版本基于:Android 16 (W)
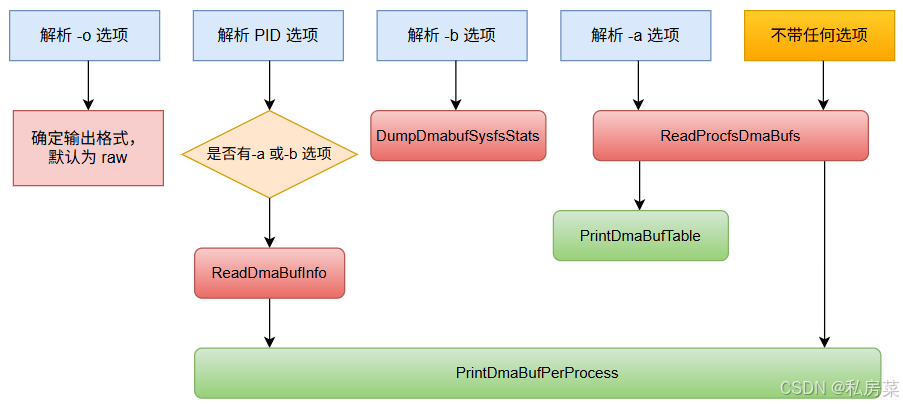
1. 命令格式
bash
shift:/ # dmabuf_dump -h
Usage: dmabuf_dump [-abh] [PID] [-o <raw|csv>]
-a show all dma buffers (ion) in big table, [buffer x process] grid
-b show DMA-BUF per-buffer, per-exporter and per-device statistics
-o [raw][csv] print output in the specified format.
-h show this help
If PID is supplied, the dmabuf information for that process is shown.
Per-buffer DMA-BUF stats do not take an argument.- -o:
- **-a:
- -b:
- **[pid]:
- 当没有
-a或-b选项时,将以进程维度,分别输出每个进程占用的 dmabuf 的每个inode 占用的内存信息,包括 PSS、RSS、nr_procs、export name。当然如果此时有[pid]参数,则只输出该 PID 的dmabuf 内存信息;
对应代码后框架如下:
2. 源码剖析
依赖节点:
- /sys/kernel/dmabuf/buffers/<inode>/
- /proc/<PID>/fdinfo/<fd>
- /proc/<PID>/maps
2.1 不带任何参数
2.1.1 输出信息格式
bash
cdsprpcd:2510
Name Rss Pss nr_procs Inode Exporter
system 4 kB 4 kB 1 56 system
system 4 kB 4 kB 1 57 system
system 256 kB 256 kB 1 58 system
PROCESS TOTAL 264 kB 264 kB
----------------------
binder:2522_2:2522
Name Rss Pss nr_procs Inode Exporter
system 32 kB 16 kB 2 661 system
system 32 kB 16 kB 2 662 system
system 32 kB 16 kB 2 663 system
system 32 kB 16 kB 2 664 system
system 32 kB 16 kB 2 665 system
PROCESS TOTAL 304 kB 152 kB
----------------------
dmabuf total: 176932 kB kernel_rss: 4240 kB userspace_rss: 331332 kB userspace_pss: 172691 kB将dmabuf 信息按照 PID 维度分离,记录每个 PID 不同的 inode 信息。
最后汇总总的内存分布:
- **
total:**统计 /sys/kernel/dmabuf/buffers 下所有inode size 之和; - **
kernel_rss:**total 中除去用户层映射的部分,也就是unmapped size; - **
userspace_rss:**用户层映射的 mapped RSS; - **
userspace_pss:**用户层映射的mapped PSS;
2.1.2 ReadProcfsDmaBufs()
cpp
main
|-->ReadProcfsDmaBufs //vector<DmaBuffer>, 每个inode对应一个DmaBuffer
|-->轮询/proc/下所有PID 目录,将pid传入下面两个函数
|-->ReadDmaBufFdRefs
|-->进入/proc/<PID>/fdinfo 目录,轮询每个<fd>
|-->ReadDmaBufFdInfo //读取<fd> 信息,解析每一行,存在exp_name信息,则认为是dmabuf
|-->如果解析的inode为-1,则从/proc/<PID>/fd/<fd> 通过stat命令解析size
|-->更新到vector<DmaBuffer>中
|-->增加DmaBuffer 的fd 引用
|-->ReadDmaBufMapRefs
|-->读取/proc/<PID>/maps信息
|-->确认每个vma,是否为 /dmabuf 开头,例如/dmabuf:system
|-->增加DmaBuffer 的map 引用
|-->ReadBufferExporter //读取/sys/kernel/dmabuf/buffers/<inode>/exporter_name
|-->ReadBufferSize //读取/sys/kernel/dmabuf/buffers/<inode>/size
|-->如果ReadBufferExporter 和ReadBufferSize 有任意一个失败,则使用vma的size每个 /proc/<PID>/fdinfo/<fd> 的信息有:
bash
pos: 0 | pos: 0
flags: 02000002 | flags: 0200001
mnt_id: 8 | mnt_id: 11
ino: 4 | ino: 108582
size: 28672 |
count: 3 |
exp_name: qcom,qseecom |
name: qcom,qseeco |左边带有 exp_name则表示该 inode 为 dmabuf。
cpp
system/memory/libmeminfo/libdmabufinfo/dmabufinfo.cpp
/**
* 该函数统计所有 dmabuf inode 信息,当dmabuf 已经使用/proc/<PID>/fdinfo/<fd> 已经创建好,
