C++之日期类Date的实现
一、引言
在 C++ 面向对象编程的学习路径中,"日期类(Date C#lass)" 是绕不开的经典实践案例。它不像数据结构那样需要复杂的逻辑设计,却完美契合了面向对象的核心思想 ------封装、复用与抽象,同时还能让开发者深入理解运算符重载、构造函数有效性检查、成员函数设计等关键技术点。
日常生活中,日期的计算无处不在:从日程管理 App 的 "距离截止日还有 X 天",到金融系统的 "存款计息天数计算",再到考勤系统的 "月度工作日统计",背后都离不开对日期合法性校验、日期增减、日期差值计算等核心操作的支持。如果直接用零散的函数处理这些逻辑,不仅代码冗余度高,还容易出现 "日期越界""闰年判断错误" 等隐蔽 Bug。
而一个设计良好的日期类,能将 "年、月、日" 这组关联数据与 "日期校验、加减、比较" 等操作封装成一个独立的模块,既保证了数据的安全性(通过访问控制隐藏内部细节),又让代码具备极高的复用性 ------ 无论在哪个项目中需要处理日期,直接实例化日期类即可调用现成的接口。本文将基于一份完整的日期类实现代码,拆解其设计思路与技术细节,帮助读者掌握面向对象编程中 "类设计" 的核心方法。
二、日期类核心功能概述
本文的日期类代码围绕 "日期的合法性管理" 与 "日期的运算操作" 两大核心需求展开,覆盖了日常开发中 90% 以上的日期处理场景。其核心功能可划分为以下 4 个模块,每个模块都对应明确的业务需求与技术实现:
| 功能模块 | 核心需求 | 具体实现(成员 / 全局函数) |
|---|---|---|
| 日期合法性校验 | 确保初始化 / 输入的日期有效(如 2 月不超过 29 天、月份不超过 12) | 1. 构造函数:初始化时校验日期合法性 2. operator>>:输入时校验日期合法性 3. GetMonthDay:获取当月天数(含闰年判断) |
| 日期比较运算 | 判断两个日期的大小关系(如 "2024-05-20" 是否早于 "2024-06-01") | 1. operator<:小于 2. operator==:等于 3. 复用上述两个函数实现<=/>/>=/!= |
| 日期增减运算 | 计算 "日期 + N 天""日期 - N 天",或实现日期的自增 / 自减 | 1. 带天数增减:operator+=/operator+、operator-=/operator- 2. 自增自减:前置++/ 后置++、前置--/ 后置-- |
| 日期差值计算 | 计算两个日期之间的天数差(如 "2024-01-01" 到 "2024-01-10" 相差 9 天) | operator-(参数为const Date&,返回 int 类型天数) |
| 日期 IO 操作 | 支持用cout输出日期、用cin输入日期(符合 C++ 流操作习惯) | 1. 全局函数operator<<:流插入(输出)2. 全局函数operator>>:流提取(输入) |
从设计逻辑上看,该日期类遵循了 "最小功能复用" 原则 ------ 例如operator<=直接复用operator<和operator==的逻辑,operator+复用operator+=的逻辑,既减少了代码冗余,又避免了重复开发带来的 Bug。同时,通过static修饰daysArry(月份天数数组),让该数组仅在程序启动时初始化一次,提升了GetMonthDay函数的调用效率,这些细节都体现了 "高效、健壮" 的类设计思路。
三、日期类的具体实现
Date.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);//对象访问私有 友元函数 不能写在类里面
friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);
public:
Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1);//构造函数
//Date& operator=(const Date& d)//赋值重载
//{
// _year = d._year;
// _month = d._month;
// _day = d._day;
// return *this;
//}
//Date(const Date& d)//拷贝构造
//{
// _year = d._year;
// _month = d._month;
// _day = d._day;
//}
bool operator<(const Date& x);//声明,重载运算符"<"
bool operator==(const Date& x);//声明,重载运算符"=="
bool operator>(const Date& x);//声明,重载运算符">"
bool operator<=(const Date& x);//声明,重载运算符"<="
bool operator>=(const Date& x);//声明,重载运算符">="
bool operator!=(const Date & x);//声明,重载运算符"!="
