缓存一般分为远程缓存和本地缓存。常见的远程缓存有 redis。与远程缓存相比本地缓存不需要进行网络的传输所以更加的快。本地缓存可以使用 map 实现,使用 get 查询缓存,put 设置缓存。本地缓存需要提供对应的缓存清理机制,否则会导致缓存溢出,并且需要保证操作的并发安全。
介绍
Guava Cache 是 Google Guava 库中的一个组件,用于在内存中实现本地缓存。它类似于 ConcurrentMap,但提供了更丰富的特性,如自动加载、过去策略、淘汰策略等。
Guava Cache 提供了丰富的构造参数:
| 参数类别 | 参数名 | 数据类型 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 容量控制 | initialCapacity | int | 初始化容量 |
| maximumSize | long | 缓存最大条目数,超过时按LRU淘汰 | |
| maximumWeight | long | 缓存最大权重和,需配合 weigher 使用,超过时淘汰条目 | |
| weigher | weigher<K,V> | 定义计算缓存条目权重的函数,与maximumWeight 配合使用 | |
| 并发控制 | concurrencyLevel | int | 设置并发级别,并发级别是指同时可以写缓存的线程数 |
| 过期策略 | expireAfterWrite | long,TimeUnit | 条目在写入后一段时间过期 |
| expireAfterAccess | long,TimeUnit | 条目在最后一次访问(读或写)后一段时间过期 | |
| refreshAfterWrite | long,TimeUnit | 条目在写入后一段时间自动刷新(仅LoadingCache支持) | |
| 引用基淘汰 | weakKeys | 将键设置为弱引用,允许GC回收 | |
| weakValues | 将值设置为弱引用,允许GC回收 | ||
| softValues | 将值设置为软应用,在内容不足时GC优先回收 | ||
| 移除监听 | removalListener | 设置缓存条目被移除时的监听器 | |
| 统计 | recordStats | 开启缓存统计功能(如命中率) |
初始化
初始容量设置
我们在构建缓存时可以为缓存设置一个合理大小初始容量,由于Guava的缓存使用了分离锁的机制,扩容的代价非常昂贵。所以合理的初始容量能够减少缓存容器的扩容次数。
java
Cache<String, String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.initialCapacity(10) // 初始化容量
.build();最大容量
Guava Cache可以在构建缓存对象时指定缓存所能够存储的最大记录数量。当Cache中的记录数量达到最大值后再调用put方法向其中添加对象,Guava会先从当前缓存的对象记录中选择一条删除掉,腾出空间后再将新的对象存储到Cache中。
java
Cache<String, String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(100) // 设置缓存最大容量,超过根据LRU算法回收
.build();监听器
removalListener() 设置缓存条目被移除时的监听器
java
package guava;
import com.google.common.cache.*;
public class GuavaCacheTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cache<String,String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(1)
.removalListener(removal -> {
System.out.println(removal.getKey() + "被删除了");
})
.build();
cache.put("key1", "value1");
cache.put("key2", "value2");
cache.put("key3", "value3");
}
}输出:
java
key1被删除了
key2被删除了缓存清除策略
基于存活时间
expireAfterWrite 写入缓存后n秒过期
java
Cache<String, String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.expireAfterWrite(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS) // 设置写缓存后n秒过期
.builder();expireAfterAccess 读写缓存后n秒过期
java
Cache<String, String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.expireAfterAccess(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS) // 设置读写缓存后n秒过期
.builder();基于最大容量容量
使用 CacheBuilder.maximumSize()方法时,当缓存数量达到该最大值时,将清除掉那些最近最少使用的缓存(LRU)
基于权重
在缓存大型文件或图片的场景下,每个缓存条目(文件内容)的大小差异很大,如果我们只限制缓存条目的数量(maximumSize)是不合理的。比如,缓存10个1MB的图片和缓存10个100MB的视频,占用的内存天差地别。
使用基于权重的回收(maximumWeight + weigher),我们可以限制缓存的总内存占用,而不是条目数量。
