一、引言
在当今的Web应用中,实时通信已成为提升用户体验的关键技术。特别是在AI对话场景下,传统的HTTP请求-响应模式难以满足"边思考边输出"的流式交互需求。本文将通过一个完整的WebSocket实战案例,深入浅出地解析如何实现类似ChatGPT的实时对话效果。
二、WebSocket核心概念与优势
WebSocket是一种在单个TCP连接上进行全双工通信的协议,其核心优势包括:
- 双向通信:服务器和客户端可同时发送数据,无需等待对方响应
- 持久连接:一次握手后保持连接状态,避免重复建立连接的开销
- 低延迟:数据可实时传输,无需HTTP请求的头部开销
- 轻量级:协议头部信息小,数据传输效率高
三、WebSocket核心方法详解
WebSocket的使用主要围绕以下四个核心事件和一个发送方法展开:
| 方法/事件 | 作用 | 触发时机 |
| new WebSocket(url) | 创建WebSocket实例 | 初始化连接时 |
| onopen | 连接建立成功回调 | 服务器响应握手请求后 |
| send(data) | 发送数据到服务器 | 需要发送消息时主动调用 |
| onmessage | 接收服务器数据回调 | 服务器发送消息时触发 |
| onerror | 连接错误处理回调 | 连接异常时触发 |
| onclose | 连接关闭回调 | 连接正常或异常关闭时触发 |
四、AI流式对话的WebSocket实现案例
以下是一个完整的React组件实现,用于模拟AI流式对话场景:
javascript
import React, { useState, useEffect, useRef } from "react";
import { Button, Input, message, List, Typography, Card, Divider } from "antd";
const { TextArea } = Input;
const { Text } = Typography;
export default function WebSocketDemo() {
// 状态管理
const [messages, setMessages] = useState<
Array<{ type: "send" | "receive" | "system"; content: string }>
>([]);
const [inputMessage, setInputMessage] = useState("");
const [isConnected, setIsConnected] = useState(false);
const [connectionStatus, setConnectionStatus] = useState("未连接");
// WebSocket实例引用
const socketRef = useRef<WebSocket | null>(null);
const messagesEndRef = useRef<HTMLDivElement>(null);
// 模拟数据(当WebSocket连接失败时使用)
const mockEchoService = (msg: string) => {
// 模拟网络延迟
setTimeout(() => {
setMessages((prev) => [
...prev,
{ type: "receive", content: `模拟回声: ${msg}` },
]);
scrollToBottom();
}, 300);
};
// 滚动到底部
const scrollToBottom = () => {
messagesEndRef.current?.scrollIntoView({ behavior: "smooth" });
};
// 建立WebSocket连接
const connectWebSocket = () => {
try {
// 使用公开的WebSocket测试服务
// const wsUrl = "wss://echo.websocket.org";
// 如果上述服务不可用,也可以使用这个备用服务
const wsUrl = "wss://ws.postman-echo.com/raw";
socketRef.current = new WebSocket(wsUrl);
// 连接建立事件
socketRef.current.onopen = () => {
console.log("WebSocket连接已建立");
setIsConnected(true);
setConnectionStatus("已连接");
setMessages((prev) => [
...prev,
{ type: "system", content: `WebSocket连接已建立: ${wsUrl}` },
]);
message.success("WebSocket连接成功");
};
// 接收消息事件
socketRef.current.onmessage = (event) => {
