建议每道题目都只用时30分钟,三十分钟一过,直接开始看答案。不然太浪费时间,很没有必要
49字母异位词分组
解法
class Solution {
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
List<List<String>> arrs=new ArrayList();
int[]signal=new int[strs.length];
for (int i=0;i<strs.length;i++){
if(signal[i]==1){
continue;
}
int l1=strs[i].length();
List<String> arr=new ArrayList();
arr.add(strs[i]);
char[] c1=strs[i].toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(c1);
for(int j=i+1;j<strs.length;j++){
int l2=strs[j].length();
if(l1!=l2) continue;
char[] c2=strs[j].toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(c2);
if(Arrays.equals(c1,c2)){
arr.add(strs[j]);
signal[j]=1;
}
}
arrs.add(arr);
}
return arrs;
}
}其中用到的我不是很熟悉的知识
增强for的用法
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
for(String str : strs){
}字符串的遍历
①字符串的遍历:
// 方法一:使用charAt(i):遍历字符串的每个元素,每个元素是字符的形式
for(int i=0;i < str.length();i++) {
System.out.println(str.charAt(i));
}
//方法二:截取字符串中的每个字符
for(int i=0;i < str.length();i++) {
System.out.println(str.substring(i,i+1));
}
//方法三:将字符串转变成字符数组
char[] c = str.toCharArray();
for(int i=0;i < c.length;i++) {
System.out.println(c[i]);
}
②字符串元素的取代
str.replace("A","B");取代字符串中的为A的元素换成B。
str.replaceAll("A","B");取代str所有的字符串中有A的元素换成B。128最长连续序列
解法
下面是解法,只在存在的连续序列的最大数,才查询此连续序列的个数,别的直接跳过。比如(1,2,3,4)这一组分散在数组各个位置的数字,只在4的位置查询个数,在1,2,3的位置的时候都直接跳过。
如何实现这一点呢,遍历数组,遍历到那个数据(假如是x)的时候,检查x+1是否存在,如果存在,说明如果他是一个比较长的序列的一员的话,他不是最大的,我们直接跳过它,因为我们只在序列最大值的时候去查询连续序列的个数。如果x+1不存在,说明其就是最大的,进行查询。、
如何查询数组中连续序列的个数呢?前面我们确定了一个连续序列的最大值,那么我们只需要确定x-1是否存在,就可以了,然后计数,循环,直到x-1不存在。
为什么只在最大的数字进行查询呢?序列中的任意一个数字,我们对他进行左右两边的查询,都可以找到这个序列的长度,但是,会做很多无用功,这些无用功会让时间复杂度涨到O(n2),就不满足题目要求了。
class Solution {
public int longestConsecutive(int[] nums) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int num : nums) {
set.add(num);
}
int longestNum=0;
for (int num : set) {
if (!set.contains(num +1)) {
int currentNum=1;
int current=num;
while (set.contains(current-1)){
current=current-1;
currentNum+=1;
}
if (currentNum>longestNum){
longestNum=currentNum;
}
}
}
return longestNum;
}
}283移动零

解法:
双指针法
这个解法跟值得借鉴,我目前还没有直接写出这种档次的算法的能力,看的出来这种解法还挺难的。
class Solution {
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
int left=0;
int right=0;
while(right<n){
if (nums[right]!=0) {
int tmp = nums[left];
nums[left] = nums[right];
nums[right] = tmp;
left++;
}
right++;
}
}
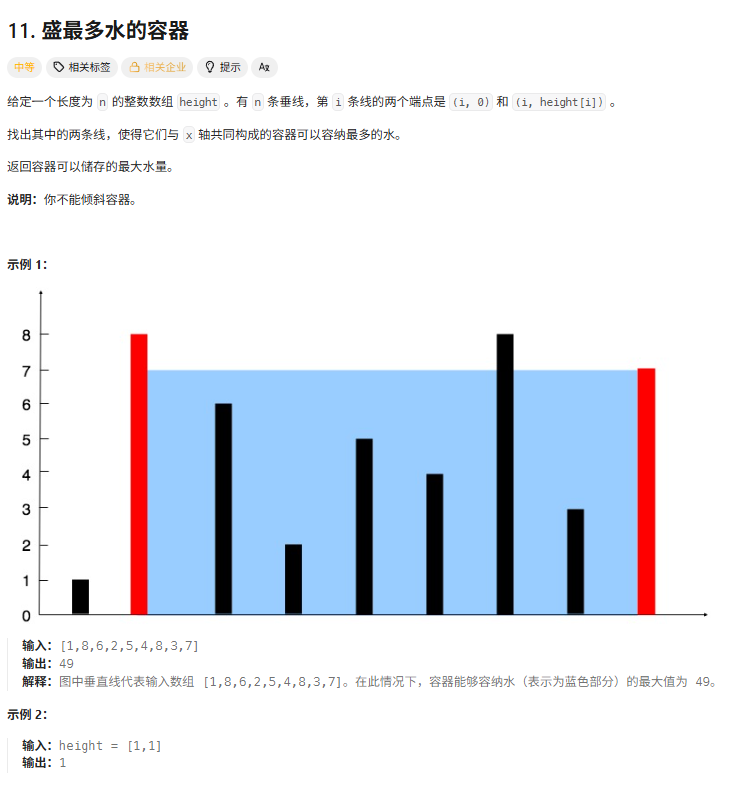
}11盛最多水的容器
解法
双指针法,左右两边各一个指针,每次选择左右两边的指针中较小的那一个,左移或右移,在移动两者中较小的那一个之前,这两个构成的面积肯定是比那个较小的值和别的值相乘更大的,宽乘高,宽最大,高选的是两者中间较小的那一个。这就是这个方法在算法层面的优势。
我之前还用了一些别的方法,时间复杂度都是O(n2),不是内存超限制,就是运行时间超限制。
后面我也将我的,在力扣中点运行成功,但点提交成功不了的代码(一个内存超出,一个运行时间超出)的代码都附在本文中。
正确代码
class Solution {
public int maxArea(int[] height) {
int n =height.length;
int left=0;
int right=n-1;
int max=0;
while(left!=right){
int h=Math.min(height[left],height[right]);
int w=right-left;
int area=h*w;
if(area>max) max=area;
if (height[left]>height[right]){
right--;
}else{
left++;
}
}
return max;
}
}历史代码
报错内存超限制的代码
class Solution {
public int maxArea(int[] height) {
int n=height.length;
int num=(n-1)*n/2;
int[] allSize=new int[num];
int poi=0;
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<=n-1;j++){
int h=Math.min(height[i],height[j]);
int w=j-i;
allSize[poi]=h*w;
poi++;
}
}
int m=0;
for(int i=0;i<num;i++){
if(allSize[i]>m){
m=allSize[i];
}
}
return m;
}
}报错超出时间限制的代码
class Solution {
public int maxArea(int[] height) {
int n=height.length;
int max=0;
int[] allSize=new int[n];
for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){
for(int j=i+1;j<=n-1;j++){
int h=Math.min(height[i],height[j]);
int w=j-i;
allSize[j]=h*w;
}
for(int p=0;p<n;p++){
if(allSize[p]>max){
max=allSize[p];
}
}
}
return max;
}
}15三数之和

解法
这道题目用到双指针的方法,双指针的思想会使得算法的时间复杂度降一个档次,为了确保我真的理解了这个算法,我专门和题解里的代码写的不一样(但是思想是一样的)。
简单讲一下这道题我被卡住的点。我不太理解,那个第二个指针和第三个指针移动的逻辑。123指针指到的数字我们分别记作a,b,c。从小到大排好序的,a从左到右,为最外层循环,b从左到右为a的内层循环,c从右到左为a的内层循环。首先外层a是定的,其次b是定的,我们看c,当a+b+c>0的时候,c--,因为比c小的c说不定有可以令其为0的。当a+b+c=0的时候,就记录。当a+b+c<0的时候,b指针右移。注意全程b在c的左边。然后还有就是不能让b=c也就是不能让b和c指向同一个数字,因为可能会造成nums数组中只出现了一次,但是在最后的结果中却出现了两次的情况。

class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
int n=nums.length;
List<List<Integer>>arrs=new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (i==0||nums[i]!=nums[i-1]){
int third=n-1;
for (int j = i+1; j < n; j++) {
if(j==i+1||nums[j]!=nums[j-1]){
while(j<third&&nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[third]>0){
third--;
}
if(j<third&&nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[third]==0){
List<Integer>arr=new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(arr,nums[i],nums[j],nums[third]);
arrs.add(arr);
}
}
}
}
}
return arrs;
}}历史错误的解法
报错少全零的解法
我在验证新加入的元素是否在集合中已经存在重复的时候,选择使用HashSet的方式,因为哈希表找到元素的时间复杂度最低,但是这是没有必要的,因为我们要验证的只有三个数字,要是数目特别多的话倒是可以考虑这个方法,当然还要再改进一下。我的这个验证的方法,在这里是行不通的,完全行不通的。比如例子中,全零,因为在前面的[-4,0,4]中存在0。所以后面全零,直接就无法通过,肯定是有很多例子都无法通过的。

class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
List<List<Integer>>allThree=new ArrayList();
for(int i=0;i<n-2;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<n-1;j++){
for(int k=j+1;k<n;k++){
int n1=nums[i];
int n2=nums[j];
int n3=nums[k];
if(n1+n2+n3==0){
boolean flag=false;
for(int p=0;p<allThree.size();p++){
Set<Integer>num_set=new HashSet<Integer>();
num_set.add(allThree.get(p).get(0));
num_set.add(allThree.get(p).get(1));
num_set.add(allThree.get(p).get(2));
if(num_set.contains(n1)&&num_set.contains(n2)&&num_set.contains(n3)){
flag=true;
break;
}
}
if(!flag){
List<Integer>three=new ArrayList();
three.add(n1);
three.add(n2);
three.add(n3);
allThree.add(three);
}
}
}
}
}
return allThree;
}
}报错超出时间限制的解法
这一次,优化了验证将要新加入集合的符合条件的集合的方法,出现这个报错,说明,我的算法已经跑通了。出现这个报错的原因是我这个算法的时间复杂度是O(n3),我知道这道题目要用双指针的方法来做,但这是我唯一能想到的方法,在磨了一个点20分钟后,我准备开始看题解了。上一道双指针的方法的题目真的是让我不禁感叹算法的美妙。希望这次的也可以。
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
List<List<Integer>>allThree=new ArrayList();
for(int i=0;i<n-2;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<n-1;j++){
for(int k=j+1;k<n;k++){
int n1=nums[i];
int n2=nums[j];
int n3=nums[k];
int[]nn={n1,n2,n3};
if(n1+n2+n3==0){
boolean flag=false;
for(int p=0;p<allThree.size();p++){
int count=0;
int[]f1=new int[3];
int[]f2=new int[3];
for(int q=0;q<3;q++){
for(int x=0;x<3;x++)
if(allThree.get(p).get(q)==nn[x]&&f1[q]==0&&f2[x]==0){
f1[q]=1;
f2[x]=1;
count++;
}
}
if(count==3)flag=true;
}
if(!flag){
List<Integer>three=new ArrayList();
three.add(n1);
three.add(n2);
three.add(n3);
allThree.add(three);
}
}
}
}
}
return allThree;
}
}42接雨水
解法
我的解法
我的算法思想是,两个指针,一个指针遍历记作a,一个指针寻找合适的值记作b。找a后面比a大的值,找到了就算面积,面积=低*高-中间的黑色小方块。
找不到的情况
判断标准:当b到最后(n-1)的时候也没有找到就说明,a后面没有比他大的了
操作:找a后面最大的数字,算面积(方法和上面的一样)。遍历a后面的数字,找到最大的数字并记下他的下标,然后算面积。并且让a指针,直接指到下标的位置(在代码中采用i=poi-1是因为循环中会i++)这就是我的解法。
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
int n=height.length;
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
boolean flag=false;
boolean fnull=false;
for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++){
if(height[j]>=height[i]){
int b=0;
for(int p=i+1;p<j;p++){
b=b+height[p];
}
int area=height[i]*(j-i-1)-b;
sum=sum+area;
i=j-1;
if(j==n-1)flag=true;
break;
}
if(j==n-1&&height[j]<height[i]){
fnull=true;
}
}
if(fnull){
int imax=0;
int poi=0;
int b=0;
for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++){
if(height[j]>imax||imax==0&&height[j]==0){
imax=height[j];
poi=j;
}
}
for(int p=i+1;p<poi;p++){
b=b+height[p];
}
int area=height[poi]*(poi-i-1)-b;
sum=sum+area;
i=poi-1;
}
if(flag==true)break;
}
return sum;
}
}历史解法
现在还没开始写代码,标着困难,我现在稍有眉目。一直找找到两个数,他们中间的数字都比他们都小,并且后面的数字要大于前面的数字,然后低乘高减去中间侵占的部分的就可以了
具体可以是这样的,遍历数组,第二个指针寻找比第一个指针大的数字,找到了就按上面说的算面积,找不到就定位道剩下的里面最大的。
报错结果偏大的解法
这次错误我感觉是当第二个指针指到最后的时候,没有及时清理掉。

class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
int n=height.length;
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
boolean flag=false;
for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++){
if(height[j]>height[i]){
int b=0;
for(int p=i+1;p<j;p++){
b=b+height[p];
}
int area=height[i]*(j-i-1)-b;
sum=sum+area;
break;
}
}
}
return sum;
}
}报错超出时间限制的方法
出现这个报错,说明~哎不对,通过了4个案例,那还有很大的改进空间。
经过检查我发现是我的imax这个遇到全局最大的值在他后面找不道比他更大的值的时候,寻找后面最大的数的临时变量,我设为0,是不合适的,当最后一个数是0的时候,就会死循环。我准备将其改为-1。
后来发现不是这里的问题,是我在这个位置,将下标和数字搞混了。
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
int n=height.length;
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
boolean flag=false;
boolean fnull=false;
for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++){
if(height[j]>=height[i]){
int b=0;
for(int p=i+1;p<j;p++){
b=b+height[p];
}
int area=height[i]*(j-i-1)-b;
sum=sum+area;
i=j-1;
if(j==n-1)flag=true;
break;
}
if(j==n-1&&height[j]<height[i]){
fnull=true;
}
}
if(fnull){
int imax=0;
int poi=0;
int b=0;
for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++){
if(height[j]>imax){
imax=height[j];
poi=j;
}
}
for(int p=i+1;p<imax;p++){
b=b+height[p];
}
int area=height[poi]*(poi-i-1)-b;
sum=sum+area;
i=poi-1;
}
if(flag==true)break;
}
return sum;
}
}3无重复字符的最长字串

解法
这道题用到了滑动窗口的方法,我的代码和官方给的稍有不同,思想是一样的
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
int n=s.length();
int sum=0;
int j=0;
Set<Character>all=new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(i!=0){
all.remove(s.charAt(i-1));
}
int tsum=all.size();
while(j<n&&!all.contains(s.charAt(j))){
all.add(s.charAt(j));
j++;
tsum++;
}
sum=Math.max(tsum,sum);
}
return sum;
}
}历史解法
没写出来的一个解法
这道题我真的没有思路,浑浑噩噩地写了两个小时还是没有任何的头绪。
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
int numMax=0;
int n=s.length();
char []all=s.toCharArray();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
boolean flag=true;
int j=i+1;
int num=1;
List<Character>check=new ArrayList();
check.add(all[i]);
while(flag){
for(int x=0;x<check.size();x++){
if(j<n){
if(check.get(x)==all[j]){
if(numMax<num)numMax=num;
num=0;
flag=false;
break;
}
check.add(all[j]);
num++;
}
}
j++;
}
if(!flag)continue;
}
return numMax;
}
}438找到字符串中所有字母异位词

解法
历史解法
报错的例子没通过的历史解法
我的这个解法是在判断s和p是否一样的这个地方搞错了。我用的是哈希表,哈希表就无法通过这个p中有重复值的这种例子。然后在让AI帮我排错的时候,不小心将看到答案了,知道了另一种方法。

class Solution {
public List<Integer> findAnagrams(String s, String p) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList();
int np = p.length();
int ns = s.length();
boolean flag = false;
Set<Character> pc = new HashSet();
Set<Character> pcc = new HashSet();
for (int i = 0; i < np; i++) {
pc.add(p.charAt(i));
}
for (int i = 0; i < np; i++) {
pcc.add(p.charAt(i));
}
for (int i = 0; i < ns - np + 1; i++) {
if(flag){
if(s.charAt(i-1)==s.charAt(i+np-1)){
result.add(i);
}else {
flag=false;
pc.add(s.charAt(i-1));
pc.add(s.charAt(i));
i++;
}
}else{
int count=pc.size();
while(count>0){
count--;
int nh=pc.size();
if(pc.contains(s.charAt(i+np-nh))){
pc.remove(s.charAt(i+np-nh));
if(pc.size()==0){
flag=true;
result.add(i);
}
}else{
if(!pcc.contains(s.charAt(i+np-nh))){
i=i+np-nh;
}
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
}560和位K的子数组

解法
这道题我直接做出来了,就两个循环,遍历,每次遍历都要找遍所有的
class Solution {
public int subarraySum(int[] nums, int k) {
int sum=0;
int n=nums.length;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int s=0;
int j=i;
while(j<n){
s=s+nums[j];
j++;
if(s==k){
sum++;
}
}
}
return sum;
}
}239滑动窗口最大值
解法
解法1
此解法在 历史解法\报错超出时间限制的解法2 的基础上做了一些改动。我观察发现,上次的报错超出时间限制的那个例子是一个有很多重复数字的由大到小的一个递减的数列。当每次的上一组的最大值实在上一组的第一个的时候,那这个时间复杂度就还是O(nk),我就在代码上将>变为了>=,就解决了这个问题。同时我有另一个想法,我准备再试一试。
class Solution {
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
int n=nums.length;
int[]result=new int[n-k+1];
int min=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(nums[i]<min)min=nums[i];
}
int fmax=min;
int poi=0;
for(int j=0;j<k;j++){
if(nums[j]>=fmax){
fmax=nums[j];
poi=j;
}
}
result[0]=fmax;
int max=fmax;
for(int i=1;i<n-k+1;i++){
if(poi>i-1&&poi<i+k-1){
if(nums[i+k-1]>=max){
max=nums[i+k-1];
poi=i+k-1;
}
result[i]=max;
}else{
max=min;
for(int j=i;j<i+k;j++){
if(nums[j]>=max){
max=nums[j];
poi=j;
}
result[i]=max;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}历史解法
报错超出时间限制的解法2
这次我优化了比较的部分,我发现当k比较大的时候,当然,当k比较小的时候也是成立的,如果上一组的最大值不是在第一个位置,那么后面那一组,只需要拿最后一个数字和上一组最大的数字比较就可以了比如1231,k=3有两组,第一组最大是3第二组只需要拿1和3比较一下就可以了, 但还是报错,确实有优化的空间,我再优化一下。
class Solution {
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
int n=nums.length;
int[]result=new int[n-k+1];
int min=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(nums[i]<min)min=nums[i];
}
int fmax=min;
int poi=0;
for(int j=0;j<k;j++){
if(nums[j]>fmax){
fmax=nums[j];
poi=j;
}
}
result[0]=fmax;
int max=fmax;
for(int i=1;i<n-k+1;i++){
if(poi>i-1&&poi<i+k-1){
if(nums[i+k-1]>max){
max=nums[i+k-1];
poi=i+k-1;
}
result[i]=max;
}else{
max=min;
for(int j=i;j<i+k;j++){
if(nums[j]>max){
max=nums[j];
poi=j;
}
result[i]=max;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}报错超出最大运行时间的解法
先找到所有的数中最小的,这样就不会在找局部最大数的时候造成不好的影响了。遍历,在局部中找到最大值。
class Solution {
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
int n=nums.length;
int[]result=new int[n-k+1];
int min=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(nums[i]<min)min=nums[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<n-k+1;i++){
int max=min;
for(int j=i;j<k+i;j++){
if(nums[j]>max)max=nums[j];
}
result[i]=max;
}
return result;
}
}76最小覆盖字串

