1、Master-Slave架构
1、Master角色
1、BlockManagerMasterEndpoint
它负责跟踪所有Slave节点的Block信息,维护整个应用程序的Block元数据,包括Block所在的位置、所占用的存储空间大小(内存、磁盘或Tachyon)以及副本位置等
blockManagerInfo:保存BlockManagerId到BlockManagerInfo的映射,记录Executor节点的内存使用情况和Block状态blockManagerIdByExecutor:保存Executor ID到BlockManagerId的映射,用于快速查找blockLocations:BlockId到BlockManagerId集合的映射,支持数据块多副本定位
2、Slave角色
1、BlockManagerStorageEndpoint
它主要负责接收来自Master的命令,执行相应的数据清理操作,并响应Master获取Block状态的请求。Slave节点会将Block状态变化主动上报给Master,但不会主动向Master发送消息。
3、消息传递
1 、Slave到Master的消息
scala
case RegisterBlockManager(//Executor启动时注册BlockManager
id, localDirs, maxOnHeapMemSize, maxOffHeapMemSize, endpoint, isReRegister) =>
context.reply(
register(id, localDirs, maxOnHeapMemSize, maxOffHeapMemSize, endpoint, isReRegister))
case _updateBlockInfo @ //数据块状态变更时上报元数据
UpdateBlockInfo(blockManagerId, blockId, storageLevel, deserializedSize, size) =>
@inline def handleResult(success: Boolean): Unit = {
// SPARK-30594: we should not post `SparkListenerBlockUpdated` when updateBlockInfo
// returns false since the block info would be updated again later.
if (success) {
listenerBus.post(SparkListenerBlockUpdated(BlockUpdatedInfo(_updateBlockInfo)))
}
context.reply(success)
}
if (blockId.isShuffle) {
updateShuffleBlockInfo(blockId, blockManagerId).foreach(handleResult)
} else {
handleResult(updateBlockInfo(blockManagerId, blockId, storageLevel, deserializedSize, size))
}
case GetLocations(blockId) =>//查询数据块位置信息
context.reply(getLocations(blockId))
case GetLocationsAndStatus(blockId, requesterHost) =>
context.reply(getLocationsAndStatus(blockId, requesterHost))
case GetLocationsMultipleBlockIds(blockIds) =>
context.reply(getLocationsMultipleBlockIds(blockIds))
case GetPeers(blockManagerId) =>
context.reply(getPeers(blockManagerId))
case GetExecutorEndpointRef(executorId) =>
context.reply(getExecutorEndpointRef(executorId))
case GetMemoryStatus =>
context.reply(memoryStatus)
case GetStorageStatus =>
context.reply(storageStatus)
case GetBlockStatus(blockId, askStorageEndpoints) =>
context.reply(blockStatus(blockId, askStorageEndpoints))
case GetShufflePushMergerLocations(numMergersNeeded, hostsToFilter) =>
context.reply(getShufflePushMergerLocations(numMergersNeeded, hostsToFilter))
case RemoveShufflePushMergerLocation(host) =>
context.reply(removeShufflePushMergerLocation(host))
case IsExecutorAlive(executorId) =>
context.reply(blockManagerIdByExecutor.contains(executorId))
case GetMatchingBlockIds(filter, askStorageEndpoints) =>
context.reply(getMatchingBlockIds(filter, askStorageEndpoints))
case RemoveRdd(rddId) =>
context.reply(removeRdd(rddId))
case RemoveShuffle(shuffleId) =>
context.reply(removeShuffle(shuffleId))
case RemoveBroadcast(broadcastId, removeFromDriver) =>
context.reply(removeBroadcast(broadcastId, removeFromDriver))
case RemoveBlock(blockId) =>
removeBlockFromWorkers(blockId)
context.reply(true)
case RemoveExecutor(execId) =>
removeExecutor(execId)
context.reply(true)
case DecommissionBlockManagers(executorIds) =>
// Mark corresponding BlockManagers as being decommissioning by adding them to
// decommissioningBlockManagerSet, so they won't be used to replicate or migrate blocks.