* 所以通过/proc/<PID>/fdinfo/<fd> 基本能够统计所有活跃的dmabuf内存。然而,可能存在fd 刚被
* close,而映射关系还没有解除,所以轮询一遍 /proc/<PID>/maps 确认是否有dmabuf 的vma 存在。
*
* 所以,这里轮询 /proc获取 PID,并调用两个函数:
* 1. ReadDmaBufFdRefs() 统计/proc/<PID>/fdinfo/<fd> 信息;
* 2. ReadDmaBufMapRefs() 统计/proc/<PID>/maps 中的dmabuf vma;
*/
bool ReadProcfsDmaBufs(std::vector<DmaBuffer>* bufs) {
bufs->clear();
std::unique_ptr<DIR, int (*)(DIR*)> dir(opendir("/proc"), closedir);
if (!dir) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to open /proc directory";
bufs->clear();
return false;
}
struct dirent* dent;
while ((dent = readdir(dir.get()))) {
if (dent->d_type != DT_DIR) continue;
int pid = atoi(dent->d_name);
if (pid == 0) {
continue;
}
if (!ReadDmaBufFdRefs(pid, bufs)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to read dmabuf fd references for pid " << pid;
}
if (!ReadDmaBufMapRefs(pid, bufs)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to read dmabuf map references for pid " << pid;
}
}
return true;
}
cpp
system/memory/libmeminfo/libdmabufinfo/dmabufinfo.cpp
//参数 procfs_path 默认为 /proc
bool ReadDmaBufFdRefs(int pid, std::vector<DmaBuffer>* dmabufs,
const std::string& procfs_path) {
constexpr char permission_err_msg[] =
"Failed to read fdinfo - requires either PTRACE_MODE_READ or root depending on "
"the device kernel";
static bool logged_permission_err = false;
//确认 /proc/<PID>/fdinfo是否可以访问,下面将轮询读取该目录下所有的 fd
std::string fdinfo_dir_path =
::android::base::StringPrintf("%s/%d/fdinfo", procfs_path.c_str(), pid);
std::unique_ptr<DIR, decltype(&closedir)> dir(opendir(fdinfo_dir_path.c_str()), &closedir);
if (!dir) {
// Don't log permission errors to reduce log spam on devices where fdinfo
// of other processes can only be read by root.
if (errno != EACCES) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "Failed to open " << fdinfo_dir_path << " directory";
} else if (!logged_permission_err) {
LOG(ERROR) << permission_err_msg;
logged_permission_err = true;
}
return false;
}
struct dirent* dent;
while ((dent = readdir(dir.get()))) {
int fd;
if (!::android::base::ParseInt(dent->d_name, &fd)) { //fd都是整数
continue;
}
// Set defaults in case the kernel doesn't give us the information
// we need in fdinfo
std::string name = "<unknown>";
std::string exporter = "<unknown>";
uint64_t count = 0;
uint64_t size = 0;
uint64_t inode = -1;
bool is_dmabuf_file = false;
auto fdinfo_result = ReadDmaBufFdInfo(pid, fd, &name, &exporter, &count, &size, &inode,
&is_dmabuf_file, procfs_path);
if (fdinfo_result != OK) {
if (fdinfo_result == NOT_FOUND) {
continue;
}
// Don't log permission errors to reduce log spam when the process doesn't
// have the PTRACE_MODE_READ permission.
