
Spring MVC常用注解
告别"XML 地狱",迎接"一行注解走天下"。在注解普及之前,Spring 几乎全靠 XML 配置。**每写一个 Bean 就要写一行<bean>**
java
<bean id="userController" class="com.demo.UserController">
<property name="userService" ref="userService"/>
</bean>每加一个请求映射就要写一段 <bean> + SimpleUrlHandlerMapping 。Bean 多了以后:XML 文件几百行,想找个类得搜索半天,改个路径要全文替换。
如今,一句 @Controller 就能让 Spring 知道"这儿有个控制器";再补上一行 @RequestMapping("/user"),前端请求就精准落地。这就是 Spring MVC 注解的魅力将繁琐的配置压缩成可读的"代码标签",开发效率瞬间翻倍,出错率直线下降。
废话不多说,让我们进入Spring MVC注解的学习
@RequestMapping
@RequestMapping 注解多用于路由映射,既可以修饰类,也可以修饰方法,当修饰类和方法时,访问的地址是类路径+方法路径。
@RequestMapping 标识一个类:设置映射请求的请求路径的初始信息
@RequestMapping 标识一个方法:设置映射请求请求的具体路径
java
@RequestMapping("/user")
@RestController
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/sayHi")
public String sayHi(){
return "hello,Spring MVC";
}
}访问地址: http://127.0.0.1:8080/user/sayHi
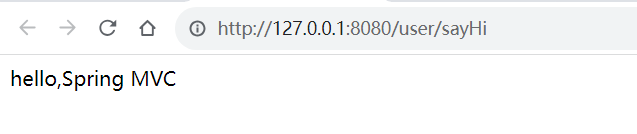
@RequestMapping 的url路径可以是多层路径。最终访问时仍然是类路径+方法路径
java
@RequestMapping("/user/m1")
@RestController
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/say/hi")
public String sayHi(){
return "hello,Spring MVC";
}
}访问地址: http://127.0.0.1:8080/user/m1/say/hi
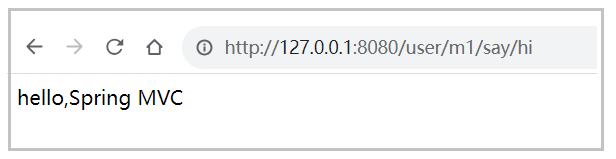
注意:@RequestMapping 既可以接收 POST 请求也可以接收 GET 请求
@PostMapping
使用该注解只能实现 POST 请求下的路由映射功能,是@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST) 的缩写。
java
//后端代码
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/test2",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String test2(String desc){
return "接收到参数desc:"+desc;
}
//或者下面这种写法,直接写@PostMapping
@PostMapping("test3")
