乐观学习,乐观生活,才能不断前进啊!!!
我的主页:optimistic_chen
我的专栏:c语言 ,Java,
Java EE初阶, Java数据结构
欢迎大家访问~
创作不易,大佬们点赞鼓励下吧~
文章目录
IoC思想
前面Spring MVC博客提到过,Spring 是一个开源框架,具体来说:Spring是包含了众多⼯具⽅法的IoC容器,Spring提供了框架,填充框架需要用到众多的IoC容器。
总结一下:Spring是容器,IoC是修饰这个容器的工具。比如:List(数据存储容器),Tomcat(Web容器)
IoC( Inversion of Control 控制反转):我们在前⾯讲到,在类上⾯添加@RestController 和@Controller 注解,就是把这个对象交给Spring管理 ,Spring框架启动时就会加载该类。把对象交给Spring管理,就是IoC思想。
那么就说:Spring是一个"控制反转"的容器。也就是"控制权反转",当需要某个对象时,我们通常去new一个即可,现在有了IoC就不需要自己创建对象,把这个任务交给容器(IoC),程序只需要依赖注⼊(DependencyInjection, DI)就可以了。
|--------------------------------------------|
| 举个例子:在公司中,员工的招聘,解雇等不是老板负责控制,而是老板下放权力给HR来处理 |
传统程序的思路
假如设计一辆汽车时:汽车根据车身设计、车身根据底盘设计、底盘根据车轮设计。

汽车跑起来,要有汽车,汽车要有车身,车身要有底盘,底盘要有车轮;按照这个逻辑写:
java
//车类
public class Car {
private Framework framework;
public Car(Integer size) {
this.framework=new Framework(size);
System.out.println("Car init");
}
public void run(){
System.out.println("car run");
}
}
//车身类
public class Framework {
private Bottom bottom;
public Framework(Integer size){
this.bottom=new Bottom(size);
System.out.println("framework init");
}
}
//底盘类
public class Bottom {
private Tire tire;
public Bottom(Integer size){
this.tire=new Tire(size);
System.out.println("bottom init");
}
}
//车轮类
public class Tire {
int size;
public Tire(Integer size){
this.size=size;
System.out.println("tire init,size:"+size);
}
}再添加一个main就能运行了。现在我们只是对车轮的大小进行了设计,如果需要再添加参数,比如颜色等等。就需要对上面的程序进行修改。

从以上代码可以看出,当底层的代码有改动,那么整个调用链上都要修改,代码耦合度非常高。
IoC程序思路
把创建⼦类的⽅式,改为注⼊传递的⽅式
java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//所有的对象都在这
Tire tire=new Tire(17,2);
Bottom bottom=new Bottom(tire);
Framework framework=new Framework(bottom);
Car car=new Car(framework);
car.run();
}
}现在如果要修改车轮只要修改两个地方就可以了。
我们发现,传统思路是Car控制并创建了Framework,Framework创建并创建了Bottom,依次往下,而IoC是把依赖对象注⼊将当前对象中,依赖对象的控制权不再由当前类控制了
观察下图,是不是控制权反转呢?
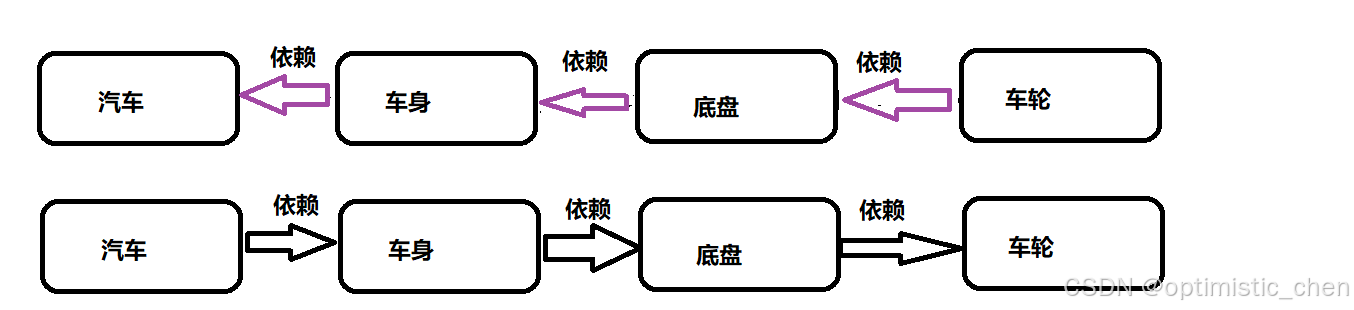
那么这就是控制反转容器,也就是IoC容器:对象交给容器管理