下面定义了一个最大权重为10的 cache,当所有条目的内存占用超过10时进行回收。
java
package guava;
import com.google.common.cache.*;
public class GuavaCacheTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 创建缓存,设置最大权重为10
LoadingCache<String, String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumWeight(10) // 总权重不能超过10
.weigher((Weigher<String, String>) (key, value) -> value.length()) // 权重=值的长度
.build(new CacheLoader<String, String>() {
@Override
public String load(String key) {
return key.toUpperCase(); // 简单的加载逻辑:转大写
}
});
// 2. 使用缓存
try {
System.out.println("获取 A: " + cache.get("a")); // 权重=1 (A)
System.out.println("获取 Hello: " + cache.get("hello")); // 权重=5 (HELLO)
System.out.println("获取 Test: " + cache.get("test")); // 权重=4 (TEST)
// 现在总权重=1+5+4=10,刚好满
// 为了看到效果,我们手动检查哪些还在
System.out.println("\n缓存中现有内容:");
System.out.println("A: " + cache.getIfPresent("a")); // 可能被回收
System.out.println("Hello: " + cache.getIfPresent("hello")); // 可能被回收
System.out.println("Test: " + cache.getIfPresent("test")); // 可能还在
System.out.println();
// 3. 尝试再放入一个,会触发回收
System.out.println("获取 World: " + cache.get("world")); // 权重=5 (WORLD)
// 为了看到效果,我们手动检查哪些还在
System.out.println("\n缓存中现有内容:");
System.out.println("A: " + cache.getIfPresent("a")); // 可能被回收
System.out.println("Hello: " + cache.getIfPresent("hello")); // 可能被回收
System.out.println("Test: " + cache.getIfPresent("test")); // 可能还在
System.out.println("World: " + cache.getIfPresent("world")); // 新加入的
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}执行结果:
java
获取 A: A
获取 Hello: HELLO
获取 Test: TEST
缓存中现有内容:
A: A
Hello: HELLO
Test: TEST
获取 World: WORLD
缓存中现有内容:
A: null
Hello: null
Test: TEST
World: WORLD显示清除
清除单个key
java
cache.invalidate("key1");清除所有key
java
cache.invalidateAll();使用弱引用储存键。在下个GC时,若键在缓存外部没有其他强引用,整个条目被回收。
java
Cache<String,String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.weakKeys()
.build();使用弱引用存储值。在下个GC时,若值在缓存外部没有其他强引用,值将会被回收,键可能仍存在
java
Cache<String,String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.weakValues()
.build();使用软引用储存值。当一个对象只被软引用关联时,如果内存充足,它就不会被垃圾回收器回收,就像强引用一样。但是,当内存不足,垃圾收集器即将抛出OutOfMemoryError时,它会清理掉这些仅被软引用关联的对象,从而释放内存
java
Cache<String,String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.softValues()
.build();写入
cache
显示put操作置入内存
java
package guava;
import com.google.common.cache.*;
public class GuavaCacheTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cache<String,String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.initialCapacity(10)
.build();
cache.put("key1","value1");
cache.put("key2","value2");
cache.put("key3","value3");
}