解法
这道题目我是看的题解的思路做的。讲一下我加工过的思路两个map分别记录t和s的含t中字母的个数。检查操作:如果在s的map中发现某个字母小于t的map说明不满足情况。如果不满足情况,就让右指针右移,并且添加到sc的map中,如果满足情况,左指针右移,并减去sc的map中的相应的数量。这就是这道题目的思路。这道题目我做了三天,最后在算法里l和r的指针的移动上也耽误了好久。终于结束了。
class Solution {
Map<Character,Integer>sc=new HashMap();
Map<Character,Integer>tc=new HashMap();
public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
int l=0;
int r=-1;
int ansl=0;
int ansr=-1;
int sn=s.length();
int tn=t.length();
int len=sn;
for(int i=0;i<tn;i++){
char c=t.charAt(i);
tc.put(c,tc.getOrDefault(c,0)+1);
}
while(r<sn){
if(!check()){
r++;
if(r<sn){
char c=s.charAt(r);
if(tc.containsKey(c)){
sc.put(c,sc.getOrDefault(c,0)+1);
}
}
}else{
if(len>=r-l+1){
ansr=r;
ansl=l;
len=r-l+1;
}
char c=s.charAt(l);
if(tc.containsKey(c)){
sc.put(c,sc.getOrDefault(c,0)-1);
}
l++;
}
}
return ansr==-1?"":s.substring(ansl,ansr+1);
}
public boolean check(){
Iterator it=tc.entrySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Map.Entry m=(Map.Entry)it.next();
Character key=(Character)m.getKey();
Integer value=(Integer)m.getValue();
if(value>sc.getOrDefault(key,0)){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}历史解法
报错超出时间限制的解法
思路:将t变为数组,52位,分别对应大小写的26个字母,前26是小写,后26是大写。数值代表个数,当数组清零后说明找到了一个匹配的子串。筛选判断.
class Solution {
public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
//先小写后大写
int[]sc=new int[52];
int[]tcc=new int[52];
int[]zeroArr=new int[52];
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
String minStr="";
int sn=s.length();
int tn=t.length();
//整理tc的特征数组
for(int i=0;i<tn;i++){
if(t.charAt(i)>='a'){
tcc[t.charAt(i)-'a']++;
}else{
tcc[t.charAt(i)-'A'+26]++;
}
}
int min=sn;
for(int i=0;i<=sn-tn;i++){
int j=i;
int []tc=tcc.clone();
while(j<sn&&!Arrays.equals(zeroArr,tc)){
int poi;
if(s.charAt(j)>=97){
poi=s.charAt(j)-'a';
}else{
poi=s.charAt(j)-'A'+26;
}
if(tc[poi]!=0){
tc[poi]--;
}
j++;
}
if(Arrays.equals(zeroArr,tc)&&j-i<=min){
min=j-i;
minStr=s.substring(i,j);
}
}
return minStr;
}
}报错超出时间限制的解法2
我在上次的基础上,添加了一个指针pass。比图t=abc,s=fhghjabc这个例子中,当i=0第一次遍历寻找的时候,显然前面5位永远都不可能有用,用pass记录下来,直接加到i上面,这样就跳过了中间无用的部分,省了好几步。但最后还是报错超出时间限制,我想这是时间复杂度方面的问题。我得好好看看,这些东西了。
经过两分钟思考,我想到了为什么还是报同样的错,我的这个方法在这个错误上没有用处,这个报错的例子t很长,一定是包含了所有的52的大小写字母的,所以我的pass会一直是0。所以我的方法确实被优化了,但是对t很大的情况,是没用的。
class Solution {
public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
//先小写后大写
int[]sc=new int[52];
int[]tcc=new int[52];
int[]zeroArr=new int[52];
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
String minStr="";
int sn=s.length();
int tn=t.length();
//整理tc的特征数组
for(int i=0;i<tn;i++){
if(t.charAt(i)>='a'){
tcc[t.charAt(i)-'a']++;
}else{
tcc[t.charAt(i)-'A'+26]++;
}
}
int min=sn;
for(int i=0;i<=sn-tn;i++){
int j=i;
int []tc=tcc.clone();
boolean f1=false;
//上一轮直到pass的位置都没有t中的字母
int pass=0;
while(j<sn&&!Arrays.equals(zeroArr,tc)){
int poi;
if(s.charAt(j)>=97){
poi=s.charAt(j)-'a';
}else{
poi=s.charAt(j)-'A'+26;
}
if(tc[poi]!=0){
tc[poi]--;
f1=true;
}
if(!f1){
pass++;
}
if(Arrays.equals(zeroArr,tc)&&j==sn-1){
f1=false;
i=i+pass;
}
j++;
}
if(Arrays.equals(zeroArr,tc)&&j-i<=min){
min=j-i;
minStr=s.substring(i,j);
}
}
return minStr;
}
}报错测试没通过但我发现问题的解法
看了题解,没看代码,知道了题解的解题思路之后,想自己实现这个地方,但是一直报错,刚刚我发现了我是错在哪里了。题解思路是左右指针,当包含t中所有指针的时候,左指针右移,当不包含所有的时候,右指针右移。代码就体现这个,但我发现,一直报错,当不包含所有的时候,右指针右移的时候可能会有里面有的数据,我没有算,导致一直没有得到正确的结果。这道题我纠结的时间太久了,我决定不看了,直接看答案。
class Solution {
public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
//先小写后大写
int[]sc=new int[52];
int[]tcc=new int[52];
int[]zeroArr=new int[52];
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
String minStr="";
int sn=s.length();
int tn=t.length();
Set<Character>tch=new HashSet();
//整理tc的特征数组
for(int i=0;i<tn;i++){
tch.add(t.charAt(i));
if(t.charAt(i)>='a'){
tcc[t.charAt(i)-'a']++;
}else{
tcc[t.charAt(i)-'A'+26]++;
}
}
int min=sn;
int a=0;
int b=0;
int[]tc=tcc.clone();
while(b<sn&&a<=b){
if(Arrays.equals(zeroArr,tc)){
if(b-a<min){
min=b-a;
minStr=s.substring(a,b);
}
if(tch.contains(s.charAt(a))){
int poi;
if(s.charAt(a)>=97){
poi=s.charAt(a)-'a';
}else{
poi=s.charAt(a)-'A'+26;
}
tc[poi]++;
}
a++;
}else{
int poi;
if(s.charAt(b)>=97){
poi=s.charAt(b)-'a';
}else{
poi=s.charAt(b)-'A'+26;
}
if(tc[poi]!=0){
tc[poi]--;
}
b++;
}
}
return minStr;
}
}看了答案的算法后仍然出错的解法
class Solution {
Map<Character,Integer>tc=new HashMap();
Map<Character,Integer>sc=new HashMap();
public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
int sn=s.length();
int tn=t.length();
int l=0;
int r=0;
int ansl=0;
int ansr=0;
int len=sn;
boolean flag=false;
for(int i=0;i<tn;i++){
char c=t.charAt(i);
tc.put(c,tc.getOrDefault(c,0)+1);
}
while(r<=sn){
if(check()){
flag=true;
if(r-1<len){
ansl=l;
ansr=r;
len=r-l;
}
if(l>=sn)break;
char cc=s.charAt(l);
if(sc.containsKey(cc)){
sc.put(cc,sc.getOrDefault(cc,0)-1);
}
l++;
}else{
if(r==sn)break;
char cc=s.charAt(r);
if(tc.containsKey(cc)){
sc.put(cc,sc.getOrDefault(cc,0)+1);
}
r++;
}
}
if(flag){
String str=s.substring(ansl,ansr);
return str;
}else{
String str="";
return str;
}
}
public boolean check(){
Iterator<Map.Entry<Character,Integer>>it=sc.entrySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Map.Entry<Character,Integer>m=it.next();
Character key=(Character)m.getKey();
Integer value=(Integer)m.getValue();
if(value<tc.getOrDefault(key,0)){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
class Solution {
Map<Character,Integer>tc=new HashMap();
Map<Character,Integer>sc=new HashMap();
public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
int sn=s.length();
int tn=t.length();
int l=0;
int r=0;
int ansl=0;
int ansr=0;
int len=sn;
boolean flag=false;
for(int i=0;i<tn;i++){
char c=t.charAt(i);
tc.put(c,tc.getOrDefault(c,0)+1);
}
while(r<sn){
if(check()){
flag=true;
if(r-l<len){
ansl=l;
ansr=r;
len=r-l;
}
if(l<sn){
char cc=s.charAt(l);
if(tc.containsKey(cc)){
sc.put(cc,sc.getOrDefault(cc,0)-1);
}
l++;
}
}else{
char cc=s.charAt(r);
if(tc.containsKey(cc)){
sc.put(cc,sc.getOrDefault(cc,0)+1);
}
r++;
}
}
if(flag){
String str=s.substring(ansl,ansr);
return str;
}else{
String str="";
return str;
}
}
public boolean check(){
Iterator<Map.Entry<Character,Integer>>it=sc.entrySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Map.Entry<Character,Integer>m=it.next();
Character key=(Character)m.getKey();
Integer value=(Integer)m.getValue();
if(value<tc.getOrDefault(key,0)){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}53最大子数组和

解法
动态规划
遍历数组,当前若干位的和小于当前位的数的时候,丢弃前面的和。因为你都比我小了,我用你为什么不直接用我当前的这个呢。当最大值比新加入了当前位的数后的前若干位的和小的时候,最大值变为加入了最新的数据后的前若干位的和
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
int sum=0;
int maxsum=nums[0];
for(int num:nums){
if(sum+num>num){
sum=sum+num;
}else{
sum=num;
}
if(sum>maxsum){
maxsum=sum;
}
}
return maxsum;
}
}贪心算法
之前和小于0,就丢弃
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
int max=nums[0];
int sum=0;
for(int num:nums){
if(sum<0){
sum=num;
}else{
sum+=num;
}
if(sum>max){
max=sum;
}
}
return max;
}
}历史解法
报错超出时间限制的解法
我的算法是定义一个遍历指针i,i的元素大于0的时候,开始往后,如果到他后面的若干位的和仍然大于零,接着往下走,并且记录其中的最大值,如果出现从i往后若干位的和小于零的情况,开始从i++。走到超出时间限制这个程度,说明我的算法跑通了。只是他本身不太行。
看了官方题解之后,我发现,我的算法是不完善的贪心算法,我的算法,如果用贪心算法一定不会报这个错误的。
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
int smax=nums[0];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(nums[i]<=0){
if(nums[i]>smax){
smax=nums[i];
}
}else{
int j=i;
int tsum=nums[j];
int tmsum=nums[j];
j++;
while(j<n&&tsum>0||i==j-1&&j==n){
if(j==n){
tsum=nums[j-1];
}else{
tsum=tsum+nums[j];
}
if(tmsum<=tsum){
tmsum=tsum;
}
j++;
if(smax<tmsum){
smax=tmsum;
}
}
}
}
return smax;
}
}56合并区间

解法
先排序,再遍历,遍历到的元素的前项和列表中的最后一个元素的后项做比较,大,就往列表中添加一个新的,小,说明可以和前面那个连成一片,更新列表中的最后一项的前项和后项。这是看了题解的做法做的。
class Solution {
public int[][] merge(int[][] intervals) {
if (intervals.length == 0) {
return new int[0][];
}
Arrays.sort(intervals, new Comparator<int[]>() {
@Override
public int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2) {
return o1[0] - o2[0];
}
});
List<int[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < intervals.length; i++) {
int l = intervals[i][0];
int r = intervals[i][1];
if (list.size() == 0 || l > list.get(list.size()-1)[1]) {
list.add(new int[]{l, r});
} else {
int l1 = list.get(list.size() - 1)[0];
int r1 = list.get(list.size() - 1)[1];
list.set(list.size() - 1, new int[]{Math.min(l, l1), Math.max(r1, r)});
}
}
return list.toArray(new int[list.size()][]);
}
}历史解法
报错解答错误的历史解法
我的这个方法我感觉很乱,哪里少东西我补哪里,就是感觉怪怪的。我准备直接看答案。不在这里纠结了。
class Solution {
public int[][] merge(int[][] intervals) {
int n=intervals.length;
int[]ends=new int[n];
int eM=intervals[0][1];
int sM=intervals[0][0];
int[]starts=new int[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
ends[i]=intervals[i][1];
if(eM<intervals[i][1]){
eM=intervals[i][1];
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
starts[i]=intervals[i][0];
if(sM>intervals[i][0]){
sM=intervals[i][0];
}
}
int len=eM-sM;
int []all=new int[len];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int s=intervals[i][0];
int e=intervals[i][1];
while(s<e){
all[s-sM]=1;
s++;
}
}
int rlen=0;
int p=sM;
while(p<eM){
if(all[p-sM]==1){
rlen++;
while(p<rlen&&all[p-sM]==1){
p++;
}
}else{
while(all[p-sM]==0){
p++;
}
}
}
int [][]result=new int[rlen][2];
int i=0;
int q=sM;
while(q<eM&&i<rlen){
if(all[q-sM]==1){
result[i][0]=all[q-sM];
while(q<rlen&&all[q-sM]==1){
q++;
}
}else{
result[i][1]=all[q-sM];
while(q<rlen&&all[q-sM]==0){
q++;
}
i++;
}
}
return result;
}
}189轮转数组

解法
这道题我用了四个半点的时间做出来。最开始找的那种方法,不到一个点就做出来了,后面的思路有些难以理清。从这道题目中我受益匪浅,没有掌握的知识点有dowhile的用法,还有找到两个数的最大公约数的方法。
class Solution {
public void rotate(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length;
k=k%n;
int c=gcd(n,k);
for(int i=0;i<c;i++){
int curr=i;
int pre=nums[i];
do{
int next=(curr+k)%n;
int tmp=nums[next];
nums[next]=pre;
pre=tmp;
curr=next;
}while(curr!=i);
}
}
public int gcd(int x,int y){
return y>0?gcd(y,x%y):x;
}
}找到两个数的最大公约数的方法
代码如下,之后可以直接定义这个方法,然后直接用就可以,后面有解释的地方,可以帮助理解
public int gcd(int x,int y){
return y>0?gcd(y,x%y):x;
}1. 算法历史与基本思想
欧几里得算法 是历史上最古老的算法之一,出现在欧几里得的《几何原本》(公元前300年左右)。它的目的是求两个整数的最大公约数。
最大公约数 :能同时整除两个数的最大正整数。
例如:gcd(12, 18) = 6,因为6是能整除12和18的最大整数。
2. 算法核心原理
关键定理:
如果 a = b * q + r(其中 q 是商,r 是余数,且 0 ≤ r < b),那么:
gcd(a, b) = gcd(b, r)为什么成立?
- 设
d = gcd(a, b),那么d能整除a和b - 因为
r = a - b * q,所以d也能整除r - 因此
d是b和r的公约数 - 同理,任何能整除
b和r的数也能整除a - 所以
gcd(a, b) = gcd(b, r)
3. 数学推导示例
手动计算 gcd(48, 18):
48 ÷ 18 = 2 余 12 → gcd(48, 18) = gcd(18, 12)
18 ÷ 12 = 1 余 6 → gcd(18, 12) = gcd(12, 6)
12 ÷ 6 = 2 余 0 → gcd(12, 6) = 6另一个例子 gcd(1071, 462):
1071 ÷ 462 = 2 余 147 → gcd(1071, 462) = gcd(462, 147)
462 ÷ 147 = 3 余 21 → gcd(462, 147) = gcd(147, 21)
147 ÷ 21 = 7 余 0 → gcd(147, 21) = 21历史解法
分别开辟了两个总长为n的空间的解法
首先,关于这道题的理解,当k<n的时候,也就是题目描述中给出的那些情况,将后半段和前半段分别存储到一个第三方空间中,再分别复制到nums数组中。当k>n的时候,k=k%n,他是这么算的,这个题目中也没有明说,感觉要是这点他明说的话,可以省去好多时间。
class Solution {
public void rotate(int[] nums, int k) {
int n=nums.length;
if(n!=1&&n>=k){
int []tmp=new int[k];
int[]t=new int[n-k];
for(int i=n-k;i<n;i++){
tmp[i-n+k]=nums[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<n-k;i++){
t[i]=nums[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
nums[i]=tmp[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<n-k;i++){
nums[i+k]=t[i];
}
}else{
k=k%n;
int []tmp=new int[k];
int[]t=new int[n-k];
for(int i=n-k;i<n;i++){
tmp[i-n+k]=nums[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<n-k;i++){
t[i]=nums[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
nums[i]=tmp[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<n-k;i++){
nums[i+k]=t[i];
}
}
}
}优化上面的那个方法
我发现那个条件判断语句可以单独列在前面。
class Solution {
public void rotate(int[] nums, int k) {
int n=nums.length;
if(n!=1&&n>=k){
k=k;
}else{
k=k%n;
}
int []tmp=new int[k];
int[]t=new int[n-k];
for(int i=n-k;i<n;i++){
tmp[i-n+k]=nums[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<n-k;i++){
t[i]=nums[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
nums[i]=tmp[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<n-k;i++){
nums[i+k]=t[i];
}
}
}目标空间复杂度为O(1)但失败的方法
这个方法,我想通过每次直接找到一个数据的准确位置,下一次直接找到被替换的数据的正确位置,这样就可以直接找到所有值的正确位置了。但是最后我发现有一个问题,我没有解决,就是当满足一些条件比如n==2k再比如n=6,k=2(可能是当n可以整除k)的时候,会来回就更新那几个数字,跑不到别的数字上面,就搞得很难受。我觉得再有一些时间我肯定能解决这个问题,但是,这道题我已经看了两个半点了,再看有些不划算了。所以,我准备直接看答案。看这种最优解法。
class Solution {
public void rotate(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length;
if (n != 1 && n >= k) {
k = k;
} else {
k = k % n;
}
int count = 0;
int i = 0;
int tmp;
int t = nums[0];
if (n != 2 * k) {
while (count < n) {
if (n == 2 && k == 2) {
break;
}
int l=n-k-1;
if (i <= l) {
tmp = nums[i + k];
nums[i + k] = t;
t = tmp;
i = i + k;
} else {
tmp = nums[i - n + k];
nums[i - n + k] = t;
t = tmp;
i = i - n + k;
}
count++;
}
} else {
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) {
tmp = nums[j];
nums[j] = nums[j + k];
nums[j + k] = tmp;
}
}
}
}对上面方法的优化
我看题解,看到了找下一个的一个好方法(i+k)%n。这个方法可以直接少了很多条件判断的语句,代码量少了一半,效果还差不多,但是那个陷入局部走不出来的方法还是没有解决。
class Solution {
public void rotate(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length;
if (n != 1 && n >= k) {
k = k;
} else {
k = k % n;
}
int count = 0;
int i = 0;
int tmp;
int t = nums[0];
if(n!=2*k){
while (count < n) {
tmp = nums[(i + k)%n];
nums[(i + k)%n] = t;
t = tmp;
i = (i + k)%n;
count++;
}
}else{
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) {
tmp = nums[j];
nums[j] = nums[j + k];
nums[j + k] = tmp;
}
}
}
}因为while()和do...while()的区别而报错的方法
我看了题解,但是一直做不出来,我总是想如果我完全理解了题解中的方法,那么我不要跟他的方法完全一样。
class Solution {
public void rotate(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length;
k=k%n;
int c=gcd(n,k);
for(int i=0;i<c;i++){
int curr=i;
int pre=nums[i];
while(curr!=i){
int next=(curr+k)%n;
int tmp=nums[next];
nums[next]=pre;
pre=tmp;
curr=next;
}
}
}
public int gcd(int x,int y){
return y>0?gcd(y,x%y):x;
}
}238除自身以外数组的乘积
解法
解法1:构建左右两边的乘积数组
l[0]=1,r[n-1]=1;然后 l[i]=l[i-1]*nums[i-1],r[j]=r[j+1]*nums[j+1]。
class Solution {
public int[] productExceptSelf(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
int[]l=new int[n];
int[]r=new int[n];
int[]result=new int[n];
l[0]=1;
r[n-1]=1;
int i=1;
int j=n-2;
while(i<n){
l[i]=l[i-1]*nums[i-1];
i++;
}
while(j>=0){
r[j]=r[j+1]*nums[j+1];
j--;
}
for(int p=0;p<n;p++){
result[p]=l[p]*r[p];
}
return result;
}
}解法2:空间复杂度为O(1)的解法
将result数组(输出答案的数组)作为L数组,先将l数组求出来,然后定义一个变量r一直更新来代替r数组的功能。
class Solution {
public int[] productExceptSelf(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
int[]result=new int[n];
int i=1;
result[0]=1;
while(i<n){
result[i]=result[i-1]*nums[i-1];
i++;
}
int j=n-2;
int r=nums[n-1];
while(j>=0){
result[j]=result[j]*r;
r=r*nums[j];
j--;
}
return result;
}
}历史解法
报错超出预期时间的解法
遍历数组,当不是当前遍历的元素的时候,找到其他元素的乘积。这种方法的时间复杂度是O(n2),不符合题意。
class Solution {
public int[] productExceptSelf(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
int[]result=new int[n];
int[]muls=new int[n-1];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int mul=1;
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(j!=i){
mul=mul*nums[j];
}
if(j==n-1||i==n-1&&j==n-2){
result[i]=mul;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}41缺失的第一个正数