// Note that BlockManagerStorageEndpoint will be notified about decommissioning when the
// executor is notified(see BlockManager.decommissionSelf), so we don't need to send the
// notification here.
val bms = executorIds.flatMap(blockManagerIdByExecutor.get)
logInfo(log"Mark BlockManagers (${MDC(BLOCK_MANAGER_IDS, bms.mkString(", "))}) as " +
log"being decommissioning.")
decommissioningBlockManagerSet ++= bms
context.reply(true)
case GetReplicateInfoForRDDBlocks(blockManagerId) =>
context.reply(getReplicateInfoForRDDBlocks(blockManagerId))
case StopBlockManagerMaster =>
context.reply(true)
stop()
case UpdateRDDBlockTaskInfo(blockId, taskId) =>
// This is to report the information that a rdd block(with `blockId`) is computed
// and cached by task(with `taskId`). And this happens right after the task finished
// computing/caching the block only when the block is not visible yet. And the rdd
// block will be marked as visible when the corresponding task finished successfully.
context.reply(updateRDDBlockTaskInfo(blockId, taskId))
case GetRDDBlockVisibility(blockId) =>
// Get the visibility status of a specific rdd block.
context.reply(isRDDBlockVisible(blockId))
case UpdateRDDBlockVisibility(taskId, visible) =>
// This is to report the information that whether rdd blocks computed by task(with `taskId`)
// can be turned to be visible. This is reported by DAGScheduler right after task completes.
// If the task finished successfully, rdd blocks can be turned to be visible, otherwise rdd
// blocks' visibility status won't change.
context.reply(updateRDDBlockVisibility(taskId, visible))2、 Master到Slave的消息
scala
case RemoveBlock(blockId) =>//删除指定数据块
doAsync[Boolean](log"removing block ${MDC(BLOCK_ID, blockId)}", context) {
blockManager.removeBlock(blockId)
true
}
case RemoveRdd(rddId) =>//删除RDD所有相关数据块
doAsync[Int](log"removing RDD ${MDC(RDD_ID, rddId)}", context) {
blockManager.removeRdd(rddId)
}
case RemoveShuffle(shuffleId) =>//删除Shuffle相关数据
doAsync[Boolean](log"removing shuffle ${MDC(SHUFFLE_ID, shuffleId)}", context) {
if (mapOutputTracker != null) {
mapOutputTracker.unregisterShuffle(shuffleId)
}
val shuffleManager = SparkEnv.get.shuffleManager
if (shuffleManager != null) {
shuffleManager.unregisterShuffle(shuffleId)
} else {
logDebug(log"Ignore remove shuffle ${MDC(SHUFFLE_ID, shuffleId)}")
true
}
}
case DecommissionBlockManager =>
context.reply(blockManager.decommissionSelf())
case RemoveBroadcast(broadcastId, _) =>//删除广播变量数据
doAsync[Int](log"removing broadcast ${MDC(BROADCAST_ID, broadcastId)}", context) {
blockManager.removeBroadcast(broadcastId, tellMaster = true)
}
case GetBlockStatus(blockId, _) =>
context.reply(blockManager.getStatus(blockId))
case GetMatchingBlockIds(filter, _) =>
context.reply(blockManager.getMatchingBlockIds(filter))
case TriggerThreadDump =>
context.reply(Utils.getThreadDump())
case TriggerHeapHistogram =>
context.reply(Utils.getHeapHistogram())
case ReplicateBlock(blockId, replicas, maxReplicas) =>
context.reply(blockManager.replicateBlock(blockId, replicas.toSet, maxReplicas))
case MarkRDDBlockAsVisible(blockId) =>
// The message is sent from driver to ask the block manager to mark the rdd block with
// `blockId` to be visible now. This happens in 2 scenarios:
// 1. A task computing/caching the rdd block finished successfully and the rdd block can be
// turned to be visible. Driver will ask all block managers hosting the rdd block to mark
// the block as visible.
// 2. Once a replica of a visible block is cached and reported, driver will also ask the
// the block manager to mark the block as visible immediately.