}LoadingCache
使用自定义 ClassLoader 加载数据,置入内存中。从 LoadingCache 中获取数据时,若数据存在则直接返回;若数据不存在,则根据 ClassLoader 的 load 方法加载数据至内存,然后返回该数据
java
package guava;
import com.google.common.cache.*;
public class GuavaCacheTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 创建缓存,设置最大权重为10
LoadingCache<String, String> cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumWeight(10) // 总权重不能超过10
.weigher((Weigher<String, String>) (key, value) -> value.length()) // 权重=值的长度
.build(new CacheLoader<String, String>() {
@Override
public String load(String key) {
return key.toUpperCase(); // 简单的加载逻辑:转大写
}
});
// 2. 使用缓存
try {
System.out.println(cache.get("hello"));
}catch (Exception e){return;}
}
}实现原理
数据结构
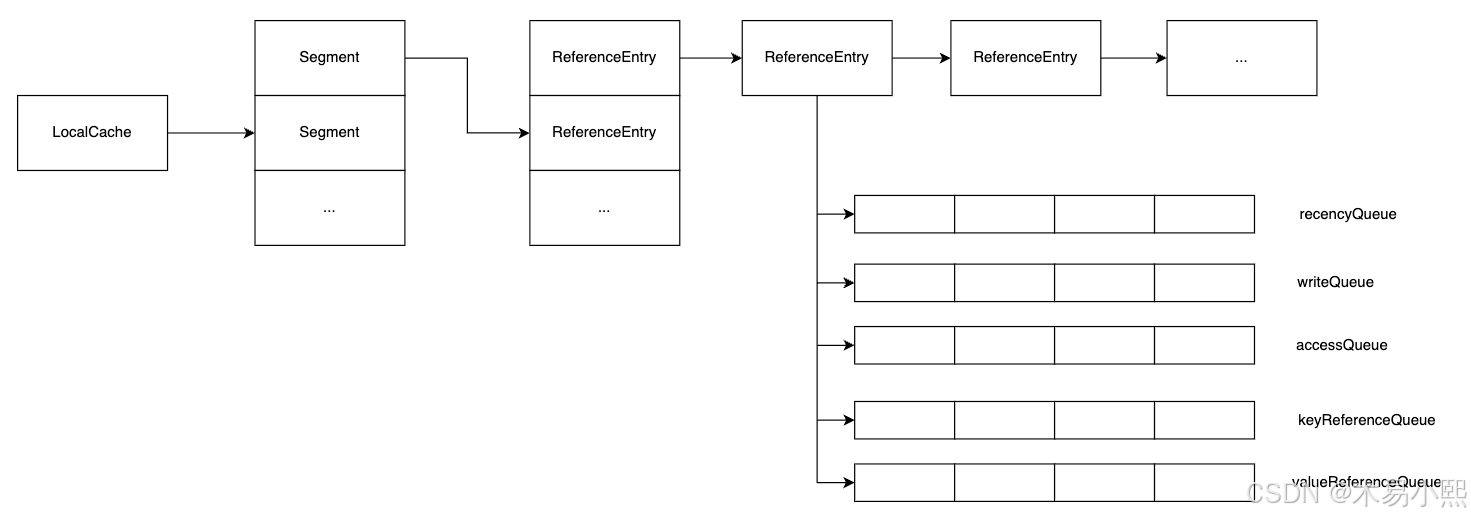
LocalMaunalCache
实现了 Cache 接口,是手动加载型缓存。需要显式调用 put() 方法向缓存中添加数据,获取数据时若不存在缓存命中,需手动处理(如返回 null 或自行加载数据)
LocalLoadingCache
实现了 LoadingCache 接口(LoadingCache 继承自 Cache),是自动加载型缓存。初始化时需传入 CacheLoader,当缓存未命中时,会自动调用 CacheLoader.load() 方法加载数据并放入缓存,无需手动 put()。
LocalMaunalCache 和 LocalLoadingCache 两者都继承自 AbstractLocalCache,共享底层的分段锁(Segment)、哈希表(table)、过期 / 淘汰策略等核心机制
LocalCache
LocalCache是 Guava Cache的核心类,本质上是一个Map
java
class LocalCache<K, V> extends AbstractMap<K, V> implements ConcurrentMap<K, V> {
// 缓存的最大容量,必须是2的幂次方且不超过1<<30
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
// 允许的最大段数,用于限制构造函数的参数
static final int MAX_SEGMENTS = 1 << 16; // slightly conservative
// 在containsValue方法中未同步的重试次数
static final int CONTAINS_VALUE_RETRIES = 3;
// 每个段的访问次数阈值
static final int DRAIN_THRESHOLD = 0x3F;
// 一次清理中可以清理的最大条目数
static final int DRAIN_MAX = 16;
static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(LocalCache.class.getName());
// 用于索引到段中的掩码值,键的哈希码的高位用于选择段
final int segmentMask;
// 用于在段内进行索引的偏移值,有助于防止最终位于同一段中的条目也最终位于同一个桶中。
final int segmentShift;
// 段组数,每个段都是一个专门的哈希表
final Segment<K, V>[] segments;
// 并发级别
final int concurrencyLevel;
// 键的比较策略
final Equivalence<Object> keyEquivalence;
// 值的比较策略
final Equivalence<Object> valueEquivalence;
// 引用键的策略
final Strength keyStrength;
// 引用值的策略
final Strength valueStrength;
// 最大重量
final long maxWeight;
// 键值对的重量
final Weigher<K, V> weigher;
// 键值对在最后一次访问后保留的时间
final long expireAfterAccessNanos;
// 键值对在最后一次写入后保留的时间
final long expireAfterWriteNanos;
// 键值对在最后一次写入后成为刷新候选的时间
final long refreshNanos;
// 等待被移除监听器消费的键值对队列
final Queue<RemovalNotification<K, V>> removalNotificationQueue;
// 键值对移除监听器
final RemovalListener<K, V> removalListener;
// 以可测试的方式测量时间的工具
final Ticker ticker;
// 创建新键值对的工厂
final EntryFactory entryFactory;
// 累积全局缓存统计信息的计数器
final StatsCounter globalStatsCounter;