解法
题解中的置换法
将数组中的每个元素都找到他应该在的位置,比如1的位置应该在0,2的位置应该在1。
然后再遍历数组,位置上没有那个数字的就是缺少的最大正整数。
class Solution {
public int firstMissingPositive(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
while(nums[i]>0&&nums[i]<=n&&nums[i]!=nums[nums[i]-1]){
int tmp=nums[i];
nums[i]=nums[tmp-1];
nums[tmp-1]=tmp;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(i+1!=nums[i]){
return i+1;
}
}
return n+1;
}
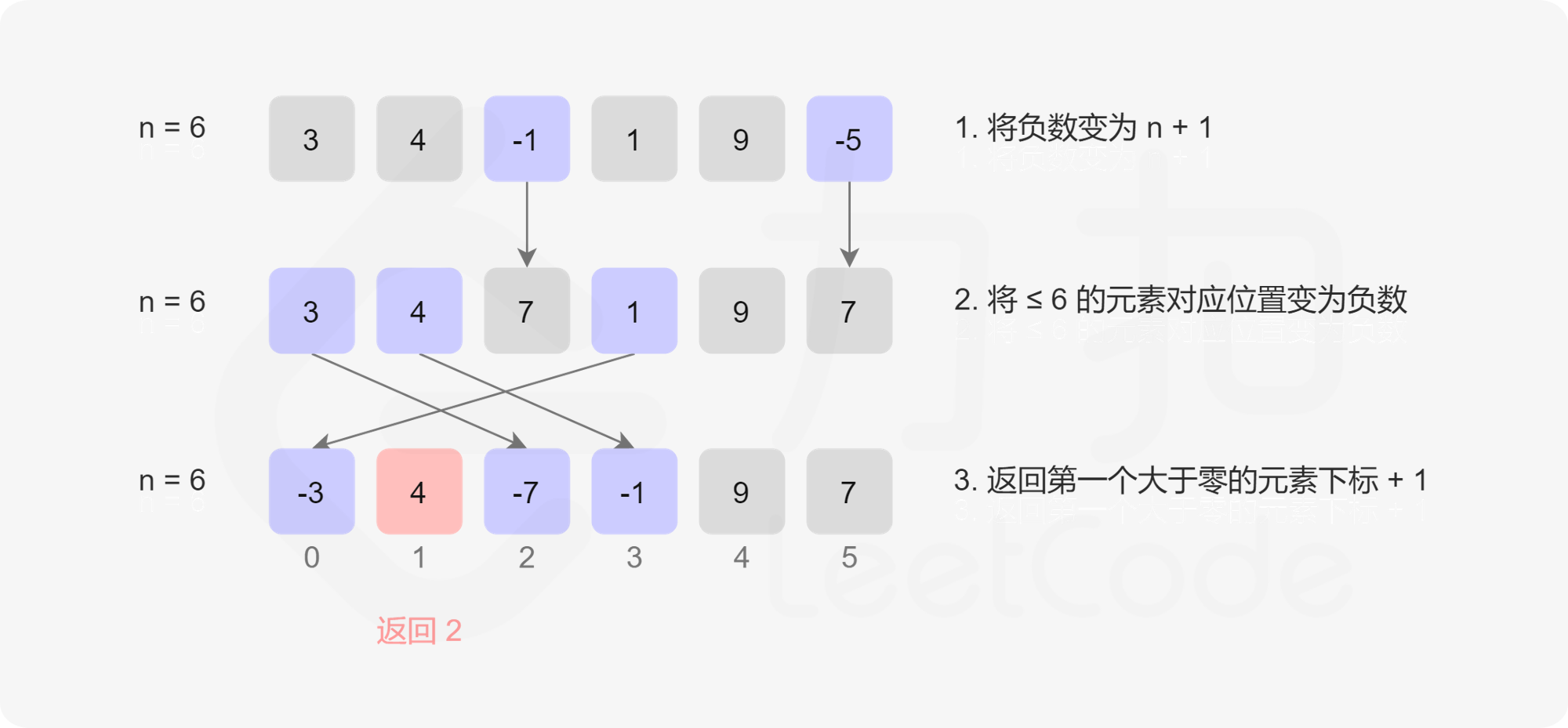
}题解中的标记法
题解中的标记法,首先将数组中所有的负数还有0都置为n+1,因为最小出现的正整数只会是1~n或者n+1的情况。然后再遍历数组,将大于0的元素的值作为下标,将下标的值置为负的这个值,前面我们将本来为负的数全部变成了n+1,本来为负的数组就不会干扰到我们了。下面这张图片很好地诠释了这个方法。
class Solution {
public int firstMissingPositive(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(nums[i]<=0)nums[i]=n+1;
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int tmp=Math.abs(nums[i]);
if(tmp<=n)nums[tmp-1]=0-Math.abs(nums[tmp-1]);
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(nums[i]>0)return i+1;
}
return n+1;
}
}自己写的用哈希表的解法
按理说这个方法不能通过的啊,这种方法的空间复杂度是O(n),但是官方给我通过了,那我就没有办法了。
这道题目我的思路是首先遍历数组,找到最大值的同时,将数组中的每个元素都放到哈希表中,然后再从1开始找到最大值的所有自然数,那个没有再哈希表中,哪个就是我们要找的值。
class Solution {
public int firstMissingPositive(int[] nums) {
HashSet<Integer>h=new HashSet();
int n=nums.length;
int max=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
h.add(nums[i]);
if(nums[i]>max)max=nums[i];
}
for(int i=1;i<max;i++){
if(!h.contains(i))return i;
}
return max+1;
}
}73矩阵置零
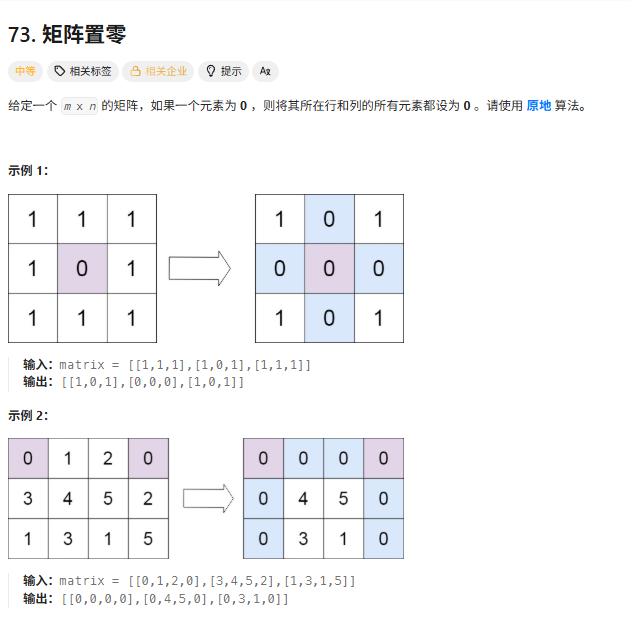
解法
先遍历一遍所有的数组,定义一个行记录数组,和一个列记录数组,如果一个元素为0,将他的行和列数组对应的值变为1,再遍历数组,将行和列数组中为1的地方变为0。
题解中优化的解法:
1:将第一列和第一行作为标记的行和列,再定义两个变量分别标记第一行和第一列原来是否有0的标记
2:只记录第一列的,第一列的第一个元素可以记录第一行中是否有0。这种方法感觉纯纯没事找事,差这一点空间吗?差这一个变量的空间吗?
class Solution {
public void setZeroes(int[][] matrix) {
int ml=matrix.length;
int nl=matrix[0].length;
int[]row=new int[ml];
int[]colnum=new int[nl];
for(int i=0;i<ml;i++){
for(int j=0;j<nl;j++){
if(matrix[i][j]==0){
row[i]=1;
colnum[j]=1;
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<ml;i++){
for(int j=0;j<nl;j++){
if(row[i]==1){
matrix[i][j]=0;
}
if(colnum[j]==1){
matrix[i][j]=0;
}
}
}
}
}历史解法
这道题有点简单,并且题解的做法也还好,不难想到,一下子就做出来了。
54螺旋矩阵
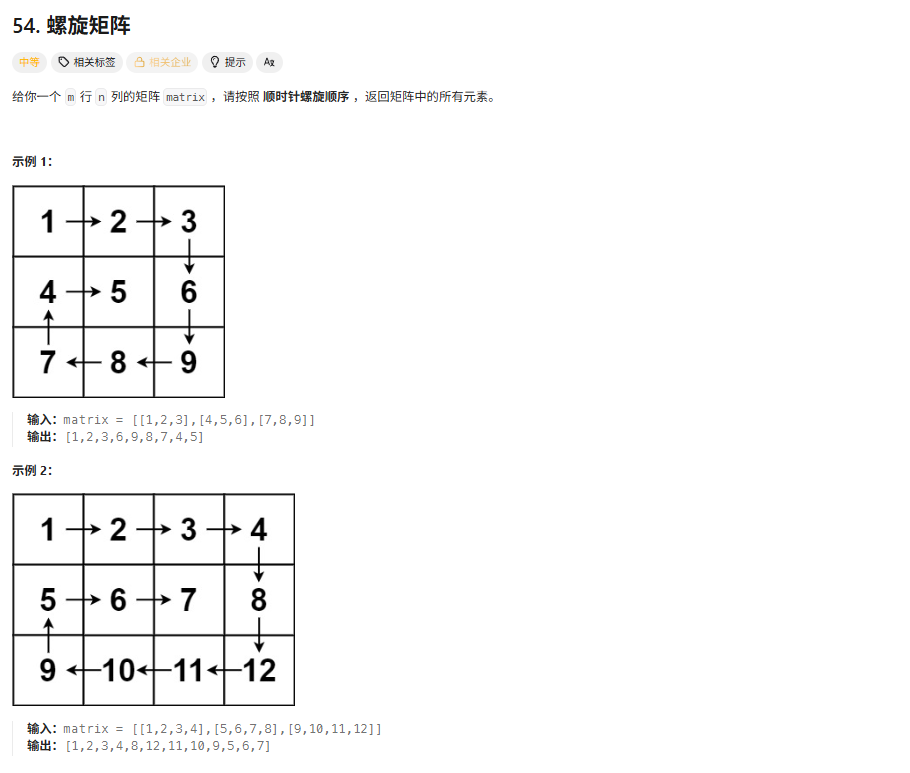
解法
直接将四个边界定义出来,然后 不断缩小这四个边界的范围,就可以得到正确的答案了。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
List<Integer>result=new ArrayList();
int m=matrix.length;
int n=matrix[0].length;
int top=0;int botton=m-1;
int left=0;int right=n-1;
while(top<=botton&&left<=right){
for(int i=left;i<=right;i++){
result.add(matrix[top][i]);
}
top++;
for(int i=top;i<=botton;i++){
result.add(matrix[i][right]);
}
right--;
if(top<=botton){
for(int i=right;i>=left;i--){
result.add(matrix[botton][i]);
}
botton--;
}
if(left<=right){
for(int i=botton;i>=top;i--){
result.add(matrix[i][left]);
}
left++;
}
}
return result;
}
}历史解法
报错边界问题的解法
思路:右下左上,这个顺序依次遍历,但是这个边界的问题我一直找不清楚。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
List<Integer>result=new ArrayList();
int m=matrix.length;
int n=matrix[0].length;
boolean [][]flag=new boolean[m][n];
int r=0;
int c=0;
int pre=1;
int count=0;
int pr=1;
int pun=2;
int pl=3;
int pup=4;
while(count<m*n){
if(pre==1&&c<n-1&&flag[r][c+1]==false||pre==4&&flag[r-1][c]){
flag[r][c]=true;
result.add(matrix[r][c]);
c++;
count++;
}else if(pre==2&&r<m-1&&!flag[r+1][c]||pre==1&&(flag[r][c+1]||c==n-1)){
flag[r][c]=true;
result.add(matrix[r][c]);
r++;
count++;
}else if(pre==3&&c>0&&!flag[r][c-1]||pre==2&&(flag[r+1][c]&&r==m-1)){
flag[r][c]=true;
result.add(matrix[r][c]);
c--;
count++;
}else if(pre==4&&r>0&&!flag[r-1][c]||pre==3&&(flag[r][c-1]||c==0)){
flag[r][c]=true;
result.add(matrix[r][c]);
r--;
count++;
}else{
result.add(matrix[r][c]);
count++;
}
}
return result;
}
}48旋转图像
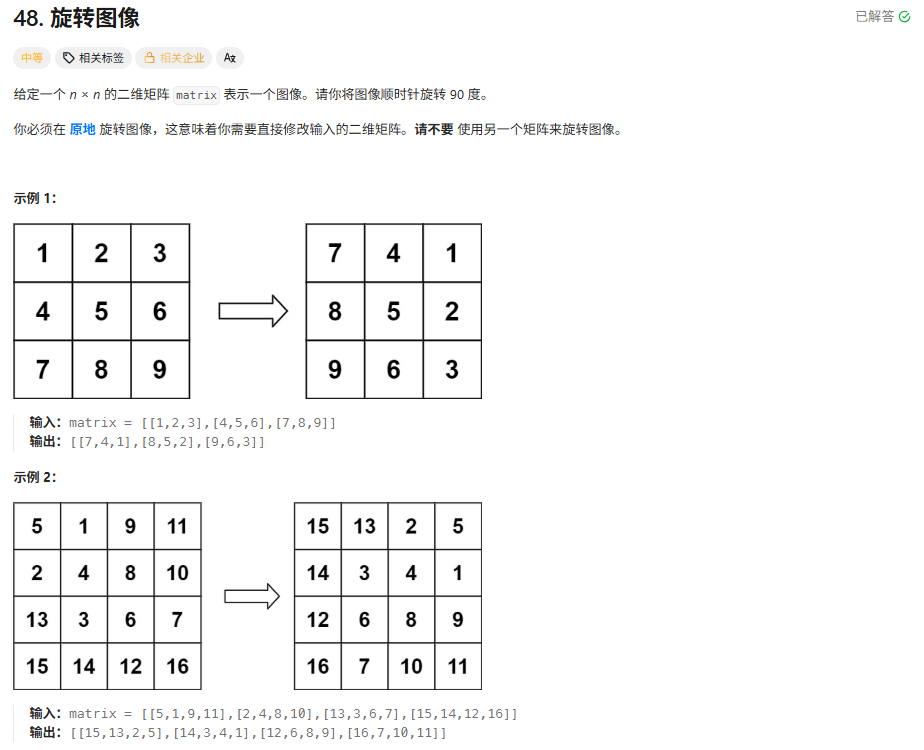
解法
通过观察我发现,旋转后的矩阵和旋转前的矩阵的是:前(x,y)------>后(y,n-1-x)。copy一个矩阵,然后在原来的矩阵上按着这个规律改就可以了。
class Solution {
public void rotate(int[][] matrix) {
int n=matrix.length;
int[][]copy=new int[n][n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
copy[i][j]=matrix[i][j];
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
matrix[j][n-1-i]=copy[i][j];
}
}
}
}74搜索二维矩阵
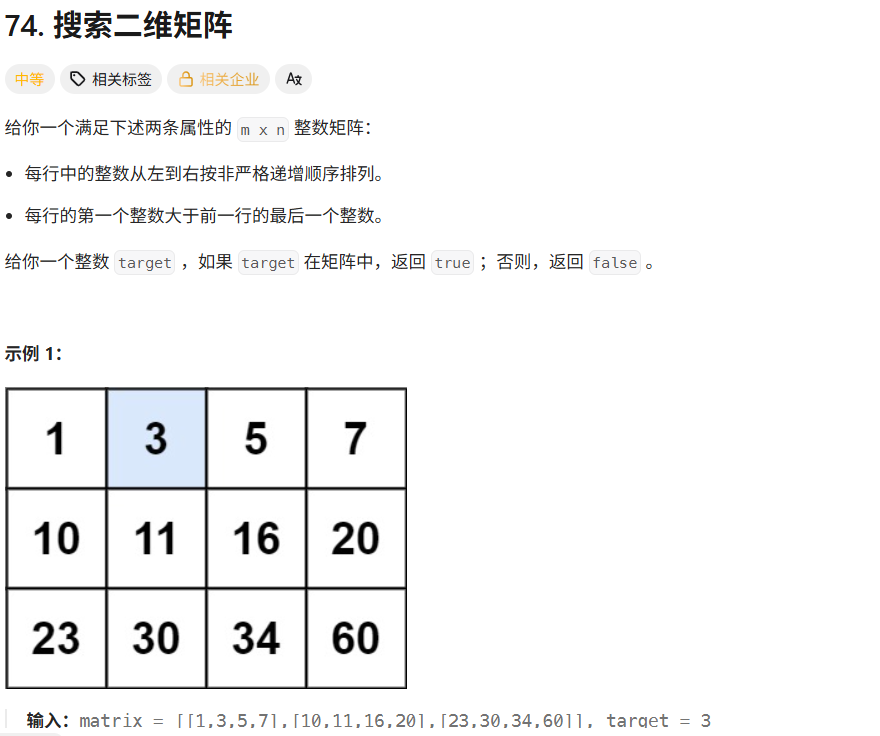
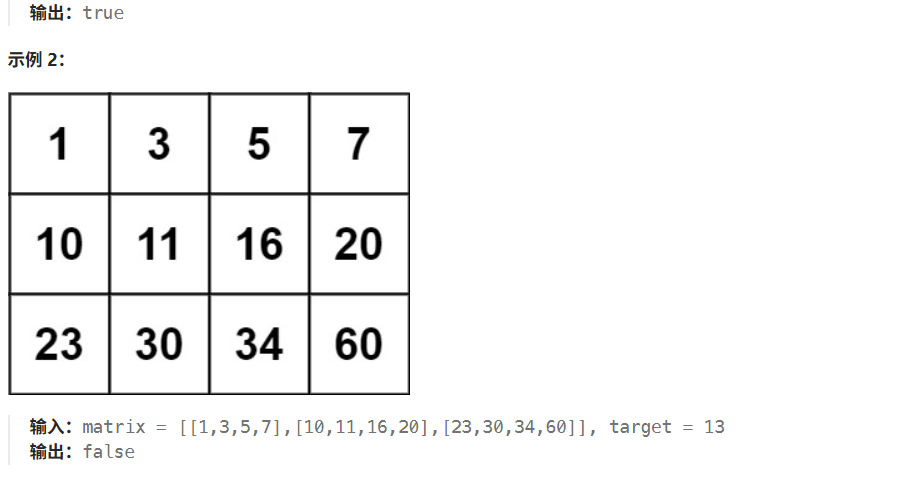
解法
自己的二分查找的方法
先查找每组的第一个元素,找到目标值在的那一行,再在这一行里面再用二分查找,找到对应的值。
class Solution {
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
int lowo=0;
int higho=matrix.length-1;
int mido=0;
while(lowo<=higho){
mido=(lowo+higho)/2;
if(matrix[mido][0]<=target){
lowo=mido+1;
}else{
higho=mido-1;
}
}
int low=0;
int high=matrix[0].length-1;
int mid=0;
if(higho<0)return false;
while(low<=high){
mid=(low+high)/2;
if(matrix[higho][mid]==target){
return true;
}else if(matrix[higho][mid]<target){
low=mid+1;
}else{
high=mid-1;
}
}
return false;
}
}160相交链表
题目:
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回 null 。
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交**:**
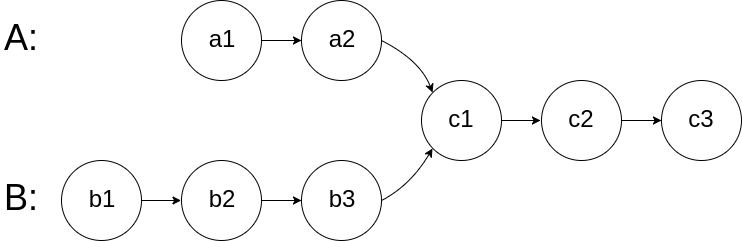
题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意 ,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
自定义评测:
评测系统 的输入如下(你设计的程序 不适用 此输入):
-
intersectVal- 相交的起始节点的值。如果不存在相交节点,这一值为0 -
listA- 第一个链表 -
listB- 第二个链表 -
skipA- 在listA中(从头节点开始)跳到交叉节点的节点数 -
skipB- 在listB中(从头节点开始)跳到交叉节点的节点数
评测系统将根据这些输入创建链式数据结构,并将两个头节点 headA 和 headB 传递给你的程序。如果程序能够正确返回相交节点,那么你的解决方案将被 视作正确答案 。
示例 1:
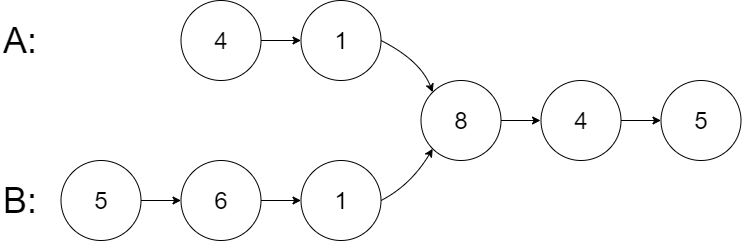
输入: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出: Intersected at '8'
解释: 相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,6,1,8,4,5]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
--- 请注意相交节点的值不为 1,因为在链表 A 和链表 B 之中值为 1 的节点 (A 中第二个节点和 B 中第三个节点) 是不同的节点。换句话说,它们在内存中指向两个不同的位置,而链表 A 和链表 B 中值为 8 的节点 (A 中第三个节点,B 中第四个节点) 在内存中指向相同的位置。
示例 2:
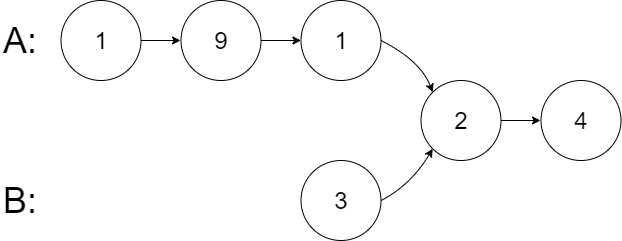
输入: intersectVal = 2, listA = [1,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出: Intersected at '2'
解释: 相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [1,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例 3:
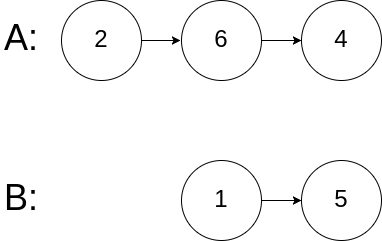
输入: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出: No intersection
解释: 从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。
由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null 。
提示:
-
listA中节点数目为m -
listB中节点数目为n -
1 <= m, n <= 3 * 104 -
1 <= Node.val <= 105 -
0 <= skipA <= m -
0 <= skipB <= n -
如果
listA和listB没有交点,intersectVal为0 -
如果
listA和listB有交点,intersectVal == listA[skipA] == listB[skipB]
解法
两个指针会在第二遍遍历的时候相遇。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if(headA==null||headB==null){
return null;
}
ListNode a=headA,b=headB;
while(a!=b){
a=a==null? headB : a.next;
b=b==null? headA : b.next;
}
return a;
}
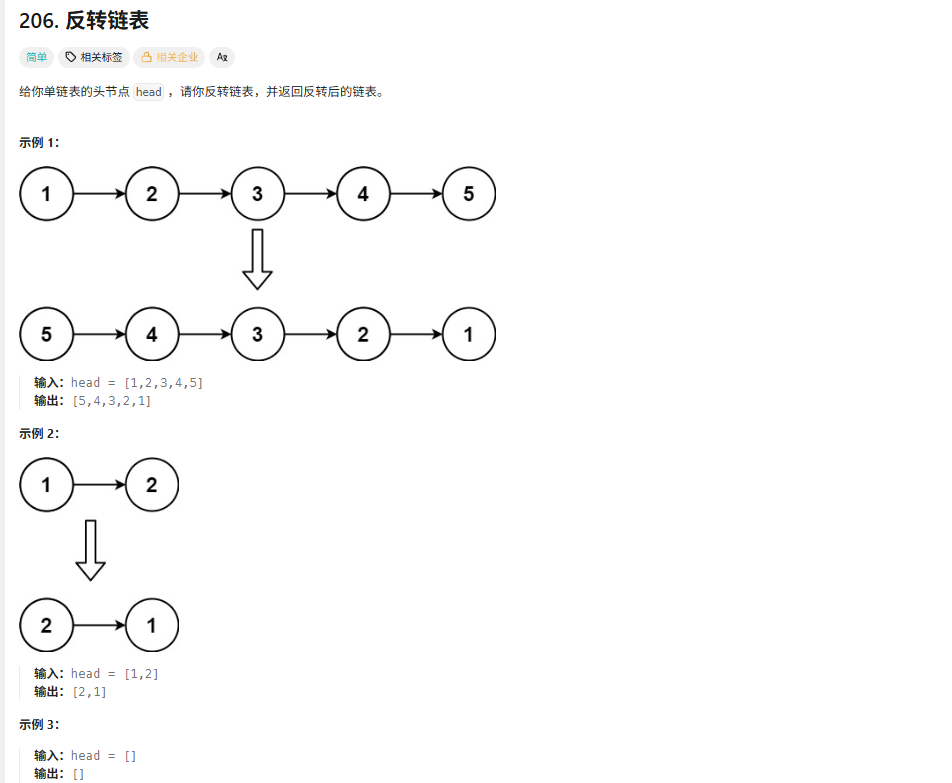
}206反转链表
解法
在原链表的基础上将链表反转的解法
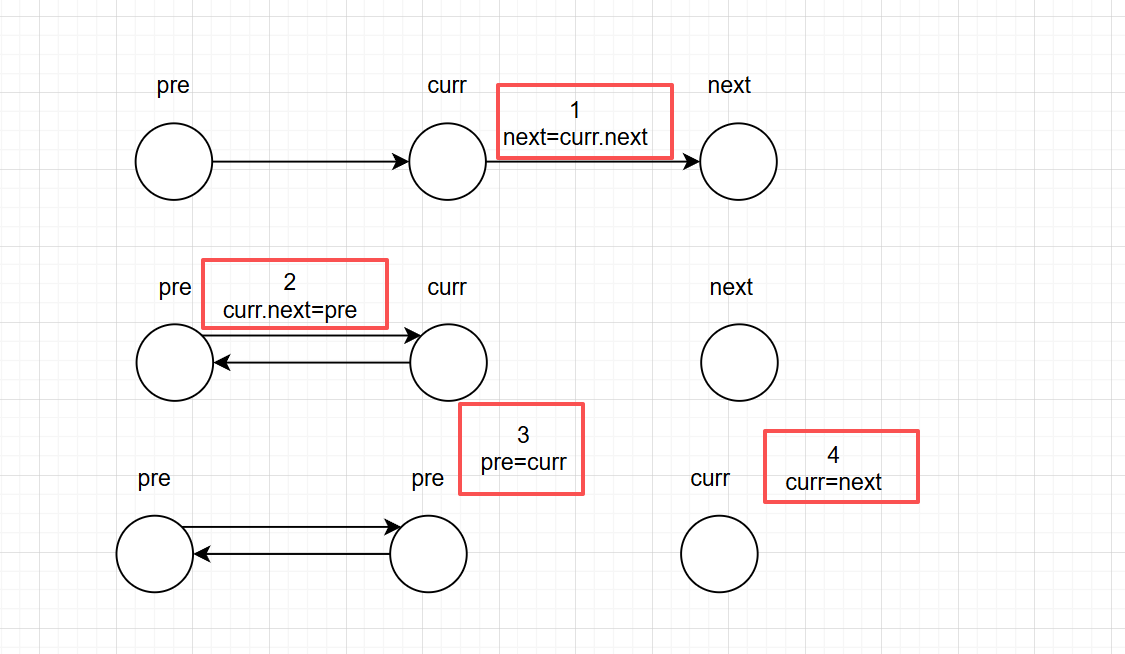
不创建新的节点,直接在原有的基础上反转链表,我画了一张表。这张表清晰地诠释了这个算法的思想。希望可以帮到你
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre=null;
ListNode curr=head;
while(curr!=null){
ListNode next=curr.next;
curr.next=pre;
pre=curr;
curr=next;
}
return pre;
}
}遍历取出所有元素再重新创建新的链表的解法
先遍历链表,将所有的值都收集到一个List集合之中,然后再遍历数组将一个一个创建ListNode对象,然后跟在结果链表的后面就可以了。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null){
return null;
}
ListNode result=new ListNode();
ListNode p=head;
List<Integer>l=new ArrayList();
int n=0;
while(p!=null){
l.add(p.val);
n++;
p=p.next;
}
if(n>0){
ListNode q=result;
n--;
q.val=l.get(n--);
while(n>=0){
ListNode tmp=new ListNode();
tmp.val=l.get(n--);
q.next=tmp;
q=tmp;
}}
return result;
}
}234回文链表