public String test3(String desc){
return "接收到参数:"+desc;
}
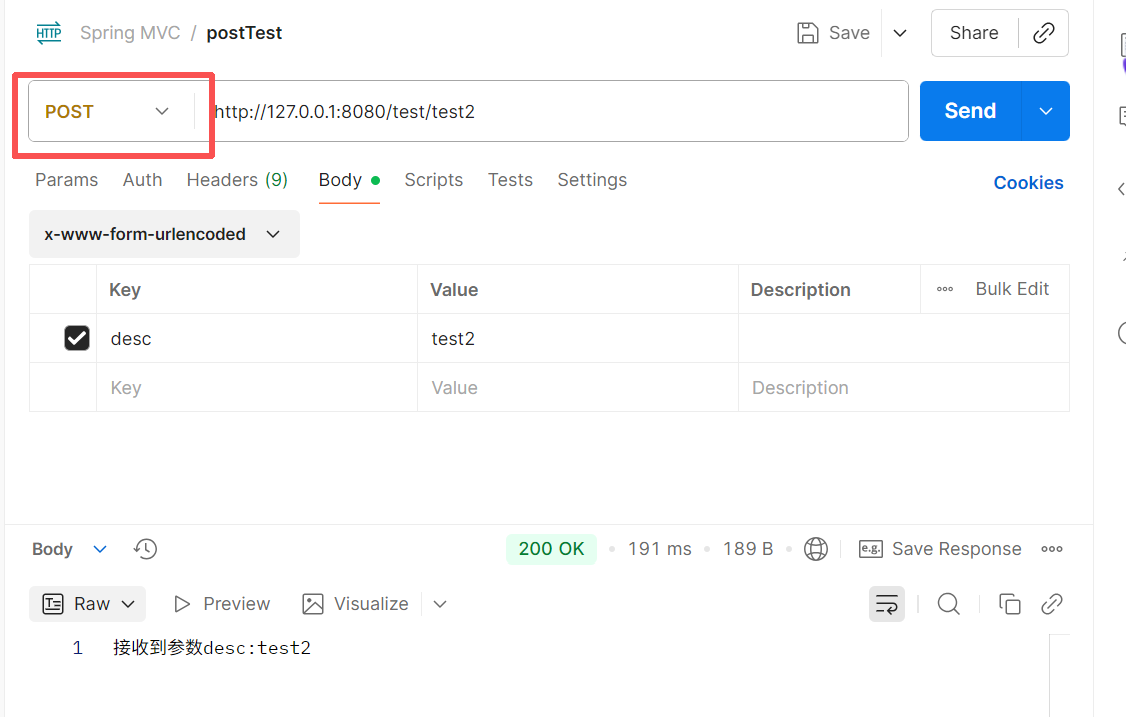
}使用postman发送消息,这里对应后端使用@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
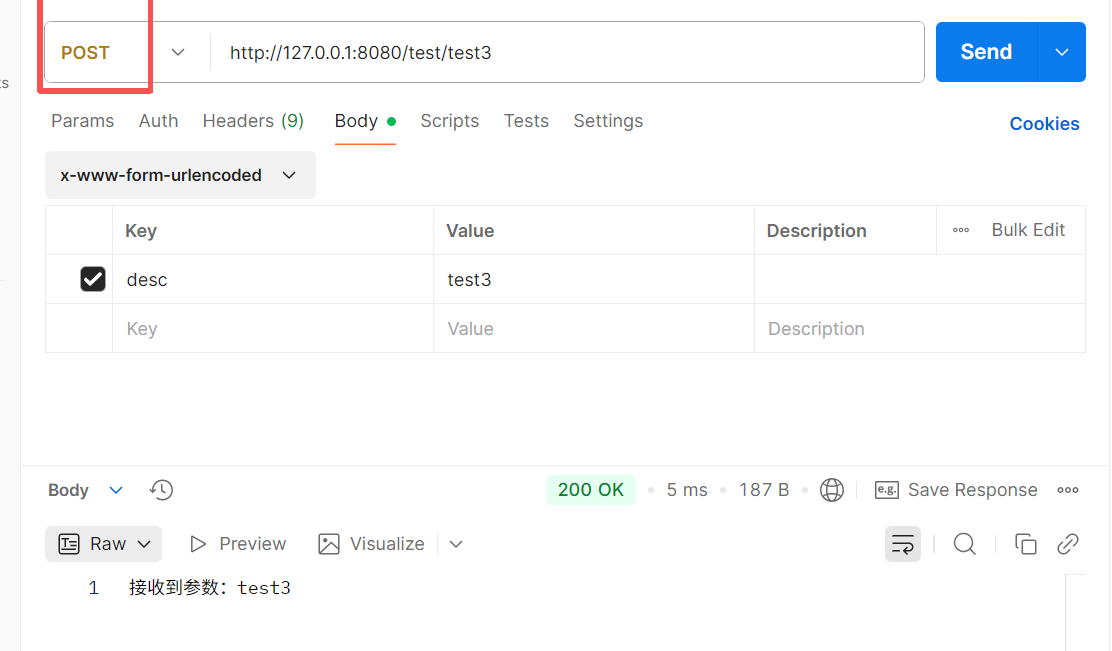
对应后端直接使用@PostMapping注解
将POST请求转变为GET请求会出现如下错误
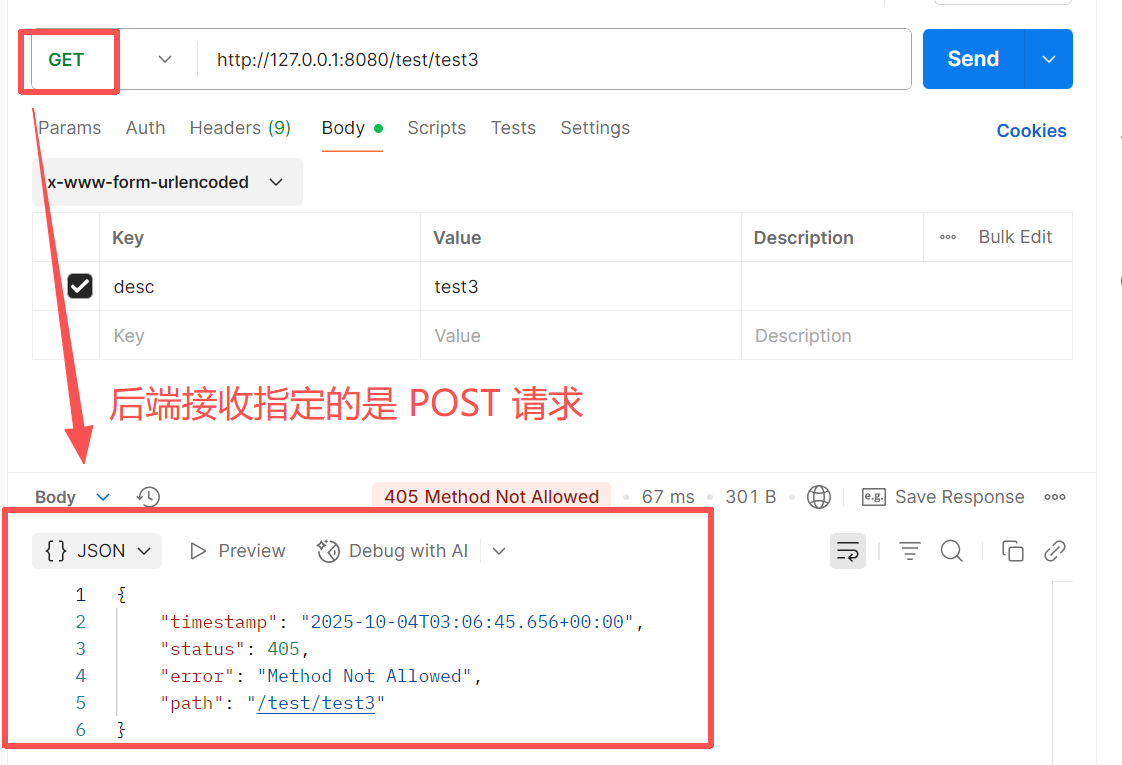
@GetMapping
使用该注解只能实现 GET 请求下的路由映射功能,是@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)的缩写。其实现与上述@PostMapping是一致的,感兴趣的小伙伴可以动手实现一下~~
@Controller
- @Controller 把类注册成 Spring Bean,并默认将方法返回值当逻辑视图名;
java
@Controller
public class IndexController {
@RequestMapping("/index")
public Object index(){
return "/index.html";
}
}index.html代码如下:
Html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Index⻚⾯</title>
</head>
<body>
Hello,Spring MVC,我是Index⻚⾯.
