✍️ 前言
在前端面试中,JS 手写题 几乎是绕不过去的考点。无论是防抖、节流,还是手写
call、apply、bind,又或者是进阶的instanceof、发布订阅模式,甚至是最重要的 Promise 的实现。最近我花时间练习了一波常见的JS手写题。这篇文章整理了我的实现过程、注释,以及测试记录,方便以后复盘。
1.实现一个防抖函数(debounce)
js
function debounce(fn,delay = 300) {
let timeId = null;
return function (...args) {
if(timeId) clearTimeout(timeId);
timeId = setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(this, args);
}, delay);
}
}
// ================= 测试用例 =================
const debouncedFn = debounce((str,n)=> {
console.log(str)
console.log(n)
}, 1000);
debouncedFn('hello debounce','123');要点解析
- 在
delay时间窗口内重复触发,会清除上一次setTimeout,最终只执行最后一次调用。 - 用
fn.apply(this, args)可以保留触发者的this。
2.实现一个节流函数(throttle)
js
function throttle(fn,delay = 300) {
let inThrottle;
return function (...args) {
if(inThrottle) return;
inThrottle = true;
fn.apply(this, args);
setTimeout(() => {
inThrottle = false;
}, delay);
}
}
// ================= 测试用例 =================
const throttleFn = throttle((str)=> {
console.log(str);
},1000)
throttleFn('hello throttle') // 输出hello throttle
throttleFn('hello throttle') // 不执行要点解析
- 典型的前缘节流(leading:true,trailing:false):窗口开始执行一次,后续调用被忽略直到窗口结束。
3.手写 call
js
Function.prototype.myCall = function (context, ...args) {
if(typeof this !== 'function') {
throw new TypeError('this is not a function');
}
const fn = Symbol('fn');
context = context === null || context === undefined ? globalThis : Object(context);
context[fn] = this;
const res = context[fn](...args);
delete context[fn];
return res;
}要点解析
- 核心思路:把函数临时挂到
context上执行以改变this,再删除。
4.手写 apply
js
Function.prototype.myApply = function (context, arr){
if(typeof this !== 'function') {
throw new TypeError('this is not a function');
}
if(!Array.isArray(arr)) {
throw new TypeError('params is not an array');
}
const fn = Symbol('fn');
context = context === null || context === undefined ? globalThis : Object(context);
context[fn] = this;
const res = context[fn](...arr);
delete context[fn];
return res;
}要点解析
- 与
call类似,区别在于第二参数为数组 ,通过展开...arr传参。
5.手写 bind
js
Function.prototype.myBind = function(context, ...args) {
if(typeof this !=='function') {
throw new TypeError('this is not a function');
}
return (...args2)=> {
console.log(args, args2);
const key = Symbol('key');
context[key] = this;
const res = context[key](...args, ...args2);
delete context[key];
return res;
}
}
// ================= 测试用例 =================
const fn = (a,b,c,d) =>{
console.log(a,b,c,d)
}
const fn2 = fn.myBind(this, 1, 2)
fn2(3,4);要点解析
- 通过返回闭包保存