context.reply(blockManager.blockInfoManager.tryMarkBlockAsVisible(blockId))2、基本概念
1、BlockData
block 抽象出块的存储方式,调用方应在完成块后调用 BlockData#dispose。
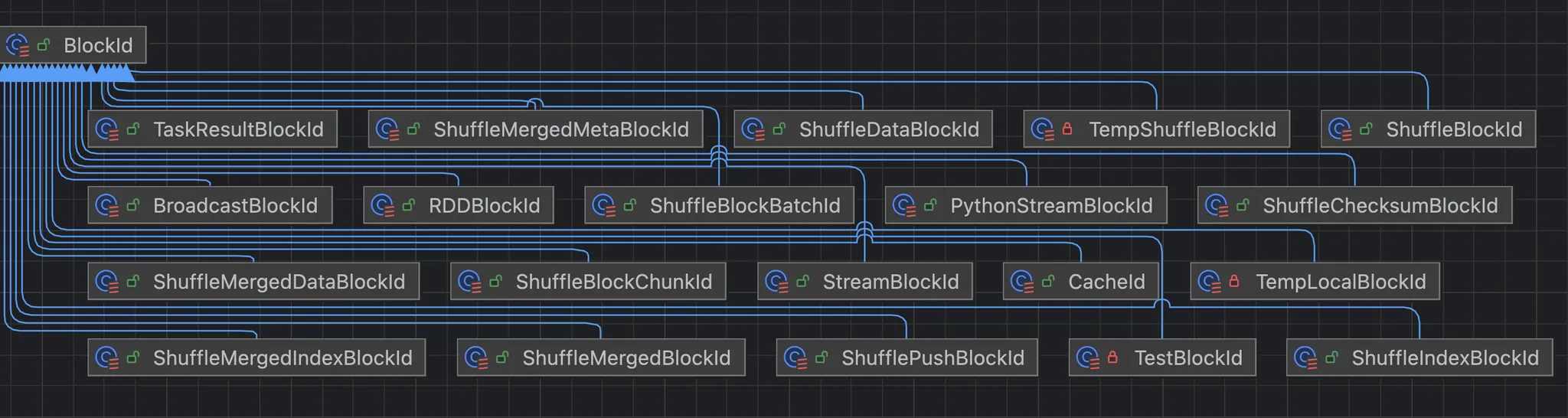
2、BlockId
块唯一标识
scala
val RDD = "rdd_([0-9]+)_([0-9]+)".r
val SHUFFLE = "shuffle_([0-9]+)_([0-9]+)_([0-9]+)".r
val SHUFFLE_BATCH = "shuffle_([0-9]+)_([0-9]+)_([0-9]+)_([0-9]+)".r
val SHUFFLE_DATA = "shuffle_([0-9]+)_([0-9]+)_([0-9]+).data".r
val SHUFFLE_INDEX = "shuffle_([0-9]+)_([0-9]+)_([0-9]+).index".r
val SHUFFLE_PUSH = "shufflePush_([0-9]+)_([0-9]+)_([0-9]+)_([0-9]+)".r
val SHUFFLE_MERGED = "shuffleMerged_([0-9]+)_([0-9]+)_([0-9]+)".r
val SHUFFLE_MERGED_DATA = "shuffleMerged_([_A-Za-z0-9]*)_([0-9]+)_([0-9]+)_([0-9]+).data".r
val SHUFFLE_MERGED_INDEX = "shuffleMerged_([_A-Za-z0-9]*)_([0-9]+)_([0-9]+)_([0-9]+).index".r
val SHUFFLE_MERGED_META = "shuffleMerged_([_A-Za-z0-9]*)_([0-9]+)_([0-9]+)_([0-9]+).meta".r
val SHUFFLE_CHUNK = "shuffleChunk_([0-9]+)_([0-9]+)_([0-9]+)_([0-9]+)".r
val BROADCAST = "broadcast_([0-9]+)([_A-Za-z0-9]*)".r
val TASKRESULT = "taskresult_([0-9]+)".r
val STREAM = "input-([0-9]+)-([0-9]+)".r
val PYTHON_STREAM = "python-stream-([0-9]+)-([0-9]+)".r
val TEMP_LOCAL = "temp_local_([-A-Fa-f0-9]+)".r
val TEMP_SHUFFLE = "temp_shuffle_([-A-Fa-f0-9]+)".r
val TEST = "test_(.*)".r3、BlockInfo
跟踪单个块的元数据,由BlockInfoManager持有
3、核心组件
1、BlockManager
BlockManager 是存储体系最核心的组件,它存在于 Spark 中的所有结点中(包括 Driver 和 Executor),BlockManager 的核心功能就是对磁盘、堆内存和堆外内存进行统一管理。
2、BlockManagerMaster
BlockManagerMaster 持有 BlockManagerMasterEndpoint 的引用。Driver 与 Executor 中的 BlockManager 信息交互都需要依赖于 BlockManagerMaster。
3、BlockInfoManager
blockInfo元数据管理
4、BlockTransferService
块传输服务
5、DiskBlockManager
磁盘块管理器
6、DiskStore
通过DiskBlockManager将逻辑BlockId映射到本地文件(/tmp/blockmgr-.../3e/rdd_<id> )
7、MemoryManager
内存管理器。负责节点内存的分配与回收
8、MemoryStore
反序列化 Java 对象的数组或序列化的 ByteBuffers
基于LinkedHashMap管理内存块,LRU策略淘汰数据。
1、MemoryEntry
DeserializedMemoryEntry 访问速度快,无需反序列化
SerializedValuesHolder 内存紧凑,占用空间小,GC 压力小