</body>
</html>访问地址: http://127.0.0.1:8080/index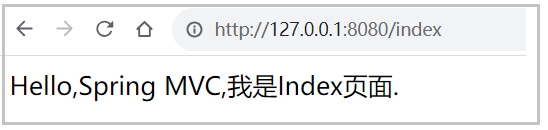
- 想返回 JSON/文本就补
@ResponseBody,加入@ResponseBody注解后,类中方法返回数据被解析为文本
java
@Controller
@ResponseBody
public class IndexController {
@RequestMapping("/index")
public Object index(){
return "/index.html";
}
}访问地址: http://127.0.0.1:8080/index
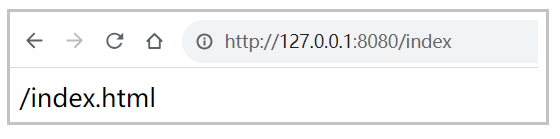
- 想跳静态页就用
redirect:,写成return "redirect:/index.html";
java
@Controller
public class IndexController {
@RequestMapping("/index")
public Object index(){
return "redirect:/index.html";
}
}→ 发 302 重定向 给浏览器,浏览器再访问 http://host/context/index.html,只要静态目录(默认 classpath:/static/)里有这个文件就能直接看到页面。
@ResponseBody
@ResponseBody : 定义返回的数据格式为非视图, 返回⼀个 text/html 信息,也就是返回数据
@ResponseBody既是方法注解又是类注解,如果注解加在方法上表示该方法返回的为数据信息,加在类上表示该类所有方法返回的都是数据信息。类上加@ResponseBody注解,也就意味着类中所有方法都加上了@ResponseBody注解。
java
@Controller
@ResponseBody
public class IndexController {
@RequestMapping("/index")
public Object index(){
return "/index.html";
}
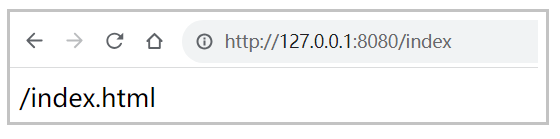
}加上 @ResponseBody 注解, 该方法就会把 "/index.html" 当做⼀个数据返回给前端.
访问地址: http://127.0.0.1:8080/index
@RestController
@RestController=@ResponseBody+@Controller
@Controller : 定义⼀个控制器, Spring 框架启动时加载, 把这个对象交给Spring管理.
@ResponseBody : 定义返回的数据格式为非视图, 返回⼀个 text/html 信息
某个类如果加上了@RestController注解,也就意味着类中所有方法都加上了@ResponseBody,返回消息均会被解析为数据信息。
@RestController源码如下:可以看到声明RestController注解上有添加Controller和Response注解
java
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Controller
@ResponseBody
public @interface RestController {
@AliasFor(
annotation = Controller.class
)
String value() default "";
}@RequestParam
作用一:@RequestParam 可以用于重命名前后端的参数值
java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/param")
public class TimeController{
@RequestMapping("/m4")
public Object method_4(@RequestParam("time") String createtime) {
return "接收到参数createtime:" + createtime;
}
}访问地址: http://127.0.0.1:8080/param/m4?time=2023-9-12
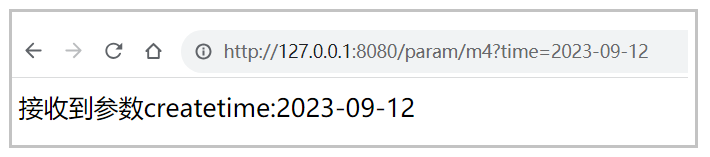
通过上面运行结果可以得知,Spring将浏览器传递的 time 参数数据绑定给了 createtime 参数 。
注意1.使用@RequsetParam注解来进行重命名时,传递的参数名必须要和@RequsetParam声明的名称一致,才能进行参数绑定和赋值。2.使用@RequsetParam注解时,此时参数变为了必传参数。
如若想要使用 @RequsetParam 又想其为非必传参数,针对上述问题,应该怎么解决呢??