解法
将链表复制到list列表中再列表判断的方法
先将链表复制到list列表中,再两头挤,如果有不一样的,返回false。否则返回true
感觉这道题肯定有更好的方法来做,但是我感觉,我的这个方法已经够了,并且这个方法,很容易就想到了,所以这道题没什么看的。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
ListNode p=head;
List<Integer>li=new ArrayList();
while(p!=null){
li.add(p.val);
p=p.next;
}
int n=li.size();
int f=0;
int r=n-1;
while(f<=r){
if(li.get(f++)!=li.get(r--)){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}141环形链表
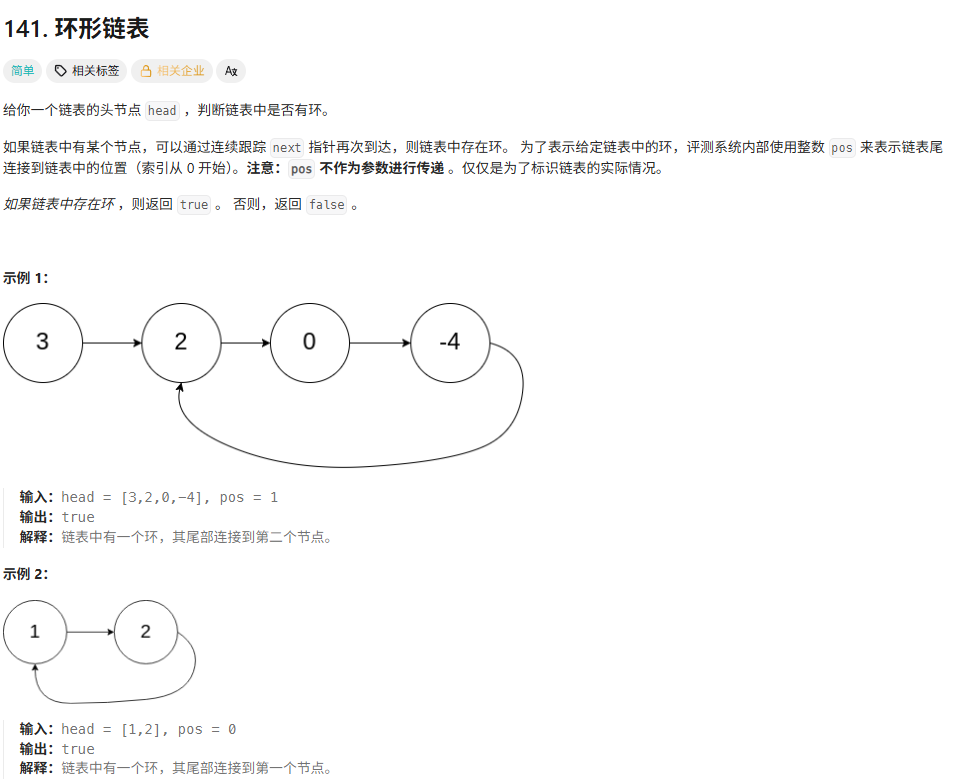
解法
题解中快慢指针的方法
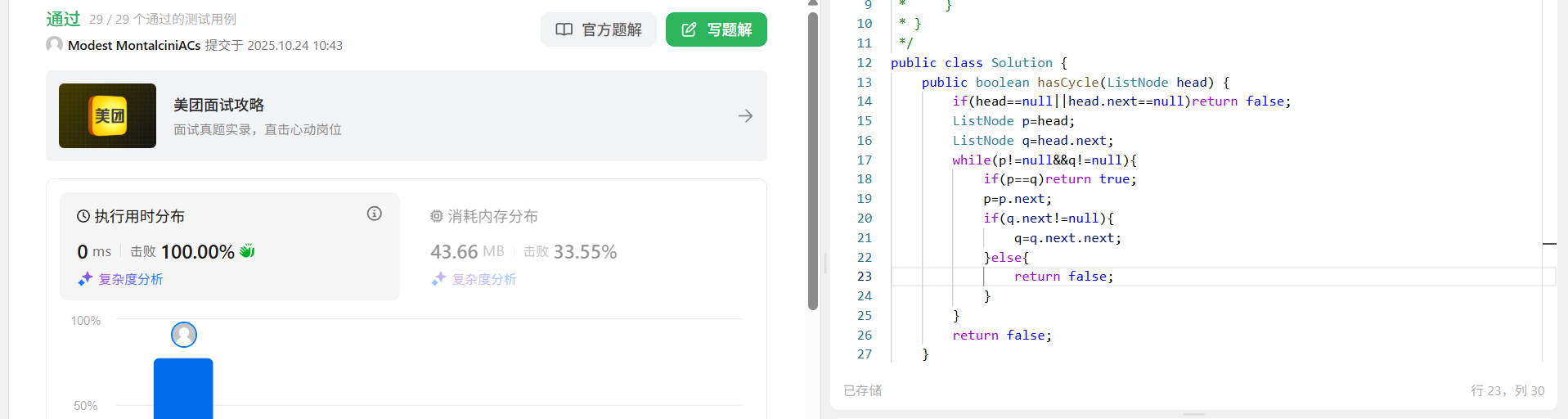
定义一个快指针,一个慢指针,快指针指向head慢指针指向head.next,快指针一次移动两个位置,慢指着一次移动一个位置,这样如果存在环,快指针就一定会跟上慢指针。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null||head.next==null)return false;
ListNode p=head;
ListNode q=head.next;
while(p!=null&&q!=null){
if(p==q)return true;
p=p.next;
if(q.next!=null){
q=q.next.next;
}else{
return false;
}
}
return false;
}
}题解中用哈希表判断元素是否已经访问过的方法
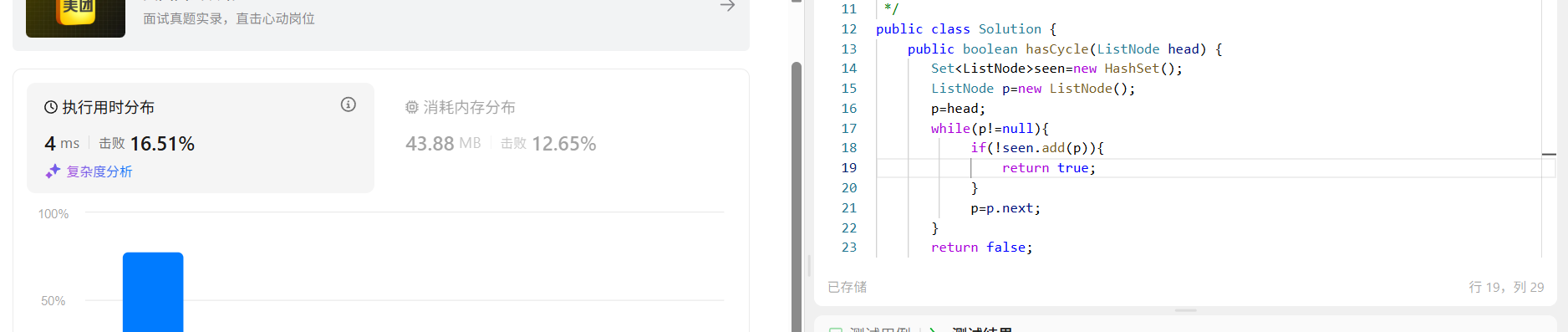
遍历链表,访问一个元素往哈希表里面加一个元素,同时判断这个元素是否访问过(add()这个方法本来就有判断元素是否添加成功的功能。)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
Set<ListNode>seen=new HashSet();
ListNode p=new ListNode();
p=head;
while(p!=null){
if(!seen.add(p)){
return true;
}
head=p.next;
}
return false;
}
}利用链表数目的上限判断
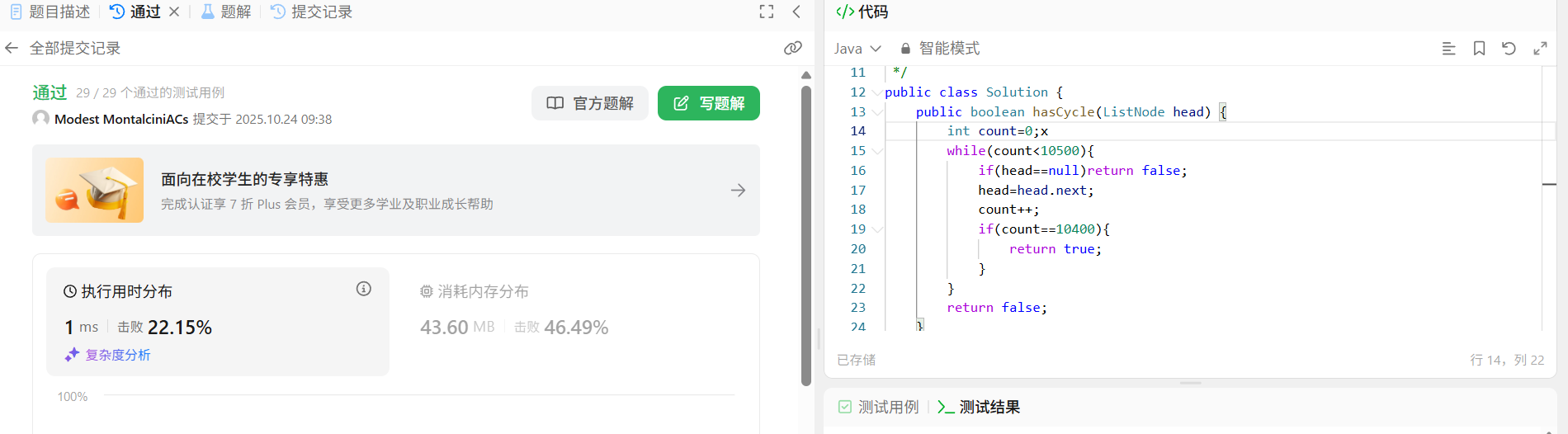
利用链表的数目上限,观察发现链表最多只有10000个元素,如果所以比10000大的数值就可以作为一个判断标准,然后加以判断,但是我觉得这个方法肯定不是正规的方法,应该有更好的方法。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
int count=0;
ListNode p=new ListNode();
p=head;
while(count<10500){
if(p==null)return false;
p=p.next;
count++;
if(count==10400){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}21.合并两个有序链表
解法
定义两个指针,如果哪个指针指的值小,将哪个指针指的值放到新的链表中去。
看了一眼题解,有一个更好的方法,但是我没耐心看了。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode p=list1;
ListNode q=list2;
ListNode r=new ListNode();
ListNode result=new ListNode();
if(p==null){
return q;
}
if(q==null){
return p;
}
if(p!=null&&q!=null){
if(p.val<=q.val){
result.val=p.val;
p=p.next;
}else{
result.val=q.val;
q=q.next;
}
}
r=result;
while(p!=null||q!=null){
ListNode tmp=new ListNode();
if(p!=null&&q!=null){
if(p.val<=q.val){
tmp.val=p.val;
p=p.next;
result.next=tmp;
result=tmp;
}else{
tmp.val=q.val;
q=q.next;
result.next=tmp;
result=tmp;
}
}else if(p==null){
tmp=q;
result.next=tmp;
result=tmp;
q=q.next;
}else if(q==null){
tmp=p;
result.next=tmp;
result=tmp;
p=p.next;
}
}
return r;
}
}2两数相加
解法
题解中的方法
看了题解中的方法,我发现我写代码太乱了,一点都不简便。
题解中的代码的思想和我一摸一样,但是代码中的逻辑是非常明显的,这段代码有很多值得借鉴值得学习的地方。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode head=null,tail=null;
int carry=0;
while(l1!=null||l2!=null){
int n1=l1==null?0:l1.val;
int n2=l2==null?0:l2.val;
int sum=n1+n2+carry;
if(head==null){
head=tail=new ListNode(sum%10);
}else{
tail.next=new ListNode(sum%10);
tail=tail.next;
}
carry=sum/10;
if(l1!=null){
l1=l1.next;
}
if(l2!=null){
l2=l2.next;
}
}
if(carry!=0){
tail.next=new ListNode(1);
tail=tail.next;
}
return head;
}
}参考了题解的自己做出来的用每一位相的解法
每一位直接相加,就像那个加法器,两个底数相加和进位相加,然后记录下进位和底数。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if(l1==null)return l2;
if(l2==null)return l1;
ListNode result=new ListNode((l1.val+l2.val)%10);
ListNode r=result;
boolean flag=false;
int ni=(l1.val+l2.val)/10;
if((l1==null&&l2!=null&&l2.next==null||l2==null&&l1!=null&&l1.next==null||l1!=null&&l2!=null&&l1.next==null&&l2.next==null)&&ni==1){
flag=true;
}
l1=l1.next;
l2=l2.next;
while(l1!=null||l2!=null){
int s=0;
if(l1!=null&&l2!=null){
s=l1.val+l2.val+ni;
}else if(l1==null&&l2!=null){
s=l2.val+ni;
}else if(l2==null&&l1!=null){
s=l1.val+ni;
}
int value=s;
if(s>=10){
value=s%10;
ni=s/10;
}else{
ni=0;
}
ListNode tmp=new ListNode(value);
r.next=tmp;
r=r.next;
if((l1==null&&l2!=null&&l2.next==null||l2==null&&l1!=null&&l1.next==null||l1!=null&&l2!=null&&l1.next==null&&l2.next==null)&&ni==1){
flag=true;
}
if(l1!=null)l1=l1.next;
if(l2!=null)l2=l2.next;
}
if(flag){
ListNode tmp=new ListNode(1);
r.next=tmp;
r=r.next;
}
return result;
}
}历史解法
报错大数溢出的历史解法
经过观察发现,逆序,刚好是一个数字从个位到高位的顺序,先求每个链表代表的数字,再求两个链表的和,再将其从数字变为链表。但是这个过程出现了一个问题,就是大数溢出,遇到的例子是有10个元素的链表,要是100个更表示不了了。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
int s1=0;
int s2=0;
int s=0;
int c1=1;int c2=1;
if(l1==null)return l2;
if(l2==null)return l1;
while(l1!=null){
int mul=1;
for(int i=1;i<c1;i++){
mul=10*mul;
}
s1=s1+mul*l1.val;
c1++;
l1=l1.next;
}
while(l2!=null){
int mul=1;
for(int i=1;i<c2;i++){
mul=10*mul;
}
s2=s2+mul*l2.val;
c2++;
l2=l2.next;
}
s=s1+s2;
ListNode result=new ListNode();
ListNode r=result;
r.val=s%10;
s=s/10;
while(s!=0){
ListNode tmp=new ListNode(s%10);
r.next=tmp;
r=tmp;
s=s/10;
}
return result;
}
}19删除链表的倒数第N个结点
解法
题解的方法
看了一下题解,我发现,我们的思路很像,然后有一点值得借鉴,就是因为删除的只有一个结点,所以不需要将节点后面的部分也加在循环里面。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
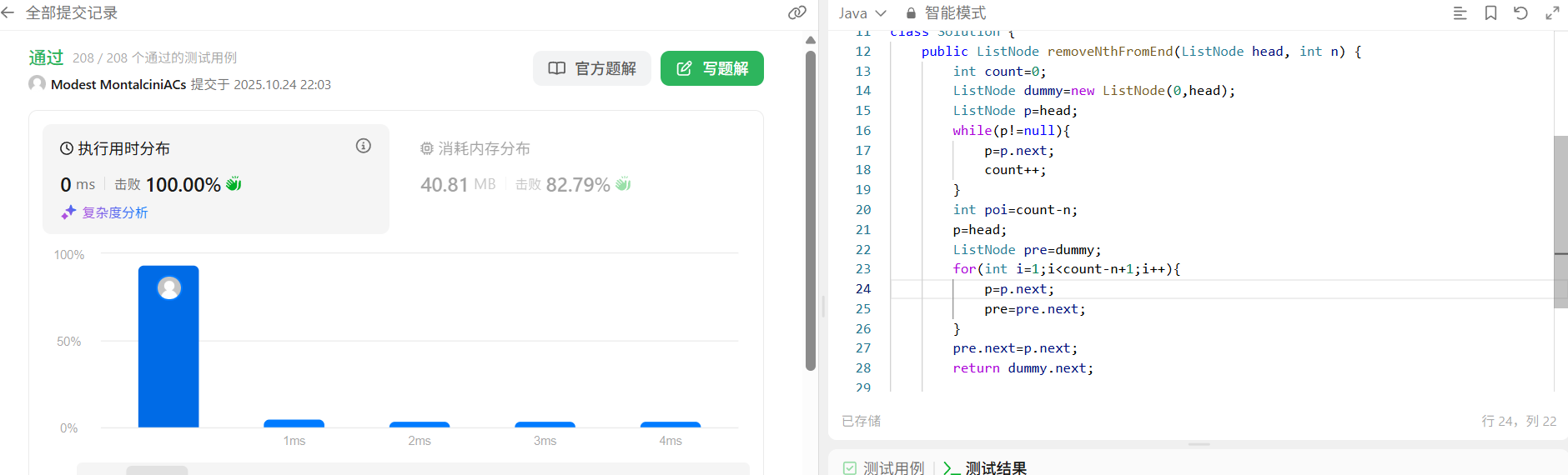
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
int count=0;
ListNode dummy=new ListNode(0,head);
ListNode p=head;
while(p!=null){
p=p.next;
count++;
}
int poi=count-n;
p=head;
ListNode pre=dummy;
for(int i=1;i<count-n+1;i++){
p=p.next;
pre=pre.next;
}
pre.next=p.next;
return dummy.next;
}
}自己做的方法
先遍历一遍得到链表长度,再根据倒数第几个找到确切的坐标,然后定义pre和p指针,一个指向前面的节点,一个指向后面一个的节点,如果到要删除的节点,就删掉具体看代码。
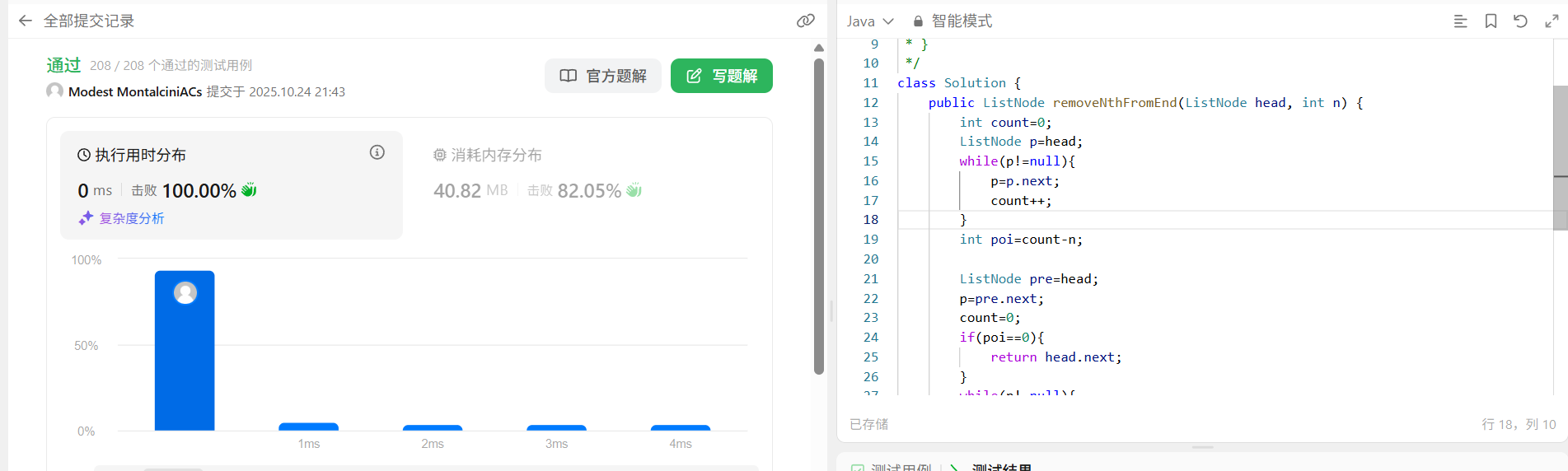
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
int count=0;
ListNode p=head;
while(p!=null){
p=p.next;
count++;
}
int poi=count-n;
ListNode pre=head;
p=pre.next;
count=0;
if(poi==0){
return head.next;
}
while(p!=null){
if(count==poi-1){
pre.next=p.next;
p=pre.next;
}else{
pre=p;
p=p.next;
pre.next=p;
}
count++;
}
return head;
}
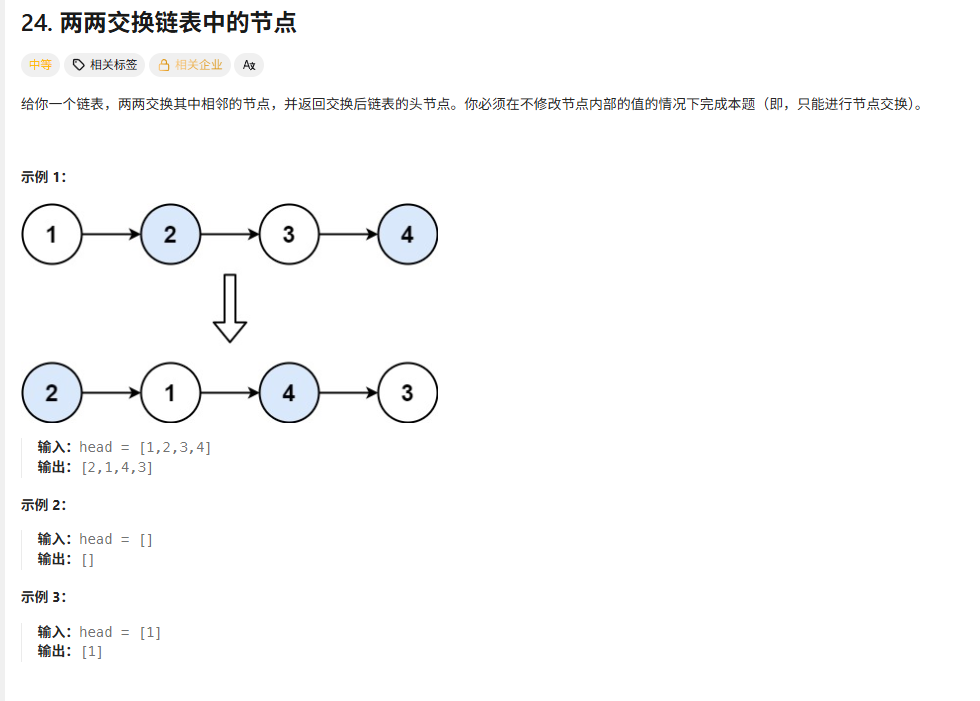
}24两两交换链表中的节点
解法
自己的解法
无敌!!时间超过100%空间超过99.99%
先定义一个dimmy节点(next指向head,为了方便后面的代码书写,这样可以少很多要考虑的情况)
pre前面的节点,p后面的节点,s上一轮的后面的节点。
pre.next=p.next;
p.next=pre;
s.next=p;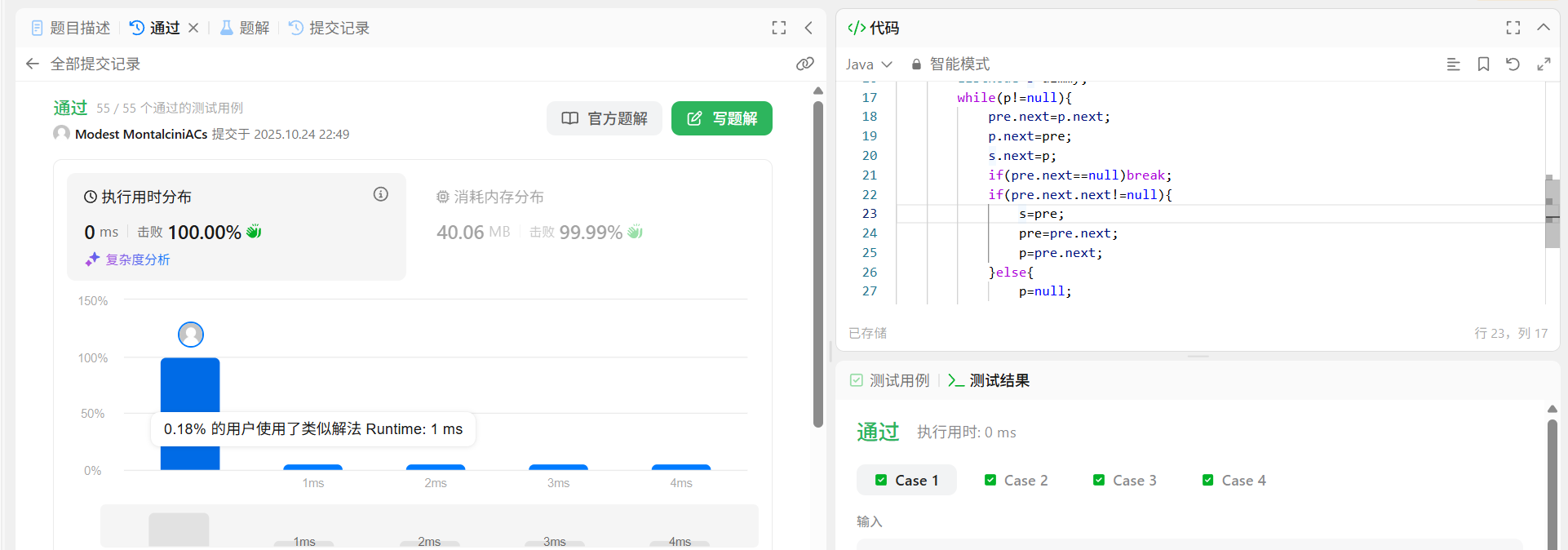
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if(head==null||head.next==null)return head;
ListNode pre=head,p=pre.next;
ListNode dimmy=new ListNode(0,head);
ListNode s=dimmy;
while(p!=null){
pre.next=p.next;
p.next=pre;
s.next=p;
if(pre.next==null)break;
if(pre.next.next!=null){
s=pre;
pre=pre.next;
p=pre.next;
}else{
p=null;
}
}
return dimmy.next;
}
}94二叉树的中序遍历

