1.1日志与策略模式
策略模式
策略模式是一种 行为型设计模式,它定义了一系列算法(策略),并将每个算法封装成独立的类,使它们可以互相替换。策略模式让算法的变化独立于使用它的客户端。
日志认识
计算机中的⽇志是记录系统和软件运⾏中发⽣事件的⽂件,主要作⽤是监控运⾏状态、记录异常信
息,帮助快速定位问题并⽀持程序员进⾏问题修复。它是系统维护、故障排查和安全管理的重要⼯
具。
⽇志格式以下⼏个指标是必须得有的
时间戳
⽇志等级
⽇志内容
以下⼏个指标是可选的⽂件名⾏号
- 进程,线程相关id信息等
这⾥我们采⽤设计模式-策略模式来进⾏⽇志的设计
我们想要的⽇志格式如下:
cpp
[可读性很好的时间] [⽇志等级] [进程pid] [打印对应⽇志的⽂件名][⾏号] - 消息内容,⽀持
可变参数
[2024-08-04 12:27:03] [DEBUG] [202938] [main.cc] [16] - hello world
[2024-08-04 12:27:03] [DEBUG] [202938] [main.cc] [17] - hello world
[2024-08-04 12:27:03] [DEBUG] [202938] [main.cc] [18] - hello world
[2024-08-04 12:27:03] [DEBUG] [202938] [main.cc] [20] - hello world
[2024-08-04 12:27:03] [DEBUG] [202938] [main.cc] [21] - hello world
[2024-08-04 12:27:03] [WARNING] [202938] [main.cc] [23] - hello worldLog.hpp
cpp
#ifndef __LOG_HPP__
#define __LOG_HPP__
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <filesystem> //C++17
#include <sstream>
#include <fstream>
#include <memory>
#include <ctime>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "Mutex.hpp"
namespace LogModule
{
using namespace MutexModule;
const std::string gsep = "\r\n";
// 策略模式,C++多态特性
// 2. 刷新策略 a: 显示器打印 b:向指定的文件写入
// 刷新策略基类
class LogStrategy
{
public:
virtual void SyncLog(const std::string& message) = 0;
~LogStrategy() = default;
};
// 显示器打印日志的策略 : 子类
class ConsoleLogStrategy : public LogStrategy
{
public:
ConsoleLogStrategy() {}
void SyncLog(const std::string& message) override
{
LockGuard lockguard(_mutex);
std::cout << message << gsep;
}
~ConsoleLogStrategy() {}
private:
Mutex _mutex;
};
// 文件打印日志的策略 : 子类
const std::string defaultpath = "./log";
const std::string defaultfile = "my.log";
class FileLogStrategy : public LogStrategy
{
public:
FileLogStrategy(const std::string& path = defaultpath, const std::string& file = defaultfile)
: _path(path), _file(file)
{
LockGuard lockguard(_mutex);
if (std::filesystem::exists(_path))
{
return;
}
try
{
std::filesystem::create_directories(_path);
}
catch (const std::filesystem::filesystem_error& e)
{
std::cerr << e.what() << '\n';
}
}
void SyncLog(const std::string& message) override
{
LockGuard lockguard(_mutex);
std::string filename = _path + (_path.back() == '/' ? "" : "/") + _file;
std::ofstream out(filename, std::ios::app);
if (!out.is_open())
{
return;
}
out << message << gsep;
out.close();
}
~FileLogStrategy() {}
private:
std::string _path; // 日志文件所在路径
std::string _file; // 日志文件本身
Mutex _mutex;
};
// 形成一条完整的日志&&根据上面的策略,选择不同的刷新方式
// 1. 形成日志等级
enum class LogLevel
{
DEBUG,
INFO,
WARNING,
ERROR,
FATAL
};
std::string Level2Str(LogLevel level)
{
switch (level)
{
case LogLevel::DEBUG:
return "DEBUG";
case LogLevel::INFO:
return "INFO";
case LogLevel::WARNING:
return "WARNING";
case LogLevel::ERROR:
return "ERROR";
case LogLevel::FATAL:
return "FATAL";
default:
return "UNKNOW";
}
}
std::string GetTimeStamp()
{