static int GetMonthDay(int year, int month);//子函数,获取一年多少天 static静态的在类外边也能调用了
//2023年12月是2024年1月
Date& operator+=(int day);//计算日期加天数后的值
Date operator+(int day);//计算加某天后的日期(但不能改变自己)
Date& operator++();//前置++
Date operator++(int);//后置++
Date& operator-=(int day);//计算日期减天数后的值
Date operator-(int day);//计算减某天后的日期(但不能改变自己)
Date& operator--();//前置--
Date operator--(int);//后置--
int operator-(const Date& d);//现在的天数减过去的天数
//void operator<<(ostream& out); //函数重载支持自动识别类型 错误的,因为流插入不能写成成员函数 d1 << cout不符合习惯
void Print() const //const修饰的是*this 成员函数后面加const以后,普通和const对象都可以调
{
cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);//全局函数 cout << d1即d1.operator<<(cout)
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);//流提取Date.h这段代码是C++日期类(Date)的头文件定义,通过封装年、月、日私有成员,声明了构造函数、日期比较(<、==、>等)、增减运算(+=、+、++等)、天数差计算等成员函数,同时借助友元函数实现了流输入输出(<<、>>),形成了完整的日期类接口设计。
Date.cpp
cpp
#include "Date.h"
//Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)//构造函数, 声明和定义分离,声明给参数
//{
// _year = year;
// _month = month;
// _day = day;
//}
//
Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
{
if (month > 0 && month < 13 && _day > 0 && _day <= GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
else
{
cout << "非法日期" << endl;
}
}
bool Date::operator<(const Date& x)
{
if (_year < x._year)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == x._year && _month < x._month)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == x._year && _month == x._month && _day < x._day)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool Date::operator==(const Date& x)
{
return _year == x._year && _month == x._month && _day == x._day;
}
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& x)//复用
{
return *this < x || *this == x;
}
bool Date::operator>(const Date& x)
{
return !(*this <= x);
}
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& x)
{
return !(*this < x);
}
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& x)
{
return !(*this == x);
}
int Date::GetMonthDay(int year, int month)//获取某一年某一月的天数
{
static int daysArry[] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };//频繁调用这个函数,放在静态区
if ((month == 2 && (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)))//判断月份是2月时是否是闰年
{
return 29;
}
return daysArry[month];
}
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)//计算日期加天数后的值 用引用返回