解法
参考题解的递归方式
本来以为自己可以直接做出来,后来发现做不出来,看了答案,发现要在方法外面再写一个用来递归的方法,怪不得我写不出来。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer>result=new ArrayList();
inOrder(root,result);
return result;
}
public void inOrder(TreeNode root,List<Integer>result){
if(root==null)return;
inOrder(root.left,result);
result.add(root.val);
inOrder(root.right,result);
}
}自己的非递归方法
最后还有30分钟,做道简单题目,撤了,之前就想做这道题目了,但是当时链表这一块不很清晰,现在链表那块题刷了不少,感觉可以做这道题了,一做。我就想起来了,之前做考研辅导,这道题目我给学生讲了好多遍,当时是用c语言写的,当然用的是非递归方式,递归方式太简单了。然后第一次用java写这个算法。
中序遍历,我们让遍历指针一直向左移动,定义一个存放栈,第一次不访问,第二次从栈里弹出的时候再访问,然后让指针向右转。这就是算法思想,这道题我不用看题解,我就是答案!!
25.K个一组翻转链表
解法
题解中的方法
这里要回头过来重新再看一遍,我现在没有耐心了,这道题目我隔了很久才看,现在有点不想看了。
自己的使用回退逻辑的解法
我发现我在判断循环或者条件分支的边界的时候总是会出一些问题。
这道题目我的解法:直接遍历全部节点,在一个交换轮回里,定义一个p指针指向要反转的值,一个r指针,指向要反转的值的前一个元素,这样就可以反转了。然后,发现凑不够k个的时候,直接最后不够的几个再重新反转回来。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode dismmy=new ListNode(0,head);
if(head==null)return head;
if(head.next==null)return head;
ListNode pre =dismmy;
ListNode r=pre.next;
ListNode p=r.next;
int flag=0;
int count=0;
while(p!=null&&flag==0){
count=0;
for(int i=0;i<k-1;i++){
count++;
r.next=p.next;
p.next=pre.next;
pre.next=p;
if(r.next!=null||r.next==null&&i==k-2){
p=r.next;
}else{
flag=1;
r=p.next;
for(int j=0;j<count;j++){
p.next=r.next;
r.next=pre.next;
pre.next=r;
r=p.next;
}
break;
}
}
if(flag==1)break;
pre=r;
if(r.next!=null){
r=r.next;
if(r.next!=null){
p=r.next;
}else{
p=null;
}
}else{
p=null;
}
}
return dismmy.next;
}
}138随机链表的复制

解法
题解解法迭代节点拆分
这个解法我懒得看了,跳过,要是以后有机会,就看看。
题解解法回溯加哈希表
只考虑一个回合的事情,然后用递归的方式。
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
Map<Node,Node>hashNode=new HashMap();
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head==null)return null;
if(!hashNode.containsKey(head)){
Node headNew=new Node(head.val);
hashNode.put(head,headNew);
headNew.next=copyRandomList(head.next);
headNew.random=copyRandomList(head.random);
}
return hashNode.get(head);
}
}自己写的解法
先遍历链表,将所有的链表的值都复制出来,再 再次遍历一遍,将每个节点的random值补上去。
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
Node p=head;
if(head==null)return null;
Node result=new Node(head.val);
Node dismmy=new Node(0,result);
Node q=dismmy;
while(p!=null){
Node tmp=new Node(p.val);
q.next=tmp;
if(p.next!=null){
q=q.next;
}
p=p.next;
}
p=head;
Node r=head;
q=dismmy.next;
while(p!=null&&q!=null){
r=head;
int count =0;
while(r!=null&&r!=p.random){
r=r.next;
count++;
}
//这里的q和p是对应的
Node qq=dismmy.next;
while(qq!=null&&count!=0){
qq=qq.next;
count--;
}
if(q!=null){
q.random=qq;
}
p=p.next;
q=q.next;
}
return dismmy.next;
}
}23合并K个升序链表
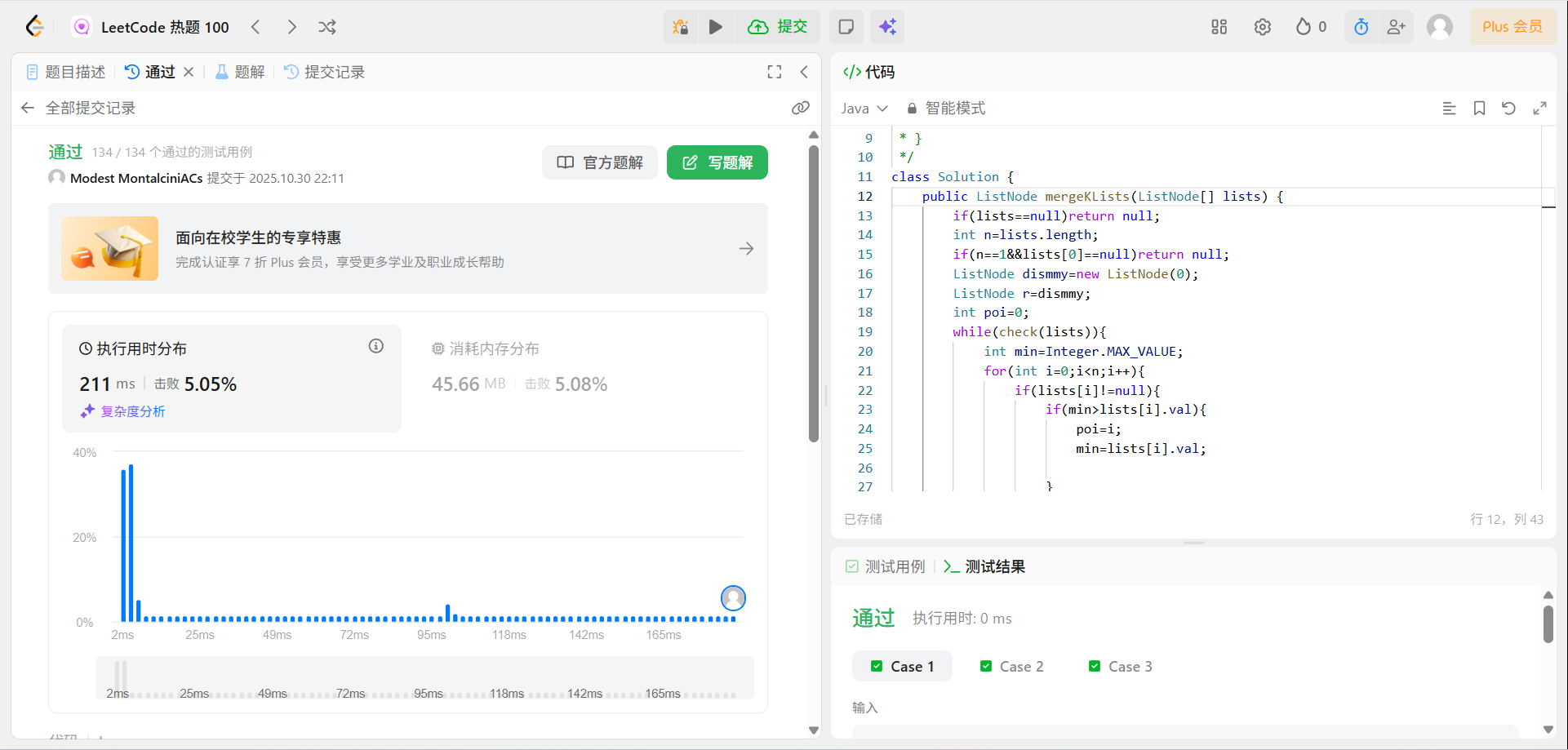
解法
自己写的通过直接遍历的解法
直接遍历每个链表的最小的也就是第一个元素,先找到最小的元素和最小的元素的下标(在lists数组中的位置)然后更新结果链表。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if(lists==null)return null;
int n=lists.length;
if(n==1&&lists[0]==null)return null;
ListNode dismmy=new ListNode(0);
ListNode r=dismmy;
int poi=0;
while(check(lists)){
int min=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(lists[i]!=null){
if(min>lists[i].val){
poi=i;
min=lists[i].val;
}
}
}
lists[poi]=lists[poi].next;
ListNode tmp=new ListNode(min);
r.next=tmp;
r=tmp;
}
return dismmy.next;
}
public boolean check(ListNode[]lists){
int n=lists.length;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(lists[i]!=null)return true;
}
return false;
}
}146LRU缓存

