😎【博主主页:晚云与城------csdn博客】😎
🤔【本文内容:C++ stack和queue 😍 】🤔
----------------------------------------------- 感谢大家的点赞 ,收藏。 ---------------------------------------------
0**.容器适配器:**
1.什么是容器适配器:
**适配器是一种设计模式(设计模式是一套被反复使用的、多数人知晓的、经过分类编目的、代码设计经验的总结),该种模式是将一个类的接口转换成客户希望的另外一个接口。**从而使原本因接口不兼容而无法一起工作的两个类能够协同工作。
2.容器适配器的主要作用:
- 复用性提升:借助已有的标准容器,通过适配快速构建满足特定需求的数据结构,减少重复开发工作。
- 接口简化:隐藏底层容器复杂的接口细节,为用户提供简洁明了、符合特定数据结构操作逻辑的接口,便于使用和理解。
- 隔离变化:当底层容器的实现方式发生变化时,只要适配器接口保持不变,上层使用适配器的代码无需改动,增强了代码的稳定性和可维护性。
3.总结:
容器适配器就像一个 "转换器" 或者 "包装器"。
想象一下:你有一个多功能的工具箱(就像 C++ 里的 vector、list 这些容器,功能很多),但你现在只需要用它来做一件很特定的事,比如只需要用它当一个杯子喝水。
容器适配器就相当于给这个工具箱套了个外壳,把多余的功能都挡住,只露出你需要的那几个功能按钮。
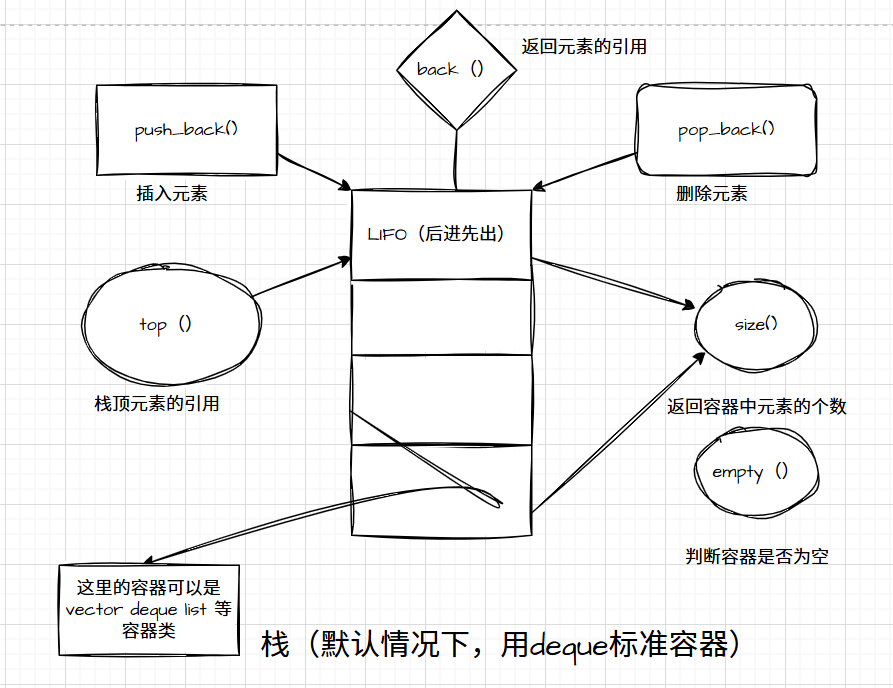
1.stack(栈)的介绍:
stack(栈)是一种容器适配器,尤其是在操作后进先出(LIFO)的情景下,其中元素仅从容器的一端进行 插入和提取**。**
stack(栈)是作为容器适配器来实现的,容器适配器是这样的类:它们把某个特定容器类的封装对象用作其底层容器,并提供一组特定的成员函数来访问其元素。元素从特定容器的 "后端" 进行压入 / 弹出操作,这个 "后端" 被称为栈的栈顶。
底层容器可以是任何标准容器类模板,或者其他一些专门设计的容器类。该容器应当支持以下操作:
- empty: 判断容器是否为空。
- size: 返回容器中元素的数量。
- back: 返回容器中尾部元素的引用。
- push_back:容器中尾部的一个元素插入。
- pop_back: 容器中尾部的一个元素删除。
标准容器类 vector、deque 和 list 满足这些要求**。默认情况下,如果没有为特定的栈类实例化指定容器类,就会使用标准容器 deque。**
2.stack(栈)的使用:
1.成员函数:

cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <deque>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
//stack的构造使用
deque<int> mydeque (3,100);
vector<int> myvector (2,200);
//默认用deque容器
stack<int> first; //空栈
stack<int> second (mydeque);
//指定用vector容器
stack<int,vector<int> > third; //用vector容器构造的空stack
stack<int,vector<int> > fourth (myvector);
cout << "size of first: " << first.size() << endl;
cout << "size of second: " << second.size() << endl;
cout << "size of third: " << third.size() << endl;
cout << "size of fourth: " << fourth.size() << endl;
//empty的使用
stack<int> mystack;
int sum (0);
for (int i=1;i<=10;i++)
{
mystack.push(i);
}
while (!mystack.empty())//以判断栈为空作为条件
{
sum += mystack.top();
mystack.pop();
}
cout << "total: " << sum << endl;