if (errno != EACCES) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to read fd info for pid: " << pid << ", fd: " << fd;
} else if (!logged_permission_err) {
LOG(ERROR) << permission_err_msg;
logged_permission_err = true;
}
return false;
}
//确认是否为dmabuf fd
if (!is_dmabuf_file) {
continue;
}
//这里是兼容性,当发现idnode为-1 时,可能inode 缺失,通过stat的方式获取sb.st_info
if (inode == static_cast<uint64_t>(-1)) {
// Fallback to stat() on the fd path to get inode number
std::string fd_path =
::android::base::StringPrintf("%s/%d/fd/%d", procfs_path.c_str(), pid, fd);
struct stat sb;
if (stat(fd_path.c_str(), &sb) < 0) {
if (errno == ENOENT) {
continue;
}
PLOG(ERROR) << "Failed to stat: " << fd_path;
return false;
}
inode = sb.st_ino;
// If root, calculate size from the allocated blocks.
size = sb.st_blocks * 512;
}
//通过dmabuf 唯一标识inode,确认是否创建过DmaBuffer对象,无论是否存在,都增加fd 引用计数
auto buf = std::find_if(dmabufs->begin(), dmabufs->end(),
[&inode](const DmaBuffer& dbuf) { return dbuf.inode() == inode; });
if (buf != dmabufs->end()) {
if (buf->name() == "" || buf->name() == "<unknown>") buf->SetName(name);
if (buf->exporter() == "" || buf->exporter() == "<unknown>") buf->SetExporter(exporter);
if (buf->count() == 0) buf->SetCount(count);
buf->AddFdRef(pid);
continue;
}
DmaBuffer& db = dmabufs->emplace_back(inode, size, count, exporter, name);
db.AddFdRef(pid);
}
return true;
}
cpp
system/memory/libmeminfo/libdmabufinfo/dmabufinfo.cpp
/**
* 参数 procfs_path:默认为/proc
* 参数dmabuf_sysfs_path:默认为 /sys/kernel/dmabuf/buffers
*/
bool ReadDmaBufMapRefs(pid_t pid, std::vector<DmaBuffer>* dmabufs,
const std::string& procfs_path,
const std::string& dmabuf_sysfs_path) {
std::string mapspath = ::android::base::StringPrintf("%s/%d/maps", procfs_path.c_str(), pid);
std::ifstream fp(mapspath);
if (!fp) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to open " << mapspath << " for pid: " << pid;
return false;
}
// Process the map if it is dmabuf. Add map reference to existing object in 'dmabufs'
// if it was already found. If it wasn't create a new one and append it to 'dmabufs'
auto account_dmabuf = [&](const android::procinfo::MapInfo& mapinfo) {
// no need to look into this mapping if it is not dmabuf
if (!FileIsDmaBuf(mapinfo.name)) { //确认 vma 是否为dmabuf
return;
}
//通过唯一的标识inode,确认是否已经创建好DmaBuffer 对象
auto buf = std::find_if(
dmabufs->begin(), dmabufs->end(),
[&mapinfo](const DmaBuffer& dbuf) { return dbuf.inode() == mapinfo.inode; });
//如果创建好了 DmaBuffer对象,增加map 引用计数
if (buf != dmabufs->end()) {
buf->AddMapRef(pid);
return;
}
//如果没有创建DmaBuffer对象,尝试获取inode下的 exporter name
std::string exporter;
bool sysfs_stats = ReadBufferExporter(mapinfo.inode, &exporter, dmabuf_sysfs_path);
if (!sysfs_stats) {
exporter = "<unknown>";
}
//尝试读取inode 下的 size,如果没有获得,则使用vma的大小
//但此时可能产生误导,有可能vma 超过实际buffer size
uint64_t size = 0;
if (!sysfs_stats || !ReadBufferSize(mapinfo.inode, &size, dmabuf_sysfs_path)) {
