😎【博主主页:晚云与城------csdn博客】😎
🤔【本文内容:C++ stack和queue 😍 】🤔
----------------------------------------------- 感谢大家的点赞 ,收藏。 ---------------------------------------------
1.deque****的介绍:
deque(双端队列):是一种双开口的"连续"空间的数据结构,双开口的含义是:可以在头尾两端进行插入和删除操作,且时间复杂度为O(1),与vector比较,头插效率高,不需要搬移元素;与list比较,空间利用率比较高。
deque的底层是 类似一个动态的二维数组,这里的连续其实是一种假象。首先可以看作,它将"列"作为一个 缓冲区用来存储地址 ,而这个地址就是每行的地址,这里 每一行用来存储数据。
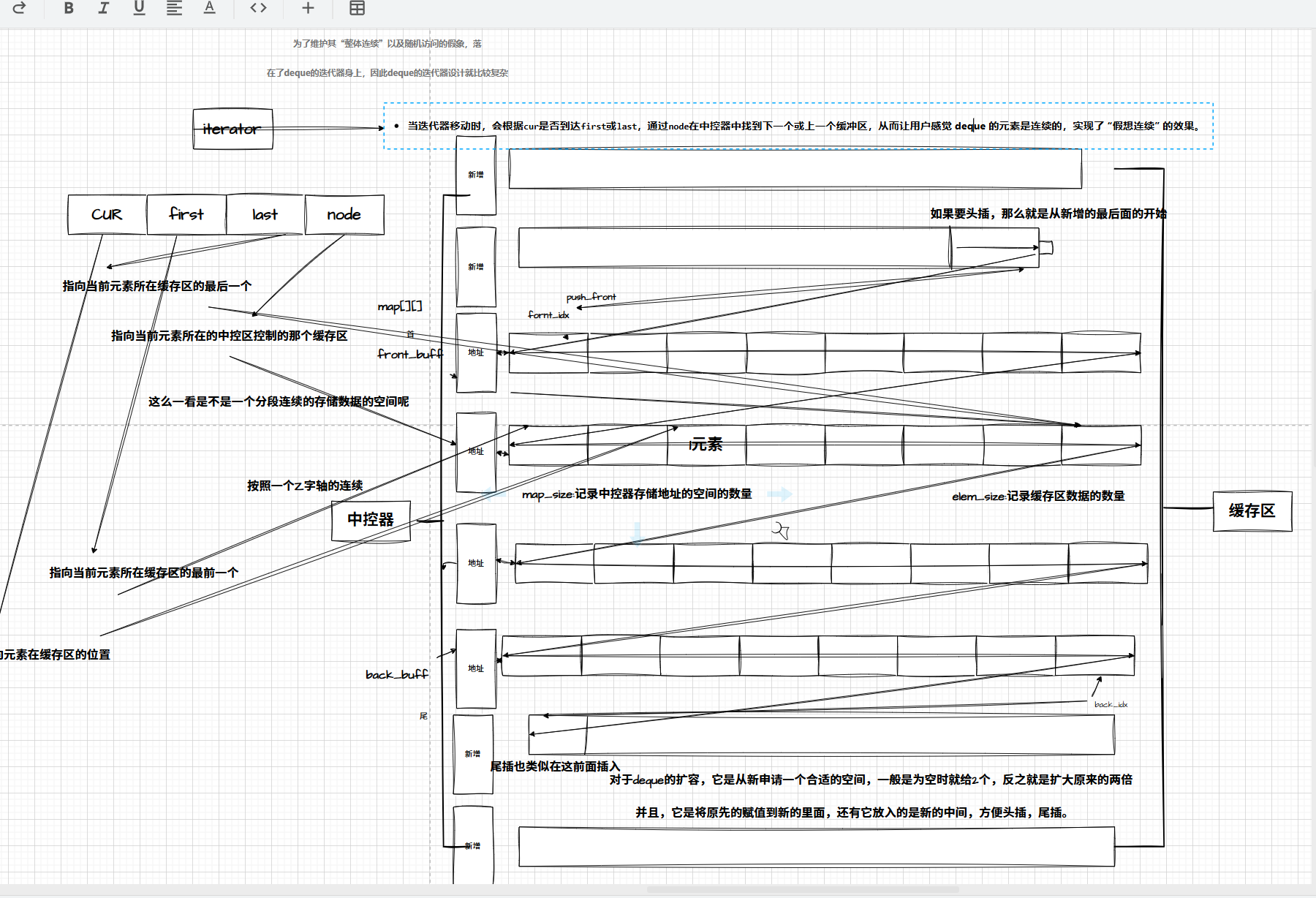
deque的缺陷:
与vector比较,deque的优势是:头部插入和删除时,不需要搬移元素,效率特别高,而且在扩容时,也不 需要搬移大量的元素,因此其效率是必vector高的。
与list比较,其底层是连续空间,空间利用率比较高,不需要存储额外字段。
但是,deque有一个致命缺陷:不适合遍历,因为在遍历时,deque的迭代器要频繁的去检测其是否移动到 某段小空间的边界,导致效率低下,而序列式场景中,可能需要经常遍历,因此在实际中,需要线性结构 时,大多数情况下优先考虑vector和list,deque的应用并不多,而目前能看到的一个应用就是:STL用其作 为stack和queue的底层数据结构。
stack是一种 后进先出的特殊线性数据结构 ,因此 只要具有push_back()和pop_back()操作的线性结构 ,都可 以 作为stack的底层容器 ,比如vector和list都可以;queue是 先进先出的特殊线性数据结构 , 只要具有push_back和pop_front操作的线性结构 ,都 可以作为queue的底层容器 ,比如list。但是STL中对stack和 queue 默认选择deque作为其底层容器 ,主要是 因为 :
1. stack和queue不需要遍历(因此stack和queue没有迭代器),只需要在固定的一端或者两端进行操作。
2. 在stack中元素增长时,deque比vector的效率高(扩容时不需要搬移大量数据);queue中的元素增长 时,deque不仅效率高,而且内存使用率高。 结合了deque的优点,而完美的避开了其缺陷。
2.priority_queue****的介绍:
优先队列是一种容器适配器,其专门设计为:根据某种严格弱序准则,它的第一个元素始终是其包含元素中最大的那个。
这种情况与堆类似,在堆中元素可随时插入,且只有最大堆元素(即优先队列顶端的那个元素)能被检索。
优先队列作为容器适配器来实现,容器适配器是使用特定容器类的封装对象作为其底层容器的类,并提供一组特定的成员函数来访问其元素。元素从特定容器的 "后端" 弹出,该 "后端" 就是优先队列的顶端。
底层容器可以是任何标准容器类模板或其他一些专门设计的容器类。该容器应能通过随机访问迭代器进行访问,并支持以下操作:
- empty()
- size()
- front()
- push_back()
- pop_back()
标准容器类 vector 和 deque 满足这些要求。默认情况下,如果没有为特定的优先队列类实例指定容器类,则使用标准容器 vector。
对随机访问迭代器的支持是为了始终在内部保持堆结构。容器适配器在需要时会通过自动调用算法函数 make_heap、push_heap 和 pop_heap 来自动完成这一操作。
3. priority_queue****的使用:

| 成员函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| (constructor) | 构造优先队列 |
| empty | 测试容器是否为空 |
| size | 返回容器的大小(元素个数) |
| top | 访问队顶元素(优先级最高的元素) |
| push | 插入一个元素到优先队列中 |
| emplace | 构造并插入一个元素到优先队列中 |
| pop | 移除队顶元素 |
| swap | 交换两个优先队列的内容 |
优先级队列默认使用vector作为其底层存储数据的容器,在vector上又使用了堆算法将vector中元素构造成堆的结构,因此priority_queue就是堆,所有需要用到堆的位置,都可以考虑使用priority_queue。注意:默认情况下priority_queue是大堆。

比较规则默认是less<T>,来实现最大堆。greater<T>,则会成为最小堆
1.构造:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <functional> //包含 std::greater 等函数对象,用于修改优先队列的比较规则。