总结:
- 资源集中管理: IoC容器会帮我们管理⼀些资源(对象等),我们需要使⽤时,只需要从IoC容器中去取就可以了
- 我们在创建实例的时候不需要了解其中的细节,降低了使⽤资源双⽅的依赖程度,也就是耦合度.
Bean的存储
在 Spring 中,你不需要自己创建对象,你只需要告诉 Spring,哪些类我需要创建出对象,然后在启动项目的时候 Spring 就会自动帮你创建出该对象,并且只存在一个类的实例。这个类的实例在 Spring 中被称为 Bean。而这种模式,我们称之为"单例模式"。也就是一个类只有一个实例的意思。
那么我如何告诉Spring 哪些类需要创建对象?
- 类注解:@Controller、@Service、@Repository、@Component、@Configuration.
- ⽅法注解:@Bean
Controller(控制器存储)
控制层,接收请求,对请求进行处理,并响应
java
//将对象存储到Spring中
@Controller
public class HelloController {
public void print(){
System.out.println(" do controller");
}
}我们怎么知道这个对象已经成功存在Spring中了呢?如何Spring容器中获取对象?
java
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context=SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
HelloController bean = context.getBean(HelloController.class);
bean.print();
}
}运行程序,成功打印,说明从Spring中获取到了Controller对象,并执行了print方法

获取Bean对象的其他方法
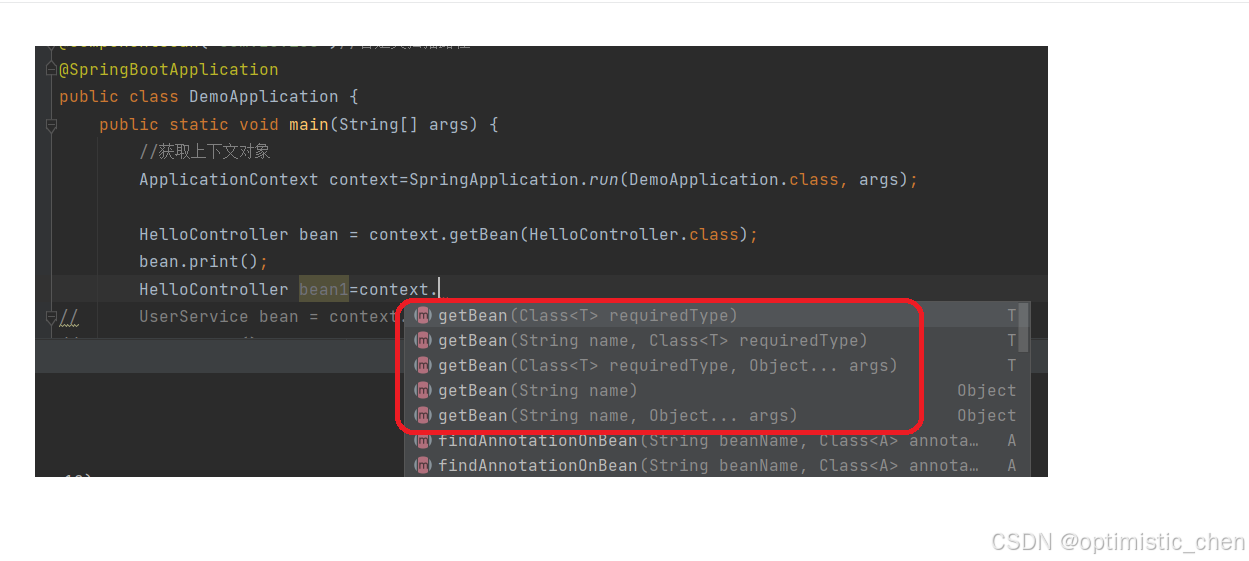
如果Spring面对同一类型存在多个bean,使用上图多个方法进行区分。Spring Bean是Spring框架运行时管理的对象,Spring会给管理的对象起名字(Bean命名约定)。
······命名约定使⽤Java标准约定作为实例字段名.也就是说,bean名称以⼩写字⺟开头,然后使⽤驼峰式⼤⼩写.
······当有多个字符并且第⼀个和第⼆个字符都是⼤写时,将保留原始的⼤⼩写
根据这些方法,我们做出一些示例:
java
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context=SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
//HelloController bean=new HelloController();
HelloController bean=context.getBean(HelloController.class);//根据类型获取对象(适合该类型下该对象只有应该)
bean.print();
HelloController bean2=(HelloController) context.getBean("helloController");//根据对象名获取对象
bean2.print();
HelloController bean3=context.getBean("helloController",HelloController.class);//根据类型和对象名获取对象
bean3.print();
}
}
获取Bean对象这个功能由⽗类BeanFactory提供的

