场景:
使用分库分表的业务有时分库数量几百甚至上千,当主管需要查询每个库中的数据,掌握数据分布情况。要你查看哪些库中的表数量大于某个量级的给找出来 ,你会怎么做。
例子 :
mysql库数量:db_xx_deviceinfo0-999 共1000个库每个库中 28个表。
一、查系统表(缺点:数据不是很精确,优点:快速。)
sql
root@localhost 14:17: [information_schema]>select TABLE_SCHEMA,TABLE_NAME,TABLE_ROWS from tables where TABLE_SCHEMA like 'db_xx_deviceinfo%' and TABLE_ROWS>200000;
+-----------------------+------------------------+------------+
| TABLE_SCHEMA | TABLE_NAME | TABLE_ROWS |
+-----------------------+------------------------+------------+
| db_xx_deviceinfo104 | electric_meter_reading | 1578844 |
| db_xx_deviceinfo696 | electric_meter_reading | 3579983 |
| db_xx_deviceinfo696 | push_data_record | 975528 |
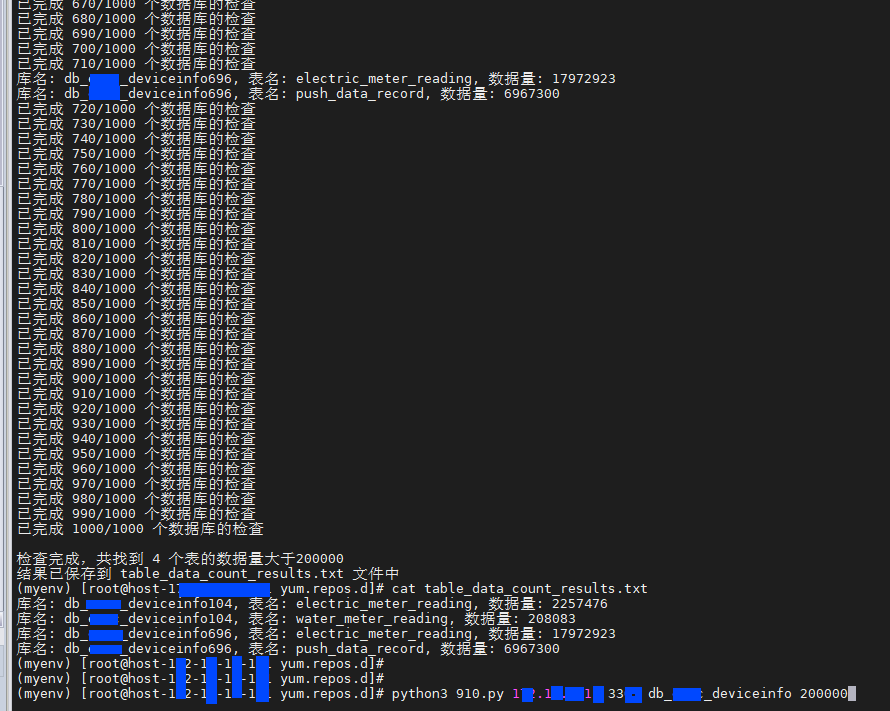
+-----------------------+------------------------+------------+二、采用查询业务表的方式(缺点:写脚本去完成,有点麻烦,优点:快速与准确)
1、脚本
python
#! _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
import pymysql
import sys
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor, as_completed
m_host = sys.argv[1]
m_user='tmp_select'
m_port = sys.argv[2] # 这里是字符串类型
m_db = sys.argv[3]
t_count = sys.argv[4]
def get_mysql_connection():
"""获取MySQL数据库连接"""
# 从密码文件中读取密码
try:
with open('/root/.ssh/.password.txt', 'r') as f:
password = f.read().strip()
except Exception as e:
print(f"无法读取密码文件: {e}")
sys.exit(1)
# 连接MySQL
try:
conn = pymysql.connect(
host=m_host, # MySQL服务器IP
port=int(m_port), # 关键修复:将字符串转换为整数
user=m_user, # 用户名
password=password, # 密码
charset='utf8mb4',
cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor,
connect_timeout=30
)
return conn
except Exception as e:
print(f"数据库连接失败: {e}")
sys.exit(1)
def check_database_exists(conn, db_name):
"""检查数据库是否存在"""
try:
with conn.cursor() as cursor:
cursor.execute("SHOW DATABASES LIKE %s", (db_name,))
return cursor.fetchone() is not None
except Exception as e:
print(f"检查数据库 {db_name} 是否存在时出错: {e}")
return False
def check_table_data_count(db_name):
"""检查单个库中所有表的数据量"""
results = []
try:
# 为每个线程创建独立的连接
with open('/root/.ssh/.pwd.txt', 'r') as f:
password = f.read().strip()
conn = pymysql.connect(
host=m_host,
port=int(m_port),
user=m_user,
password=password,
database=db_name,
charset='utf8mb4',
cursorclass=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor,
connect_timeout=10
)
with conn.cursor() as cursor:
# 获取当前数据库中的所有表
cursor.execute("SHOW TABLES")
tables = cursor.fetchall()
for table in tables:
table_name = list(table.values())[0]
# 查询表的数据量
try:
cursor.execute(f"SELECT COUNT(*) as count FROM `{table_name}`")
count_result = cursor.fetchone()
data_count = count_result['count']
# 如果数据量大于t_count,记录结果
if data_count > int(t_count):
result_str = f"库名: {db_name}, 表名: {table_name}, 数据量: {data_count}"
results.append(result_str)
except Exception as e:
print(f"查询表 {db_name}.{table_name} 数据量时出错: {e}")
continue
conn.close()
except Exception as e:
print(f"检查数据库 {db_name} 时出错: {e}")
return results
def main():
"""主函数"""
print("开始检查各库表数据量...")
print(f"连接MySQL服务器: %s:%s, 用户: %s" %(m_host,m_port,m_user))
# 生成所有数据库名
database_names = [f"{m_db}{str(i)}" for i in range(1000)]
# 先检查哪些数据库存在
conn = get_mysql_connection()
existing_dbs = []
print("正在检查存在的数据库...")
for db_name in database_names:
if check_database_exists(conn, db_name):
existing_dbs.append(db_name)
conn.close()
print(f"发现 {len(existing_dbs)} 个数据库存在")
# 使用多线程并行检查每个数据库
all_results = []
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=20) as executor:
# 提交所有任务
future_to_db = {executor.submit(check_table_data_count, db_name): db_name for db_name in existing_dbs}
# 处理完成的任务
for i, future in enumerate(as_completed(future_to_db)):
db_name = future_to_db[future]
try:
results = future.result()
all_results.extend(results)
# 实时输出结果
for result in results:
print(result)
# 显示进度
if (i + 1) % 10 == 0:
print(f"已完成 {i + 1}/{len(existing_dbs)} 个数据库的检查")
except Exception as e:
print(f"处理数据库 {db_name} 时发生错误: {e}")
# 保存结果到文件
if all_results:
with open('table_data_count_results.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for result in all_results:
f.write(result + '\n')
print(f"\n检查完成,共找到 {len(all_results)} 个表的数据量大于{t_count}")
print("结果已保存到 table_data_count_results.txt 文件中")
else:
print(f"未找到数据量大于{t_count}的表")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()2、运行查询
python3 910.py 1x2.1x.5.x1 3305 db_xx_deviceinfo 200000