解法
看题解中的答案
class LRUCache {
class dlinknode{
int key;
int value;
dlinknode pre;
dlinknode next;
public dlinknode(){}
public dlinknode(int k,int v){
key=k;
value=v;
}
}
private int size;
private Map<Integer,dlinknode>cache=new HashMap();
private int capacity;
private dlinknode head;
private dlinknode tail;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity =capacity;
this.size=0;
head=new dlinknode();
tail=new dlinknode();
head.next=tail;
tail.pre=head;
}
public int get(int key) {
dlinknode node=cache.get(key);
if(node==null){
return -1;
}else{
moveth(node);
return node.value;
}
}
public void put(int key, int v) {
dlinknode f= cache.get(key);
if(f!=null){
f.value=v;
moveth(f);
}else{
dlinknode node=new dlinknode(key,v);
addHead(node);
cache.put(node.key,node);
if(size>capacity){
dlinknode tail =removeTail();
cache.remove(tail.key);
}
}
}
public void moveth(dlinknode node){
remove(node);
addHead(node);
}
public void addHead(dlinknode node){
head.next.pre=node;
node.next=head.next;
node.pre=head;
head.next=node;
size++;
}
public void remove(dlinknode node ){
node.pre.next=node.next;
node.next.pre=node.pre;
size--;
}
public dlinknode removeTail(){
dlinknode res=tail.pre;
remove(res);
return res;
}
}
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj.get(key);
* obj.put(key,value);
*/历史解法
报错不能用数组来承载的解法
class LRUCache {
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
int[]cap=new int[3*capacity];
for(int i=0;i<3*capacity;i++){
if(i%3!=2){
cap[i]=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}else{
cap[i]=0;
}
}
}
public int get(int key) {
for(int i=0;i<3*capacity;i++){
if(cap[i]==key){
cap[i+2]=0;
return cap[i+1];
}
i++;
i++;
}
return -1;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
boolean flag=false;
int poi=0;
int nullpoi=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i<3*capacity;i++){
if(cap[i]==key){
flag=true;
poi=i;
}
if(cap[i]!=Integer.MAX_VALUE){
nullpoi=i;
}
i++;
i++;
}
if(flag){
//找到了
cap[poi+1]=value;
//最近使用时间更新
for(int j=0;j<3*capacity;j++){
if(cap[j]!=Integer.MAX_VALUE){
cap[j+2]++;
}
}
}else{
//没有找到
//没有爆满
if(nullpoi!=Integer.MAX_VALUE){
cap[nullpoi]=key;
cap[nullpoi+1]=value;
//最近使用时间更新
for(int j=0;j<3*capacity;j++){
if(cap[j]!=Integer.MAX_VALUE){
cap[j+2]++;
}
}
}
//爆满
int poimax=2;
int max=0;
for(int j=0;j<3*capacity;j++){
if(cap[i]!=Integer.MAX_VALUE){
if(cap[i+2]>max){
max=cap[i+2];
poimax=i;
}
}
i++;
i++;
}
cap[poimax]=key;
cap[poimax+1]=value;
cap[poimax+2]=0;
}
}
}
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj.get(key);
* obj.put(key,value);104二叉树的最大深度
解法
题解中的广度优先搜索方法
好长,懒得看,回头有机会再看。
题解中的使用递归的解法
题解中的递归解法,和我的几乎一样,不一样的是我用的是if...else判断。题解中直接用Math.max来判断,显然题解中的更加简洁。值得学习
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root!=null){
int l= maxDepth( root.left);
int r= maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(l,r)+1;
}else{
return 0;
}
}
}自己写的用递归的思想
将每一个节点和他的左右孩子作为一个系统,如果左孩子的最大深度比右孩子的大,就返回左孩子的最大深度为自己的最大深度,如果右孩子的最大深度更大,就返回右孩子的。如果节点为null,直接返回0。这样就不影响了。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root!=null){
int l= maxDepth( root.left);
int r= maxDepth(root.right);
if(l>=r){
return l+1;
}else{
return r+1;
}
}else{
return 0;
}
}
}本题目中值得学习的点
这行代码可以替代下面的好多行代码
return Math.max(l,r)+1;
if(l>=r){
return l+1;
}else{
return r+1;
}148排序链表
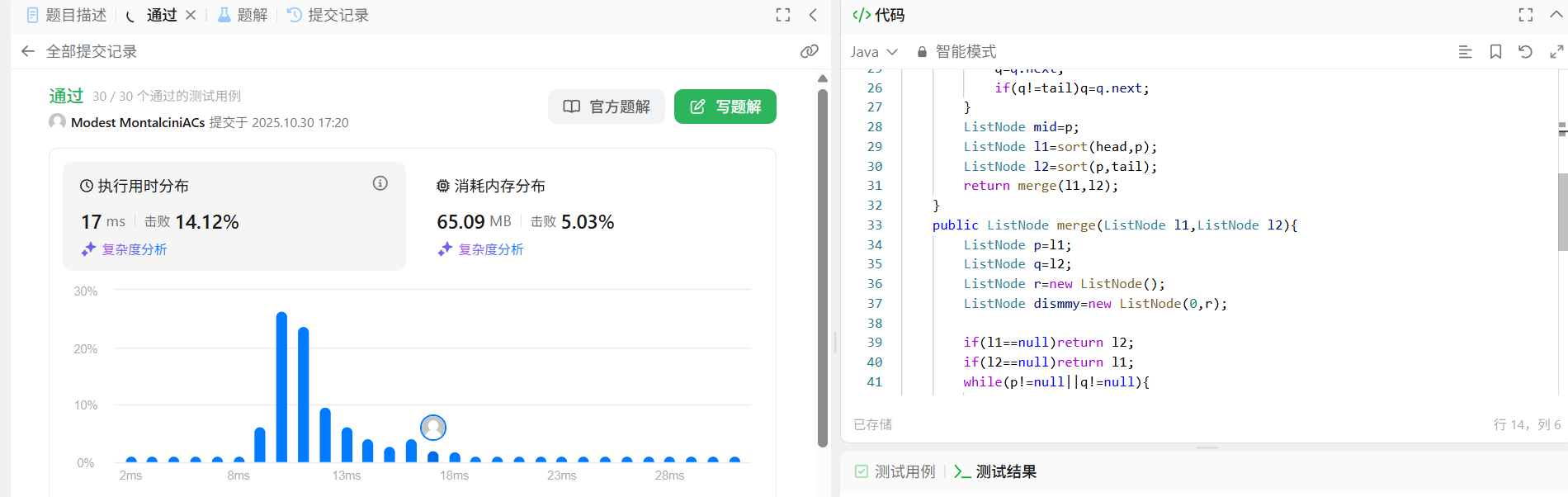
解法
题解中归并排序的方法
归并排序的方法,我之前一直没太搞明白。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
return sort(head,null);
}
public ListNode sort(ListNode head,ListNode tail){
if(head==null)return head;
if(head.next==tail){
head.next=null;
return head;
}
ListNode p=head;
ListNode q=head;
while(q!=tail){
p=p.next;
q=q.next;
if(q!=tail)q=q.next;
}
ListNode mid=p;
ListNode l1=sort(head,p);
ListNode l2=sort(p,tail);
return merge(l1,l2);
}
public ListNode merge(ListNode l1,ListNode l2){
ListNode p=l1;
ListNode q=l2;
ListNode r=new ListNode();
ListNode dismmy=new ListNode(0,r);
if(l1==null)return l2;
if(l2==null)return l1;
while(p!=null||q!=null){
ListNode tmp=new ListNode();
if(p==null){
tmp.val=q.val;
q=q.next;
}else if(q==null){
tmp.val=p.val;
p=p.next;
}else{
if(p.val<=q.val){
tmp.val=p.val;
p=p.next;
}else{
tmp.val=q.val;
q=q.next;
}
}
r.next=tmp;
r=tmp;
}
return dismmy.next.next;
}
}历史解法
超出时间限制的历史解法
这种解法时间复杂度O(n2),每次将后面序列中的最小值和第一个值的位置进行交换,好吧我的代码是将每一个比当次第一个小的都进行一次交换。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null)return head;
ListNode q=head;
ListNode p=head;
ListNode result=new ListNode(0);
ListNode r=result;
while(q!=null){
int min=q.val;
ListNode tmp=new ListNode(min);
while(p!=null){
if(p.val<min){
min=p.val;
p.val=q.val;
q.val=min;
}
p=p.next;
}
tmp.val=min;
r.next=tmp;
r=r.next;
q=q.next;
p=q;
}
return result.next;
}
}
ListNode result=new ListNode(0);
ListNode r=result;
int n=0;
ListNode p=head;
while(p!=null){
n++;
p=p.next;
}
p=head;
ListNode q=head;
for(int i=0;i<n/2;i++){
q=q.next;
}
ListNode poi=q;
while(p!=poi||q!=null){
ListNode tmp=new ListNode();
if(q==null){
tmp.val=p.val;
}
if(p==poi){
tmp.val=q.val;
}
if(p!=poi&&q!=null){
if(p.val<=q.val){
tmp.val=p.val;
p=p.next;
}else{
tmp.val=q.val;
q=q.next;
}
}
r.next=tmp;
r=r.next;
}
return result.next;
}226翻转二叉树
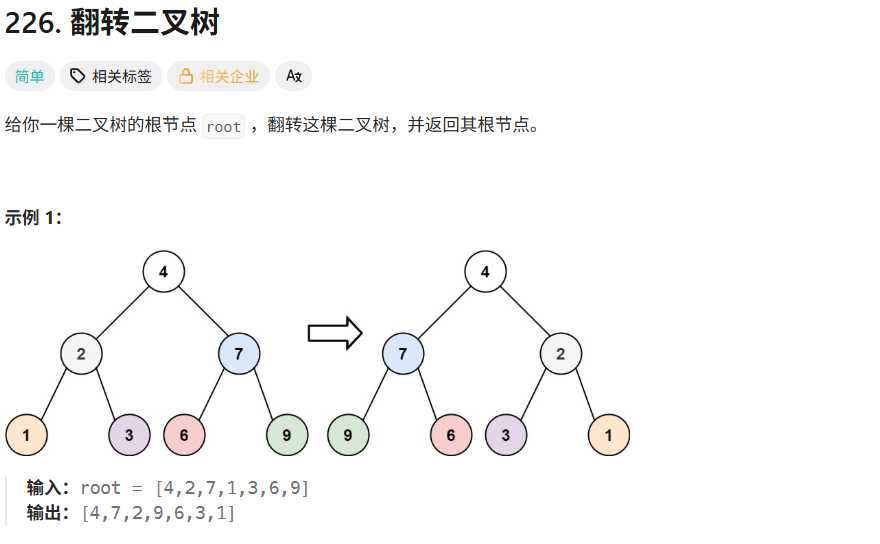
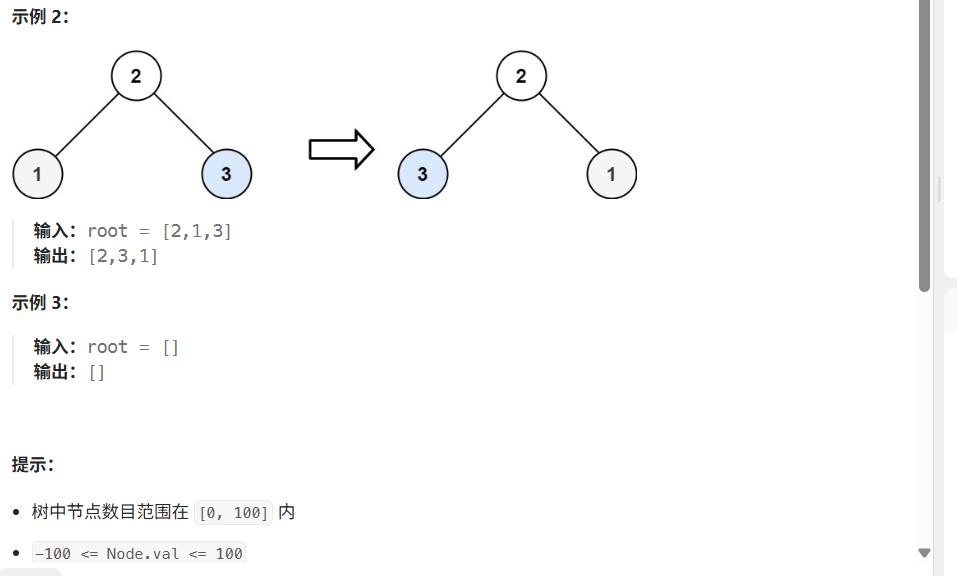
解法
自己的递归法
对左子树采用方法,对右子树采用方法。让左子树=右子树,让右子树=左子树。这样就可以了。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){
return null;
}else{
invertTree(root.left);
invertTree(root.right);
}
TreeNode tmp=root.left;
root.left=root.right;
root.right=tmp;
return root;
}
}101对称二叉树
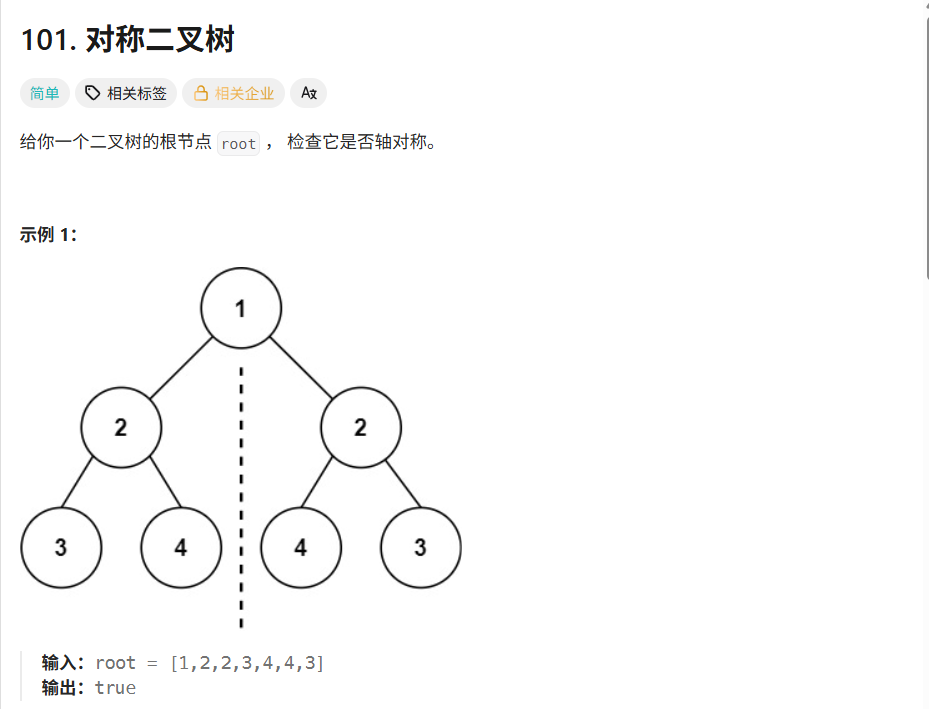
解法
看了题解的思想后自己写的迭代的解法
这种方法用到了二叉树遍历中的层序遍历,我之前也想过这种方法,但是我当时想的是先序遍历或者中序遍历,不是很适合这道题目。层序遍历完美适配这道题目。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
boolean flag=true;
List<TreeNode>queuel=new ArrayList();
List<TreeNode>queuer=new ArrayList();
TreeNode p=root;
queuel.add(p);
queuer.add(p);
while(!queuel.isEmpty()||!queuer.isEmpty()){
TreeNode tl=queuel.get(0);
TreeNode tr=queuer.get(0);
if(tl==null&&tr!=null||tl!=null&&tr==null){
flag=false;
}
if(tl!=null&&tr!=null){
if(tl.val!=tr.val){
flag=false;
}
}
queuel.remove(0);
queuer.remove(0);
if(tl!=null){
queuel.add(tl.left);
queuel.add(tl.right);
}
if(tr!=null){
queuer.add(tr.right);
queuer.add(tr.left);
}
}
return flag;
}
}题解中的递归解法
我一直没搞明白那个是左边子树和右边子树是怎么递归的,然后现在明白了。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
boolean flag=true;
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return check(root.left,root.right);
}
public boolean check(TreeNode p,TreeNode q){
if(p==null&&q==null){
return true;
}
if(p==null&&q!=null||p!=null&&q==null){
return false;
}
return p.val==q.val&&check(p.left,q.right)&&check(p.right,q.left);
}
}历史解法
这个错误是因为将题意理解为左右子树一样,但实际上是左右对称的一样才对。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
boolean flag=true;
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){
return false;
}else{
isSymmetric(root.left);
isSymmetric(root.right);
int l=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int r=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
if(root.left!=null) l=root.left.val;
if(root.right!=null) r=root.right.val;
if(l!=r){
flag=false;
return false;
}
}
return flag;
}
}543二叉树的直径
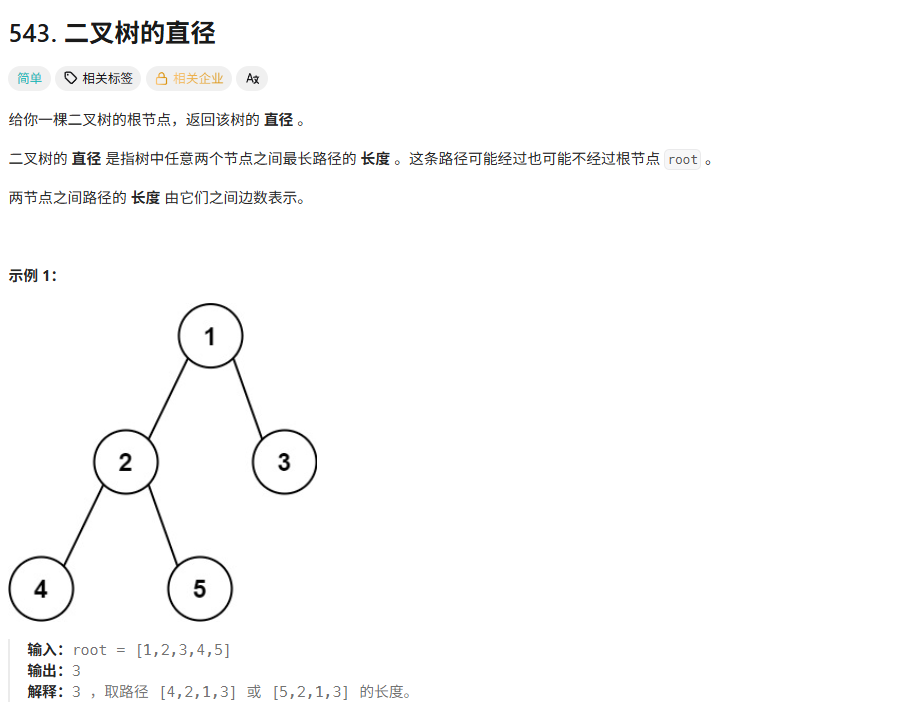
解法
题解中的深度优先的解法
这道题我不会做,这个递归我没整明白。现在倒是整明白了。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int ans=0;
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
ans=1;
depth(root);
return ans-1;
}
public int depth(TreeNode p){
if(p==null)return 0;
int l=depth(p.left);
int r=depth(p.right);
ans=Math.max(ans,l+r+1);
return Math.max(l,r)+1;
}
}102二叉树的层序遍历
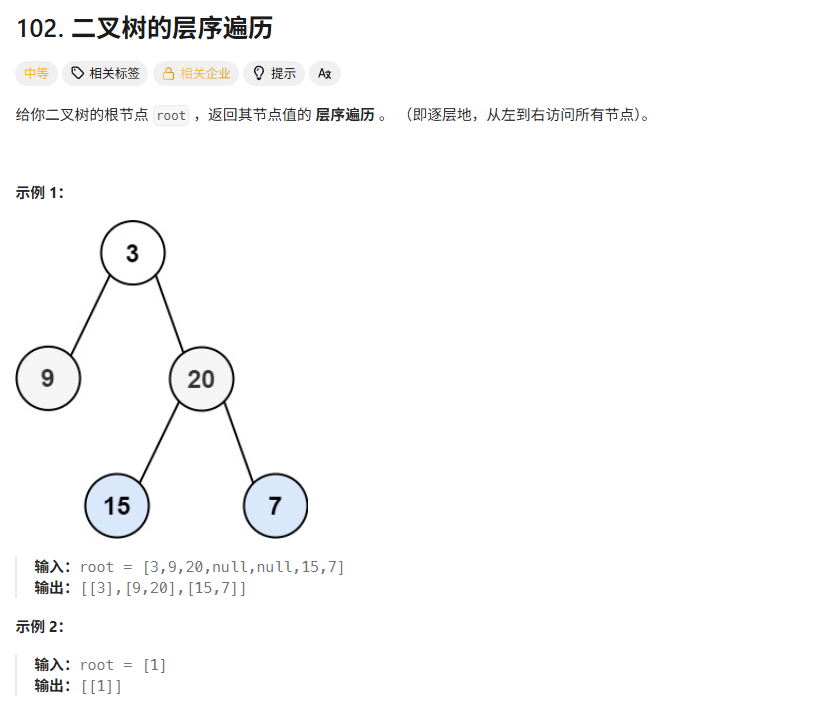
解法
自己写的解法
因为要按层输出(层放到一个列表中,最后再放到一个列表中一块输出)。所以我创建两个列表(list和list1)来放两层的元素,这样就可以实现按层输出。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<TreeNode>list=new ArrayList();
List<TreeNode>list1=new ArrayList();
List<List<Integer>>result=new ArrayList();
if(root==null)return result;
List<Integer>r=new ArrayList();
list.add(root);
int flag=1;
while(list.size()!=0||list1.size()!=0){
if(flag==1&&list.size()!=0){
TreeNode tmp=list.get(0);
if(tmp.left!=null){
list1.add(tmp.left);
}
if(tmp.right!=null){
list1.add(tmp.right);
}
r.add(tmp.val);
list.remove(0);
if(list.size()==0){
flag=0;
result.add(r);
r=new ArrayList();
}
}
if(flag==0&&list1.size()!=0){
TreeNode tmp=list1.get(0);
if(tmp.left!=null){
list.add(tmp.left);
}
if(tmp.right!=null){
list.add(tmp.right);
}
r.add(tmp.val);
list1.remove(0);
if(list1.size()==0){
flag=1;
result.add(r);
r=new ArrayList();
}
}
}
return result;
}
}108将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
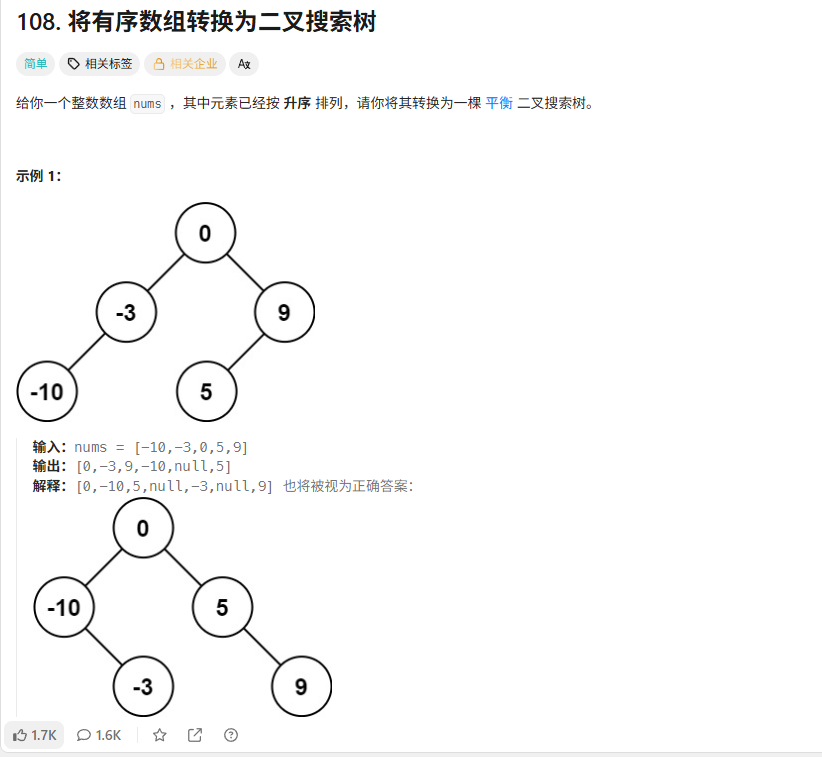
解法
自己写的解法
递归,从中间砍两半,分别找左边和右边的中间节点,然后就可以了。
这道题目,我在递归的出口那里的判断出了好几次错误。关于递归,我觉得我在判断出界条件这块还要提升提升。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
return balance(nums,0,n-1);
}
public TreeNode balance(int []nums,int start,int end){
int mid=(start+end)/2;
if(start>end){
return null;
}
TreeNode l= balance(nums,start,mid-1);
TreeNode r=balance(nums,mid+1,end);
TreeNode m=new TreeNode(nums[mid],l,r);
return m;
}
}历史解法
判断边界搞错的解法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
return balance(nums,0,n-1);
}
public TreeNode balance(int []nums,int start,int end){
int mid=(start+end)/2;
if(mid==start){
return new TreeNode(nums[start],null,null);
}
TreeNode l= balance(nums,start,mid);
TreeNode r=balance(nums,mid+1,end);
TreeNode m=new TreeNode(nums[mid],l,r);
return m;
}
}98验证二叉搜索树
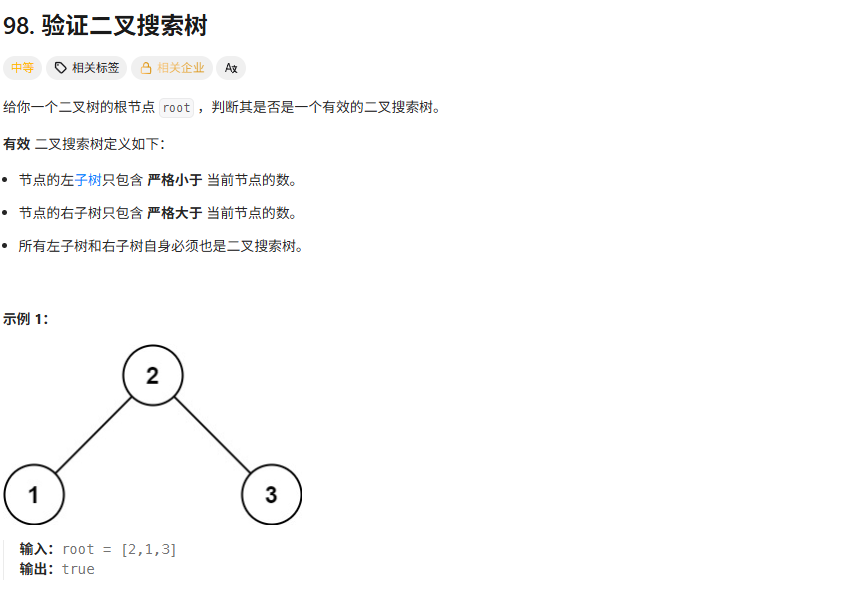
解法
题解中的递归的做法
从上往下,不断缩小递归的范围,这样就可以照顾到右子树的左孩子小于根节点的情况,还有另一种情况,这个方法很妙。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
return check(root,Long.MIN_VALUE,Long.MAX_VALUE);
}
public boolean check(TreeNode p,long l,long r){
if(p==null)return true;
if(p.val<=l||p.val>=r)return false;
return check(p.left,l,p.val)&&check(p.right,p.val,r);
}
}自己写的中序遍历的方法
中序遍历刚好是左中右,只需要确定中序序列中一个数字和他前面的那个数字大就可以了,我写的这个感觉不够好,我准备再看看题解中的方法。
我看了,和我的方法一样,就是他专门用了栈这个数据结构,而我是通过列表的添加和删除来实现的栈的结构的。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
List<TreeNode>list=new ArrayList();
TreeNode p=root;
long pre=Long.MIN_VALUE;
while(list.size()!=0||p!=null){
if(p!=null){
list.add(p);
p=p.left;
}else{
p=list.get(list.size()-1);
if(p.val<=pre){
return false;
}
pre=p.val;
p=p.right;
list.remove(list.size()-1);
}
}
return true;
}
}自己写的对每个节点都遍历左子树和遍历右子树的方法
写了两个方法,一个是验证以某个节点为根的节点的树的每个节点的值是否都比给的值小,另一个相反,然后遍历整棵树,我用的是层序遍历。代码行数稍微有些多。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
List<TreeNode>list=new ArrayList();
list.add(root);
while(list.size()!=0){
TreeNode p=list.get(0);
if(p.left!=null){
list.add(p.left);
if(checksmall(p.left,p.val)==false){
return false;
}
}
if(p.right!=null){
list.add(p.right);
if(!checkbig(p.right,p.val)){
return false;
}
}
list.remove(0);
}
return true;
}
public boolean checksmall(TreeNode p,int r){
List<TreeNode>q=new ArrayList();
q.add(p);
while(q.size()!=0){
TreeNode tmp=q.get(0);
if(tmp.left!=null){
q.add(tmp.left);
}
if(tmp.right!=null){
q.add(tmp.right);
}
if(tmp.val>=r){
return false;
}
q.remove(0);
}
return true;
}
public boolean checkbig(TreeNode p,int r){
if(p==null)return true;
List<TreeNode>q=new ArrayList();
q.add(p);
while(q.size()!=0){
TreeNode tmp=q.get(0);
if(tmp.left!=null){
q.add(tmp.left);
}
if(tmp.right!=null){
q.add(tmp.right);
}
if(tmp.val<=r){
return false;
}
q.remove(0);
}
return true;
}
}历史解法
没能检测出来下面节点和根节点关系的解法
用递归,判断节点和他的左右孩子的关系是否满足条件,不满足就返回false
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
boolean flag=true;
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
check(root);
return flag;
}
public boolean check(TreeNode p){
if(p==null)return true;
check(p.left);
check(p.right);
if(p.left!=null&&p.val<=p.left.val||p.right!=null&&p.val>=p.right.val){
flag=false;
return false;
}
return true;
}
}230二叉搜索树中第K小的元素