// 在加载操作中使用的默认缓存加载器
final @Nullable CacheLoader<? super K, V> defaultLoader;
}Segment
LocalCache里维护了一个Segment数组
java
static class Segment<K, V> extends ReentrantLock {
// 指向外部 LocalCache 实例的弱引用,用于访问缓存
@Weak final LocalCache<K, V> map;
// 记录当前段Segment中活跃元素的数量
volatile int count;
// 当前段中所有活跃元素的总权重,受this锁保护,确保线程安全
@GuardedBy("this")
long totalWeight;
// 记录对段结构进行修改的次数,用于在批量读取操作中检测一致性,若在遍历过程中modCount发生变化,需要重试
int modCount;
// 扩容阈值,元素数量超过此值时触发扩容,计算公式为 capacity * 0.75
int threshold;
// 哈希表,存储具体数据
volatile @Nullable AtomicReferenceArray<ReferenceEntry<K, V>> table;
// 最大权重。默认为无限制
final long maxSegmentWeight;
// 键的引用队列。用于清理被回收的键
final @Nullable ReferenceQueue<K> keyReferenceQueue;
// 值的引用队列。用于清理被回收的值
final @Nullable ReferenceQueue<V> valueReferenceQueue;
// 用于记录哪些条目被访问过,以更新访问列表的顺序
final Queue<ReferenceEntry<K, V>> recencyQueue;
// 记录自上次写入以来的读操作次数,用于在少量读操作上排空队列
final AtomicInteger readCount = new AtomicInteger();
// 按写入时间排序的元素队列,用于管理键值对的顺序
@GuardedBy("this")
final Queue<ReferenceEntry<K, V>> writeQueue;
// 按访问时间排序的元素队列,用于管理键值对的顺序
@GuardedBy("this")
final Queue<ReferenceEntry<K, V>> accessQueue;
// 用于累积缓存统计信息
final StatsCounter statsCounter;
}源码分析
put
调用 put 方法写入key value的链路如下:
-
对 key 进行哈希运算,定位分段 segment
-
段内加锁,保证线程安全
-
更新当前活动元素数量,如果超过阈值则进行两倍扩容
-
计算获取对应位置的 table,遍历,判断 key 是否已经存在
-
如果 key 已存在
- 如果 value为空且 value的引用仍为活跃状态,则将原键值对的移除事件写入通知队列,并更新数据
- 如果 value不为空且仅当key不存在时更新,则返回旧值
- 如果vlaue不为空,则将原键值对的移除事件写入通知队列,并更新数据
-
如果 key 不存在,插入数据
-
-
如果设置了 maxSegmentWeight 且当前超重,则执行清理逻辑
- 如果新插入的键值对的重量超过 maxSegmentWeight,则删除当前键值对
- 从 accessQueue 中依次删除队头元素(最久未访问),直到当前段的 totalWeight <= maxSegmentWeight
java
@Nullable
V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
// 加锁,保证线程安全
lock();
try {
long now = map.ticker.read();
preWriteCleanup(now);
// 更新当前活动元素数量
int newCount = this.count + 1;
// 如果当前活动元素数量大于阈值,触发扩容
if (newCount > this.threshold) { // ensure capacity
expand();
newCount = this.count + 1;
}
// 计算插入的表,并获取该表的首个元素 first
AtomicReferenceArray<ReferenceEntry<K, V>> table = this.table;
int index = hash & (table.length() - 1);
ReferenceEntry<K, V> first = table.get(index);
// 遍历table,查找是否已经存在相同的键
for (ReferenceEntry<K, V> e = first; e != null; e = e.getNext()) {
K entryKey = e.getKey();
if (e.getHash() == hash
&& entryKey != null
&& map.keyEquivalence.equivalent(key, entryKey)) {
// 如果 key 已存在,获取 value
ValueReference<K, V> valueReference = e.getValueReference();
V entryValue = valueReference.get();
if (entryValue == null) {
// 更新修改次数
++modCount;
if (valueReference.isActive()) {
// 如果值引用活跃的,将原数据移除事件封装成通知并放入通知队列
enqueueNotification(