time_t curr = time(nullptr);
struct tm curr_tm;
// struct tm *localtime_r(const time_t *timep, struct tm *result);
localtime_r(&curr, &curr_tm);
char timebuffer[128];
snprintf(timebuffer, sizeof(timebuffer), "%4d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d",
curr_tm.tm_year + 1900,
curr_tm.tm_mon + 1,
curr_tm.tm_mday,
curr_tm.tm_hour,
curr_tm.tm_min,
curr_tm.tm_sec);
return timebuffer;
}
// 1. 形成日志 && 2. 根据不同的策略,完成刷新
// Logger的职责:
// 1.管理日志策略(如控制台/文件输出)
// 2.提供入口函数(operator())创建日志消息的"壳"(LogMessage)
// LogMessage的职责:
// 1.构造完整日志内容(前缀 + 用户消息)
// 2.在析构时触发实际输出(RAII 机制)
class Logger
{
public:
Logger()
{
EnableConsoleLogStrategy();
}
void EnableFileLogStrategy()
{
_fflush_strategy = std::make_unique<FileLogStrategy>();
}
void EnableConsoleLogStrategy()
{
_fflush_strategy = std::make_unique<ConsoleLogStrategy>();
}
// 表示的是未来的一条日志
class LogMessage
{
public:
LogMessage(LogLevel& level, std::string& src_name, int line_number, Logger& logger)
: _curr_time(GetTimeStamp()),
_level(level),
_pid(getpid()),
_src_name(src_name),
_line_number(line_number),
_logger(logger)
{
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "[" << _curr_time << "] "
<< "[" << Level2Str(_level) << "] "
<< "[" << _pid << "] "
<< "[" << _src_name << "] "
<< "[" << _line_number << "] "
<< "- ";
_loginfo = ss.str();
}
template <typename T>
// LogMessage() << "hell world" << "XXXX" << 3.14 << 1234
LogMessage& operator<<(const T& info)
{
std::stringstream ss;
ss << info;
_loginfo += ss.str();
return *this;
}
~LogMessage()
{
if (_logger._fflush_strategy)
{
_logger._fflush_strategy->SyncLog(_loginfo);
}
}
private:
std::string _curr_time;
LogLevel _level;
pid_t _pid;
std::string _src_name;
int _line_number;
std::string _loginfo; // 合并之后,一条完整的信息
Logger& _logger;
};
// 这里故意写成返回临时对象
LogMessage operator()(LogLevel level, std::string name, int line)
{
return LogMessage(level, name, line, *this);
}
~Logger()
{
}
private:
std::unique_ptr<LogStrategy> _fflush_strategy;
};
// 全局日志对象
Logger logger;
// 使用宏,简化用户操作,获取文件名和行号
#define LOG(level) logger(level, __FILE__, __LINE__)
#define Enable_Console_Log_Strategy() logger.EnableConsoleLogStrategy()
#define Enable_File_Log_Strategy() logger.EnableFileLogStrategy()
}
#endif
样例
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "hello world";这⾥我们直接⽤我们⾃⼰封装的锁
2.线程池设计
线程池:
⼀种线程使⽤模式。线程过多会带来调度开销,进⽽影响缓存局部性和整体性能。⽽线程池维护着多个线程,等待着监督管理者分配可并发执⾏的任务。这避免了在处理短时间任务时创建与销毁线程的代价。线程池不仅能够保证内核的充分利⽤,还能防⽌过分调度。可⽤线程数量应该取决于可⽤的并发处理器、处理器内核、内存、⽹络sockets等的数量。
线程池的应用场景:
- 需要⼤量的线程来完成任务,且完成任务的时间⽐较短。 ⽐如WEB服务器完成⽹⻚请求这样的任务,使⽤线程池技术是⾮常合适的。因为单个任务⼩,⽽任务数量巨⼤,你可以想象⼀个热⻔⽹站的点击次数。 但对于⻓时间的任务,⽐如⼀个Telnet连接请求,线程池的优点就不明显了。因为Telnet会话时间⽐线程的创建时间⼤多了。
- 对性能要求苛刻的应⽤,⽐如要求服务器迅速响应客⼾请求。
- 接受突发性的⼤量请求,但不⾄于使服务器因此产⽣⼤量线程的应⽤。突发性⼤量客⼾请求,在没有线程池情况下,将产⽣⼤量线程,虽然理论上⼤部分操作系统线程数⽬最⼤值不是问题,短时间内产⽣⼤量线程可能使内存到达极限,出现错误。
线程池的种类:
- 创建固定数量线程池,循环从任务队列中获取任务对象,获取到任务对象后,执⾏任务对象中的任务接⼝
