在大型软件系统设计时,业务一般会相对复杂,假如所有业务实现的代码都纠缠在一起,会出现逻辑不清晰、可读性差,维护困难,改动一处就牵一发而动全身等问题。为了更好解决这个问题就有了我们现在常说的分层架构设计。
分层设计的本质其实就是将复杂问题简单化,首先基于单一职责原则让每个对象各司其职,各尽所能。然后再基于"高内聚,低耦合"的设计思想实现相关层对象之间的交互。这样可以更好提高程序的可维护性和可扩展性
MVC(Model--view--controller)是软件工程中的一种软件架构模式,基于此模式把软件系统分为三个基本部分:模型(Model)、视图(View)和控制器(Controller)。目的是通过这样的设计使程序结构更加简洁、直观,降低问题的复杂度。其中MVC各个组成部分为:视图:设计人员进行图形界面设计,负责实现与用户交互,例如html、css、js等都属于这一层的技术
控制器:负责获取请求,处理请求,响应结果,在java中充当控制器对象的一般是servlet。
模型:实现业务逻辑,数据逻辑实现。(@Service-描述业务层对象,@Repository-描述数据层对象)
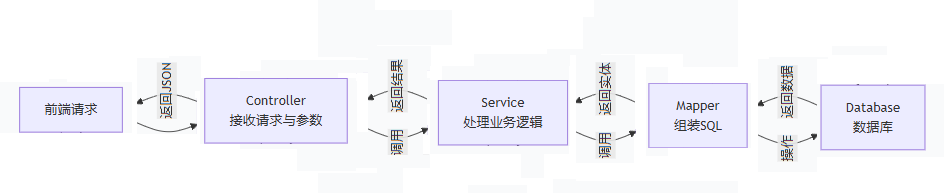
Spring MVC执行流程
-
客户端发送请求至前端控制器DispatcherServlet;
-
DispatcherServlet收到请求后,调用处理器映射器HandlerMapping;
-
HandlerMapping根据请求URL找到具体的Controller;
-
通过处理器适配器HandlerAdapter适配具体执行该Controller的方式;
-
Controller处理请求,并返回ModelAndView;
-
DispatcherServlet通过ViewReslover(视图解析器)确定负责显示数据的具体View;
-
DispatcherServlet对View进行渲染视图(即将Model填充至视图组件中),并将完整的视图响应到客户端。
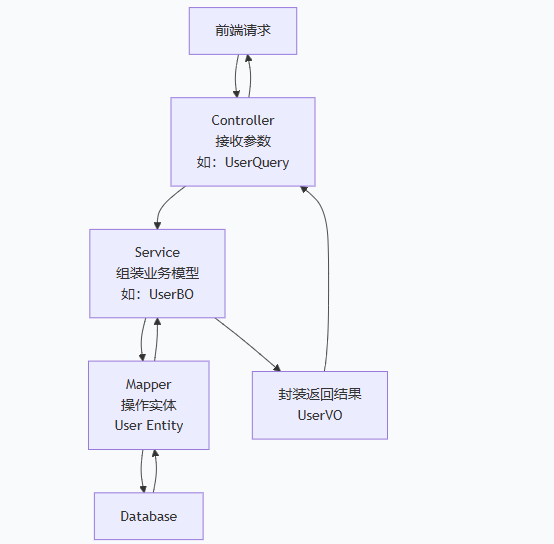
下面来实现一个消息业务,因为比较简单,暂时就先不要service层。
在src-main-java下的包创建三个包:controller,作为控制层 **,**它是应用程序的总入口和总出口,接收前端请求,返回后端响应,接收请求:接收前端发送的 HTTP 请求(GET, POST, PUT, DELETE等)。调用服务:将请求参数处理后,调用 service 层(业务层)来处理核心业务逻辑。返回响应:将 service 层处理后的结果封装成 JSON 或 XML 等格式,通过 HTTP 响应返回给前端;mapper,数据持久层。它负责与数据库进行直接对话, 提供增、删、改、查等操作数据库的方法。它定义了操作,但不实现细节。具体的 SQL 实现通常写在对应的 XML 文件或使用注解在接口中定义。常见技术: MyBatis 的 Mapper 接口,或 JPA 的 Repository 接口;pojo,普通的Java 对象。它代表的是应用程序中的核心数据模型,可以用于封装客户端输入,可以封装还给客户端的数据,也可以是实体类。根据这些功能不同,pojo又可以细分为与数据库表结构直接映射的entity;用于前后端或服务间的数据传输数据传输对象的dto;用于返回给前端的数据模型的视图对象的vo
为了完成后端和数据库交互的映射,需要创建必要的接口,这里在mapper包里面创建一个NoticeMapper的接口,所有的方法都只是在这声明而不实现,真正实现应该到对应的.xml文件中用SQL语句实现。还需要创建一个NoticeMapper.xml文件,是在resource包下新建一个mappers包中新建,为了明确它们之间的映射关系,可以保持取名一致。

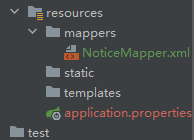
创建好必要的包以后就开始创建类,最先创建的应该是实体类notice,并自动生成tostring和各种属性的get、set方法,注意它是实体类所以在pojo下面的entity中创建。
java
public class Notice {
private Long id;
private String title;
private String content;
private Integer type;
private Long userId;
private Date createTime;
private Date updateTime;
private Integer status;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Notice{" +
"id=" + id +
", title='" + title + '\'' +
", content='" + content + '\'' +
", type=" + type +
", userId=" + userId +
", createTime=" + createTime +
", updateTime=" + updateTime +
", status=" + status +
'}';
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public Integer getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(Integer type) {
this.type = type;
}
public Long getUserId() {
return userId;
}
public void setUserId(Long userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
public Date getCreateTime() {
return createTime;
}
public void setCreateTime(Date createTime) {
this.createTime = createTime;
}
public Date getUpdateTime() {
return updateTime;
}
public void setUpdateTime(Date updateTime) {
this.updateTime = updateTime;
}
public Integer getStatus() {
return status;
}
public void setStatus(Integer status) {
this.status = status;
}