//size的使用
stack<int> myints;
cout << "0. size: " << myints.size() << endl;
for (int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
myints.push(i);
}
cout << "1. size: " << myints.size() << endl;
myints.pop();
cout << "2. size: " << myints.size() << endl;
//top的使用
stack<int> mystack1;
mystack1.push(10);
mystack1.push(20);
mystack1.top() -= 5;
std::cout << "mystack1.top() is now " << mystack1.top() << endl;
//emplace的使用
stack<string> mystack2;
mystack2.emplace ("First sentence");
mystack2.emplace ("Second sentence");
cout << "mystack2 contains:"<<endl;
while (!mystack2.empty())
{
cout << mystack2.top() <<endl;
mystack2.pop();
}
//swap的使用
stack<int> foo,bar;
foo.push (10);
foo.push(20);
foo.push(30);
bar.push (111);
bar.push(222);
foo.swap(bar);
cout << "size of foo: " << foo.size() << endl;
cout << "size of bar: " << bar.size() << endl;
return 0;
}最小栈:
cpp
class MinStack
{
public:
void push(int x)
{
_elem.push(x);
if (_min.empty() || x <= _min.top())
{
_min.push(x);
}
}
void pop()
{
if (_min.top() == _elem.top())
{
_min.pop();
}
_elem.pop();
}
int top()
{
return _elem.top();
}
int getmin()
{
return _min.top();
}
private:
stack<int> _elem;
stack<int> _min;
};_elem 保存栈中的元素 _min保存栈的最小元素(记录_elem中的最小值在_min的栈顶)。
栈的弹出压入序列:
cpp
class solution {
bool IsPopOrder(vector<int> pushV,vector<int> popV)
{
if (pushV.size() != popV.size())
{
return false;
}
int outIdx = 0;
int inIdx = 0;
stack<int> s;
while (outIdx <= popV.size())
{
while (s.empty() || s.top() != popV[outIdx])
{
if (inIdx <= pushV.size())
{
s.push(pushV[inIdx++]);
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
s.pop();
++outIdx;
}
return true;
}
};这个是指用两个容器存储元素,一个是压栈的,一个是出栈的。比如12345是压栈的,45321是出栈的,我们建一个栈,先将1234压进去,因为这4个数到4就跟出栈的相等了,就出栈,然后再压5,5又是一样的,就出5,后面一样出完.这样就是一个合格的两个压入弹出序列。
逆波兰表达式求值(计算器):
cpp
class Solution
{
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens)
{
stack<int> s;
for (int i = 0;i < tokens.size();i++)
{
string& str = tokens[i];
if (!(str == "+" || str == "-" || str == "*" || str == "/"))
{
s.push(atoi(str.c_str()));
}
else
{
if (s.size() < 2)
{
return 0;
}
int right = s.top();
if (str[0] == '/' && right == 0)
{
cout << "除数不能为零" << endl;
return 0;
}
s.pop();
int left = s.top();
s.pop();
switch (str[0])
{
case '+':
s.push(left + right);
break;
case '-':
s.push(left - right);
break;
case '*':
s.push(left * right);
break;
case '/':
s.push(left / right);
break;
}
}
}
return s.size() == 1 ? s.top() : 0;
}
};3.stack(栈)的模拟:
cpp
//模拟stack
//我们要知道stack是容器适配器,需要用容器,为了好使用各种容器作为底层的,所以我们要用模板
//deque能以最小的代价,高效满足stack的操作需求,并兼顾性能和空间开销
template<class T,class Container = deque<T>>
class my_stack
{
public:
size_t size()const
{
return _c.size();
}
bool empty()const
{
return _c.size() == 0;
}
const T& top()const
{
return _c.back();
}
T& top()
{
return _c.back();
}
void push(const T& x)
{
_c.push_back(x);
}
void pop()
{
_c.pop_back();
}
private:
Container _c;
};在 C++ 中,
std::stack(栈适配器)默认选用std::deque作为底层容器,主要是因为deque能很好地适配栈的操作特性,且在性能与内存管理等方面表现出色:
- 操作适配 :栈仅需尾部的入栈、出栈和访问栈顶操作,
deque对尾部操作(push_back、pop_back、back)的支持高效且时间复杂度为 (O(1)),完美契合栈的核心操作需求。- 性能与内存优势 :
deque是分段连续的内存结构,相比vector,扩容时无需大规模复制元素,内存管理更优;相比list,缓存友好性更好,空间开销也更小,在性能和内存使用上达到了较好的平衡。- 标准库设计选择 :综合各容器特性,
deque能为栈提供良好支持,因此被选为默认底层容器,同时stack也支持用户根据需求指定其他符合操作要求的容器(如vector、list)作为底层容器。
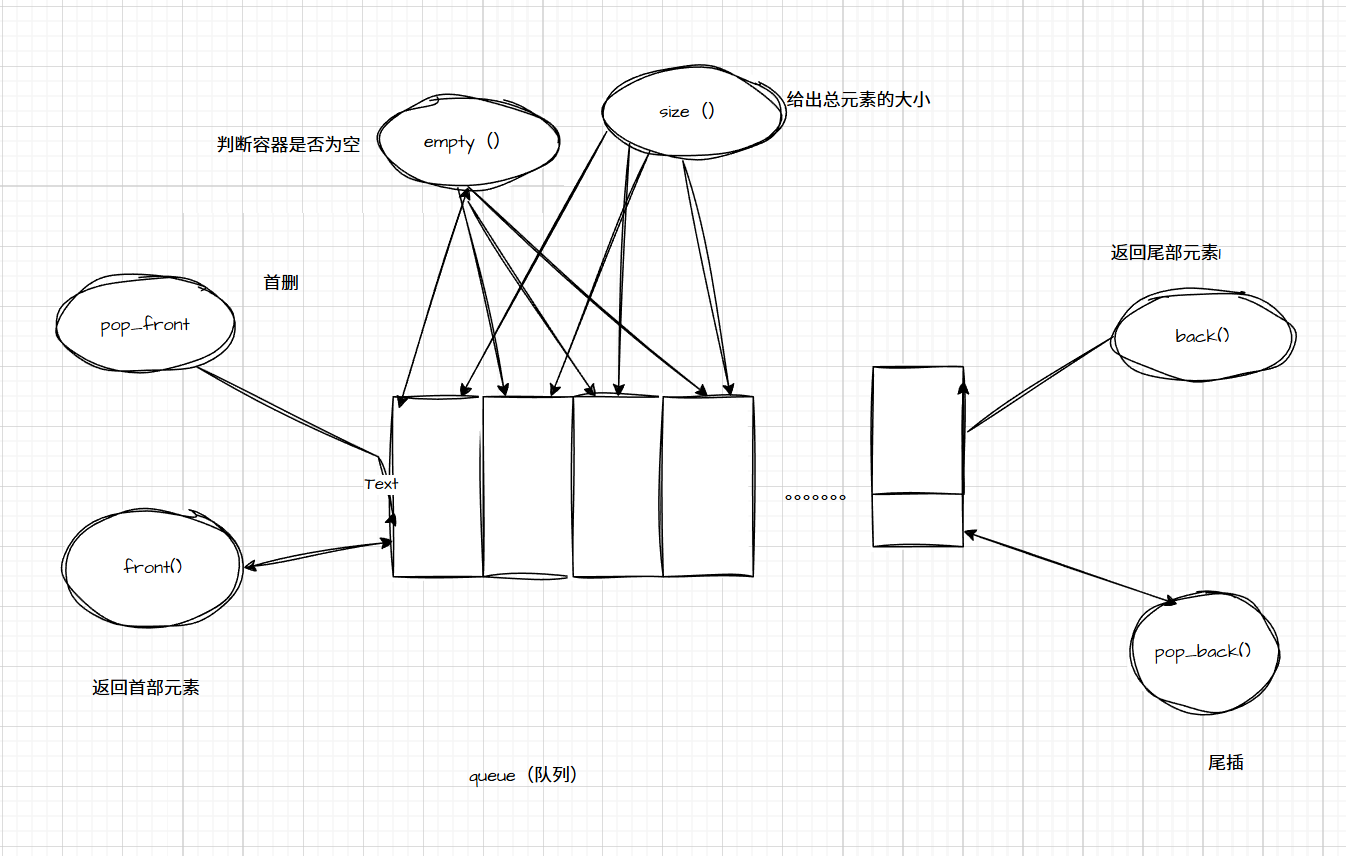
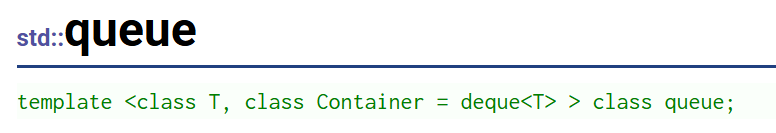
4.**queue(队列)**的介绍:
queue(队列)是一种容器适配器,尤其是在操作先进先出(FIFO)的情景下,其中元素即元素从容器的一端插入,从另一端提取。
queue(队列)是作为容器适配器来实现的,容器适配器是这样的类:它们把某个特定容器类的封装对象用作其底层容器,并提供一组特定的成员函数来访问其元素。元素从特定容器的 "后端(back)" 进行插入 ,并从其 "前端(front)" 弹出。
底层容器可以是任何标准容器类模板,或者其他一些专门设计的容器类。该容器应当支持以下操作:
- empty(判断是否为空)
- size(获取大小)
- front(访问前端元素)
- back(访问后端元素)
- push_back(在后端添加元素)
- pop_front(从前端弹出元素)
在标准库设计里面:
标准容器类deque(双端队列)和list(链表)满足这些要求。默认情况下,如果在特定的队列类实例化时没有指定容器类,就会使用标准容器deque。
5.queue(队列)的使用:
1.成员函数:
这里的push和pop分别是push_back 和 pop_back.
| 函数声明 | 接口说明 |
|---|---|
queue() |
构造空的队列 |
empty() |
检测队列是否为空,是返回true,否则返回false |
size() |
返回队列中有效元素的个数 |
front() |
返回队头元素的引用 |
back() |
返回队尾元素的引用 |
push() |
在队尾将元素val入队列 |
pop() |
将队头元素出队列 |
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <deque>
#include <list>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
//队列的构造
deque<int> mydeck (3,100);
list<int> mylist (2,200);
queue<int> first;
queue<int> second (mydeck);
queue<int,list<int> > third;
queue<int,list<int> > fourth (mylist);
cout << "size of first: " << first.size() << endl;
cout << "size of second: " << second.size() << endl;
cout << "size of third: " << third.size() << endl;
cout << "size of fourth: " << fourth.size() << endl;
//empty的使用
queue<int> myqueue;
int sum (0);
for (int i=1;i<=10;i++) myqueue.push(i);
while (!myqueue.empty())
{
sum += myqueue.front();
myqueue.pop();
}
cout << "total: " << sum << endl;
//size的使用
queue<int> myints;
cout << "0. size: " << myints.size() << endl;
for (int i=0; i<5; i++) myints.push(i);
cout << "1. size: " << myints.size() << endl;
myints.pop();
cout << "2. size: " << myints.size() << endl;
//front的使用
queue<int> myqueue1;
myqueue1.push(77);
myqueue1.push(16);
myqueue1.front() -= myqueue1.back(); // 77-16=61
cout << "myqueue.front() is now " << myqueue.front() << endl;
//back的使用
queue<int> myqueue2;
myqueue2.push(12);
myqueue2.push(75); // this is now the back
myqueue2.back() -= myqueue2.front();
cout << "myqueue.back() is now " << myqueue.back() << endl;
//pop的使用
queue<int> myqueue3;
int myint1;
cout << "Please enter some integers (enter 0 to end):\n";
do {
cin >> myint1;
myqueue3.push (myint1);
} while (myint1);
cout << "myqueue contains: ";
while (!myqueue.empty())
{
cout << ' ' << myqueue3.front();
myqueue3.pop();
}
cout << '\n';
//push的使用
queue<int> myqueue4;
int myint2;
cout << "Please enter some integers (enter 0 to end):\n";
do {
cin >> myint2;
myqueue.push (myint2);
} while (myint2);
cout << "myqueue contains: ";
while (!myqueue4.empty())
{
cout << ' ' << myqueue4.front();
myqueue4.pop();
}
cout << '\n';
return 0;
}6.queue(队列)的模拟:
因为queue的接口中存在头删和尾插,因此使用vector来封装效率太低,故可以借助deque和list来模拟实现queue。
这里用list作为容器。
cpp
template<class T,class Container = list<T>>
class my_queue
{
public:
queue()
{}
void push(const T& x)
{
_c.push_back(x);
}
void pop()
{
_c.pop_front();
}
T& back()
{
return _c.back();
}
const T& back()const
{
return _c.back();
}
T& front()
{
return _c.front();
}
const T& front()const
{
return _c.front();
}
size_t size()const
{
return _c.size();
}
bool empty()const
{
return _c.empty();
}
private:
Container _c;
};❤️总结

相信坚持下来的你一定有了满满的收获。那么也请老铁们多多支持一下,点点关注,收藏,点赞。❤️