查看 @RequsetParam 注解实现细节如下
java
@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface RequestParam {
@AliasFor("name")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor("value")
String name() default "";
boolean required() default true;
String defaultValue() default
"\n\t\t\n\t\t\n\ue000\ue001\ue002\n\t\t\t\t\n";
}不难发现,上述 requied 属性默认值为 true,required = true,其含义为该注解的参数为必须要传递,将required = false即可表示为非必传参数。
java
@RequestMapping("/m4")
public Object method4(@RequestParam(value = "time", required = false) String
createtime) {
return "接收到参数createtime:" + createtime;
}作用二:@RequestParam 注解除了上述功能外,在浏览器传递集合中也需要使用到其注解。
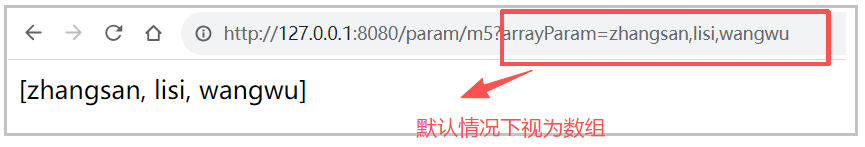
默认情况下,请求中参数名相同的多个值,是封装到数组。 如果要封装到集合,要使用@RequestParam 绑定参数关系
浏览器传参:
⽅式⼀: http://127.0.0.1:8080/param/m6?listParam=zhangsan&listParam=lisi&listParam=wangwu
⽅式⼆: http://127.0.0.1:8080/param/m6?listParam=zhangsan%2Clisi%2Cwangwu
