【LetMeFly】3027.人员站位的方案数 II:简单一个排序O(n^2)------ASCII图解
力扣题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-the-number-of-ways-to-place-people-ii/
给你一个 n x 2 的二维数组 points ,它表示二维平面上的一些点坐标,其中 points[i] = [xi, yi] 。
我们定义 x 轴的正方向为 右 (x 轴递增的方向 ),x 轴的负方向为 左 (x 轴递减的方向 )。类似的,我们定义 y 轴的正方向为 上 (y 轴递增的方向 ),y 轴的负方向为 下 (y 轴递减的方向)。
你需要安排这 n 个人的站位,这 n 个人中包括 Alice 和 Bob 。你需要确保每个点处 恰好 有 一个 人。同时,Alice 想跟 Bob 单独玩耍,所以 Alice 会以 Alice的坐标为 左上角 ,Bob 的坐标为 右下角 建立一个矩形的围栏(注意 ,围栏可能 不 包含任何区域,也就是说围栏可能是一条线段)。如果围栏的 内部 或者 边缘 上有任何其他人,Alice 都会难过。
请你在确保 Alice 不会 难过的前提下,返回 Alice 和 Bob 可以选择的 点对 数目。
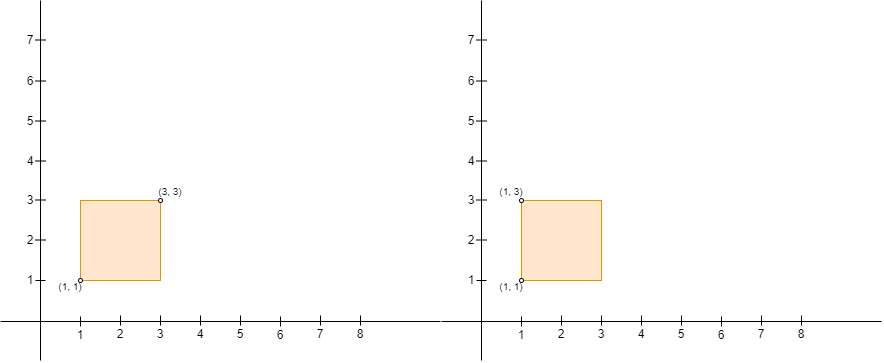
注意 ,Alice 建立的围栏必须确保 Alice 的位置是矩形的左上角,Bob 的位置是矩形的右下角。比方说,以 (1, 1) ,(1, 3) ,(3, 1) 和 (3, 3) 为矩形的四个角,给定下图的两个输入,Alice 都不能建立围栏,原因如下:
- 图一中,Alice 在
(3, 3)且 Bob 在(1, 1),Alice 的位置不是左上角且 Bob 的位置不是右下角。 - 图二中,Alice 在
(1, 3)且 Bob 在(1, 1),Bob 的位置不是在围栏的右下角。
示例 1:
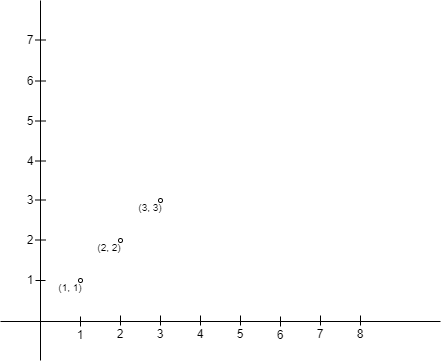
输入:points = [[1,1],[2,2],[3,3]]
输出:0
解释:没有办法可以让 Alice 的围栏以 Alice 的位置为左上角且 Bob 的位置为右下角。所以我们返回 0 。示例 2:
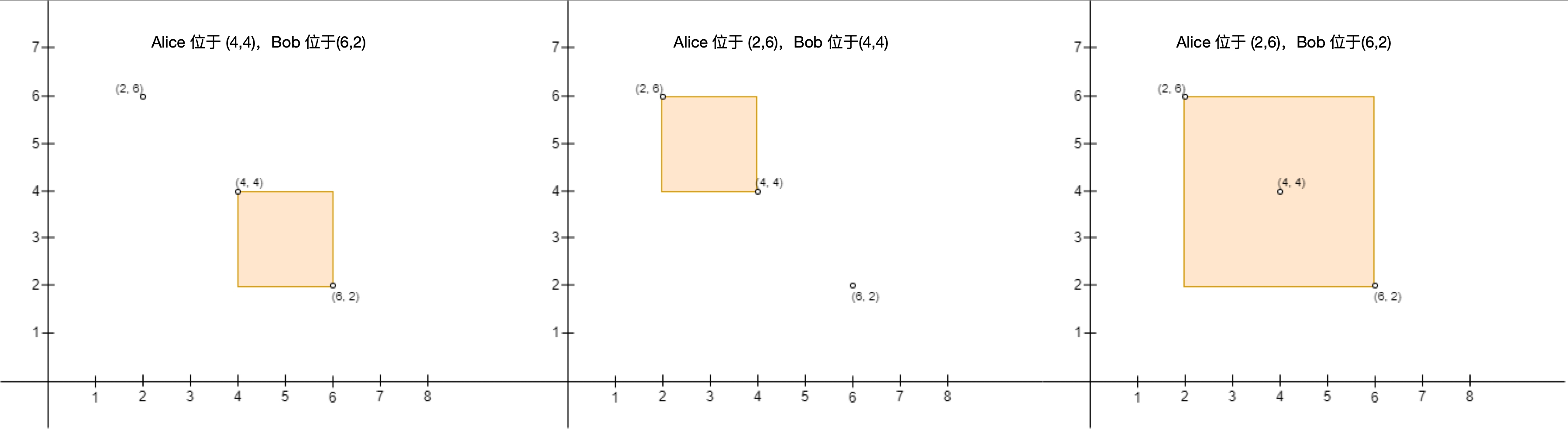
输入:points = [[6,2],[4,4],[2,6]]
输出:2
解释:总共有 2 种方案安排 Alice 和 Bob 的位置,使得 Alice 不会难过:
- Alice 站在 (4, 4) ,Bob 站在 (6, 2) 。
- Alice 站在 (2, 6) ,Bob 站在 (4, 4) 。
不能安排 Alice 站在 (2, 6) 且 Bob 站在 (6, 2) ,因为站在 (4, 4) 的人处于围栏内。示例 3:
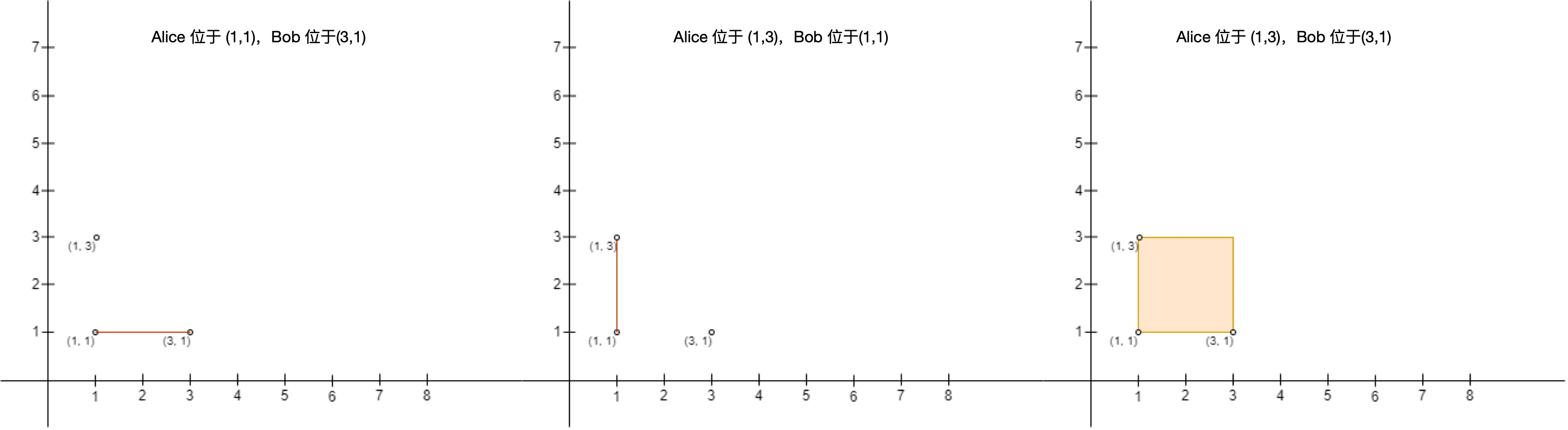
输入:points = [[3,1],[1,3],[1,1]]
输出:2
解释:总共有 2 种方案安排 Alice 和 Bob 的位置,使得 Alice 不会难过:
- Alice 站在 (1, 1) ,Bob 站在 (3, 1) 。
- Alice 站在 (1, 3) ,Bob 站在 (1, 1) 。
不能安排 Alice 站在 (1, 3) 且 Bob 站在 (3, 1) ,因为站在 (1, 1) 的人处于围栏内。
注意围栏是可以不包含任何面积的,上图中第一和第二个围栏都是合法的。提示:
2 <= n <= 1000points[i].length == 2-109<= points[i][0], points[i][1] <= 109points[i]点对两两不同。
解题方法:排序
数据范围是 1 0 3 10^3 103,因此可以二重循环:第一层循环枚举左上角的Alice,第二层循环枚举右下角的Bob,如果可以在O(1)时间内判断出Alice和Bob之间有无第三者,问题就解决了。
