目标
书接上文,之前已经实现好一个铺满整个窗口的渐变色。
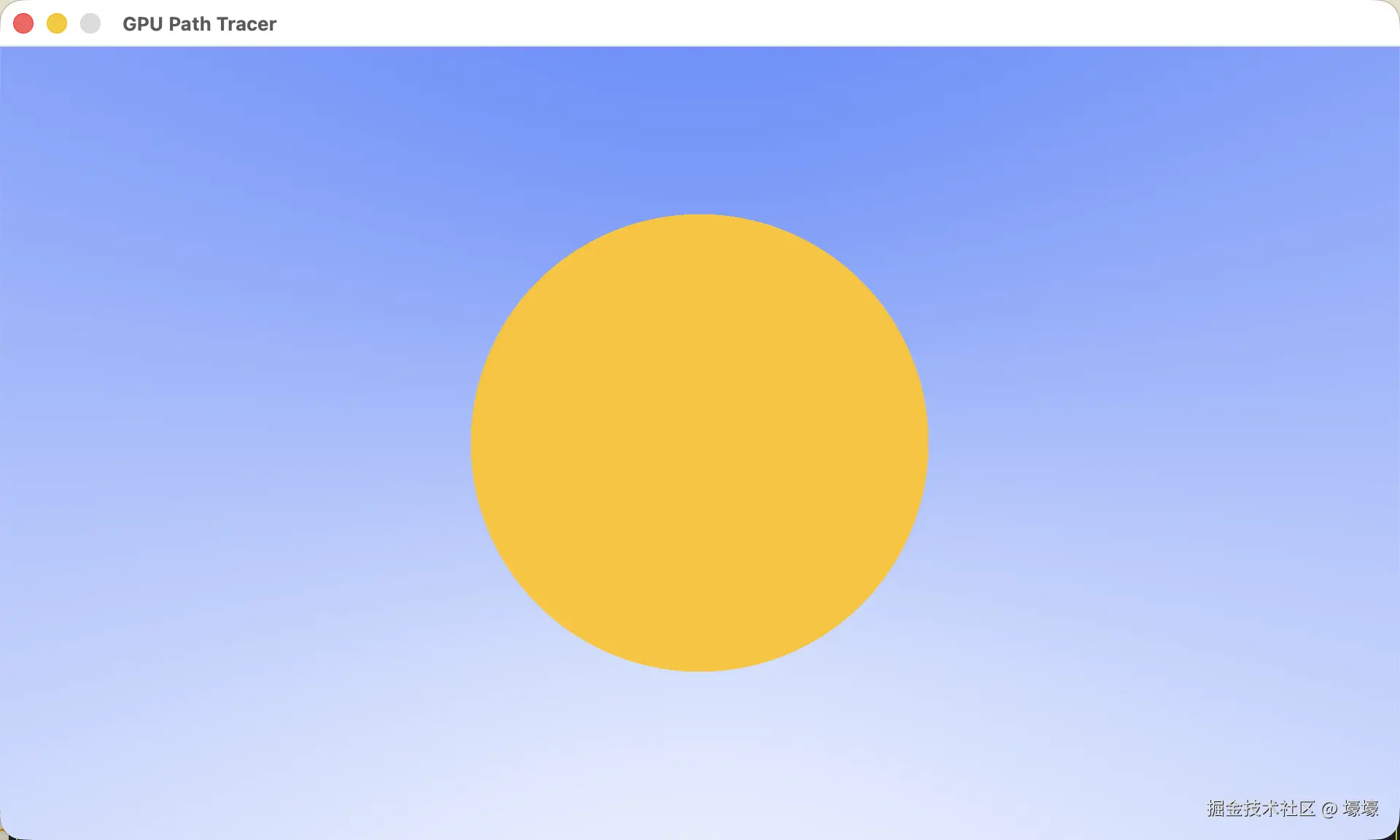
本节最终效果

先处理一些简单的宏定义
开始之前,先把一些基础设施处理一下,有了这些别名后,能减少一部分 C/Cpp 风格的内容
cpp
#define let const auto
#define var auto
using vec2f = float2;
using vec3f = float3;
using vec4f = float4;
using u8 = uchar;
using i8 = char;
using u16 = ushort;
using i16 = short;
using i32 = int;
using u32 = uint;
using f16 = half;
using f32 = float;
using usize = size_t;画个实心圆在窗口中央
根据我们之前总结的理论,"从相机处开始发射一束射线,射线撞到哪些'物体',就计算跟该'物体'相交的颜色" ,其实现在要解决的问题就是怎么算出射线撞到这个球。
现在来点理论知识,根据小学数学上讲得,我们知道射线有起点、方向,然后沿该方向无限延伸,就是讲有个原点向量 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> P \mathbf{P} </math>P 跟方向 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> d ⃗ \vec{d} </math>d 来表示射线,射线上的所有点 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> R \mathbf{R} </math>R 由一个线性方程描述:
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="block"> R ( t ) = P + t ⋅ d \mathbf{R}(t) = \mathbf{P} + t \cdot \mathbf{d} </math>R(t)=P+t⋅d
也就是讲,只要 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> t > 0 t > 0 </math>t>0 就是从原点出发的所有的点。
再回到我们目标要画得这个球的内容,球是由中心点 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> C \mathbf{C} </math>C 跟半径 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> r r </math>r 表示,球上所有的点 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> X \mathbf{X} </math>X 都满足
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="block"> ( X − C ) ⋅ ( X − C ) = r 2 (\mathbf{X} - \mathbf{C}) \cdot (\mathbf{X} - \mathbf{C}) = r ^ 2 </math>(X−C)⋅(X−C)=r2
然后我们把射线的公式替换掉 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> X \mathbf{X} </math>X