%2c 是逗号的转义编码, 解码后的url为: http://127.0.0.1:8080/param/m6?listParam=zhangsan,lisi,wangwu
后端接收的代码:
java
@RequestMapping("/m6")
public String method6(@RequestParam List<String> listParam){
return "size:"+listParam.size() + ",listParam:"+listParam;
}@RequstBody
@RequestBody 注解用于接收JSON对象并反序列化成对象,进行数据的绑定
RequestBody:请求正文,意思是这个注解作用在请求正文的数据绑定,请求参数必须写在请求正文中。
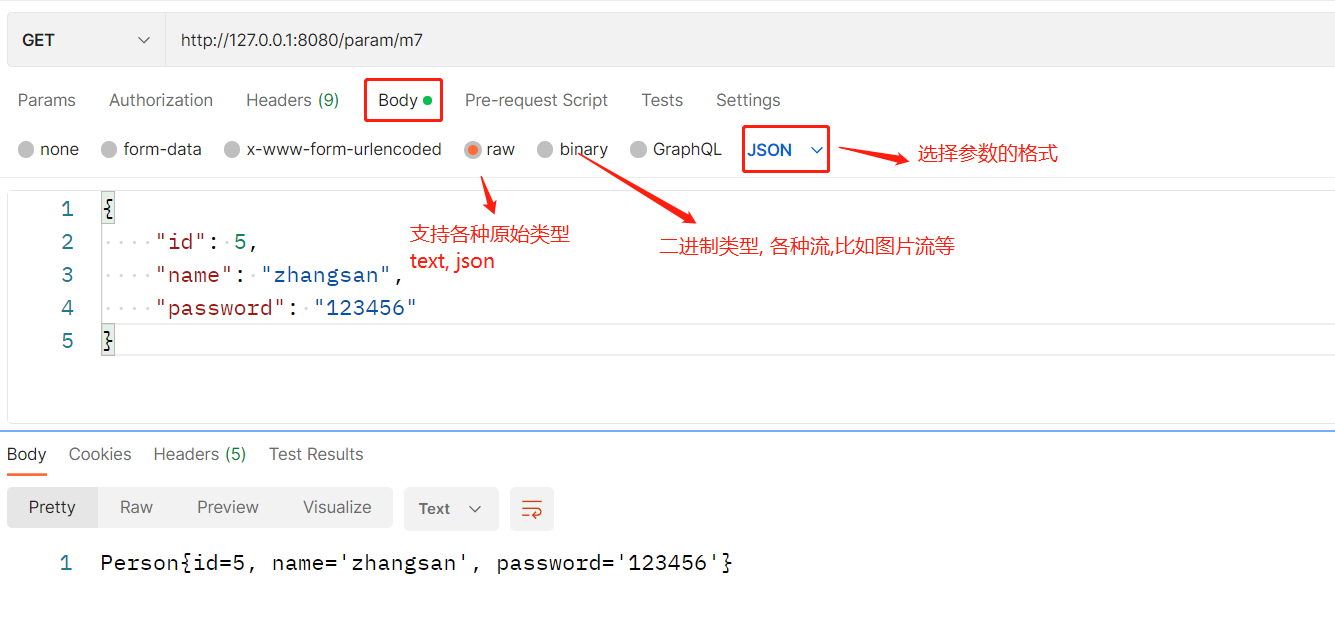
java
@RequestMapping(value = "/m7")
public Object method7(@RequestBody Person person) {
return person.toString();
}Person类的属性如下,这里 Getter 和 Setter 注解用于给属性提供get,set方法,使用这两个注解需要引入lombook的依赖。
java
@Setter
@Getter
public class Person{
private int id;
private String name;
private String password;
}这里使用postman来模拟前端
 当去掉 @RequestBody 注解时
当去掉 @RequestBody 注解时
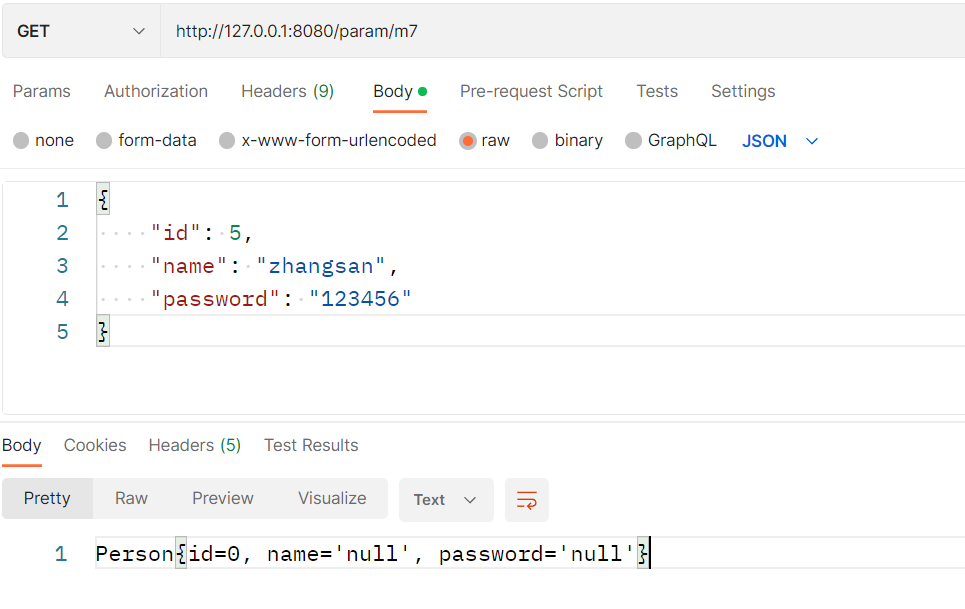
运行结果可知给Person对象赋值失败。
注意:1.在传递json对象时,除了确保@RequestBody 注解还需要注意json中key和对象属性的类型和名称保持一致,且默认大小写敏感。
- @RequestBody 只