context+ 预置参数(柯里化)。 - 用了箭头函数 返回,有个好处:箭头函数的
this会捕获定义时的this(即原函数对象),所以context[key] = this实际上是把原函数挂过去调用。
6.实现一个 instanceof
js
/**
* 手写实现 instanceof 的功能
* @param {Object} obj - 要检测的对象
* @param {Function} constructor - 构造函数
* @returns {boolean} 是否是 constructor 的实例
*/
function myInstanceOf(obj, constructor) {
// 1. 非对象直接返回 false(排除 null 和基本类型)
if (obj === null || (typeof obj !== 'object' && typeof obj !== 'function')) {
return false;
}
// 2. 取构造函数的 prototype
const prototype = constructor.prototype;
// 3. 获取 obj 的原型
let proto = Object.getPrototypeOf(obj); // obj.__proto__
// 4. 遍历原型链,逐层向上查找
while (proto !== null) {
if (proto === prototype) {
return true;
}
proto = Object.getPrototypeOf(proto);
}
// 5. 查到顶层 Object.prototype 仍未匹配
return false;
}
// ================= 测试用例 =================
console.log(myInstanceOf([], Array)); // true
console.log(myInstanceOf({}, Object)); // true
console.log(myInstanceOf(function(){}, Function)); // true
// 简易写法
function myInstanceOf(obj, constructor) {
const proto = obj.__proto__;
if(!proto) return false;
if(proto === constructor.prototype) {
return true;
}
return myInstanceOf(proto, fn);
}
// ================= 测试用例 =================
console.log(myInstanceOf([], Array)); // true
console.log(myInstanceOf({}, Object)); // true
console.log(myInstanceOf('', String)); // true
console.log(myInstanceOf('', Boolean)); // false要点解析
- 沿着原型链逐级查找,直到命中
fn.prototype或到达null。
7.实现一个发布订阅模式(Event Emitter)
js
class MyEmitter {
#events = {}
constructor() {
this.#events = {};
}
$on(eventName,callback) {
// if(!this.#events[eventName]){
// this.#events[eventName] = [];
// }
// this.#events[eventName].push(callback);
(this.#events[eventName] ??= []).push(callback);
}
$emit(eventName, ...args){
if(this.#events[eventName]) {
this.#events[eventName].forEach(cb => {
cb(...args);
})
}
}
$off(eventName) {
if (this.#events[eventName]) {
delete this.#events[eventName];
}
}
$once(eventName, callback) {
this.$on(eventName, (...args) => {
callback(...args);
this.$off(eventName);
});
}
}
const bus = new MyEmitter();
bus.$on('on-ok',(payload)=> {
console.log(payload);
});
bus.$emit('on-ok', { name:'张三' });
bus.$emit('on-ok', { name:'李四' });8.手写一个 Promise(并跑 Promise A+ 测试)
js
/**
* 异步执行一个函数
* @param {Function} cb - 回调函数
*/
function runAsyncTask(cb) {
if(typeof cb !== 'function') {
throw new TypeError('cb must be a function');
}
if(typeof queueMicrotask === 'function'){
queueMicrotask(cb);
}else {
setTimeout(() => {
cb();
}, 0);
}
}
// 初始值