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="block"> ( P + t d − C ) ⋅ ( P + t d − C ) = r 2 (\mathbf{P} + t \mathbf{d} - \mathbf{C}) \cdot (\mathbf{P} + t \mathbf{d} - \mathbf{C}) = r ^ 2 </math>(P+td−C)⋅(P+td−C)=r2
然后把 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> P − C \mathbf{P} - \mathbf{C} </math>P−C 先用一个 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> v \mathbf{v} </math>v 来表示
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="block"> ( v + t d ) ⋅ ( v + t d ) = r 2 (\mathbf{v} + t \mathbf{d}) \cdot (\mathbf{v} + t \mathbf{d}) = r ^ 2 </math>(v+td)⋅(v+td)=r2
根据初中数学知识化简一下
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="block"> ( v ⋅ v ) + t d v + t d v + t d ⋅ t d = r 2 ( v ⋅ v ) + 2 ( v ⋅ d ) t + ( d ⋅ d ) t 2 − r 2 = 0 ( d ⋅ d ) t 2 + 2 ( v ⋅ d ) t + ( ( v ⋅ v ) − r 2 ) = 0 (\mathbf{v} \cdot \mathbf{v}) + t \mathbf{d} \mathbf{v} + t \mathbf{d} \mathbf{v} + t \mathbf{d} \cdot t \mathbf{d} = r ^ 2 \\ (\mathbf{v} \cdot \mathbf{v}) + 2 (\mathbf{v} \cdot \mathbf{d}) t + (\mathbf{d} \cdot \mathbf{d}) t ^ 2 - r ^ 2 = 0 \\ (\mathbf{d} \cdot \mathbf{d}) t ^ 2 + 2 (\mathbf{v} \cdot \mathbf{d}) t + ( (\mathbf{v} \cdot \mathbf{v}) - r ^ 2) = 0 </math>(v⋅v)+tdv+tdv+td⋅td=r2(v⋅v)+2(v⋅d)t+(d⋅d)t2−r2=0(d⋅d)t2+2(v⋅d)t+((v⋅v)−r2)=0
现在其实是一个一元二次方程
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="block"> a t 2 + 2 b t + c = 0 at ^ 2 + 2bt + c = 0 </math>at2+2bt+c=0
然后利用一下一元二次方程的求根公式,可以先把它每项乘以 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 2 \frac{1}{2} </math>21
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="block"> a 2 t 2 + b t + c 2 = 0 \frac{a}{2}t ^ 2 + bt + \frac{c}{2} = 0 </math>2at2+bt+2c=0