- 浮动线程池,其他同上
此处,我们选择固定线程个数的线程池。
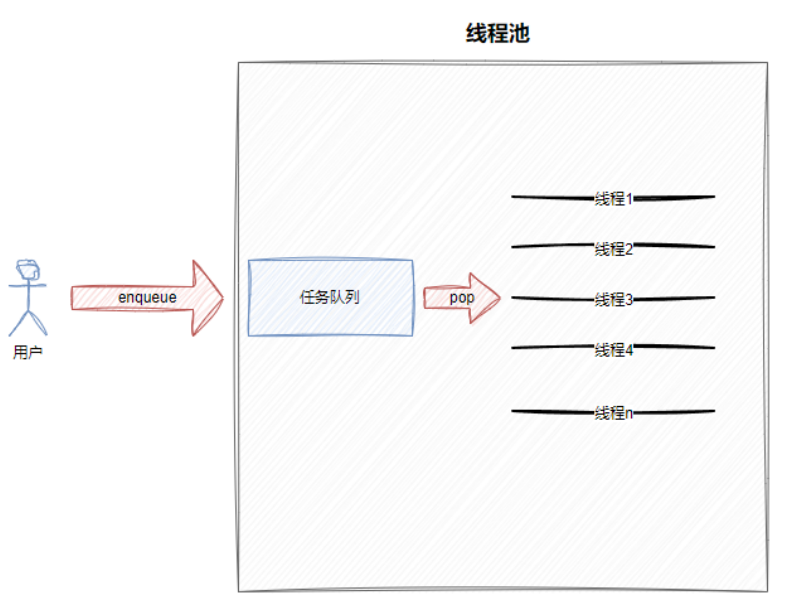
ThreadPool.hpp
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include "Log.hpp"
#include "Thread.hpp"
#include "Cond.hpp"
#include "Mutex.hpp"
// 单例模式
namespace ThreadPoolModule
{
using namespace ThreadModlue;
using namespace LogModule;
using namespace CondModule;
using namespace MutexModule;
static const int gnum = 5;
template <typename T>
class ThreadPool
{
private:
void WakeUpAllThread()
{
LockGuard lockguard(_mutex);
if (_sleeper)
_cond.Broadcast();
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "唤醒所有的休眠线程";
}
void WakeUpOne()
{
_cond.Signal();
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "唤醒一个休眠线程";
}
void Start()
{
if (_isrunning)
return;
_isrunning = true;
for (auto &thread : _threads)
{
thread.Start();
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "start new thread success: " << thread.Name();
}
}
ThreadPool(int num = gnum) : _num(num), _isrunning(false), _sleeper(0)
{
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
_threads.emplace_back(
[this]()
{
HandlerTask();
});
}
}
//[this]是一个 lambda 表达式捕获列表 中的内容,
// 表示该 lambda 捕获了当前 ThreadPool对象的指针(this),
// 使得 lambda 内部可以访问当前对象的成员变量和成员函数
ThreadPool(const ThreadPool<T> &) = delete;
ThreadPool<T> &operator=(const ThreadPool<T> &) = delete;
public:
static ThreadPool<T> *GetInstance()
{
if (inc == nullptr)
{
LockGuard lockguard(_lock);
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "获取单例....";
if (inc == nullptr)
{
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "首次使用单例, 创建之....";
inc = new ThreadPool<T>();
inc->Start();
}
}
return inc;
}
// 第一次判断单例是否存在,防止无意义竞争锁降低性能
void Stop()
{
if (!_isrunning)
return;
_isrunning = false;
// 唤醒所有的线程
WakeUpAllThread();
}
void Join()
{
for (auto &thread : _threads)
{
thread.Join();
}
}
void HandlerTask()
{
char name[128];
pthread_getname_np(pthread_self(), name, sizeof(name));
while (true)
{
T t;
{
LockGuard lockguard(_mutex);
// 1. a.队列为空 b. 线程池没有退出
while (_taskq.empty() && _isrunning)
{
_sleeper++;
_cond.Wait(_mutex);
_sleeper--;
}
// 2. 内部的线程被唤醒
if (_taskq.empty() && !_isrunning)
{
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << name << " 退出了, 线程池退出&&任务队列为空";
break;
}
// 一定有任务
t = _taskq.front(); // 从q中获取任务,任务已经是线程私有的了!!!
_taskq.pop();
}
t();
}
}
bool Enqueue(const T &in)
{
if (_isrunning)
{
LockGuard lockguard(_mutex);
_taskq.push(in);
if (_sleeper == _threads.size())
{
WakeUpOne();
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
~ThreadPool() {}
private:
std::vector<Thread> _threads;
int _num; // 线程池中,线程的个数
std::queue<T> _taskq;
Mutex _mutex;
Cond _cond;
bool _isrunning;
int _sleeper;
static ThreadPool<T> *inc; // 单例指针
static Mutex _lock;
};
template <typename T>
ThreadPool<T> *ThreadPool<T>::inc = nullptr;
template <typename T>
Mutex ThreadPool<T>::_lock;
}