一、Series基本操作
Series序列是一种类似于一维数组的对象,它由一组数据(各种Numpy数据类型)以及一组与之相关的数据标签(即索引)组成。我们打印Series时,它的表现形式为:索引在左边,值在右边。如果没有为数据指定索引,会自动创建一个0-N-1(N为数据的长度)的整数型索引,我们可以通过索引来引用Series中的数据。
- 创建一个基本的Series
python
import pandas as pd
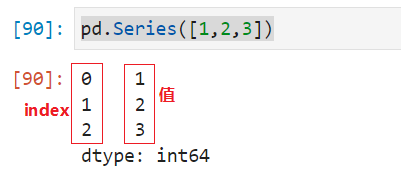
pd.Series([1,2,3])
输出结果:
0 1
1 2
2 3
dtype: int64注意,生成的Series默认是0开始的隐式index,可以自己通过参数的形式指定index的值。
- 指定显式索引
python
pd.Series([1,2,3], index=['a', 'b', 'c'])
输出结果:
a 1
b 2
c 3
dtype: int64
注意,索引的值个数必须跟值的个数匹配,否则报错。- 查看索引和值
python
s = pd.Series([1,2,3], index=['a', 'b', 'c'])
s.index
Index(['a', 'b', 'c'], dtype='object')
s.values
array([1, 2, 3], dtype=int64)- 通过ndarray创建Series
python
pd.Series(np.arange(5), index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'])
输出结果:
a 0
b 1
c 2
d 3
e 4
dtype: int32- 字典转化为Series
python
dict1 = {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c':3}
pd.Series(dict1) # 直接将字典的键和值转化为Series的值和索引
输出结果:
a 1
b 2
c 3
dtype: int64
# 如果指定了索引,则要看该索引有没有在字典的键里面,如果有则会对应,如果没有,则会生成NaN值
pd.Series(dict1, index=['a', 'b', '李四', '王五'])
输出结果:
a 1.0
b 2.0
李四 NaN
王五 NaN
dtype: float64二、索引
索引是Series自带的,如果我们没有通过参数显式指定索引,会默认设置0开始的索引值。我们可以通过索引获取或者指定Series中的一个或一组值。
python
# 查看series的index和values
s = pd.Series([1,2,3], index=['a', 'b', 'c'])
print(s.index)
print(s.index[1:3])
# 通过索引获取元素
s = pd.Series([1,2,3], index=['a', 'b', 'c'])
s.a # 通过显式索引获取值
s['a'] # 通过显式索引获取值
s[0] # 通过隐式索引获取值
注意,设置索引值时,索引中的值是可以重复的。但实际使用中,我们最好不要设置重复的值。- 索引的切片
python
s = pd.Series([1,2,3,4,5], index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'])
s[1:5] # 通过默认索引切片。注意是左闭右开的。
输出结果:
b 2
c 3
d 4
e 5
dtype: int64
s['a':'c'] # 通过指定的索引值切片,注意是两边闭合的。
输出结果:
a 1
b 2
c 3
dtype: int64
注意,如果是切片的索引写错了,则无法得到对应的值。
s['d':'a']
输出结果:
Series([], dtype: int64)
s[1:4:2] # 指定步长
输出结果:
b 2
d 4
dtype: int64
s[['a', 'c']] # 选择特定的元素
输出结果:
a 1
c 3
dtype: int64- 修改索引值
python
ser1 = pd.Series(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']) # 默认是0开始的索引
# 要改只能全部一起改,不能只改其中一部分
ser1.index = ['one', 'two', 'three', 'four']
# 单独修改会报错!!
ser1.index[1:3] = ['one1', 'one2']- 修改value值
python
# 不能通过values属性修改value的值
ser1.values = [1,2,3,4]
# 那么如何才能修改series的value?答案:先选择值,再修改值
# 通过列表切片表达式选择值
ser1[:] = ['哈哈','呵呵', '嗯嗯', '哦哦']
print(ser1)
# 修改其中某些值
ser1[['one', 'two']] = ['haha', 'hehe']
ser1三、筛选和过滤
在Series中,我们可以根据条件来筛选和过滤需要的元素。
python
s[s>3] # 根据条件进行过滤
输出结果:
d 4
e 5
dtype: int64
s[(s>3) & (s<5)] # 组合条件筛选,and
输出结果:
d 4
dtype: int64
s[(s>3) | (s<2)] # 组合条件筛选,or
输出结果:
a 1
d 4
e 5
dtype: int64
s[s==5] # 筛选特定条件
输出结果:
e 5
dtype: int64
s[(s.index=='a') | (s.index=='c')] # 基于index的条件筛选
输出结果:
a 1
c 3
dtype: int64四、序列的运算
序列和单个值进行计算:
python
s*2 # 乘法运算
输出结果:
a 2
b 4
c 6
d 8
e 10
dtype: int64多个不同的Series之间进行运算时,是通过索引值对两个Series中对应的元素进行计算的,只有索引相同的值才会进行运算,索引不同的值无法进行运算。
python
s1 = pd.Series([1,2,3,4], index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])
s2 = pd.Series([5,6,7,8], index=['e','a', 'b', 'f'])
s1+s2 # 两个索引不同的Series进行加法运算
输出结果:
a 7.0
b 9.0
c NaN
d NaN
g NaN
h NaN
dtype: float64
注意,这里由于s1和s2中,只有a和b两个索引的值相同,所以相同索引的值会进行对应的运算。其他没有对应索引值的运算结果为NaN五、缺失值处理
缺失值处理涉及到三个部分,
- 缺失值判断
- 缺失值的选择和统计
- 缺失值的填充和删除
python
# 判断缺失值
s1 = pd.Series([1,2,3,4], index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])
s2 = pd.Series([5,6,7,8], index=['b','a', 'g', 'h'])
s3 = s1+s2
s3.isnull() # 判断s3中的值是否为空
输出结果:
a False
b False
c True
d True
g True
h True
dtype: bool
# 筛选和统计缺失值
s3[s3.notnull()] # 删选出不是空的值
输出结果:
a 7.0
b 7.0
dtype: float64
s3.isnull().sum() # 统计空值的个数
输出结果:
4
# 缺失值的填充
s3.fillna(0) # 用0来填充s3中的缺失值
输出结果:
a 7.0
b 7.0
c 0.0
d 0.0
g 0.0
h 0.0
dtype: float64
# 删除缺失值
s3.dropna() # 删除缺失值
输出结果:
a 7.0
b 7.0
dtype: float64
s3.dropna(inplace=True) # 删除缺失值,原地删除
s3
输出结果:
a 7.0
b 7.0
dtype: float64
python
Series练习
(1)利用姓名、性别、年龄、身高、体重这几个字段以字典形式构造一个Series对象
dic = {'姓名': 'woniu', '性别': '男', '年龄': 19, '身高': 180, '体重': 150}
ser = pd.Series(dic)
(2)打印出series的index和value
print(ser.index)
print(ser.values)
(3)修改index为name, sex, age, height, weight
ser.index = ['name', 'sex', 'age', 'height', 'weight']
ser
(4)将series中的身高和年龄值分别加10
ser[['age', 'height']] = [ser['height']+10, ser['age']+10]