key, hash, entryValue, valueReference.getWeight(), RemovalCause.COLLECTED);
// 更新值
setValue(e, key, value, now);
newCount = this.count; // count remains unchanged
} else {
// 如果值引用不活跃,直接更新数据
setValue(e, key, value, now);
newCount = this.count + 1;
}
this.count = newCount;
// 如果设置了 maxSegmentWeight 且当前超重,则执行清理逻辑:
// 1. 如果新插入的键值对的重量超过 maxSegmentWeight,则删除当前键值对
// 2. 从 accessQueue 中依次删除队头元素(最久未访问),直到当前段的 totalWeight <= maxSegmentWeight
evictEntries(e);
return null;
} else if (onlyIfAbsent) {
// 如果 key 不为空仅当 key 不存在时更新,则返回旧值
recordLockedRead(e, now);
return entryValue;
} else {
// 如果key不为空,且onlyIfAbsent为fasle,覆盖现有键值对,计数保持不变
++modCount;
// 将原数据移除事件封装成通知并放入通知队列
enqueueNotification(
key, hash, entryValue, valueReference.getWeight(), RemovalCause.REPLACED);
// 更新值
setValue(e, key, value, now);
evictEntries(e);
return entryValue;
}
}
}
// 如果key不存在,插入新的键值对
++modCount;
ReferenceEntry<K, V> newEntry = newEntry(key, hash, first);
setValue(newEntry, key, value, now);
table.set(index, newEntry);
newCount = this.count + 1;
this.count = newCount; // write-volatile
evictEntries(newEntry);
return null;
} finally {
unlock();
postWriteCleanup();
}
}get
调用get方法的执行链路如下:
- 对 key 进行哈希运算,定位分段 segment
- 如果当前key不存在,则加载并返回 loader 方法的返回值
- 如果当前key存在,检查该键值对是否有效
- 如果值有效,更新该键值对的最后读取时间,增加命中统计,并尝试刷新该值
- 如果值无效,但条目的应用正在加载,则等待加载完成
LocalMaunalCache:
java
public V get(K key, final Callable<? extends V> valueLoader) throws ExecutionException {
checkNotNull(valueLoader);
// 调用 LocalCache的get方法
return localCache.get(
key,
new CacheLoader<Object, V>() {
@Override
public V load(Object key) throws Exception {
return valueLoader.call();
}
});
}LocalCache:
java
V get(K key, CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) throws ExecutionException {
int hash = hash(checkNotNull(key));
// 通过hash定位到segment,再调用segment的get方法
return segmentFor(hash).get(key, hash, loader);
}Segment:
java
V get(K key, int hash, CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) throws ExecutionException {
checkNotNull(key);
checkNotNull(loader);
try {
// 如果 count == 0 不会存在数据
if (count != 0) {
// 定位键值对,并判断该键值对是否有效
ReferenceEntry<K, V> e = getEntry(key, hash);
if (e != null) {
long now = map.ticker.read();
// 获取还没过去的value,如果过期了,则返回null
V value = getLiveValue(e, now);
if (value != null) {
// 如果缓存过期策略为expireAfterAccess,刷新键值对的访问时间
// 将该键值对添加到 recencyQueue
recordRead(e, now);
// 增加命中统计
statsCounter.recordHits(1);
// 尝试刷新缓存
return scheduleRefresh(e, key, hash, value, now, loader);
}
// 如果值无效但键值对的应用正在加载中,则等待加载完成
ValueReference<K, V> valueReference = e.getValueReference();
if (valueReference.isLoading()) {