最后就可以变成这种形式
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="block"> t = − b ± b 2 − a c a t = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b ^ 2 - ac}}{a} </math>t=a−b±b2−ac
现在就很直观了
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="block"> a = d ⋅ d b = ( P − C ) ⋅ d c = ( P − C ) ⋅ ( P − C ) − r 2 a = d \cdot d \\ b = (\mathbf{P} - \mathbf{C}) \cdot d \\ c = (\mathbf{P} - \mathbf{C}) \cdot (\mathbf{P} - \mathbf{C}) - r ^ 2 </math>a=d⋅db=(P−C)⋅dc=(P−C)⋅(P−C)−r2
然后根据算出的结果,就能表示射线跟球的相交关系
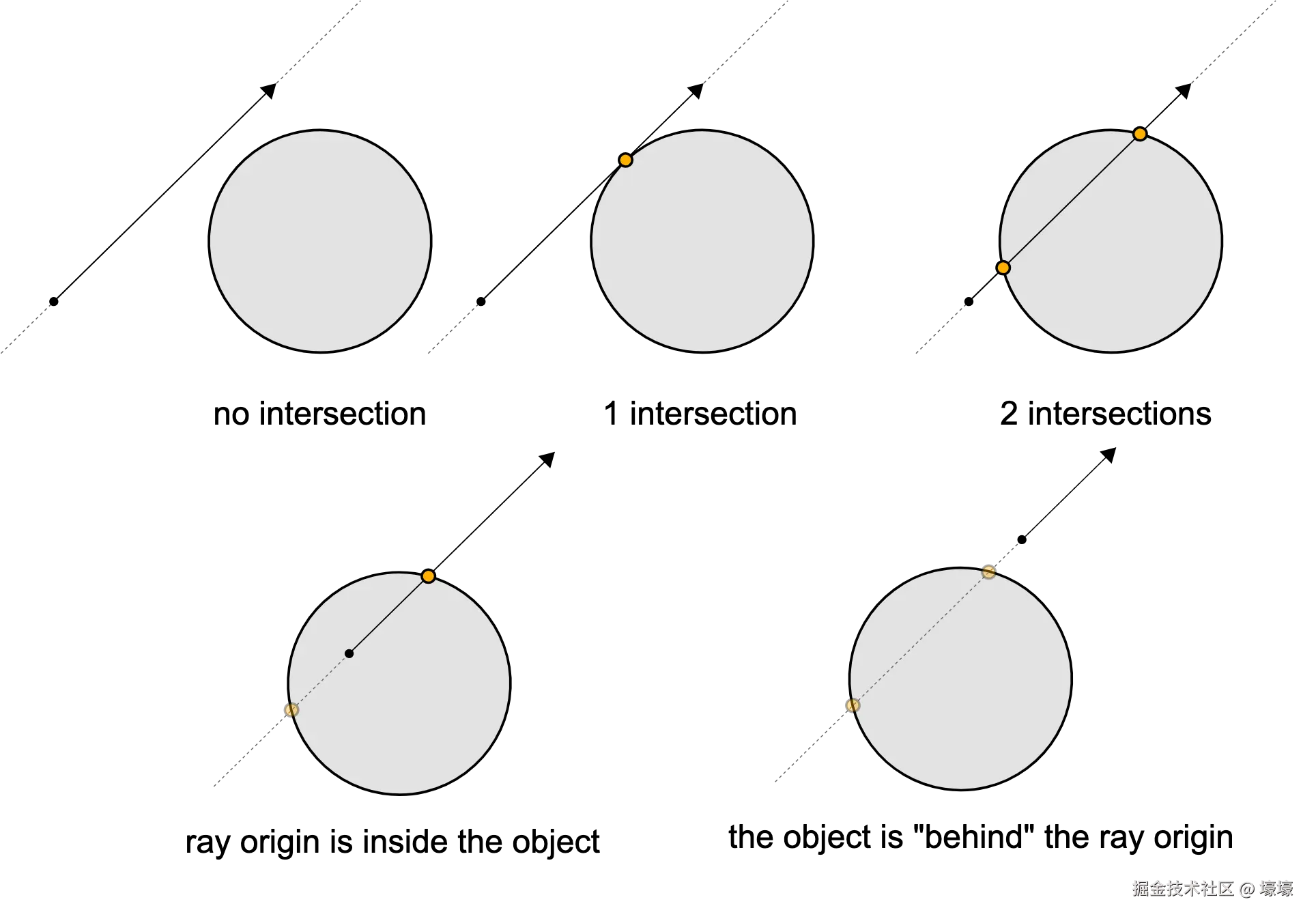
写代码实现
现在来根据上面的理论来写一个计算相交的函数,首先肯定是要定义球的结构,主要是球心跟半径
cpp
struct Sphere {
vec3f center;
f32 radius;
};然后再写一个函数,根据我们上面的理论, <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> P − C \mathbf{P} - \mathbf{C} </math>P−C 可以算出 v,a 就是光线方向的点积 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> d ⋅ d \mathbf{d} \cdot \mathbf{d} </math>d⋅d,b 就是 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> v ⋅ d \mathbf{v} \cdot \mathbf{d} </math>v⋅d,c 就是 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> ( P − C ) ⋅ ( P − C ) − r 2 (\mathbf{P} - \mathbf{C}) \cdot (\mathbf{P} - \mathbf{C}) - r ^ 2 </math>(P−C)⋅(P−C)−r2
cpp
f32 intersect_sphere(const Ray ray, const Sphere sphere) {
let v = ray.origin - sphere.center;
let a = dot(ray.direction, ray.direction);
let b = dot(v, ray.direction);
let c = dot(v, v) - sphere.radius * sphere.radius;
}接着就纯代数操作了, <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> b 2 − a c b ^ 2 - ac </math>b2−ac,再开平方,而且开平方不能处理负数,总之就是代公式计算就完事了
cpp
f32 intersect_sphere(const Ray ray, const Sphere sphere) {
// ...
