代码清单3-5 多头注意力
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class MultiHeadAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_in, d_out,
context_length, dropout, num_heads, qkv_bias=False):
super().__init__()
assert (d_out % num_heads == 0), \
"d_out must be divisible by num_heads"
self.d_out = d_out
self.num_heads = num_heads
# 减少投影维度以匹配所需的输出维度
self.head_dim = d_out // num_heads
self.W_query = nn.Linear(d_in, d_out, bias=qkv_bias)
self.W_key = nn.Linear(d_in, d_out, bias=qkv_bias)
self.W_value = nn.Linear(d_in, d_out, bias=qkv_bias)
# 使用一个线性层来组合头的输出
self.out_proj = nn.Linear(d_out, d_out)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.register_buffer(
"mask",
torch.triu(torch.ones(context_length, context_length),
diagonal=1)
)
def forward(self, x):
b, num_tokens, d_in = x.shape # (2, 6, 3)
# shape: (b, num_tokens, d_out)
keys = self.W_key(x) # (2, 6, 3) @ (3, 2) => (2, 6, 2)
queries = self.W_query(x)
values = self.W_value(x)
# 通过添加一个 num_heads 维 度来隐式地分隔矩阵。然后 展开最后一个维度:
# (b, num _tokens, d_ out) -> (b, num_tokens, num_heads, head_dim)
keys = keys.view(b, num_tokens, self.num_heads, self.head_dim) # (2, 6, 2) => (2, 6, 2, 1)
values = values.view(b, num_tokens, self.num_heads, self.head_dim)
queries = queries.view(
b, num_tokens, self.num_heads, self.head_dim
)
# 从形状(b, num_tokens, num_heads, head_dim) 转换到(b, num_heads, num_tokens, head_dim)
keys = keys.transpose(1, 2) # (2, 6, 2, 1) => (2, 2, 6, 1)
values = values.transpose(1, 2)
queries = queries.transpose(1, 2)
# 计算每个头的点积
attn_scores = queries @ keys.transpose(2, 3) # (2, 2, 6, 1) @ (2, 2, 1, 6) => (2, 2, 6, 6)
mask_bool = self.mask.bool()[:num_tokens, :num_tokens]
attn_scores.masked_fill_(mask_bool, -torch.inf)
attn_weights = torch.softmax(
attn_scores / keys.shape[-1]**0.5, dim=-1)
attn_weights = self.dropout(attn_weights)
# 张量形状: (b, num_tokens, n_heads, head_dim)
context_vec = (attn_weights @ values).transpose(1, 2) # (2, 2, 6, 6) @ (2, 2, 6, 1) => (2, 2, 6, 1) => (2, 6, 2, 1)
# 组合头,其中 self.d_out = self.num_heads * self.head_dim
context_vec = context_vec.contiguous().view(
b, num_tokens, self.d_out
) # (2, 6, 2, 1) => (2, 6, 2)
# 添加一个可选 的线性投影
context_vec = self.out_proj(context_vec)
return context_vec
inputs = torch.tensor(
[[0.43, 0.15, 0.89], # Your (x^1)
[0.55, 0.87, 0.66], # journey (x^2)
[0.57, 0.85, 0.64], # starts
[0.22, 0.58, 0.33], # with
[0.77, 0.25, 0.10], # one
[0.05, 0.80, 0.55]] # step
)
batch = torch.stack((inputs, inputs), dim=0)
torch.manual_seed(123)
batch_size, context_length, d_in = batch.shape # (2, 6, 3)
d_out = 2
mha = MultiHeadAttention(d_in, d_out, context_length, 0, num_heads=2)
context_vecs = mha(batch)
print(context_vecs.shape, context_vecs)代码清单4-2 层归一化类
层归一化:减去均值,并将结果除以方差的平方根(也就是标准差)。归一化后的层输出也包含负值,其均值为 0,方差为 1
层归一化,提高神经网络训练的稳定性和效率。层归一化的主要思想是调整神经网络层的激活(输出),使其均值为 0 且方差(单位方差)为 1。这种调整有助于加速权重的有效收敛,并确保训练过程的一致性和可靠性。
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
torch.manual_seed(123)
batch_example = torch.randn(2, 5)