size = mapinfo.end - mapinfo.start;
}
DmaBuffer& dbuf = dmabufs->emplace_back(mapinfo.inode, size, 0, exporter, "<unknown>");
dbuf.AddMapRef(pid);
};
for (std::string line; getline(fp, line);) {
if (!::android::procinfo::ReadMapFileContent(line.data(), account_dmabuf)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to parse " << mapspath << " for pid: " << pid;
return false;
}
}
return true;
}2.2 带有PID 参数
通常带有 PID 参数是想要获取某个特定进程的 dmabuf 信息,所以不会跟 -a 或 -b 同时出现。
当不带任何参数时,会轮询 /proc/ 下所有 PID 进行解析。而带有 PID 选项,则无需轮询,直接通过函数 ReadDmaBufInfo() 进行解析。
2.2.1 输出信息格式
bash
shift:/proc/1919/fdinfo # dmabuf_dump 2390
mediaserver:2390
Name Rss Pss nr_procs Inode Exporter
system 32 kB 32 kB 1 501 system
system 32 kB 32 kB 1 505 system
system 32 kB 32 kB 1 510 system
system 32 kB 32 kB 1 512 system
system 32 kB 32 kB 1 661 system
system 32 kB 32 kB 1 662 system
system 32 kB 32 kB 1 663 system
system 32 kB 32 kB 1 664 system
system 32 kB 32 kB 1 665 system
system 16 kB 16 kB 1 666 system
system 16 kB 16 kB 1 667 system
system 16 kB 16 kB 1 668 system
system 32 kB 32 kB 1 670 system
system 32 kB 32 kB 1 671 system
system 32 kB 32 kB 1 672 system
PROCESS TOTAL 432 kB 432 kB
----------------------
dmabuf total: 176932 kB kernel_rss: 176500 kB userspace_rss: 432 kB userspace_pss: 432 kB这里不过多解释,详细看上文第 2.1.1 节。
2.2.1 ReadDmaBufInfo()
cpp
system/memory/libmeminfo/libdmabufinfo/dmabufinfo.cpp
/**
* 该函数用以解析某特定 PID 的dmabuf 信息,其实就是ReadProcfsDmaBufs()的一个PID分支
*
* 参数 read_fdrefs:默认为 true
* 参数 procfs_path:默认为 /proc
* 参数 dmabuf_sysfs_path:默认为/sys/kernel/dmabuf/buffers
*/
bool ReadDmaBufInfo(pid_t pid, std::vector<DmaBuffer>* dmabufs, bool read_fdrefs,
const std::string& procfs_path, const std::string& dmabuf_sysfs_path) {
//只解析一个 PID 信息,这里做一下clear
dmabufs->clear();
if (read_fdrefs) {
if (!ReadDmaBufFdRefs(pid, dmabufs, procfs_path)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to read dmabuf fd references";
return false;
}
}
if (!ReadDmaBufMapRefs(pid, dmabufs, procfs_path, dmabuf_sysfs_path)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to read dmabuf map references";
return false;
}
return true;
}2.3 选项 -b
用以解析 /sys/kernel/dmabuf/buffers 下每个buffer 的export_name 和 size, 不排序。
2.3.1 输出信息格式
bash
----------------------- DMA-BUF per-buffer stats -----------------------
Dmabuf Inode | Size(bytes) | Exporter Name |
619 | 13004800 | system
57 | 4096 | system
250 | 32768 | system
...
...
721 | 13004800 | system
665 | 32768 | system
9 | 516096 | system
27 | 4096 | system
----------------------- DMA-BUF exporter stats -----------------------
Exporter Name | Total Count | Total Size(bytes) |
system | 47| 176926720
...
----------------------- DMA-BUF total stats -----------------------
Total DMA-BUF count: 91, Total DMA-BUF size(bytes): 181178368分三块:
- **第一块:**按照 inode 维度输出,包括size 和 exporter name;