let d = b * b - a * c;
if (d < 0.) {
return -1.;
}
let sqrt_d = sqrt(d);
let recip_a = 1. / a;
let mb = -b;
let t = (mb - sqrt_d) * recip_a;
if (t > 0.) {
return t;
}
return (mb + sqrt_d) * recip_a;
}有了这个计算函数,我们再在片段着色器函数去计算颜色,先复制之前那篇文章的渲染渐变背景的代码,然后把计算相交球的内容放进去
cpp
fragment vec4f fragmentFn(Vertex in [[stage_in]], constant Uniforms &uniforms [[buffer(1)]]) {
let origin = vec3f(0);
let focus_distance = 1.0;
let aspect_ratio = f32(uniforms.width) / f32(uniforms.height);
var uv = in.position.xy / vec2f(f32(uniforms.width - 1), f32(uniforms.height - 1));
uv = (2 * uv - vec2f(1)) * vec2f(aspect_ratio, -1);
let direction = vec3f(uv, -focus_distance);
let ray = Ray { origin, direction };
// new start
let sphere = Sphere { .center = vec3f(0, 0, -1), .radius = 0.5 };
if (intersect_sphere(ray, sphere) > 0) {
return vec4f(1, 0.76, 0.03, 1);
}
// new end
return vec4f(sky_color(ray), 1);
}最后总结一下整体代码
cpp
#include <metal_stdlib>
#define let const auto
#define var auto
using namespace metal;
using vec2f = float2;
using vec3f = float3;
using vec4f = float4;
using u8 = uchar;
using i8 = char;
using u16 = ushort;
using i16 = short;
using i32 = int;
using u32 = uint;
using f16 = half;
using f32 = float;
using usize = size_t;
struct VertexIn {
vec2f position;
};
struct Vertex {
vec4f position [[position]];
};
struct Uniforms {
u32 width;
u32 height;
};
struct Ray {
vec3f origin;
vec3f direction;
};
struct Sphere {
vec3f center;
f32 radius;
};
f32 intersect_sphere(const Ray ray, const Sphere sphere) {
let v = ray.origin - sphere.center;
let a = dot(ray.direction, ray.direction);
let b = dot(v, ray.direction);
let c = dot(v, v) - sphere.radius * sphere.radius;
let d = b * b - a * c;
if (d < 0.) {
return -1.;
}
let sqrt_d = sqrt(d);
let recip_a = 1. / a;
let mb = -b;
let t = (mb - sqrt_d) * recip_a;
if (t > 0.) {
return t;
}
return (mb + sqrt_d) * recip_a;
}
vec3f sky_color(Ray ray) {
let a = 0.5 * (normalize(ray.direction).y + 1);
return (1 - a) * vec3f(1) + a * vec3f(0.5, 0.7, 1);
}
vertex Vertex vertexFn(constant VertexIn *vertices [[buffer(0)]], uint vid [[vertex_id]]) {
return Vertex { vec4f(vertices[vid].position, 0, 1) };
}
fragment vec4f fragmentFn(Vertex in [[stage_in]], constant Uniforms &uniforms [[buffer(1)]]) {
let origin = vec3f(0);
let focus_distance = 1.0;
let aspect_ratio = f32(uniforms.width) / f32(uniforms.height);
var uv = in.position.xy / vec2f(f32(uniforms.width - 1), f32(uniforms.height - 1));
uv = (2 * uv - vec2f(1)) * vec2f(aspect_ratio, -1);
let direction = vec3f(uv, -focus_distance);
let ray = Ray { origin, direction };
let sphere = Sphere { .center = vec3f(0, 0, -1), .radius = 0.5 };
if (intersect_sphere(ray, sphere) > 0) {
return vec4f(1, 0.76, 0.03, 1);
}
return vec4f(sky_color(ray), 1);
}