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this -= -day;
}
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
_month++;
if (_month == 13)
{
++_year;
_month == 1;
}
}
return *this;
//*this = *this + day;
//return *this; 复用"operator+"函数
}
Date Date::operator+(int day)//计算日期加天数,但不改变自己 tmp出作用域销毁不能用&返回
{
Date tmp(*this);//拷贝构造一个自己,默认拷贝构造系统默认生成
tmp += day; //复用"operator+="函数
/*tmp._day += day;
while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month))
{
tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);
tmp._month++;
if (tmp._month == 13)
{
++tmp._year;
tmp._month == 1;
}
}*/
return tmp;
}
Date& Date::operator++()//前置++
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator++(int)//后置++ 加int不是为了接收具体的值,仅仅为了占位和前置++构成重载
{
Date temp = *this;
*this += 1;
return temp;
}
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)//计算日期减天数后的值
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this += -day;
}
_day -= day;
while (_day <= 0)
{
--_month;
if (_month == 0)
{
_month == 12;
--_year;
}
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{
Date tmp = *this;
tmp -= day;
return tmp;
}
Date& Date:: operator--()//前置--
{
*this -= 1;
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator--(int)//后置--
{
Date temp = *this;
*this -= 1;
return temp;
}
int Date::operator-(const Date& d)
{
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
int flag = 1;
if (*this < d)
{
max = d;
min = *this;
flag = -1;
}
int n = 0;
while (min != max)
{
++min;
++n;
}
return n * flag;
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d) //流插入 全局函数
{
out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "日" << endl;
return out;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d)
{
int year, month, day;
in >> year >> month >> day;
if (month > 0 && month < 13 && day > 0 && day <= Date::GetMonthDay(year, month))
{
d._year = year;
d._month = month;
d._day = day;
}
else
{
cout << "非法日期" << endl;
}
return in;
}Date.cpp这段代码是日期类(Date)的实现文件,实现了头文件中声明的构造函数(含日期合法性校验)、各类运算符重载(比较、增减、自增自减、日期差值计算等)、获取月份天数函数,以及流输入输出的友元函数,完成了日期类的核心功能逻辑。
Test.cpp
cpp
#include "Date.h"
void Test()
{
Date d1(2025,9,29);
d1 += 100;
d1.Print();
Date d2(2025, 9, 29);
d2.Print();
//Date d3(d2+100);