- **第二块:**按照exporter name维度输出,这里省略了system 之外的其他 exporter;
- **第三块:**总的信息;
更多信息可以查看 DumpDmabufSysfsStats() 函数。
2.4 选项 -a
以表的形式显示dmabuf 信息
2.4.1 输出信息格式
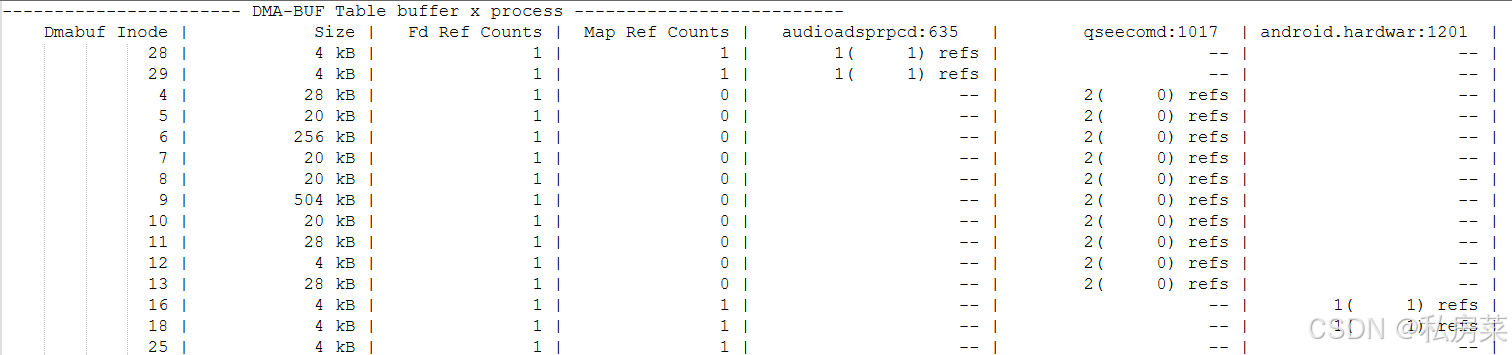
这是文本形式的信息,后面还有很多进程信息。
- **第一列:**dmabuf 的inode;
- **第二列:**该dmabuf 的size;
- **第三列:**该inode 被fd 引用的次数;
- **第四列:**该inode 被mapped 的引用次数;
- **第五列开始:**各个进程的引用统计;
统计的信息来自函数 ReadProcfsDmaBufs() 函数,打印函数为 **PrintDmaBufTable(),**可以查看上文框架图。
2.5 选项 -o
用以指定print 时的输出格式,raw 或 csv,默认为 raw,上面输出的格式都是文本信息。
也可以指定为 csv 格式,例如带有 PID 参数的输出csv 格式:
bash
mediaserver:2390
"Name","Rss(kB)","Pss(kB)","nr_procs","Inode","Exporter"
"system",32,32,1,501,system
"system",32,32,1,505,system
"system",32,32,1,510,system
"system",32,32,1,512,system
"system",32,32,1,661,system
"system",32,32,1,662,system
"system",32,32,1,663,system
"system",32,32,1,664,system
"system",32,32,1,665,system
"system",16,16,1,666,system
"system",16,16,1,667,system
"system",16,16,1,668,system
"system",32,32,1,670,system
"system",32,32,1,671,system
"system",32,32,1,672,system
PROCESS TOTAL
"Rss total(kB)","Pss total(kB)"
432,432
----------------------
TOTALS
"dmabuf total (kB)","kernel_rss (kB)","userspace_rss (kB)","userspace_pss (kB)"3. 实用
dmabuf_dump 命令在user 版本中可能存在缺陷:
-
dmabuf_dump 命令会失败;
-
没有进入/proc/<PID>/fdinfo 权限;
bash
dr-xr-xr-x 2 system system u:r:tee:s0 0 2025-10-02 11:13 fdinfo- 没有进入 /sys/kernel/dmabuf/buffers 权限;
bash
drwxr-xr-x 125 root root u:object_r:sysfs_dmabuf_stats:s0 0 2025-10-01 20:39 buffers可以使用 libdmabufinfo.so 这个静态库,模拟dmabuf_dump 中的函数调用,调用 ReadProcfsDmaBuf() 或 ReadDmaBufInfo() 函数。
bash
#include <dmabufinfo/dmabuf_sysfs_stats.h>
#include <dmabufinfo/dmabufinfo.h>
struct PidMemoryInfo {
uint64_t rss;
uint64_t pss;
};
std::unordered_map<pid_t, PidMemoryInfo> gPidMemoryMap;
uint64_t gDmabufTotal;
int parseDmabuf()
{
ALOGV("parseDmabuf start...");
std::vector<DmaBuffer> bufs;
if (!ReadProcfsDmaBufs(&bufs)) {
ALOGE("Failed to ReadProcfsDmaBufs, check logcat for info");
return -1;
}
if (bufs.empty()) {
ALOGE("parsed dmabuf is empty....");
gPidMemoryMap.clear();
return 0;
}
std::unordered_map<ino_t, DmaBuffer> inode_to_dmabuf;
std::unordered_map<pid_t, std::set<ino_t>> pid_to_inodes = {};
for (auto& buf : bufs) {
inode_to_dmabuf[buf.inode()] = buf;
for (auto pid : buf.pids()) {
pid_to_inodes[pid].insert(buf.inode());
}
}
gPidMemoryMap.clear();
for (auto& [pid, inodes] : pid_to_inodes) {
uint64_t pss = 0;
uint64_t rss = 0;
for (auto& inode : inodes) {
DmaBuffer& buf = inode_to_dmabuf[inode];
rss += buf.size();
pss += buf.Pss();
}
PidMemoryInfo memInfo = {rss, pss};
gPidMemoryMap[pid] = memInfo;
}
if (!GetDmabufTotalExportedKb(&gDmabufTotal)) {
ALOGE("Warning: Could not get total exported dmabufs. Kernel size will be 0.");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}经过上面统计之后,就可以根据业务需要显示:
cpp
for (auto& [pid, memInfo] : gPidMemoryMap) {
ALOGD("%6d %llu", pid, memInfo.pss);
}