return waitForLoadingValue(e, key, valueReference);
}
}
}
// 之前没有写入过数据 || 数据已经过期 || 数据不是在加载中
return lockedGetOrLoad(key, hash, loader);
} catch (ExecutionException ee) {
Throwable cause = ee.getCause();
if (cause instanceof Error) {
throw new ExecutionError((Error) cause);
} else if (cause instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw new UncheckedExecutionException(cause);
}
throw ee;
} finally {
postReadCleanup();
}
}
// 如果键值对无效返回null,有效返回value
V getLiveValue(ReferenceEntry<K, V> entry, long now) {
// 被GC回收
if (entry.getKey() == null) {
tryDrainReferenceQueues();
return null;
}
V value = entry.getValueReference().get();
// 被GC回收
if (value == null) {
tryDrainReferenceQueues();
return null;
}
// 判断是否过期
if (map.isExpired(entry, now)) {
tryExpireEntries(now);
return null;
}
return value;
}scheduleRefresh
java
如果 entry 还没过期,则会调用此方法,尝试刷新数据
V scheduleRefresh(
ReferenceEntry<K, V> entry,
K key,
int hash,
V oldValue,
long now,
CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) {
// 1. 配置了refreshAfterWrite
// 2. 用writeTime判断是否达到刷新时间
// 3. 是否在加载中,如果是则没必要再进行刷新
if (map.refreshes()
&& (now - entry.getWriteTime() > map.refreshNanos)
&& !entry.getValueReference().isLoading()) {
// 异步刷新数据
V newValue = refresh(key, hash, loader, true);
// 返回新值
if (newValue != null) {
return newValue;
}
}
return oldValue;
}
// refresh
V refresh(K key, int hash, CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader, boolean checkTime) {
// 为key插入一个LoadingValueReference
final LoadingValueReference<K, V> loadingValueReference =
insertLoadingValueReference(key, hash, checkTime);
if (loadingValueReference == null) {
return null;
}
// 通过loader异步加载数据
ListenableFuture<V> result = loadAsync(key, hash, loadingValueReference, loader);
// 判断Futer是否已经完成,如果是则返回结果。否则返回null
if (result.isDone()) {
try {
return Uninterruptibles.getUninterruptibly(result);
} catch (Throwable t) {
// don't let refresh exceptions propagate; error was already logged
}
}
return null;
}
LoadingValueReference<K, V> insertLoadingValueReference(
final K key, final int hash, boolean checkTime) {
ReferenceEntry<K, V> e = null;
// segment加锁
lock();
try {
long now = map.ticker.read();
// 预清理
preWriteCleanup(now);
AtomicReferenceArray<ReferenceEntry<K, V>> table = this.table;
int index = hash & (table.length() - 1);
ReferenceEntry<K, V> first = table.get(index);
// 如果key对应的entry存在.
for (e = first; e != null; e = e.getNext()) {
K entryKey = e.getKey();
if (e.getHash() == hash
&& entryKey != null
&& map.keyEquivalence.equivalent(key, entryKey)) {
// We found an existing entry.