const PENDING ='pending';
// 成功
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled';
// 失败
const REJECTED = 'rejected';
class MyPromise {
#promiseStatus = PENDING;
#promiseResult = undefined;
#thenables = [];
constructor(executor) {
const resolve = (data) => {
// if(this.#promiseStatus !== PENDING) return;
// this.#promiseStatus = FULFILLED;
// this.#promiseResult = data;
this.changeStatus(FULFILLED ,data);
}
const reject = (err) => {
// if(this.#promiseStatus !== PENDING) return;
// this.#promiseStatus = REJECTED;
// this.#promiseResult = err;
this.changeStatus(REJECTED, err);
}
try {
executor(resolve, reject);
} catch(err) {
reject(err)
}
}
/**
* 改变Promise状态
* @param {*} status
* @param {*} data
*/
changeStatus(status,data) {
if(this.#promiseStatus !== PENDING) return;
this.#promiseStatus = status;
this.#promiseResult = data;
this.#thenables.forEach(({ onResolve,onReject })=> {
if(status === FULFILLED){
onResolve(data);
} else if(status === REJECTED) {
onReject(data);
}
})
}
/**
* 处理返回Promise
* @param {*} p 新的Promise
* @param {*} x 上一个then回调的返回值
* @param {*} resolve 新的Promise的resolve
* @param {*} reject 新的Promise的reject
*/
#resolvePromise(p, x, resolve, reject) {
if (p === x) {
return reject(new TypeError('Chaining cycle detected for promise #<Promise>'));
}
// 原生/外部 thenable 兼容
if ((x !== null && (typeof x === 'object' || typeof x === 'function'))) {
let then;
try {
then = x.then; // 取 getter 可能抛错
} catch (e) {
return reject(e);
}
if (typeof then === 'function') {
let called = false;
try {
then.call(
x,
y => { if (called) return; called = true; this.#resolvePromise(p, y, resolve, reject); },
r => { if (called) return; called = true; reject(r); }
);
} catch (e) {
if (!called) reject(e);
}
return;
}
}
// 非 thenable
resolve(x);
}
then(onResolve, onReject) {
onResolve = typeof onResolve === 'function' ? onResolve : x => x;
onReject = typeof onReject === 'function' ? onReject : x => {
throw x
}
const p = new MyPromise((resolve,reject)=> {
if(this.#promiseStatus === FULFILLED){
runAsyncTask(()=> {
try {
const x = onResolve(this.#promiseResult)
this.#resolvePromise(p, x, resolve, reject);
// if(x instanceof MyPromise) {
// x.then(res=> resolve(res), err=> reject(err));
// } else {
// resolve(x)
// }
} catch(err) {
reject(err)
}
})
} else if(this.#promiseStatus === REJECTED) {
runAsyncTask(()=> {
try {
const x = onReject(this.#promiseResult);
this.#resolvePromise(p, x, resolve, reject);
// reject(x);
} catch(err) {