using namespace std;
//自定义比较类 mycomparison:
//这个类用于自定义优先队列的比较逻辑。
//成员 reverse 是一个标记,决定比较是 "小于"(默认,小的优先级低)还是 "大于"(大的优先级低,即小的优先级高)。
//重载 operator(),实现对两个 int 类型元素的比较:
//如果 reverse 为 true,返回 lhs > rhs(此时优先队列按 "大的元素优先级低" 排序,队首是最小的元素)。
//否则返回 lhs < rhs(默认,优先队列按 "大的元素优先级高" 排序,队首是最大的元素)
class mycomparison
{
private:
bool reverse;
public:
mycomparison(const bool& revparam=false)
{
reverse=revparam;
}
bool operator() (const int& lhs, const int&rhs) const
{
if (reverse)
{
return (lhs>rhs);
}
else
{
return (lhs<rhs);
}
}
};
int main ()
{
int myints[]= {10,60,50,20};
priority_queue<int> first;//比较规则是 std::less<int>(即 "大的元素优先级高",队首是最大的元素)。
priority_queue<int> second (myints,myints+4);//比较规则是 std::less<int>(即 "大的元素优先级高",队首是最大的元素)。
priority_queue<int, vector<int>,greater<int>> third (myints,myints+4);//比较规则为 std::greater<int>("小的元素优先级高")。此时队首会是最小的元素 10
typedef priority_queue<int,vector<int>,mycomparison> mypq_type;
mypq_type fourth; //使用自定义的 mycomparison 作为比较规则。
mypq_type fifth (mycomparison(true)); //用 mycomparison(true) 初始化,此时 reverse 为 true,比较规则是 lhs > rhs(小的元素优先级高)。
return 0;
}2.empty:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
priority_queue<int> mypq;
int sum (0);
for (int i=1;i<=10;i++) mypq.push(i);
while (!mypq.empty())
{
sum += mypq.top();
mypq.pop();
}
cout << "total: " << sum << endl;
return 0;
}3.size:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <queue> 】
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
priority_queue<int> myints;
cout << "0. size: " << myints.size() << endl;
for (int i=0; i<5; i++) myints.push(i);
cout << "1. size: " << myints.size() << endl;
myints.pop();
cout << "2. size: " << myints.size() << endl;
return 0;
}4.top:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
priority_queue<int> mypq;
mypq.push(10);
mypq.push(20);
mypq.push(15);
cout << "mypq.top() is now " << mypq.top() << '\n';
return 0;
}5.push:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
priority_queue<int> mypq;
mypq.push(30);
mypq.push(100);
mypq.push(25);
mypq.push(40);
cout << "Popping out elements...";
while (!mypq.empty())
{
cout << ' ' << mypq.top();
mypq.pop();
}
cout << '\n';
return 0;