解法
自己写的中序遍历的方法
就是正常的中序遍历的过程,然后有一点就是在遍历指针向左边移的时候,不能用if要用while不然直接给pop出来了。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
Deque<TreeNode>stack=new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
List<Integer>list=new ArrayList();
TreeNode p=root;
while(p!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){
while(p!=null){
stack.push(p);
p=p.left;
}
p=stack.pop();
list.add(p.val);
p=p.right;
}
return list.get(k-1);
}
}历史解法
报错索引溢出但是AI告诉我没问题的解法
就神奇。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
Deque<TreeNode>stack=new LinkedList();
List<Integer>list=new ArrayList();
TreeNode p=root;
while(p!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){
if(p!=null){
stack.push(p);
p=p.left;
}
p=stack.pop();
list.add(p.val);
p=p.right;
}
return list.get(k-1);
}
}199二次树的右视图
解法
自己的层序遍历的解法
层序遍历,两个队列,轮着将同一层的元素放到同一个队列中,然后只有当最后一个元素的时候才将其加入到结果列表中去。官方题解看起来也挺长的,我就不看了。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer>result=new ArrayList();
if(root==null)return result;
Queue<TreeNode>q1=new LinkedList();
Queue<TreeNode>q2=new LinkedList();
q1.offer(root);
TreeNode p=root;
while(!q1.isEmpty()||!q2.isEmpty()){
while(!q1.isEmpty()){
TreeNode tmp=q1.peek();
if(tmp.left!=null){
q2.offer(tmp.left);
}
if(tmp.right!=null){
q2.offer(tmp.right);
}
if(q1.size()==1){
result.add(q1.poll().val);
}else{
q1.poll();
}
}
while(!q2.isEmpty()){
TreeNode tmp=q2.peek();
if(tmp.left!=null){
q1.offer(tmp.left);
}
if(tmp.right!=null){
q1.offer(tmp.right);
}
if(q2.size()==1){
result.add(q2.poll().val);
}else{
q2.poll();
}
}
}
return result;
}
}114二叉树展开为链表

解法
自己的先序遍历的方法
创建一个列表,先序遍历树,将其存放到列表中去,然后再将其一个一个找出来,就可以了。这道题感觉不用看题解,直接就做出来了。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
List<TreeNode>list=new ArrayList();
Deque<TreeNode>stack=new LinkedList();
TreeNode p=root;
while(!stack.isEmpty()||p!=null){
while(p!=null){
list.add(p);
stack.push(p);
p=p.left;
}
p=stack.pop();
p=p.right;
}
for(int i=1;i<list.size();i++){
root.left=null;
root.right=list.get(i);
root=root.right;
}
}
}105从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
解法
自己借助AI找边界的递归的方法
思想:在先序序列中找第一个为根节点,在中序遍历中找到和他一样的,分为左右子树,再在左子树和右子树中分别重复就可以了。
递归方法,三个参数,sp:先序序列中的指针,定位跟节点。si中序序列中指向开始位置的指针,ei中序序列中指向结束位置的指针,后两个指针将子树的范围圈起来,第一个指针在这个子树的范围内找到其根节点。递归,就解决了这个问题。要注意递归的出口还有左右子树的遍历的边界问题。
这道题目最让我头疼的地方在边界的问题,什么时候该返回,以及向左子树遍历和向右子树遍历的边界。因为开始我是用的两个参数,后来改为三个参数,在改的时候没有改完全。
我看了一眼题解,感觉代码量好像我的更少,哈哈哈,那就先偷个懒,不看答案了。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
Deque<Integer>stack=new LinkedList();
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
return createtree(preorder,inorder,0,0,inorder.length-1);
}
public TreeNode createtree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder,int sp,int si,int ei){
int n=inorder.length;
if(ei==si){
return new TreeNode(inorder[ei]);
}
if(si>ei)return null;
//sp表示preorder中的开始。ei表示inorder中的结束
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(preorder[sp]);
//rp找相同的
int rp=si;
while(rp<n&&inorder[rp]!=preorder[sp])rp++;
if(rp>si){
TreeNode l=createtree(preorder,inorder,sp+1,si,rp-1);
root.left=l;
}
if(rp<ei){
TreeNode r=createtree(preorder,inorder,sp+(rp-si)+1,rp+1,ei);
root.right=r;
}
return root;
}
}历史解法
边界报错没有正确输出的方法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
Deque<Integer>stack=new LinkedList();
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
return createtree(preorder,inorder,0,0,inorder.length-1);
}
public TreeNode createtree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder,int sp,int si,int ei){
int n=inorder.length;
if(ei==si){
return new TreeNode(inorder[ei]);
}
//sp表示preorder中的开始。ei表示inorder中的结束
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(preorder[sp]);
//rp找相同的
int rp=0;
while(rp<n&&inorder[rp]!=preorder[sp])rp++;
if(rp>0){
TreeNode l=createtree(preorder,inorder,sp+1,si,rp-1);
root.left=l;
}
if(rp>=sp&&rp!=n-1){
TreeNode r=createtree(preorder,inorder,rp+1,rp+1,ei);
root.right=r;
}
return root;
}
}未完成的递归我找不到出口
这个方法我找不好递归的出口,这道题目我已经看了很久了,我准备直接看答案。不再看别的了。
我的思路是先看先序遍历,找到根节点,再看中序遍历,找出左子树和右子树,再分别在上面找。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
Deque<Integer>stack=new LinkedList();
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
return createtree(preorder,inorder,0,inorder.length-1);
}
public TreeNode createtree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder,int sp,int ei, stack){
int n=inorder.length;
if(!stack.isEmpty()&&sp<stack.peek()){
}
//sp表示preorder中的开始。ei表示inorder中的结束
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(preorder[sp]);
//rp找相同的
int rp=sp;
while(inorder[rp]!=preorder[sp]&&rp<stack.peek()&&!stack.isEmpty())rp++;
stack.push(rp);
TreeNode l=createtree(preorder,inorder,sp+1,rp-1);
TreeNode r=createtree(preorder,inorder,rp+1,ei);
root.left=l;
root.right=r;
return root;
}
}437路径总和三
解法
题解中的递归法
遍历整棵树,每次都从一个节点找他的所有的子节点,看有没有符合条件的。递归传下去的后面的目标值可以做差,这样就可以完美传递下去了。
还有一个题解我没有看,要是有缘,可以看一看
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if(root==null)return 0;
int r=sum(root,targetSum);
r+=pathSum(root.left,targetSum);
r+=pathSum(root.right,targetSum);
return r;
}
public int sum(TreeNode root,long targetSum){
if(root==null)return 0;
int ret=0;
int v=root.val;
if(v==targetSum){
ret++;
}
ret+=sum(root.left,targetSum-v);
ret+=sum(root.right,targetSum-v);
return ret;
}
}历史解法
没跑完的遍历两次的解法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
int sum=0;
Deque<TreeNode>s=new LinkedList();
TreeNode p=root;
while(p!=null||!s.isEmpty()){
while(p!=null){
s.push(p);
p=p.left;
}
p=s.pop();
int count=check(p,targetSum);
sum=sum+count;
p=p.right;
}
return sum;
}
public int check(TreeNode root,int targetSum){
int count=0;
List<TreeNode>stack=new ArrayList();
TreeNode p=root;
while(p!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){
while(p!=null){
stack.add(p);
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<stack.size();i++){
sum=sum+stack.get(i).val;
if(sum==targetSum){
count++;
}
}
p=p.left;
}
// int sum=0;
// for(int i=0;i<stack.size();i++){
// sum=sum+stack.get(i).val;
// if(sum==targetSum){
// count++;
// }
// }
p=stack.get(stack.size()-1);
stack.remove(stack.size()-1);
p=p.right;
}
return count;
}
}236二叉树的最近公共祖先

解法
题解中的存储父节点解法
我的这个方法和题解中的代码的区别还是挺大的,中间有一部分我借鉴了链表那一块的一道题的解法,好像是寻找公共节点的那个地方。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
Map<TreeNode,TreeNode>map=new HashMap();
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
makehash(root);
TreeNode A=p;
TreeNode B=q;
while(A!=B){
A=map.containsKey(A)?map.get(A):q;
B=map.containsKey(B)?map.get(B):p;
}
return A;
}
public void makehash(TreeNode root){
if(root!=null){
if(root.left!=null){
map.put(root.left,root);
makehash(root.left);
}
if(root.right!=null){
map.put(root.right,root);
makehash(root.right);
}
}
}
}题解中的递归解法
一个满足条件的节点,只有两种情况,左右子树分别包含p,q。或者此节点就是p或q另一个节点在他的左右子树上面。递归方法,检查节点状态,看是否满足上面的情况,满足返回答案,不满足,接着往下递归,返回值为,左子树包含pq的情况,右子树包含pq的情况,本节点和Pq的情况的一个交叉的反应情况。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
TreeNode ans=new TreeNode(0);
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
check(root,p,q);
return ans;
}
public boolean check(TreeNode root,TreeNode p,TreeNode q){
if(root==null)return false;
boolean l=check(root.left,p,q);
boolean r=check(root.right,p,q);
if(l&&r||(root.val==p.val||root.val==q.val)&&(l||r)){
ans=root;
}
return l||r||root.val==p.val||root.val==q.val;
}
}自己的解法
遍历树,分别找到两个节点,将其父节点分别存储到两个列表中,然后按顺序比较,就可以了。
额,这道题目没耐心了,直接看题解了,做了个半成品,放这里了
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
List<TreeNode>l1=new ArrayList();
List<TreeNode>l2=new ArrayList();
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
}
public TreeNode find(TreeNode root,TreeNode target){
if(root==null{
return null;
}
if(root==target){
l1.add(root);
return root;
}
if(root!=target){
l1.add(root);
}
}
}124二叉树中的最大路径和
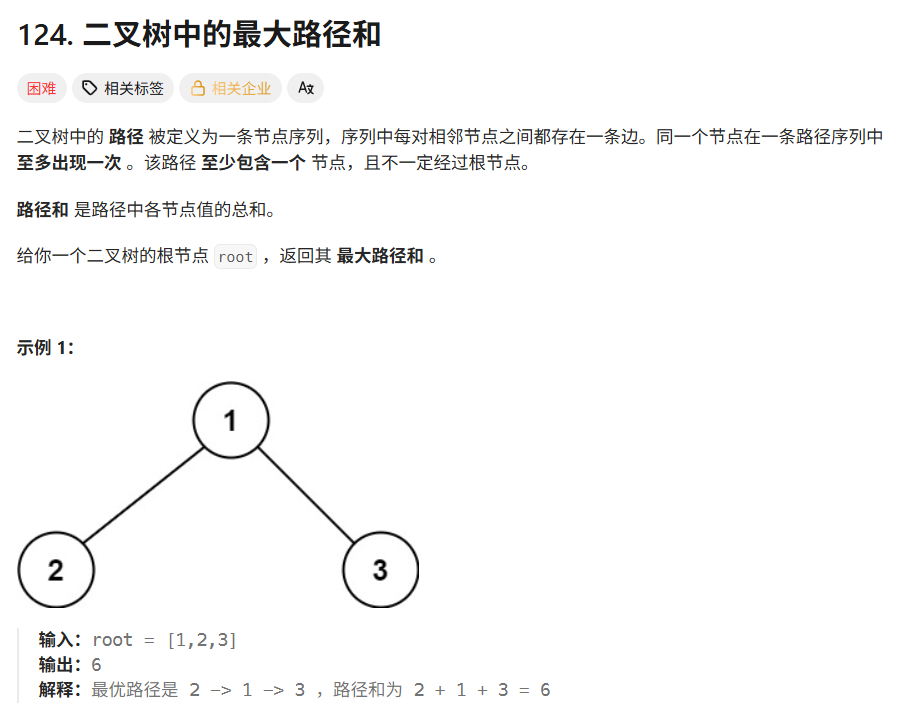 解法
解法
自己的递归解法
计算以每个节点为根节点的树的最大路径和,然后向上传递,(左右子树中路径和值比较大的加上本身传上去)如果节点的路径和值小于零,返回0.如果大于零,直接返回。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int maxP=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {
int v=check(root);
return maxP;
}
public int check(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return 0;
}
int v=root.val;
int l=check(root.left);
int r=check(root.right);
if(l+r+v>maxP)maxP=l+r+v;
if(l+v>=0||r+v>0){
int m=Math.max(r+v,l+v);
return m;
}else{
return 0;
}
}
}历史解法
第一次写通过三分之二的例子的解法
递归法,递归判断一个节点的值。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int maxP=0;
public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {
int v=check(root);
return maxP;
}
public int check(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return 0;
}
int v=root.val;
int l=check(root.left);
int r=check(root.right);
if(l+r+v>maxP)maxP=l+r+v;
if(l+v>=0||r+v>0){
int m=Math.max(r+v,l+v);
return m;
}
return v;
}
}35搜索插入位置