console.log("收到消息:", event.data);
setMessages((prev) => [
...prev,
{ type: "receive", content: event.data },
]);
scrollToBottom();
};
// 错误事件
socketRef.current.onerror = (error) => {
console.error("WebSocket错误:", error);
setConnectionStatus("连接错误");
message.error("WebSocket连接错误,使用模拟模式");
setMessages((prev) => [
...prev,
{ type: "system", content: `连接错误,切换到模拟模式` },
]);
};
// 连接关闭事件
socketRef.current.onclose = (event) => {
console.log("WebSocket连接已关闭");
setIsConnected(false);
setConnectionStatus("已关闭");
setMessages((prev) => [
...prev,
{ type: "system", content: `连接已关闭 (代码: ${event.code})` },
]);
socketRef.current = null;
};
} catch (error) {
console.error("WebSocket初始化失败:", error);
message.error("WebSocket初始化失败,使用模拟模式");
setMessages((prev) => [
...prev,
{ type: "system", content: `初始化失败,切换到模拟模式` },
]);
}
};
// 关闭WebSocket连接
const disconnectWebSocket = () => {
if (socketRef.current) {
socketRef.current.close();
}
};
// 发送消息
const sendMessage = () => {
if (!inputMessage.trim()) {
message.warning("请输入消息内容");
return;
}
// 添加发送的消息到列表
setMessages((prev) => [...prev, { type: "send", content: inputMessage }]);
if (socketRef.current && socketRef.current.readyState === WebSocket.OPEN) {
// 通过WebSocket发送消息
socketRef.current.send(inputMessage);
} else {
// 使用模拟服务
mockEchoService(inputMessage);
}
// 清空输入框
setInputMessage("");
scrollToBottom();
};
// 组件挂载时自动连接
useEffect(() => {
connectWebSocket();
// 组件卸载时关闭连接
return () => {
disconnectWebSocket();
};
}, []);
// 监听输入框的Enter键
const handleKeyPress = (e: React.KeyboardEvent) => {
if (e.key === "Enter" && !e.shiftKey) {
e.preventDefault();
sendMessage();
}
};
// 格式化消息时间
const formatTime = () => {
const now = new Date();
return now.toLocaleTimeString();
};
return (
<div style={{ maxWidth: 800, margin: "0 auto", padding: 20 }}>
<Typography.Title level={2}>WebSocket 示例</Typography.Title>
<Card
title={`连接状态: ${connectionStatus}`}
extra={
isConnected ? (
<Button type="default" danger onClick={disconnectWebSocket}>
断开连接
</Button>
) : (
<Button type="primary" onClick={connectWebSocket}>
连接WebSocket
</Button>
)
}
>
<div
style={{
height: 400,
overflowY: "auto",
border: "1px solid #f0f0f0",
borderRadius: 4,
padding: 10,