reject(err)
}
})
} else {
this.#thenables.push({
onResolve:()=> {
runAsyncTask(()=> {
try {
const x = onResolve(this.#promiseResult);
this.#resolvePromise(p, x, resolve, reject);
// reject(x);
} catch(err){
reject(err);
}
})
},
onReject:()=> {
runAsyncTask(()=> {
try {
const x = onReject(this.#promiseResult);
this.#resolvePromise(p, x, resolve, reject);
// reject(x);
} catch(err){
reject(err);
}
})
}
})
}
})
return p;
}
/**
* catch方法,实际上就是在触发then方法
* 调用then方法,参数1:undefined 参数2:catch传入的cb
*/
catch(onReject) {
return this.then(undefined, onReject);
}
/**
* finally方法
* @param {function} onFinally 成功或者失败,执行的cb
* @returns MyPromise
* 调用then方法,参数1:finally传入的cb 参数2:finally传入的cb
*/
finally(onFinally) {
return this.then(onFinally ,onFinally);
}
/**
* 静态方法,resolve
* 如果传入一个MyPromise实例,则直接返回这个实例,否则返回一个MyPromise实例
* @param {*} value
* @returns MyPromise
*/
static resolve(value){
if(value instanceof MyPromise) {
return value;
}
return new MyPromise((resolve)=> {
resolve(value);
})
}
/**
* 静态方法,reject
* 传入拒绝的原因,通过返回MyPromise,调用reject()方法将错误原因返回
* @param {*} error 拒绝的原因
* @returns MyPromise
* 传入如果是MyPromise实例直接返回,否则包装成MyPromise返回
*/
static reject(error) {
if(error instanceof MyPromise) {
return error;
}
return new MyPromise((undefined,reject)=> {
reject(error);
})
}
/**
* 实现静态race方法
* @param {Array} promiseList 传入一个数组,并返回一个Promise
* @returns MyPromise 返回的 promise 会随着第一个 promise 的敲定而敲定。
* 如果第一个敲定的 promise 被兑现,那么返回的 promise 也会被兑现;如果第一个敲定的 promise 被拒绝,那么返回的 promise 也会被拒绝
*/
static race(promiseList) {
const res = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
if(!Array.isArray(promiseList)) {
throw new TypeError('promiseList must is an array');
}
promiseList.forEach(p=> {
MyPromise.resolve(p).then((res)=> {
resolve(res);
},err=> {
reject(err);
})
})
});
return res;
}
/**
* 实现静态All方法
* @param {Array} promiseList 传入一个数组,并返回一个Promise
* 1.判断传入的参数是否为数组,不是数组的话直接reject('错误信息')
* 2.判断传入的数组是否为空,为空的话直接resolve([])
* 3.遍历传入的数组,将每个promise的返回结果放入一个数组中,并记录已经完成的次数,当完成的次数等于数组的长度时,将数组返回
* 4.处理第一个拒绝,有拒绝的话直接reject(err)
*/
static all (promiseList) {
const r = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
if(!Array.isArray(promiseList)) {
throw new TypeError('promiseList must is an array');
}
if(promiseList.length === 0) {
resolve([]);
}
let count = 0;
const arr = [];
promiseList.forEach((p,index)=> {
MyPromise.resolve(p).then(res=> {
arr[index] = res;
count++;
if(count === promiseList.length) resolve(arr);
},err => {
reject(err);
})
})
})
return r;
}
/**