很容易想到排个序,最左边为最优先,最上边为次优先。
那么,对于一个Alice,在遍历Bob时,我们只需要使用一个变量mxY记录遍历过的合法Bob中最上边的那个。
↑
| * Bob4
|
| * Alice
| *Bob3
|
| - - - * - - - - - - - - mxY
| Bob1
|
| * Bob2
|
+---------------------------→
↑
当前遍历到例如合法的Bob1会把mxY提高到他的高度,后续所有Bob中(一定在Bob1的右下方),只要低于mxY(如Bob2),那么他和Alice之间一定会存在其他Bob;相反,只要后续Bob高于mxY且不低于Alice(如Bob3),那么他和Alice之间一定没有其他Bob(因为他左边的所有不高于Alice的Bob都比他低)。
而可怜的Bob4,由于他太高了,一定不会处在Alice的下方,不在此Alice的考虑范围内,不参与更新mxY。
别怕,代码很简单,一看就懂了。
- 时间复杂度 O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2)
- 空间复杂度 O ( log n ) O(\log n) O(logn),空间复杂度来自排序
OMG,一个Alice要面试好多个Bob(bushi)
AC代码
Python
python
'''
Author: LetMeFly
Date: 2025-09-05 09:55:20
LastEditors: LetMeFly.xyz
LastEditTime: 2025-09-05 10:35:32
'''
from typing import List
class Solution:
def numberOfPairs(self, points: List[List[int]]) -> int:
points.sort(key=lambda x: (x[0], -x[1]))
ans = 0
for i in range(len(points)):
mxY = -1000000001
for j in range(i + 1, len(points)):
if mxY < points[j][1] <= points[i][1]:
mxY = points[j][1]
ans += 1
return ansPython放前面是因为这次Python更便于理解。
C++
cpp
/*
* @Author: LetMeFly
* @Date: 2025-09-05 09:55:20
* @LastEditors: LetMeFly.xyz
* @LastEditTime: 2025-09-05 10:05:44
*/
class Solution {
public:
int numberOfPairs(vector<vector<int>>& points) {
sort(points.begin(), points.end(), [](const vector<int>& a, const vector<int>& b) {
return a[0] == b[0] ? a[1] > b[1] : a[0] < b[0];
});
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) {
int mxY = -1000000001;
for (int j = i + 1; j < points.size(); j++) {
if (points[j][1] > mxY && points[j][1] <= points[i][1]) {
ans++;
mxY = points[j][1];
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};Java
java
/*