marginBottom: 16,
}}
>
<List
dataSource={messages}
renderItem={(item) => (
<List.Item style={{ marginBottom: 8 }}>
<div
style={{
textAlign: item.type === "send" ? "right" : "left",
color:
item.type === "system"
? "#888"
: item.type === "send"
? "#1890ff"
: "#333",
fontSize: item.type === "system" ? 12 : 14,
}}
>
{item.type !== "system" && (
<Text type={item.type === "send" ? "secondary" : "success"}>
{item.type === "send" ? "我" : "服务器"} {formatTime()}
</Text>
)}
<div
style={{
display: "inline-block",
background:
item.type === "system"
? "#f5f5f5"
: item.type === "send"
? "#e6f7ff"
: "#f6ffed",
padding: 8,
borderRadius: 4,
maxWidth: "70%",
wordBreak: "break-word",
marginTop: item.type !== "system" ? 4 : 0,
}}
>
{item.content}
</div>
</div>
</List.Item>
)}
/>
<div ref={messagesEndRef} />
</div>
<Divider>发送消息</Divider>
<div style={{ display: "flex", gap: 8 }}>
<TextArea
value={inputMessage}
onChange={(e) => setInputMessage(e.target.value)}
placeholder="输入消息,按Enter发送,Shift+Enter换行"
autoSize={{ minRows: 2, maxRows: 4 }}
style={{ flex: 1 }}
onPressEnter={handleKeyPress}
/>
<Button
type="primary"
onClick={sendMessage}
disabled={!inputMessage.trim()}
>
发送
</Button>
</div>
<div
style={{
marginTop: 20,
padding: 10,
background: "#f5f5f5",
borderRadius: 4,
}}
>
<Typography.Text type="secondary" strong>
WebSocket测试说明:
</Typography.Text>
<ul style={{ marginTop: 8 }}>
<li>本示例使用公开的WebSocket测试服务: wss://echo.websocket.org</li>
<li>该服务会将您发送的消息原样返回(回声测试)</li>
<li>如果WebSocket连接失败,会自动切换到模拟模式</li>
<li>您可以尝试发送各种类型的消息进行测试</li>
</ul>
</div>
</Card>
</div>
);
}五、实现要点与优化技巧
-
DOM自动滚动 :使用
scrollIntoView({behavior: "smooth"})实现新消息出现时自动滚动到底部,提升用户体验 -
状态管理:合理使用React状态管理连接状态、消息列表和输入内容
-
错误处理:全面覆盖初始化、连接、发送、接收等各环节的异常处理
-
组件生命周期管理:在组件卸载时正确关闭WebSocket连接,避免内存泄漏
-
输入优化:支持Enter键发送消息,添加输入校验
六、与AI流式对话的关联
在实际的AI对话场景中,WebSocket的应用更为复杂:
- 流式响应:AI模型会将生成的文本分批次通过WebSocket推送,前端实时拼接并展示
- 多模态支持:可扩展支持文本、图像等多种数据类型的实时传输
- 心跳机制:为保持长连接稳定,通常会实现定时心跳检测
- 认证授权:实际应用中需添加身份验证机制
七、总结
WebSocket为实现实时交互的AI对话提供了技术基础,通过掌握其核心方法和事件处理,我们可以构建出响应迅速、体验流畅的对话系统。本文的实战案例不仅展示了WebSocket的基本用法,也为进一步开发复杂的AI交互应用提供了参考框架。
通过这个案例,我们不仅学习了WebSocket技术,更重要的是理解了现代Web应用中实时通信的实现思路,这对于开发各种需要即时反馈的应用场景都具有重要价值。
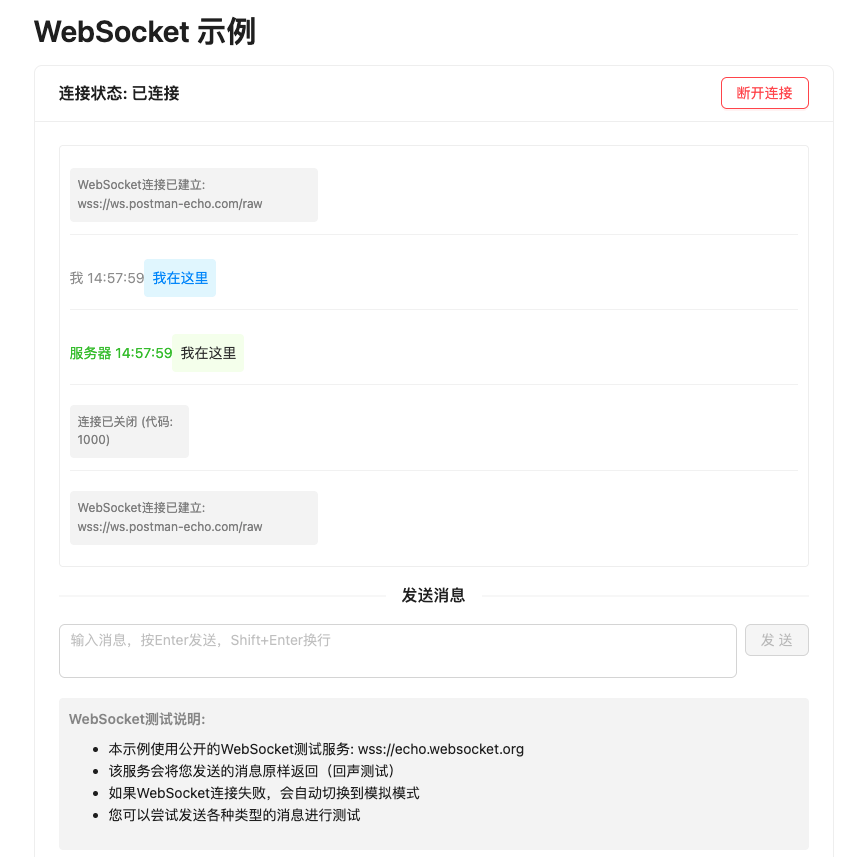
效果图展示