"读请求 body 里的纯 JSON 文本",而 GET/DELETE 没有 body,所以用不了;同时服务端要识别这段数据是 JSON,必须客户端把请求头Content-Type 设成 application/json,否则直接报 415(Unsupported Media Type)。
@PathVariable
@PathVariable可以用来获取URL中的参数,path variable: 路径变量,用于请求URL中的数据绑定。
默认传递参数写在URL上,Spring MVC可以获取到。
java
//后端代码
@RequestMapping("/m8/{id}/{name}")
public String method8(@PathVariable Integer id, @PathVariable("name") String
userName){
return "解析参数id:"+id+",name:"+userName;
}使用浏览器发送请求: http://127.0.0.1:8080/param/m8/5/zhangsan
或者使用postman发送请求
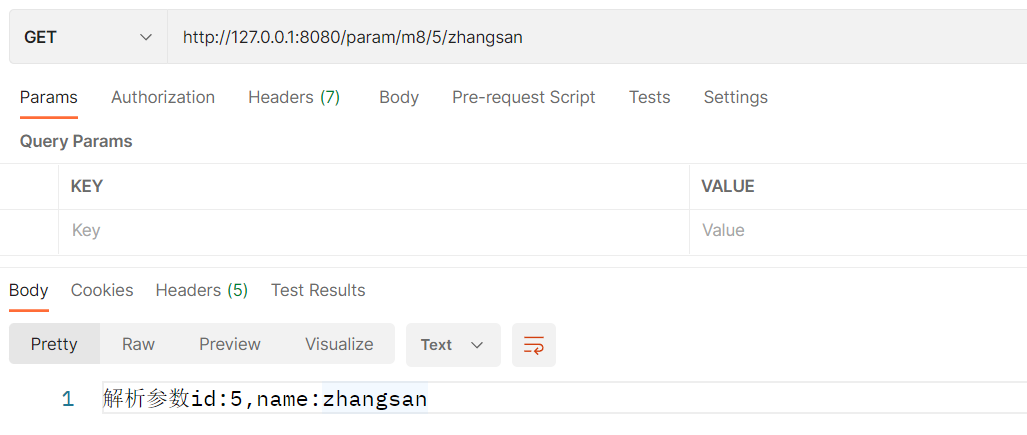
对应参数关系如下:
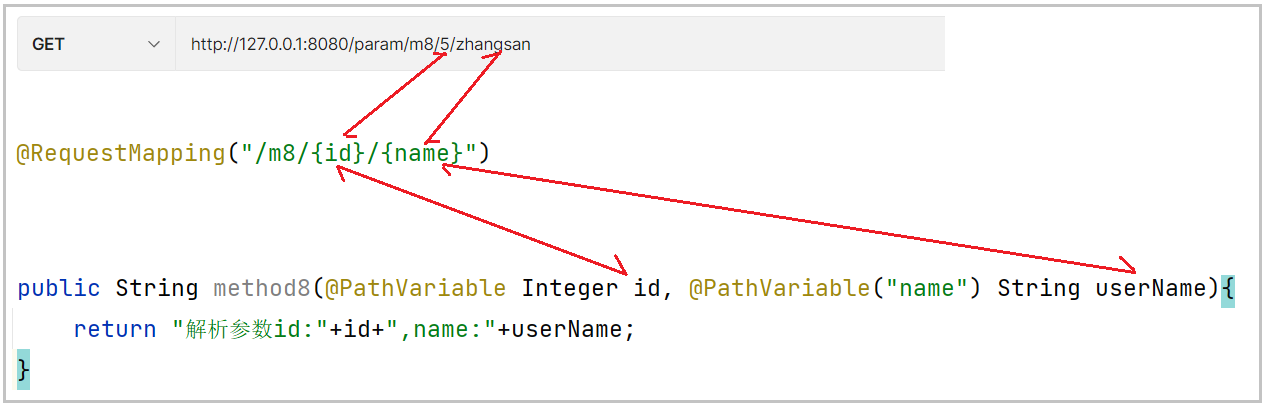
注意:如果方法参数名称和需要绑定的URL中变量的名称一致时,可以简写,不用给@PathVariable的属性赋值,对应上述例子中的id变量。
如果方法参数名称和需要绑定的URL中变量的名称不一致时,需要给@PathVariable的属性value赋值,对应上述例子中的userName变量。
@RequestPart
@RequestPart用于上传文件
java
//后端实现
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
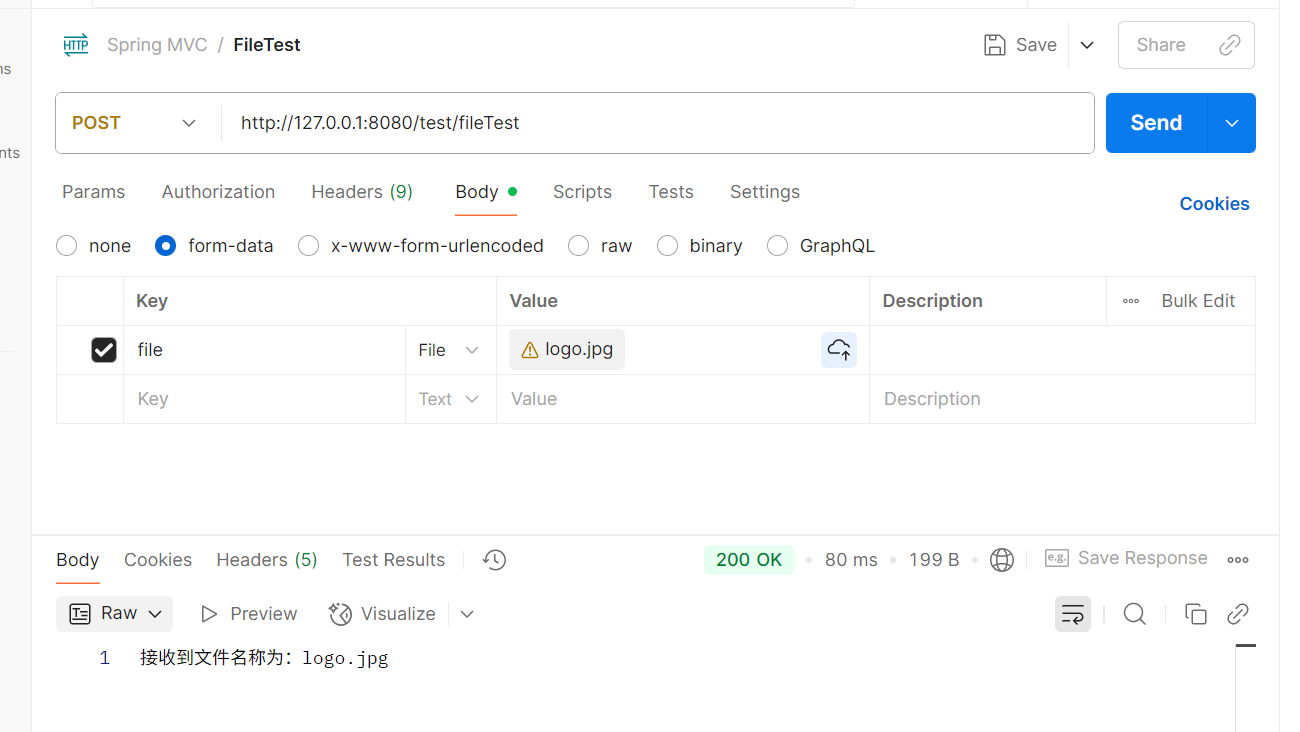
@RequestMapping("/fileTest")
public String test1(@RequestPart MultipartFile file) throws IOException {