}其次是controller,作为连接前端请求和后端服务的一个枢纽,处理客户请求的业务,首先应该加上@controller注解说明我是controller层专门和客户进行交互的,并定义一个noticeMapper的接口。先来实现新增消息的功能,客户提供title、content、type、status信息,其他信息可以不提供。这时候就要用到dto,将这些必填的信息封装到一个NoticeAddParam类中放到dto包下。回到controller层,在新增功能的函数上需要加上两个注解 :@PostMapping和@ResponseBody,用户是需要新增,@PostMapping专门用来映射和处理 HTTP POST 请求,并在括号中给定方法的路径;@ResponseBody注解告诉 Spring MVC这个方法的返回值,不要把它当成一个视图名称去解析了,请直接把它写入 HTTP 响应体中。然后传参的时候也不应该直接将这个NoticeAddParam类的对象传过去,SQL语句是不认识的,应该封装成Notice实体类再传过去。
java
public class NoticeAddParam {
private String title;
private String content;
private Integer type;
private Integer status;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "NoticeAddParam{" +
"title='" + title + '\'' +
", content='" + content + '\'' +
", type=" + type +
", status=" + status +
'}';
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public Integer getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(Integer type) {
this.type = type;
}
public Integer getStatus() {
return status;
}
public void setStatus(Integer status) {
this.status = status;
}
}
java
@Controller
public class NoticeController {
@Autowired
private NoticeMapper noticeMapper;
@PostMapping("v1/notice/noticeAdd")
@ResponseBody
public String noticeAdd(NoticeAddParam noticeAddParam)
{
System.out.println(noticeAddParam);
Notice notice = new Notice();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(noticeAddParam,notice);
notice.setUserId(1L);
notice.setCreateTime(new Date());
notice.setUpdateTime(new Date());
int x=noticeMapper.insert(notice);
if(x>0)
return "添加成功";
return "添加失败";
}
}
java
public interface NoticeMapper {
int insert(Notice notice);
}接下来是真正处理插入业务,在NoticeMapper.xml文件中用SQL语句处理,在这之前先完成一些初始化工作,在namespace中应该填上正确的路径,也就是工程名.mapper.NoticeMapper,填好路径后就是简单的SQL语句,处理插入业务就在专门的insert标签中处理。
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="cn.tedu.project1.mapper.NoticeMapper">
<insert id="insert">
INSERT INTO notice (title,content,type,user_id,create_time,update_time,status)
VALUES (#{title},#{content},#{type},#{userId},#{createTime},#{updateTime},#{status})
</insert>
</mapper>完事后我想看看对不对想测试一下,有一个专门的test文件,在里面创建一个http的包,里面再创建一个Notice_test.http的文件。在这里想要测试可以直接点左上角的+号,新增业务属于POST请求,所以选择第三个。然后修改路径http://localhost:8080/v1/notice/noticeAdd因为是要调用这个函数,并在下面给出必要的信息,中间用\&符号连接。在主函数中运行程序(工程项目名Application)运行无误后再点击POST旁边的绿色箭头即可测试。



XML
POST http://localhost:8080/v1/notice/noticeAdd
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
title=小康&type=1&content=红警3player&status=1
###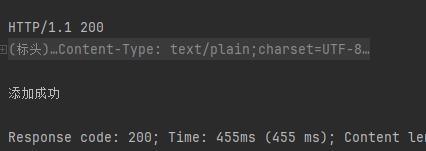
当显示为200的时候就说明添加成功了,然后去数据库里面去查看,果然添加成功了。
完成新增功能后,在继续完成查看、修改、删除功能,查看分为列表查询和详细查看。当使用列表查询的时候可以通过输入关键词如title和content的模糊查询,然后返回所有的返回结果,用一个VO包中的一个NoticeListVO封装后返回,里面包含了便于展示的title,type等属性;而不便于展示的内容需要通过详细查看才能展示,展示的内容可以通过另外一个NoticeVO来封装。在查询的时候要注意判断传进来的是否为空,所以还需要使用<select><if>等标签来动态查询。
java
@RestController
public class NoticeController {
@Autowired
private NoticeMapper noticeMapper;
@PostMapping("v1/notice/noticeAdd")
@ResponseBody
public String noticeAdd(NoticeAddParam noticeAddParam)
{
System.out.println(noticeAddParam);
Notice notice = new Notice();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(noticeAddParam,notice);
notice.setUserId(1L);
notice.setCreateTime(new Date());
notice.setUpdateTime(new Date());
noticeMapper.insert(notice);
return "添加成功";
}
@GetMapping("v1/notice/noticeList")
public List<NoticeListVO> noticeList(NoticeListQuery noticeListQuery)