* @Author: LetMeFly
* @Date: 2025-09-05 09:55:20
* @LastEditors: LetMeFly.xyz
* @LastEditTime: 2025-09-05 10:44:46
*/
import java.util.Arrays;
class Solution {
public int numberOfPairs(int[][] points) {
Arrays.sort(points, (a, b) -> a[0] == b[0] ? b[1] - a[1] : a[0] - b[0]);
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < points.length; i++) {
int mxY = -1000000001;
for (int j = i + 1; j < points.length; j++) {
if (points[j][1] > mxY && points[j][1] <= points[i][1]) {
mxY = points[j][1];
ans++;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}Go
go
/*
* @Author: LetMeFly
* @Date: 2025-09-05 09:55:20
* @LastEditors: LetMeFly.xyz
* @LastEditTime: 2025-09-05 10:40:12
*/
package main
import "sort"
func numberOfPairs(points [][]int) (ans int) {
sort.Slice(points, func(i int, j int) bool {
if points[i][0] == points[j][0] {
return points[i][1] > points[j][1]
}
return points[i][0] < points[j][0]
})
for i := range points {
mxY := -1000000001
for j := i + 1; j < len(points); j++ {
if points[j][1] > mxY && points[j][1] <= points[i][1] {
mxY = points[j][1]
ans++
}
}
}
return
}Rust
rust
/*
* @Author: LetMeFly
* @Date: 2025-09-05 09:55:20
* @LastEditors: LetMeFly.xyz
* @LastEditTime: 2025-09-05 10:49:59
*/
impl Solution {
pub fn number_of_pairs(mut points: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 { // 想原地sort points的话记得在points前面加上mut
points.sort_by(|a, b| {
if a[0] == b[0] {
b[1].cmp(&a[1])
} else {
a[0].cmp(&b[0])
}
});
let mut ans: i32 = 0;
for i in 0..points.len() {
let mut mx_y: i32 = -1000000001;
for j in (i+1)..points.len() {
if points[j][1] > mx_y && points[j][1] <= points[i][1] {
mx_y = points[j][1];
ans += 1;
}
}
}
ans
}
}同步发文于CSDN和我的个人博客,原创不易,转载经作者同意后请附上原文链接哦~
千篇源码题解已开源