}6.emplace:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
priority_queue<std::string> mypq;
mypq.emplace("orange");
mypq.emplace("strawberry");
mypq.emplace("apple");
mypq.emplace("pear");
cout << "mypq contains:";
while (!mypq.empty())
{
cout << ' ' << mypq.top();
mypq.pop();
}
cout << '\n';
return 0;
}7.pop:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
priority_queue<int> mypq;
mypq.push(30);
mypq.push(100);
mypq.push(25);
mypq.push(40);
cout << "Popping out elements...";
while (!mypq.empty())
{
cout << ' ' << mypq.top();
mypq.pop();
}
cout << '\n';
return 0;
}8.swap:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
priority_queue<int> foo,bar;
foo.push (15); foo.push(30); foo.push(10);
bar.push (101); bar.push(202);
foo.swap(bar);
cout << "size of foo: " << foo.size() << endl;
cout << "size of bar: " << bar.size() << endl;
return 0;4.priority_queue的模拟实现:
1.仿函数/函数对象
类的对象可以像函数一样使用operator()特点:
在优先队列里,仿函数是决定其底层的堆是大堆还是小堆,起着这样的一个作用。
Less<T>:表示建大堆。
cpp
template<class T>
class Less
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x < y;
}
};Greater<T>:表示建小堆。
cpp
template<class T>
class Greater
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x > y;
}
};其简单来说,在堆里面的向上调整,和向下调整里面做一个判断大小的作用。
2.priority_queue的private域:
我这里的swap函数使用库里面的,不是自己写的。
cpp
template <class T, class Container = vector<T>,class Compare = Less<T>>
class my_priority_queue
{
public:
private:
Container _con;
void AdjustDown(int parent)
{
Compare com;
size_t child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child < _con.size())
{
if (child + 1 < _con.size() && com( _con[child],_con[child + 1]))
{
child++;
}
if (com(_con[parent],_con[child]))
{
swap(_con(child),_con(parent));
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void AdjustUp(int child)
{
Compare com;
size_t parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (com(_con[parent], _con[child]))
{
swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else {
break;
}
}
}
};向下调整:

向上调整类似。
3.priority_queue的public域:
cpp
template <class T, class Container = vector<T>,class Compare = Less<T>>
class my_priority_queue
{
public:
my_priority_queue()
{}
//通过迭代器建堆
template<class Inputiterator>