* 实现静态方法allSettled
* @param {Array} promiseList 传入一个数组,并返回一个Promise
* @returns MyPromise 当所有传入的 Promise 都已敲定时(无论成功或失败),返回的 Promise 将被兑现
* 成功:{ status: 'fulfilled', value: 'success' }, 失败 {status:'rejected',reason:err}
*/
static allSettled(promiseList) {
const r = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
if(!Array.isArray(promiseList)) {
throw new TypeError('promiseList must is an array');
}
if(promiseList.length === 0) resolve([]);
let count = 0;
const arr = [];
promiseList.forEach((p,index)=> {
MyPromise.resolve(p).then(res=> {
arr[index] = {status:'fulfilled', value:res };
},err=> {
arr[index] = { status:'rejected',reason:err }
})
.finally(()=> {
count+=1;
if(count === promiseList.length) {
resolve(arr);
}
})
})
});
return r;
}
/**
* 实现静态方法any
* @param {Array} promiseList 传入一个数组,并返回一个Promise
* @returns MyPromise
* 当有一个 Promise 敲定且敲定值为成功时,返回的 Promise 将被兑现
* 当所有Promise都敲定且都敲定的状态为拒绝时,返回的Promise将被拒绝,并返回error数组
*/
static any(promiseList) {
const r = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {
if(!Array.isArray(promiseList)) {
throw new TypeError('promiseList must is an array');
}
if(promiseList.length === 0) {
resolve(new AggregateError(promiseList,'All promises were rejected'));
}
const errArr = [];
let count = 0;
promiseList.forEach((p,index)=> {
MyPromise.resolve(p).then(res=> {
resolve(res);
},(err)=> {
errArr[index] = err;
count++;
if(count === promiseList.length){
reject(new AggregateError(errArr,'All promises were rejected'));
}
})
})
})
return r;
}
}Promise 实现的要点
- 通过私有字段维护
status/result/thenables,解决多次then与异步回调入队。 runAsyncTask使用queueMicrotask优先,保证微任务语义(A+ 要求异步触发 then 回调)。then中包装返回新的MyPromise,并执行 Promise 解析过程 (#resolvePromise)。
使用 promises-aplus-tests 进行 Promise A+ 测试
1)安装测试工具
bash
npm i -D promises-aplus-tests2)导出你的 Promise 构造器
新建 my-promise-adapter.js(适配器文件,按规范暴露):
js
// my-promise-adapter.js
const MyPromise = require('./path/to/your/MyPromise.js'); // 若是 ESM,请转为 CJS 导出
module.exports = {
deferred: () => {
let resolve, reject;
const p = new MyPromise((res, rej) => {
resolve = res;
reject = rej;
});
return {
p,
resolve,
reject
};
}
};3)运行测试
bash
npx promises-aplus-tests my-promise-adapter.js4)完成测试
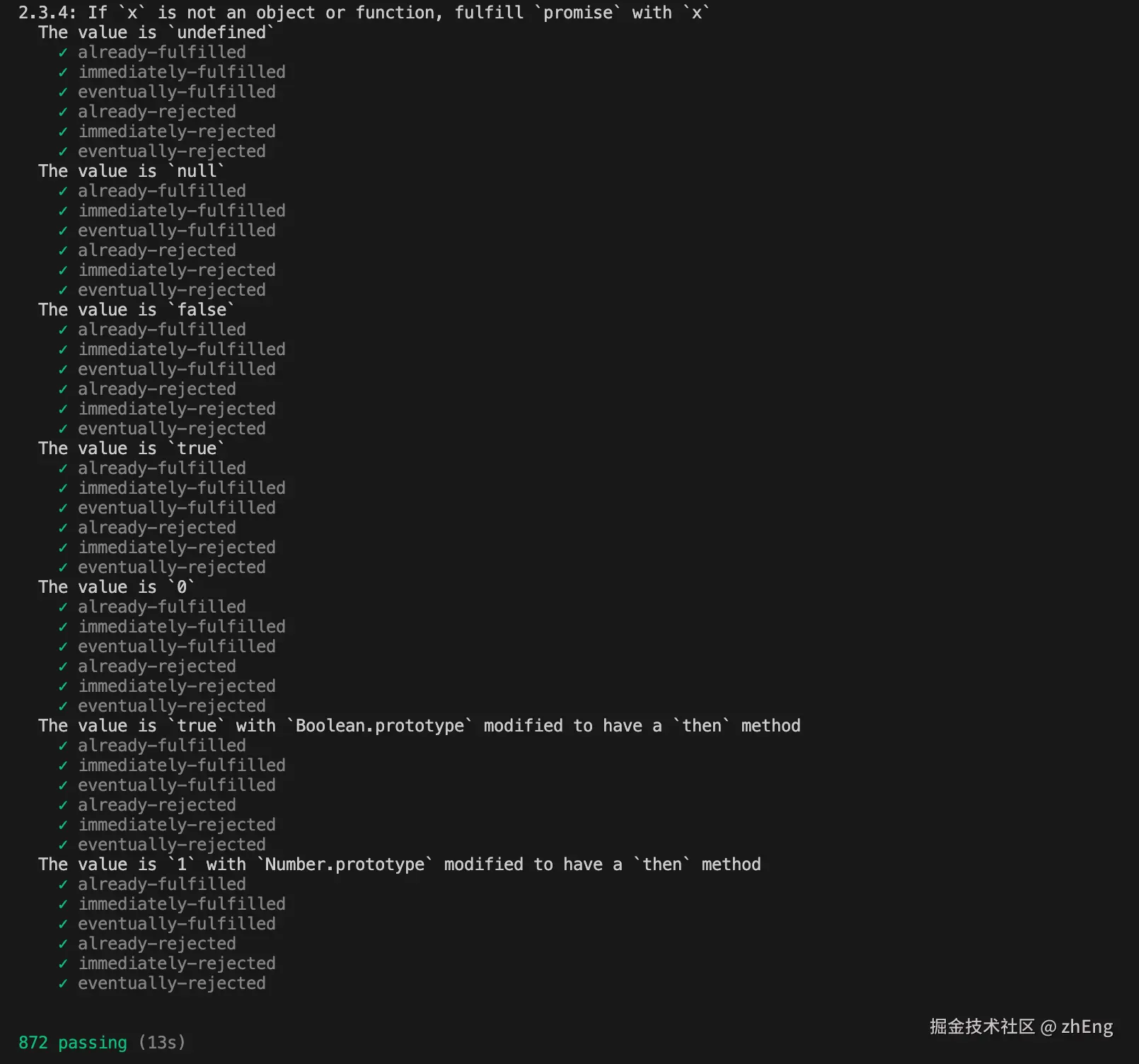
✅ 总结
通过这次的练习,从0实现了 前端开发中高频的 8 个 JavaScript 核心能力 。
在动手实现的过程中,你会发现:
- 防抖与节流 ,本质上是对 函数执行时机的控制;
- call / apply / bind ,考察了
this的绑定机制与函数调用的底层逻辑; - instanceof,实际上就是沿着原型链查找;
- 发布订阅模式,是事件总线和状态管理的基础;
- Promise 的实现,最能考察你对 异步编程、状态机、事件循环 的理解。
这些题目并不仅仅是"面试题",更是写出高质量前端代码的底层能力。