//获取到文件名
String fileName=file.getOriginalFilename();
//上传文件到指定路径
file.transferTo(new File("C:/test/"+fileName));
return "接收到文件名称为:"+fileName;
}
}使用postman发送请求
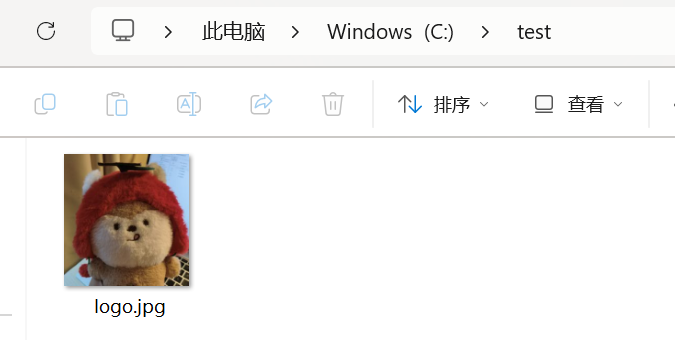
查看一下 C:/test/中是否有刚刚上传的图片
注解小结
@RequestMapping:类/方法上的 URL 路由,可配 method/post/get/put/delete
@PostMapping:只接 POST 的缩写
@GetMapping:只接 GET 的缩写
@Controller:把类注册成 Spring Bean,默认走视图解析(JSP/Thymeleaf)
@ResponseBody:把返回值直接写回 HTTP 响应体(JSON/文本),不跳页面。可打在方法或类上
@RestController:= @Controller + @ResponseBody合体;整类所有方法都返数据
@RequestParam:接收 查询参数或表单字段;可重命名、设必填/选填。不传且 required=true 抛 400
@RequestBody:接收 请求体里整条 JSON/XML 并反序列化成对象。只能用于 POST/PUT 且有 Content-Type: application/json
@PathVariable:取 URL 路径段 如 /m8/{id}/{name}。变量名要一致或用 @PathVariable("id") 指定
@RequestPart:接收 multipart/form-data 中的文件或复杂字段。常与 MultipartFile 搭配,文件上传专用
有关路由的一般使用*Mapping,参数用 @RequestParam/@PathVariable/@RequestBody,文件用 @RequestPart