ValueReference<K, V> valueReference = e.getValueReference();
if (valueReference.isLoading()
|| (checkTime && (now - e.getWriteTime() < map.refreshNanos))) {
// 如果是在加载中,或者还没达到刷新时间,则返回null
return null;
}
// new一个LoadingValueReference,然后把entry的valueReference替换掉
++modCount;
LoadingValueReference<K, V> loadingValueReference =
new LoadingValueReference<>(valueReference);
e.setValueReference(loadingValueReference);
return loadingValueReference;
}
}
// 如果key对应的entry不存在,则新建一个entry
++modCount;
LoadingValueReference<K, V> loadingValueReference = new LoadingValueReference<>();
e = newEntry(key, hash, first);
e.setValueReference(loadingValueReference);
table.set(index, e);
return loadingValueReference;
} finally {
unlock();
postWriteCleanup();
}
}lockedGetOrLoad
如果之前没有写如果数据 || 数据已过期 || 数据不是在加载中,则会调用lockedGetOrLoad
java
V lockedGetOrLoad(K key, int hash, CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) throws ExecutionException {
ReferenceEntry<K, V> e;
ValueReference<K, V> valueReference = null;
LoadingValueReference<K, V> loadingValueReference = null;
// 是否需要创建一个新的entry
boolean createNewEntry = true;
// segment加锁
lock();
try {
// re-read ticker once inside the lock
long now = map.ticker.read();
// 预清理
preWriteCleanup(now);
int newCount = this.count - 1;
AtomicReferenceArray<ReferenceEntry<K, V>> table = this.table;
int index = hash & (table.length() - 1);
// 定位到具体的table
ReferenceEntry<K, V> first = table.get(index);
for (e = first; e != null; e = e.getNext()) {
K entryKey = e.getKey();
// 定位key
if (e.getHash() == hash
&& entryKey != null
&& map.keyEquivalence.equivalent(key, entryKey)) {
valueReference = e.getValueReference();
// 如果value在加载中则不需要重复创建entry
if (valueReference.isLoading()) {
createNewEntry = false;
} else {
V value = valueReference.get();
// value为null说明已经过期且被清理掉了
if (value == null) {
// 写通知queue
enqueueNotification(
entryKey, hash, value, valueReference.getWeight(), RemovalCause.COLLECTED);
// 过期但还没被清理
} else if (map.isExpired(e, now)) {
// 写通知queue
// This is a duplicate check, as preWriteCleanup already purged expired
// entries, but let's accommodate an incorrect expiration queue.
enqueueNotification(
entryKey, hash, value, valueReference.getWeight(), RemovalCause.EXPIRED);
} else {
recordLockedRead(e, now);
statsCounter.recordHits(1);
// 其他情况直接返回value
// we were concurrent with loading; don't consider refresh
return value;
}
// immediately reuse invalid entries
writeQueue.remove(e);
accessQueue.remove(e);
this.count = newCount; // write-volatile
}
break;
}
}
// 创建一个 entry,切set一个新的LoadingValueReference
if (createNewEntry) {
loadingValueReference = new LoadingValueReference<>();
if (e == null) {
e = newEntry(key, hash, first);
e.setValueReference(loadingValueReference);
table.set(index, e);
} else {
e.setValueReference(loadingValueReference);
}
}
} finally {
unlock();
postWriteCleanup();
}
// 同步加载数据
if (createNewEntry) {
try {
// Synchronizes on the entry to allow failing fast when a recursive load is
// detected. This may be circumvented when an entry is copied, but will fail fast most
// of the time.
synchronized (e) {
return loadSync(key, hash, loadingValueReference, loader);
}
} finally {
statsCounter.recordMisses(1);
}
} else {
// The entry already exists. Wait for loading.
return waitForLoadingValue(e, key, valueReference);
}
}总结
Guava Cache 作为一个成熟的本地缓存实现,在很多场景下都能很好地满足需求。理解其内部实现(如分段锁机制、过期策略实现等)有助于我们更好地使用它,并在出现问题时能够快速定位和解决。