Service(服务存储)
业务逻辑层,处理业务的具体逻辑
java
@Service
public class UserService {
public void print(){
System.out.println("do service");
}
}
java
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取上下文对象
ApplicationContext context=SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
UserService bean = context.getBean(UserService.class);
bean.print();//使用对象
}
}
Component(组件存储)
存
java
@Component
public class UserComponent {
public void print(){
System.out.println("do Component");
}
}读
java
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取上下文对象
ApplicationContext context=SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
UserComponent bean3=context.getBean(UserComponent.class);
bean3.print();
}
}
Repository(仓库存储)
数据访问层,也叫做持久层,负责数据访问操作
java
@Repository
public class UserRepository {
public void print(){
System.out.println("do UserRepository");
}
}
java
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取上下文对象
ApplicationContext context=SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
UserRepository bean2=context.getBean(UserRepository.class);
bean2.print();
}
}
Configuration(配置存储)
配置层,处理项目中的配置信息
java
@Configuration
public class UserConfig {
public void print(){
System.out.println("do Config");
}
}
java
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取上下文对象
ApplicationContext context=SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
UserConfig bean4=context.getBean(UserConfig.class);
bean4.print();
}
}
总结:
观察@Controller / @Service / @Repository / @Configuration四个注解的源码,
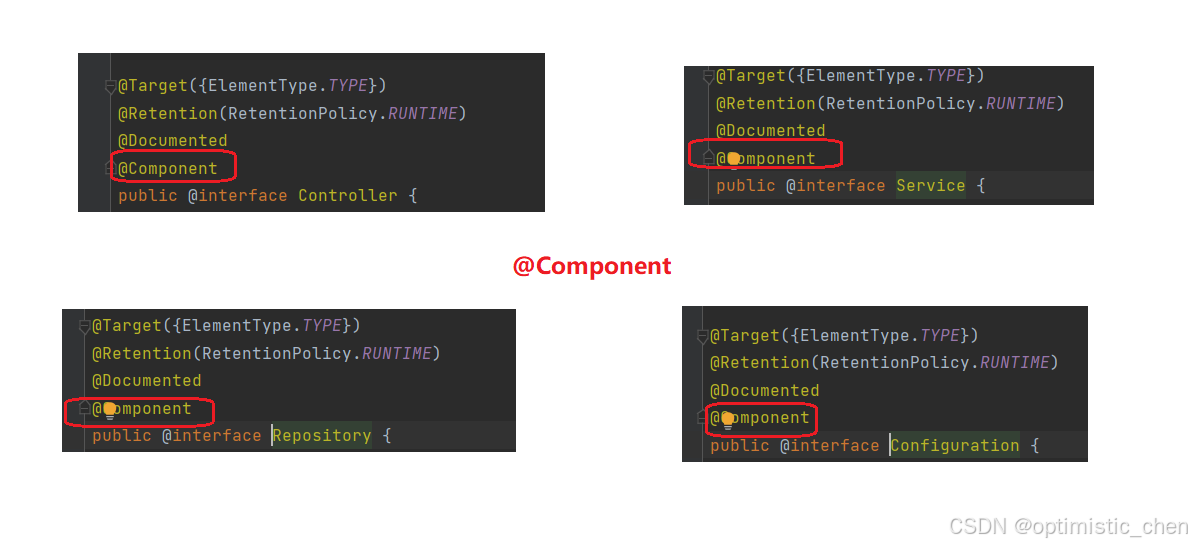
说明它们都是@Component的"子类"
方法注解@Bean
单个对象
java
@Component
public class StudentComponent {
@Bean
public Student student() {
Student student=new Student();
student.setName("zhangsan");
student.setAge(12);
return student;
}
}获取对象
java
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取上下文对象
ApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
Student bean6 = context.getBean(Student.class);
System.out.println(bean6);
}
}⽅法注解要配合类注解使⽤

多个Bean对象
如果有多个Bean对象,我们获取对象的时候应该获取哪个呢?
肯定会报错,Spring不知道要选择哪个,所以需要加@Primary注解
java
@Component
public class StudentComponent {
@Bean
public Student student() {
Student student=new Student();
student.setName("zhangsan");
student.setAge(12);
return student;
}
@Primary
@Bean
public Student student2() {
return new Student("da",13);
}
}
完结
 点一个免费的赞并收藏起来~
点一个免费的赞并收藏起来~
点点关注,避免找不到我~
我的主页:optimistic_chen我们下期不见不散 ~ ~ ~