layer = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(5, 6), nn.ReLU())
out = layer(batch_example)
print(out)
"""
tensor([[0.2260, 0.3470, 0.0000, 0.2216, 0.0000, 0.0000],
[0.2133, 0.2394, 0.0000, 0.5198, 0.3297, 0.0000]],
grad_fn=<ReluBackward0>)
"""
# 均值
mean = out.mean(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
# 方差
var = out.var(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
print("Mean:", mean)
print("Variance:", var)
"""
Mean: tensor([[0.1324],
[0.2170]], grad_fn=<MeanBackward1>)
Variance: tensor([[0.0231],
[0.0398]], grad_fn=<VarBackward0>)
"""
# 归一化
out_norm = (out - mean) / torch.sqrt(var)
mean = out_norm.mean(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
var = out_norm.var(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
print("out_norm:", out_norm)
"""
out_norm: tensor([[ 0.6159, 1.4126, -0.8719, 0.5872, -0.8719, -0.8719],
[-0.0189, 0.1121, -1.0876, 1.5173, 0.5647, -1.0876]],
grad_fn=<DivBackward0>)
"""
torch.set_printoptions(sci_mode=False)
print("mean:", mean)
print("variance:", var)
"""
mean: tensor([[ 0.0000],
[ 0.0000]], grad_fn=<MeanBackward1>)
variance: tensor([[1.0000],
[1.0000]], grad_fn=<VarBackward0>)
"""
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class LayerNorm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, emb_dim):
super().__init__()
self.eps = 1e-5
self.scale = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(emb_dim))
self.shift = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(emb_dim))
def forward(self, x):
mean = x.mean(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
var = x.var(dim=-1, keepdim=True, unbiased=False)
norm_x = (x - mean) / torch.sqrt(var + self.eps)
return self.scale * norm_x + self.shift
torch.manual_seed(123)
batch_example = torch.randn(2, 5)
ln = LayerNorm(emb_dim=5)
out_ln = ln(batch_example)
mean = out_ln.mean(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
var = out_ln.var(dim=-1, unbiased=False, keepdim=True)
torch.set_printoptions(sci_mode=False)
print("Mean:", mean)
print("Variance:", var)
"""
Mean: tensor([[ 0.0000],
[ -0.0000]], grad_fn=<MeanBackward1>)
Variance: tensor([[1.0000],
[1.0000]], grad_fn=<VarBackward0>)
"""代码清单4-3 GELU激活函数

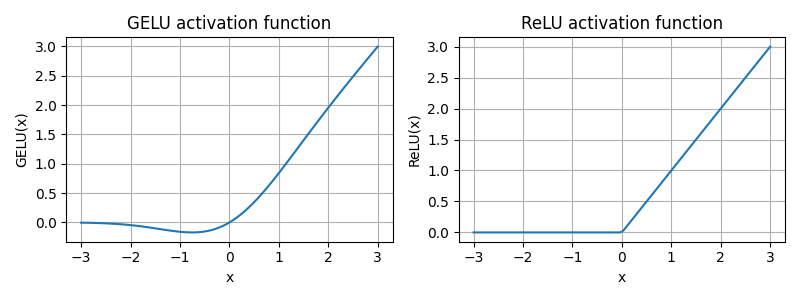
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class GELU(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, x):
return 0.5 * x * (1 + torch.tanh(
torch.sqrt(torch.tensor(2.0 / torch.pi)) *
(x + 0.044715 * torch.pow(x, 3))
))
gelu, relu = GELU(), nn.ReLU()
x = torch.linspace(-3, 3, 100) # 在-3 和 3 之间创建 100 个样本数据点
y_gelu, y_relu = gelu(x), relu(x)
plt.figure(figsize=(8,3))
for i, (y, label) in enumerate(zip([y_gelu, y_relu], ["GELU", "ReLU"]), 1):
plt.subplot(1, 2, i)
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.title(f"{label} activation function") # 图标标题
plt.xlabel("x") # X轴标签
plt.ylabel(f"{label}(x)")
plt.grid(True) # 显示网格
plt.tight_layout() # 自动调整图表布局,防止标签重叠
plt.savefig('gelu_relu')
plt.show()