解法
二分查找的经典方法,两个指针low和high,一次缩减一半的检索范围。
class Solution {
public int searchInsert(int[] nums, int target) {
int low=0;
int high=nums.length-1;
int mid=0;
while(low<=high){
mid=(low+high)/2;
if(nums[mid]==target){
return mid;
}else if(nums[mid]>target){
high=mid-1;
}else{
low=mid+1;
}
}
return low;
}
}200岛屿的数量

解法
题解中的深度优先搜索方法
定义一个dfs方法,递归地将一个连成片的1全部变为0,通过将一个1的上下左右都递归一下来实现。然后在主方法中遍历所有节点,每次遍历到一个岛屿,就可以直接将所有的岛屿的节点变为1,这样就不会重复了。
class Solution {
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
int count = 0;
int row = grid.length;
int col = grid[0].length;
for(int i=0;i<row;i++){
for(int j=0;j<col;j++){
if(grid[i][j]=='1'){
count++;
dfs(grid,i,j);
}
}
}
return count;
}
public void dfs(char[][]grid,int r,int c){
int row = grid.length;
int col = grid[0].length;
if(r<0||c<0||r>=row||c>=col||grid[r][c]=='0'){
return;
}
grid[r][c]='0';
dfs(grid,r-1,c);
dfs(grid,r+1,c);
dfs(grid,r,c+1);
dfs(grid,r,c-1);
}
}历史错误解法
下面的方法都是我想通过直接检查一个节点的上下左右的节点来判断是否加1或者减一。
class Solution {
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
int count=0;
int row=grid.length;
int col=grid[0].length;
for(int i=0;i<row;i++){
for(int j=0;j<col;j++){
boolean flag=false;
//可加1的条件:
//为1,且为行第一或前一个不为1,且列第一或者上面一个不为1
if(grid[i][j]=='1'&&(j==0||grid[i][j-1]!='1')&&(i==0||grid[i-1][j]=='0')&&(j!=col-1&&grid[i][j+1]=='0')){
count++;
flag=true;
}
}
}
return count;
}
}
class Solution {
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
int count=0;
int row=grid.length;
int col=grid[0].length;
for(int i=0;i<row;i++){
boolean flag=false;
for(int j=0;j<col;j++){
//可加1的条件:
//为1,且为行第一或前一个不为1,且列第一或者上面一个不为1
if(grid[i][j]=='1'&&(j==0||grid[i][j-1]!='1')&&(i==0||grid[i-1][j]=='0')&&(!flag||i==row-1||i!=row-1&&grid[i+1][j]=='0')&&(!flag||j==col-1||j!=col-1&&grid[i][j+1]=='0')){
count++;
flag=true;
}
if(flag&&grid[i][j]=='1'&&(j!=0&&i!=0&&grid[i][j-1]=='1'&&grid[i-1][j]=='1'&&grid[i-1][j-1]=='0')){
count--;
}
}
}
return count;
}
}994腐烂的橘子

解法
自己的解法
今天下午脑袋比较昏沉,本来打算放弃了,但是看了一眼答案,感觉答案没有那种让我焕然一新的思路,而且过程也很冗长,我决定还是自己写吧。最后写出来了。
思路:首先将所有初始2找到,两个列表,一个记录没腐蚀完的节点,一个记录被正在腐蚀的节点的临近节点,也就是下一轮要遍历的节点(我在这里用的是一个轮换,一直用l列表)感觉中间检查上下左右节点的按个部分可以抽象出来。
class Solution {
int count = -1;
List<Integer> l = new ArrayList();
List<Integer> r = new ArrayList();
int ctl = 1;
public int orangesRotting(int[][] grid) {
if(checkfrash(grid))return 0;
for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 2) {
l.add(i);
l.add(j);
}
}
}
change(grid);
if (checkfrash(grid)) {
return count;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
public void change(int[][] grid) {
boolean flag = false;
while (!l.isEmpty() || !r.isEmpty()) {
if (l.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> tmp = l;
l = r;
r = tmp;
}
while (!l.isEmpty()) {
int i = l.get(0);
l.remove(0);
int j = l.get(0);
l.remove(0);
if (i != 0 && grid[i - 1][j] == 1) {
flag = true;
grid[i - 1][j] = 2;
r.add(i - 1);
r.add(j);
}
if (i != grid.length - 1 && grid[i + 1][j] == 1) {
flag = true;
grid[i + 1][j] = 2;
r.add(i + 1);
r.add(j);
}
if (j != 0 && grid[i][j - 1] == 1) {
flag = true;
grid[i][j - 1] = 2;
r.add(i);
r.add(j - 1);
}
if (j != grid[0].length - 1 && grid[i][j + 1] == 1) {
flag = true;
grid[i][j + 1] = 2;
r.add(i);
r.add(j + 1);
}
}
if (flag) {
count++;
}
}
}
public boolean checkfrash(int[][] grid) {
for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}优化后代码(少了13行)
class Solution {
int count = -1;
List<Integer> l = new ArrayList();
List<Integer> r = new ArrayList();
int ctl = 1;
public int orangesRotting(int[][] grid) {
if(checkfrash(grid))return 0;
for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 2) {
l.add(i);
l.add(j);
}
}
}
change(grid);
if (checkfrash(grid)) {
return count;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
public void change(int[][] grid) {
boolean flag = false;
while (!l.isEmpty() || !r.isEmpty()) {
if (l.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> tmp = l;
l = r;
r = tmp;
}
while (!l.isEmpty()) {
int i = l.get(0);
l.remove(0);
int j = l.get(0);
l.remove(0);
int[][]dirs={{-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}};
for(int[]d:dirs){
int ii=i+d[0];
int jj=j+d[1];
if(ii>=0&&ii<grid.length&&jj>=0&&jj<grid[0].length&&grid[ii][jj]==1){
r.add(ii);
r.add(jj);
grid[ii][jj]=2;
flag=true;
}
}
}
if (flag) {
count++;
}
}
}
public boolean checkfrash(int[][] grid) {
for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}历史错误解法
通过127个用例的解法
遍历网格,找到所有初始腐烂橘子(值为 2)的坐标,存入 l1(横纵坐标交替存入)。
一旦找到一个腐烂橘子,立即调用 change扩散腐烂,扩散完检查是否还有新鲜橘子,如果没有就返回分钟数。
change方法中,用两个列表 l1和 l2交替作为当前层和下一层的容器,模拟 BFS 扩散。
这道题目,我不想再看了,直接看答案。如果后面又看到这个部分,倒是可以尝试着将这个思路实现出来。
class Solution {
int count=0;
List<Integer>l1=new ArrayList();
List<Integer>l2=new ArrayList();
public int orangesRotting(int[][] grid) {
for(int i=0;i<grid.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<grid[0].length;j++){
if(grid[i][j]==2){
l1.add(i);
l1.add(j);
change(grid);
if(checkfrash(grid)){
return count;
}
}
}
}
if(checkfrash(grid)){
return count;
}else{
return -1;
}
}
public void change(int[][] grid){
boolean flag=false;
List<Integer>l=l1.isEmpty()?l2:l1;
List<Integer>r=l1.isEmpty()?l1:l2;
while(!l.isEmpty()){
int i=l.get(0);
l.remove(0);
int j=l.get(0);
l.remove(0);
if(i!=0&&grid[i-1][j]==1){
flag=true;
grid[i-1][j]=2;
r.add(i-1);
r.add(j);
}
if(i!=grid.length-1&&grid[i+1][j]==1){
flag=true;
grid[i+1][j]=2;
r.add(i+1);
r.add(j);
}
if(j!=0&&grid[i][j-1]==1){
flag=true;
grid[i][j-1]=2;
r.add(i);
r.add(j-1);
}
if(j!=grid[0].length-1&&grid[i][j+1]==1){
flag=true;
grid[i][j+1]=2;
r.add(i);
r.add(j+1);
}
}
if(flag){
count++;
}
}
public boolean checkfrash(int[][]grid){
for(int i=0;i<grid.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<grid[0].length;j++){
if(grid[i][j]==1)return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}20有效的括号

解法
自己做的方法
遍历字符串,如果是前括号,就入栈,如果是后括号,就和出栈的元素进行不比较,如果出现不一样的,返回false。注意可能先入栈的是后括号,这种栈会是空的,所以在判断的时候可以加上判断栈是否为空的这个东西来判断
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Deque<Character>stack=new LinkedList();
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
if(s.charAt(i)=='('||s.charAt(i)=='{'||s.charAt(i)=='['){
stack.push(s.charAt(i));
}else{
char c='l';
char cc= s.charAt(i);
if(cc==')')c='(';
if(cc==']')c='[';
if(cc=='}')c='{';
if(stack.isEmpty()||c!=stack.pop())return false;
}
}
if(!stack.isEmpty())return false;
return true;
}
}84柱状图中最大的矩阵
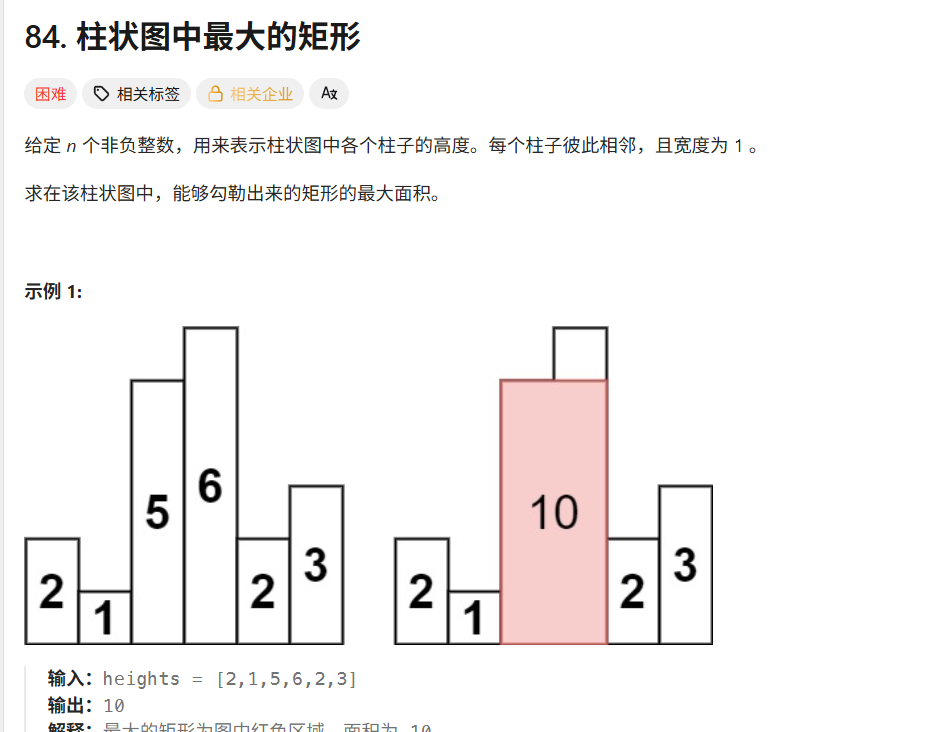
解法
单调栈的做法AI的解法
确保栈里的元素是单调递增的,如果遍历到的元素比栈顶元素不小,将目前的元素的索引入栈。
当比栈顶元素小的时候,出栈,开始结算栈里的数据:
如果此刻栈为空(经历了刚刚的出栈)那么说明此时遍历的元素就是前面所有元素的最小元素,宽度(width)=i,高度等于现在的这个元素。
如果此时栈不为空,高度等于栈顶元素的高,宽度等于i-栈顶元素索引-1,计算面积如果比之前的最大面积还要大,就取代他
重复这个过程,直到最后。
class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
int n = heights.length;
Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();
int max=0;
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){
int h=i==n?0:heights[i];
while(!stack.isEmpty()&&h<heights[stack.peek()]){
int height=heights[stack.pop()];
int width=stack.isEmpty()?i:i-stack.peek()-1;
max=Math.max(max,height*width);
}
stack.push(i);
}
return max;
}
}核心思想:以每个柱子为高度,它能向两边扩展多远?
对于输入 [2,1,5,6,2,3],我们想知道每个柱子能形成的最大矩形:
第一步:理解问题本质
-
我们要找的是由相邻柱子组成的最大矩形
-
矩形的高度由最矮的柱子决定
-
矩形的宽度由左右边界决定
第二步:单调栈的作用
单调栈帮我们快速找到每个柱子的左右边界:
-
左边界:左边第一个比当前柱子矮的柱子位置
-
右边界:右边第一个比当前柱子矮的柱子位置
第三步:具体过程演示(以 [2,1,5,6,2,3] 为例)
索引: 0 1 2 3 4 5
高度: 2 1 5 6 2 3
我们用栈来存储索引 ,保持栈内对应的高度是递增的:
步骤1:i=0,高度=2
- 栈空,入栈:
stack = [0]
步骤2:i=1,高度=1
-
1 < 2(破坏递增),弹出索引0:
-
高度 = heights[0] = 2
-
左边界 = 栈空 ? -1 : stack.peek() = -1
-
右边界 = i = 1
-
宽度 = 1 - (-1) - 1 = 1
-
面积 = 2 × 1 = 2
-
-
入栈1:
stack = [1]
步骤3:i=2,高度=5
- 5 > 1,保持递增,入栈:
stack = [1,2]
步骤4:i=3,高度=6
- 6 > 5,保持递增,入栈:
stack = [1,2,3]
步骤5:i=4,高度=2
-
2 < 6,弹出索引3:
-
高度 = 6
-
左边界 = stack.peek() = 2
-
右边界 = i = 4
-
宽度 = 4 - 2 - 1 = 1
-
面积 = 6 × 1 = 6
-
-
2 < 5,弹出索引2:
-
高度 = 5
-
左边界 = stack.peek() = 1
-
右边界 = i = 4
-
宽度 = 4 - 1 - 1 = 2
-
面积 = 5 × 2 = 10 ← 找到当前最大值
-
-
2 > 1,入栈4:
stack = [1,4]
步骤6:i=5,高度=3
- 3 > 2,入栈:
stack = [1,4,5]
步骤7:处理栈中剩余元素(虚拟右边界=n=6)
-
弹出索引5:高度=3,宽度=6-4-1=1,面积=3
-
弹出索引4:高度=2,宽度=6-1-1=4,面积=8
-
弹出索引1:高度=1,宽度=6-(-1)-1=6,面积=6
历史解法
另一个错误的做法
不做了,看答案
class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
int n=heights.length;
Deque<Integer>stack=new LinkedList();
int i=0;
int j=1;
int max=heights[i]*1;
while(i<n){
if(j<n&&heights[j]>=heights[i]){
int area=heights[i]*(j-i);
if(area>max)max=area;
if(j==n-1){
i++;
}
j++;
}else{
i++;
j=i+1;
}
}
return max;
}
}算法错误的做法
想错了,先排序后计算的方法是行不通的。会改变整个数组的情况。
class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
int n=heights.length;
int max=0;
Arrays.sort(heights);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int area=heights[i]*(n-i);
if(area>max)max=area;
}
return max;
}
}报错超出时间限制的暴力法
直接遍历所有情况,得出结果。
class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
int n=heights.length;
int max=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int min=heights[i];
for(int j=i;j<n;j++){
if(heights[j]<min)min=heights[j];
int area=min*(j-i+1);
if(area>max)max=area;
}
}
return max;
}
}215数组中的第K个最大元素

解法
题解中的堆的解法
这个解法用到了我不会的一种数据结构PriorityQueue还有匿名内部类,这种方法得学!!别的思路倒是跟我的挺像
class Solution {
public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
Map<Integer,Integer>map=new HashMap();
for(int num:nums){
map.put(num,map.getOrDefault(num,0)+1);
}
PriorityQueue<int[]>queue=new PriorityQueue<int[]>(new Comparator<int []>(){
public int compare(int []m,int []n){
return m[1]-n[1];
}
});
for(Map.Entry<Integer,Integer>entry:map.entrySet){
int num=entry.getKey()
int count=entry.getValue();
if(queue.size()==k){
if(queue.peek()[1]<count){
queue.poll();
}
queue.offer(new int[]{num,count});
}else{
queue.offer(new int []{nums,count});
}
}
int ret=new int[k];
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
ret[i]=queue.poll()[0];
}
return ret;
}
}借鉴了题解思想的自己写出来的解法
题解中的一个思想感觉非常不错,虽然最后跑出来没有我第一次单纯用堆排序跑出来的效率高,但是也很不错了
下面是思路:
首先用HashMap将所有的数字和数字的数量都收集起来,再用一个数组(all)将其全部都变成可以直接索引的。
然后分析题目,我们可以构建一个数量为k的小根堆,当数量不够k的时候就直接往小根堆数组里面加,当数量够了之后,直接开始构建小根堆。然后后面的数据就跟小根堆的第一个元素比较(目前最小的值),如果比小根堆里最小的值还小,就直接将其替换掉,然后让其下沉到他该在的位置,保证,小根堆里的第一个元素是最小的。遍历完all数组(记录着nums数组的数字和个数的数组)后,再将从结果数组中提取出我们要的答案(在本代码中,我的是直接找到所有奇数索引的值)。
记录做这个思路时的一个关键报错
在遇到像是这道题目需要用数组来记录一对数据为一组(比如这道题目中需要记录数字本身还有数字对应的个数)在遍历的时候一定要直接在外层for遍历的时候,直接写i=i+2不要写i++然后在循环体里面再i++;这样很容易报错;切记切记
for(int i=0;i<2*size;i++){
if(count<k){
int num=count*2;
r[num]=all[i++];
r[num+1]=all[i];
swap(r,0,num);
swap(r,1,num+1);
beHeap(r,0,count+1);
count++;
}else{
if(all[i+1]>r[1]){
r[0]=all[i++];
r[1]=all[i];
swap(r,0,2*k-2);
swap(r,1,2*k-1);
beHeap(r,0,k);
}
}
}
int c=0;
for(int i=0;i<2*k;i++){
result[c++]=r[i++];
}
return result;
}自己做的大根堆的解法
首先用HashMap来将所有的数据的值和数量统计下来,在用一个数组(all)将所有的值和数量放进去,一个数字一个数量,然后构建大根堆,只不过,这些东西都需要稍微调整一下。别的倒是都还好。刚刚看了一眼题解,我发现题解也是将数字和数量都存储到同一个数组里面,我感觉我的做法更好理解。然后我看到了一种优化的点,大概是这样的:
我的方法是构建大根堆,然后除了最初构建大根堆,后面还需要不断地交换第一个和最后一个元素,但是如果构建的是小根堆就不需要了,小根堆的叶子节点一定是大于他的非叶子结点的,所以如果K的值大于叶子节点的数量的时候,叶子节点就可以直接抄到结果的数组中去。剩下的只需要在非叶子节点上再稍微拍个序就好了。我刚刚试了一下,这个方法不行。是我理解错了题解中的思想。(此思路是失败的思考,前面我自己做的是正确的,我想优化,但优化错了)
class Solution {
Map<Integer,Integer>map=new HashMap();
public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
int n=nums.length;
int []result=new int [k];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int value=map.getOrDefault(nums[i],0)+1;
map.put(nums[i],value);
}
//size表示有多少对
int size=map.size();
int [] all=new int [2*size];
Set<Integer>keys=map.keySet();
int index=0;
for(Integer key:keys){
Integer value=map.get(key);
all[index++]=key;
all[index++]=value;
}
buildHeap(all);
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
result[i]=all[0];
swap(all,0,2*(size-1-i));
swap(all,1,2*(size-1-i)+1);
beHeap(all,0,size-i-1);
}
return result;
}
public void buildHeap(int []nums){
int n=nums.length/2;
for(int i=n/2-1;i>=0;i--){
beHeap(nums,i,n);
}
}
//nums两个值看作是一个,前面的是键,后面的是值,n表示有多少对
public void beHeap(int [] nums,int k,int n ){
int i=k;
while(i<n/2){
int li=2*i+1;
int ri=2*i+2;
int lari=li;
if(ri<=n-1&&nums[2*ri+1]>nums[2*li+1])lari=ri;
if(nums[2*lari+1]>nums[2*i+1]){
swap(nums,2*lari+1,2*i+1);
swap(nums,2*lari,2*i);
}else{
break;
}
i=lari;
}
}
public void swap(int []a ,int i,int j){
int tmp=a[i];
a[i]=a[j];
a[j]=tmp;
}
}