.METRIC_CPU_USAGE:
// CPU使用率高时自动降低阈值
if (currentCpuUsage > 0.7) {
rule.setHighestCpuUsage(0.7);
} else if (currentCpuUsage < 0.4) {
rule.setHighestCpuUsage(0.9);
}
break;
case SystemRule.METRIC_QPS:
// 系统负载高时自动降低QPS阈值
if (currentLoad > 5.0) {
rule.setQps(rule.getQps() * 0.8);
} else if (currentLoad < 2.0) {
rule.setQps(rule.getQps() * 1.2);
}
break;
}
}
SystemRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
}
}5.3 网关层限流集成
Spring Cloud Gateway 集成方案:
XML
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: user_service
uri: lb://user-service
predicates:
- Path=/api/users/**
filters:
- name: RequestRateLimiter
args:
redis-rate-limiter.replenishRate: 10 # 每秒令牌数
redis-rate-limiter.burstCapacity: 20 # 突发容量
redis-rate-limiter.requestedTokens: 1 # 每个请求消耗令牌数
- name: SentinelGatewayFilter
args:
resourceMode: CUSTOM
resources:
- user_service_route
# Sentinel网关流控规则
sentinel:
gateway:
rules:
- resource: user_service_route
resourceMode: CUSTOM
count: 100
grade: 1 # QPS模式
intervalSec: 1 # 统计间隔
controlBehavior: 0 # 直接拒绝自定义网关过滤逻辑:
java
@Component
public class CustomGatewayBlockExceptionHandler implements GatewayCallbackManager.BlockRequestHandler {
private final ObjectMapper objectMapper;
private final MetricRegistry metricRegistry;
public CustomGatewayBlockExceptionHandler(ObjectMapper objectMapper, MetricRegistry metricRegistry) {
this.objectMapper = objectMapper;
this.metricRegistry = metricRegistry;
GatewayCallbackManager.setBlockHandler(this);
}
@Override
public Mono<ServerResponse> handleRequest(ServerWebExchange exchange, Throwable ex) {
metricRegistry.counter("gateway.block.requests").inc();
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<>();
result.put("code", determineErrorCode(ex));
result.put("message", determineErrorMessage(ex));
result.put("timestamp", System.currentTimeMillis());
result.put("path", exchange.getRequest().getURI().getPath());
// 记录详细阻断信息
if (ex instanceof BlockException) {
BlockException blockException = (BlockException) ex;
result.put("rule", blockException.getRule().toString());
result.put("limitApp", blockException.getRule().getLimitApp());
// 区分不同类型的阻断
if (blockException instanceof FlowException) {
metricRegistry.counter("gateway.block.flow").inc();
} else if (blockException instanceof DegradeException) {
metricRegistry.counter("gateway.block.degrade").inc();
} else if (blockException instanceof ParamFlowException) {
metricRegistry.counter("gateway.block.param").inc();
} else if (blockException instanceof SystemBlockException) {
metricRegistry.counter("gateway.block.system").inc();
} else if (blockException instanceof AuthorityException) {
metricRegistry.counter("gateway.block.authority").inc();
}
}
return ServerResponse.status(determineHttpStatus(ex))
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.bodyValue(result);
}
private int determineErrorCode(Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof FlowException) return 429001;
if (ex instanceof DegradeException) return 429002;
if (ex instanceof ParamFlowException) return 429003;
if (ex instanceof SystemBlockException) return 429004;
if (ex instanceof AuthorityException) return 429005;
return 429000;
}
private String determineErrorMessage(Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof FlowException) return "接口流量超限,请稍后重试";
if (ex instanceof DegradeException) return "服务暂时不可用,请稍后重试";
if (ex instanceof ParamFlowException) return "热点参数限流,请稍后重试";
if (ex instanceof SystemBlockException) return "系统保护模式已启用,请稍后重试";
if (ex instanceof AuthorityException) return "授权验证失败,拒绝访问";
return "请求被限流,请稍后重试";
}
private HttpStatus determineHttpStatus(Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof AuthorityException) return HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED;
return HttpStatus.TOO_MANY_REQUESTS;
}
}六、未来发展与展望
- 多语言支持:Sentinel Go 的持续发展和完善,提供跨语言流量控制能力
- Service Mesh 集成:与 Istio、Linkerd 等 Service Mesh 方案的深度融合
- AI 智能调控:基于机器学习的自适应流量控制和异常检测
- 扩展场景支持:数据库访问、消息队列消费等更多场景的流量控制
- 边缘计算场景:适配边缘计算环境的轻量级流量控制方案
结语
Spring Cloud Alibaba Sentinel 为微服务架构提供了全方位、多维度、高效率的稳定性保障解决方案。通过深入理解其核心原理和责任链架构,结合生产环境的最佳实践,开发者可以构建出更加健壮、可靠的分布式系统。
Sentinel 的优势在于:
- 精细化控制:支持多种流量控制策略和熔断降级规则
- 高性能统计:基于滑动窗口算法实现毫秒级实时统计
- 丰富生态集成:与 Spring Cloud 生态无缝集成
- 动态规则管理:支持多种数据源和热更新机制
- 集群流控能力:提供分布式环境下的统一流量控制
在实际生产环境中,建议根据具体业务场景灵活运用各种流量控制和容错策略,建立完善的监控和告警体系,定期进行压力测试和规则调整,以达到最佳的系统稳定性和性能表现。
延伸阅读与资源: