 一、list的介绍及使用
一、list的介绍及使用
- list是可以在常数范围内在任意位置进行插入和删除的序列式容器,并且该容器可以前后双向迭代。
- list的底层是双向链表结构,双向链表中每个元素存储在互不相关的独立节点中,在节点中通过指针指向其前一个元素和后一个元素。
- list与forward_list非常相似:最主要的不同在于forward_list是单链表,只能朝前迭代,已让其更简单高效。
- 与其他的序列式容器相比(array,vector,deque),list通常在任意位置进行插入、移除元素的执行效率更好。
- 与其他序列式容器相比,list和forward_list最大的缺陷是不支持任意位置的随机访问,比如:要访问list的第6个元素,必须从已知的位置(比如头部或者尾部)迭代到该位置,在这段位置上迭代需要线性的时间开销;list还需要一些额外的空间,以保存每个节点的相关联信息(对于存储类型较小元素的大list来说这可能是一个重要的因素)
list是双向带头链表
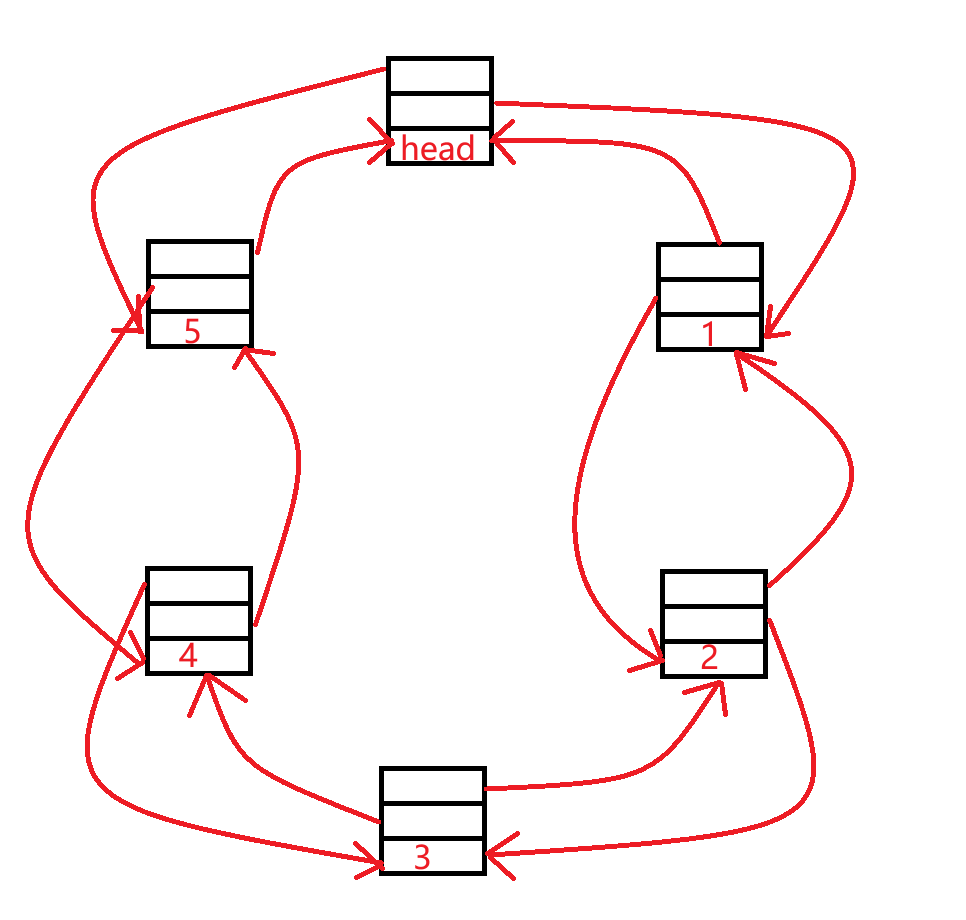
注意:
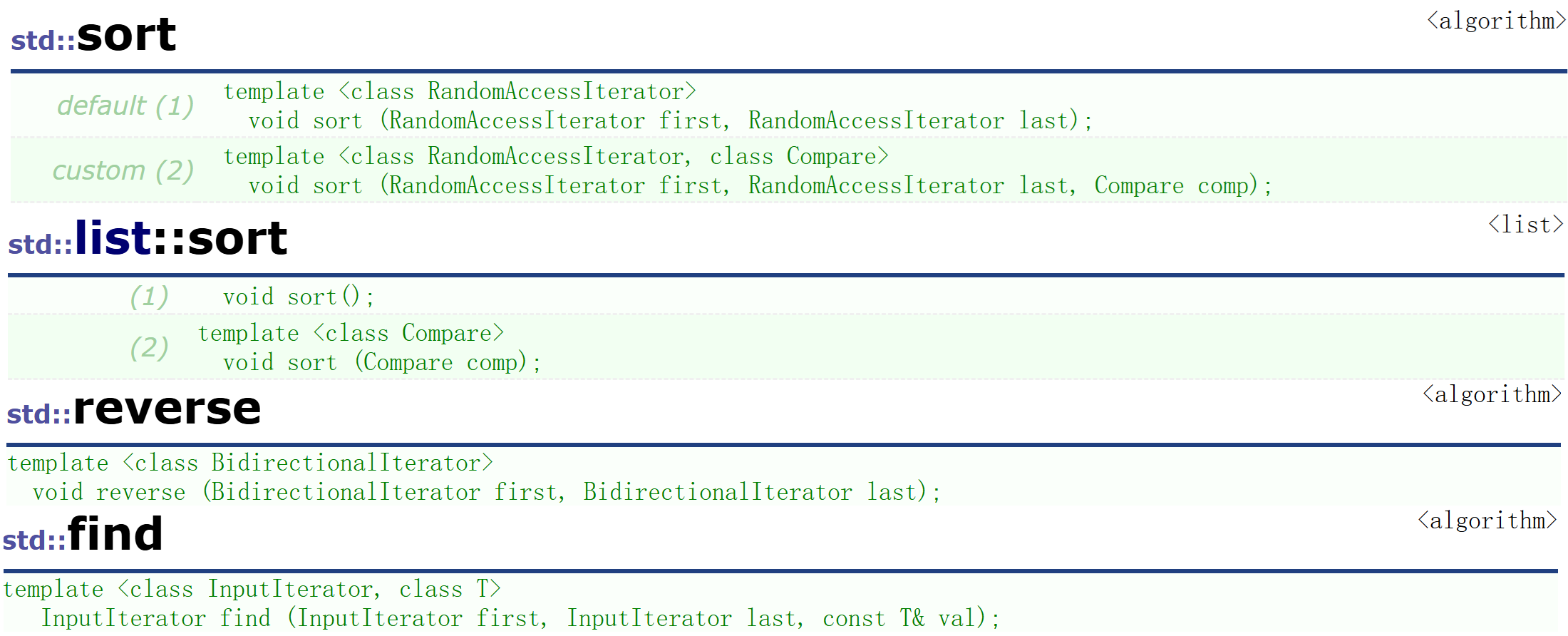
在阅读list文档时会发现list有自己sort函数
因为list的迭代器属于双向迭代器,而std算法库里的sort是使用随机迭代器的,所以list不适合用std算法库里的sort。但是list的sort底层是归并排序效率比不过算法库里的sort,如果遇到少量数据可以使用list的sort,遇到大量数据可以将list的数据放到vector中使用std算法库的sort排序。
 类似于长方形的性质可以用在正方形上,反之不行。
类似于长方形的性质可以用在正方形上,反之不行。
二、list的模拟实现
list的模拟实现重点在于list的迭代器实现,list的迭代器是个自定义类型
list的迭代器使用了三个模板参数

cpp
namespace List
{
template<class T>
struct list_node
{
list_node* _next;
list_node* _prev;
T _val;
list_node(const T& val = T())
:_next(nullptr)
,_prev(nullptr)
,_val(val)
{
}
};
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct list_iterator
{
typedef list_node<T> Node;
typedef list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;
Node* _node;
list_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{
}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_val;
}
self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
self operator++(int)
{
self tmp = *this;
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
self operator--(int)
{
self tmp = *this;
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
bool operator==(const self it) const
{
return _node == it._node;
}
bool operator!=(const self it) const
{
return _node != it._node;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_val;
}
};
template<class T>
class list
{
typedef list_node<T> Node;
public:
typedef list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
list()
:_size(0)
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
}
list(size_t n, const T& val = T())
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
while (n--)
{
push_back(val);
}
}
list(const list<T>& lt)
:_size(0)
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
for (auto e : lt)
{
push_back(e);
}
}
~list()
{
clear();
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}
iterator begin()
{
return _head->_next;
}
iterator end()
{
return _head;
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _head->_next;
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _head;
}
const_iterator cbegin() const
{
return _head->_next;
}
const_iterator cend() const
{
return _head;
}
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos != _head);
Node* prev = pos._node->_prev;
Node* next = pos._node->_next;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
_size--;
delete pos._node;
return next;
}
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* prev = pos._node->_prev;
Node* NewNode = new Node(x);
cur->_prev = NewNode;
prev->_next = NewNode;
NewNode->_next = cur;
NewNode->_prev = prev;
NewNode->_val = x;
_size++;
return NewNode;
}
void push_back(const T& x)
{
//Node* tail = new Node;
//tail->_val = x;
//_head->_prev->_next = tail;
//tail->_prev = _head->_prev;
//_head->_prev = tail;
//tail->_next = _head;
//_size++;
insert(end(), x);
}
void pop_back()
{
erase(_head->_prev);
}
void push_front(const T& x)
{
insert(_head->_next, x);
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(_head->_next);
}
size_t size()
{
return _size;
}
void clear()
{
for (size_t i = _size; i > 0; --i)
{
pop_back();
}
_size = 0;
}
void swap(list& lt)
{
std::swap(_head, lt._head);
std::swap(_size, lt._size);
}
private:
Node* _head;
size_t _size;
};
}单参数的构造函数支持隐式类型的转化

->运算符重载 可以用于访问结构体成员变量的成员变量
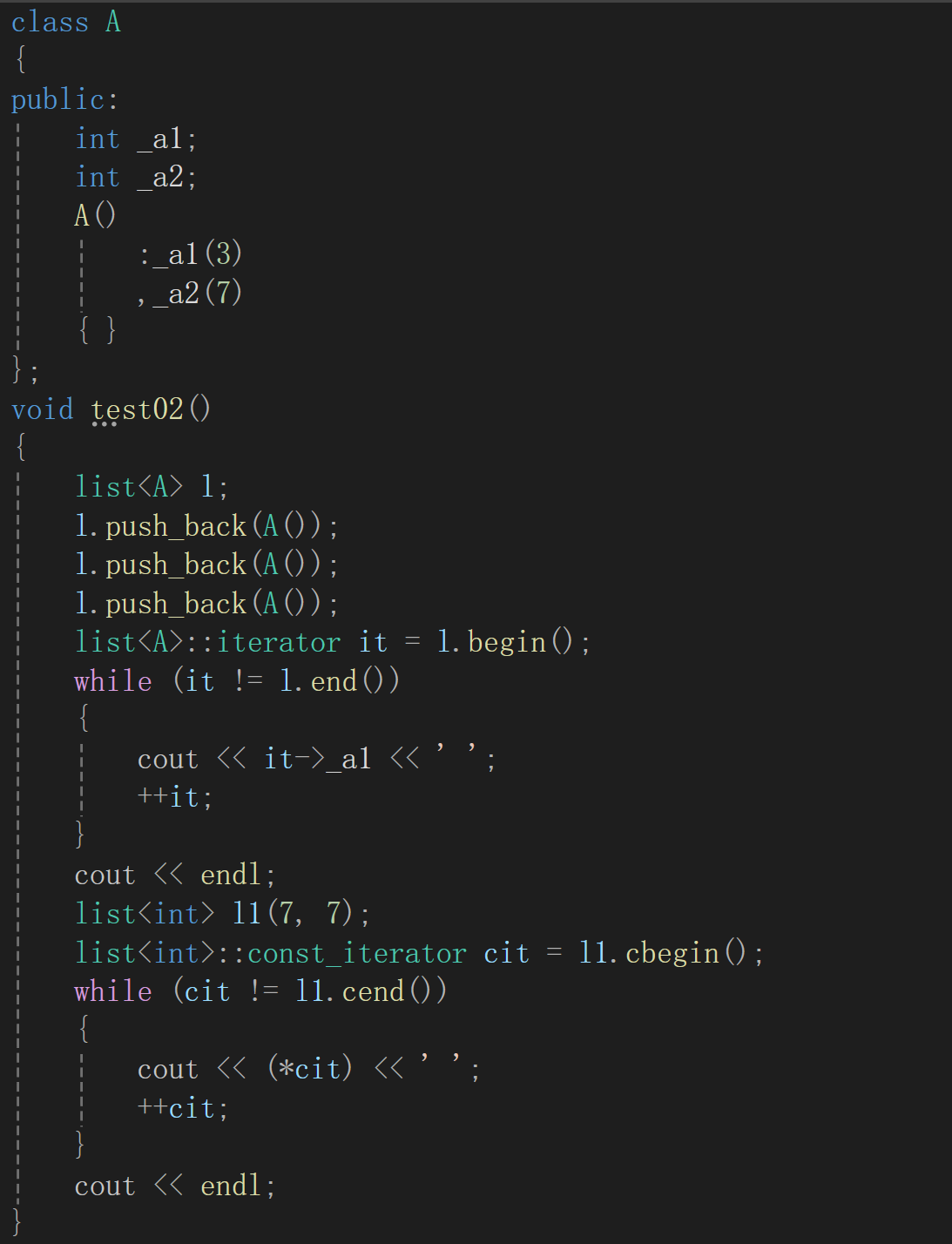
严格来说,it->->_a1 这样写才符合语法要求;因为运算符重载要求可读性,所以编译器特殊处理,省略了一个->。
注意:
类模板在类里面写时,既可以写类名也可以写类型