my_priority_queue(Inputiterator first,Inputiterator last)
{
//插入数据
while (firrt != last)
{
_con.push_back(*first);
first++;
}
//建堆
for (int i = ((_con.size()-1-1)/2);i >= 0;i--)
{
AdjustDown(i);
}
}
头删
void pop()
{
//先将尾部的数据与头部交换
swap(_con[0], _con[_con.size() - 1]);
在将尾部的数据删除
_con.pop_back();
//由于对数据的位置改动会影响堆,所以要对改动的位置进行向下调整
AdjustDown(0);
}
bool empty()
{
return _con.empty();
}
size_t size()
{
return _con.size();
}
const T& top()
{
return _con[0];
}
void push(const T& x)
{
//尾插
_con.push_back(x);
//向上调整到合适的位置
AdjustUp(_con.size() - 1);
}
private:
Container _con;
void AdjustDown(int parent)
{
Compare com;
size_t child = 2 * parent + 1;
while (child < _con.size())
{
if (child + 1 < _con.size() && com( _con[child],_con[child + 1]))
{
child++;
}
if (com(_con[parent],_con[child]))
{
swap(_con(child),_con(parent));
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void AdjustUp(int child)
{
Compare com;
size_t parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (com(_con[parent], _con[child]))
{
swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else {
break;
}
}
}
};4.注意事项
你们会有所疑问:仿函数的比较不就是只能对比内置类型吗,这怎么还用模板呢?因此对于自定义类型里面用重载<和>。
Data日期类:
cpp
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
: _year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{
}
bool operator<(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year < d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month < d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day);
}
bool operator>(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year > d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month > d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day);
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d);
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d)
{
_cout << d._year << "-" << d._month << "-" << d._day;
return _cout;
}
void test_priority_queue2()
{
priority_queue<Date*, vector<Date*>, LessPDate> pq;
pq.push(new Date(2023, 7, 20));
pq.push(new Date(2023, 6, 20));
pq.push(new Date(2023, 8, 20));
while (!pq.empty())
{
cout << *pq.top() << " ";
pq.pop();
}
cout << endl;❤️总结

相信坚持下来的你一定有了满满的收获。那么也请老铁们多多支持一下,点点关注,收藏,点赞。❤️