{
System.out.println("noticeListQuery"+noticeListQuery);
List<NoticeListVO> l=noticeMapper.list(noticeListQuery);
return l;
}
@GetMapping("v1/notice/noticeDetail")
public NoticeVO noticeDetail(long id)
{
System.out.println(id);
NoticeVO detail=noticeMapper.getDetail(id);
return detail;
}
@DeleteMapping("v1/notice/delete")
public String delete(Long id)
{
int x=noticeMapper.del(id);
if(x>0)
return "finish";
return "error";
}
@PostMapping("v1/notice/update")
public String update(NoticeUpdateParam param)
{
Notice notice = new Notice();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(param,notice);
notice.setUpdateTime(new Date());
int x=noticeMapper.updateNotice(notice);
if(x>0)
return "finish";
return "error";
}
}
java
@Mapper
public interface NoticeMapper {
int insert(Notice notice);
List<NoticeListVO> list(NoticeListQuery query);
NoticeVO getDetail(long id);
int del(Long id);
int updateNotice(Notice notice);
}
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="cn.tedu.project1.mapper.NoticeMapper">
<insert id="insert">
INSERT INTO notice (title,content,type,user_id,create_time,update_time,status)
VALUES (#{title},#{content},#{type},#{userId},#{createTime},#{updateTime},#{status})
</insert>
<select id="list">
SELECT id,title,type,user_id,create_time,update_time,status
FROM notice
<where>
<if test="title!=null and title!=''">
AND title LIKE CONCAT('%',#{title},'%')
</if>
<if test="type!=null">
AND type=#{type}
</if>
</where>
</select>
<delete id="del">
DELETE FROM notice
WHERE id=#{id}
</delete>
<select id="getDetail">
SELECT id,title,type,user_id,create_time,update_time,status,content
FROM notice WHERE id=#{id}
</select>
<update id="updateNotice">
UPDATE notice
<set>
<if test="title!=null and title!=''">
title=#{title},
</if>
<if test="content!=null and content!=''">
content=#{content},
</if>
<if test="type!=null">
type=#{type},
</if>
<if test="status!=null">
status=#{status},
</if>
<if test="updateTime!=null">
update_time=#{updateTime}
</if>
</set>
WHERE id=#{id}
</update>
</mapper>这种业务一旦某个小地方出了一丁点错误,可能就会导致很严重的错误。如果出错了一定要检查路径是否正确;复制的时候有些地方需要修改的要第一时间就改过来不然后面很难找到错误所在;还有SQL语句也需要检查;test测试的时候路径一定要和方法的路径一致......
完成这个业务的基本逻辑后,再进行一些优化。
每一个Mapping里面都有冗余的v1/notice/那么就可以把公共部分提取出来放到类上面的RequestMapping注解中去,同时一定要注意每个方法的注解,增和改用PostMapping注解,查询用GetMapping,删除就用它独有的DeleteMapping。
java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("v1/notice/")
public class NoticeController {
@Autowired
private NoticeMapper noticeMapper;
@PostMapping("noticeAdd")
@ResponseBody
public String noticeAdd(NoticeAddParam noticeAddParam)
{
System.out.println(noticeAddParam);
Notice notice = new Notice();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(noticeAddParam,notice);
notice.setUserId(1L);
notice.setCreateTime(new Date());
notice.setUpdateTime(new Date());
int x=noticeMapper.insert(notice);
if(x>0)
return "添加成功";
return "添加失败";
}
}该项目仅仅使用了一个mapper,但如果项目比较大,用了很多个mapper类,那就需要在每个mapper类前面加上@mapper注解。那么可以在mapper所在包下创建一个包,然后里面创建这个装配类,工程启动时会优先加载这个配置类,再加上@MapperScan注解会自动扫描给定的路径并为所有给定的路径下的mapper类加上注解Mapper。

java
@Configuration
@MapperScan("cn.tedu.project1.mapper")
public class MybatisConfig {
}