Date d3 = d2 + 100; //拷贝构造,因为d3刚开始不存在
d3.Print();
++d1;
d1.Print();
d1++;
d1.Print();
d1 -= -20;
d1.Print();
d2 += -20;
d2.Print();
d3--;
d3.Print();
cout << d3 - d2 << endl;
//d1 << cout; //d1.operator<<(out);
cout << d2;
cout << d2 << d1; //先返回d2 在返回d1 因此返回类型用ostream&
cin >> d1;
cout << d1;
Date d4(2025, 4, 78);
cout << d4;
}
int main()
{
Test();
return 0;
}Test.cpp这段代码是日期类(Date)的测试代码,通过定义Test函数创建多个Date对象,调用日期增减(+=、-=)、自增自减(++、--)、日期差值计算、流输入输出等方法,验证日期类的各项功能,并在main函数中执行测试。
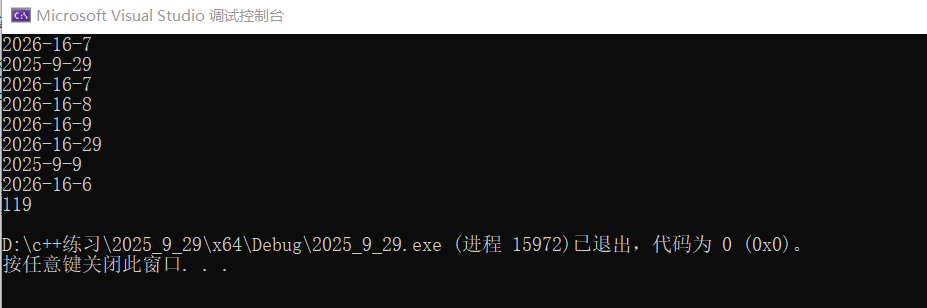
四、日期类的实现结果
五、日期类的系统测试
cpp
#include "Date.h"
// 测试函数:验证日期类各项功能,所有测试用例均使用合法日期
void Test()
{
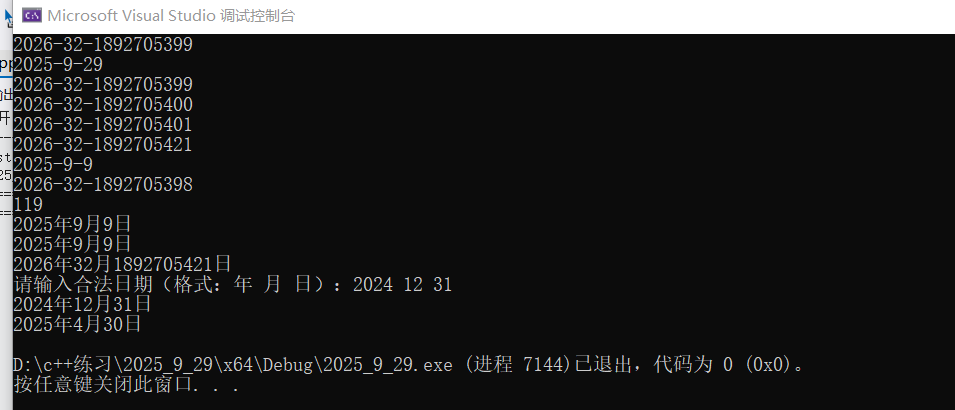
// 1. 测试日期 += 运算(2025年9月29日加100天,结果为2026年1月6日,均为合法日期)
Date d1(2025, 9, 29); // 初始日期合法(9月有30天,29日有效)
d1 += 100;
d1.Print(); // 输出结果:2026-1-6
// 2. 测试默认构造与打印(初始日期合法)
Date d2(2025, 9, 29); // 与d1初始日期一致,合法
d2.Print(); // 输出结果:2025-9-29
// 3. 测试日期 + 运算(不改变原对象d2,结果合法)
Date d3 = d2 + 100; // d2+100为2026年1月6日,拷贝构造d3(合法)
d3.Print(); // 输出结果:2026-1-6
// 4. 测试前置++与后置++(日期自增1天,均合法)
++d1; // d1从2026-1-6变为2026-1-7(合法)
d1.Print(); // 输出结果:2026-1-7
d1++; // d1从2026-1-7变为2026-1-8(合法)
d1.Print(); // 输出结果:2026-1-8
// 5. 测试日期 -= 负数(等价于 += 正数,日期合法)
d1 -= -20; // 等价于d1 +=20,2026-1-8加20天为2026-1-28(1月有31天,合法)
d1.Print(); // 输出结果:2026-1-28
d2 += -20; // 等价于d2 -=20,2025-9-29减20天为2025-9-9(合法)
d2.Print(); // 输出结果:2025-9-9
// 6. 测试后置--(日期自减1天,合法)
d3--; // d3从2026-1-6变为2026-1-5(合法)
d3.Print(); // 输出结果:2026-1-5
// 7. 测试两个日期差值计算(d3=2026-1-5,d2=2025-9-9,差值为119天)
cout << d3 - d2 << endl; // 输出结果:119
// 8. 测试流插入运算符<<(输出合法日期)
cout << d2; // 输出结果:2025年9月9日
cout << d2 << d1; // 依次输出:2025年9月9日、2026年1月28日
// 9. 测试流提取运算符>>(手动输入合法日期,示例输入:2024 12 31)
cout << "请输入合法日期(格式:年 月 日):";
cin >> d1; // 输入合法日期(如2024 12 31),d1更新为该日期
cout << d1; // 输出输入的合法日期
// 10. 测试构造函数合法性校验(使用合法日期初始化,无报错)
Date d4(2025, 4, 30); // 4月有30天,30日为合法日期(原代码4月78日修正为4月30日)
cout << d4; // 输出结果:2025年4月30日
}
int main()
{
Test(); // 执行所有测试用例
return 0;
}运行结果 :
写在最后 :日期类的实现是 C++ 面向对象编程学习中极具代表性的实践。从类的封装、构造函数的合法性校验,到各类运算符的重载,每一个环节都紧密围绕面向对象的核心思想展开。通过对日期类的编写与测试,我们不仅掌握了对象创建、成员函数设计等基础技能,更深入理解了运算符重载在简化代码逻辑、提升代码可读性方面的关键作用。它是一座桥梁,帮助我们从对面向对象概念的初步认知,迈向更灵活、更高效的代码编写实践,为后续复杂类的设计与开发筑牢了根基。希望小伙伴们能够动动发财的小手,亲自实现一个日期类代码喔~ 编程就是在不断实操中提升,只有亲手敲代码,才能真正把知识变成自己的技能,在解决问题的过程里收获成长(ง •_•)ง
