从整体上理解 Suspense 组件源码实现
与其他内置组件一样,Suspense 组件的实现也依赖于渲染器的底层支持。但是为了避免渲染器逻辑代码"膨胀",当用户没有使用 Suspense 组件时,可以利用 TreeShaking 机制在最终的 bundle 中删除 Suspense 相关的代码,使得最终构建包的体积变小 ,Vue 已将 Suspense 组件的渲染逻辑从渲染器中分离出来。
Tips:本文中的源码均摘自 Vue.js 3.5.5,为了方便理解,会省略与本文主题无关的代码。
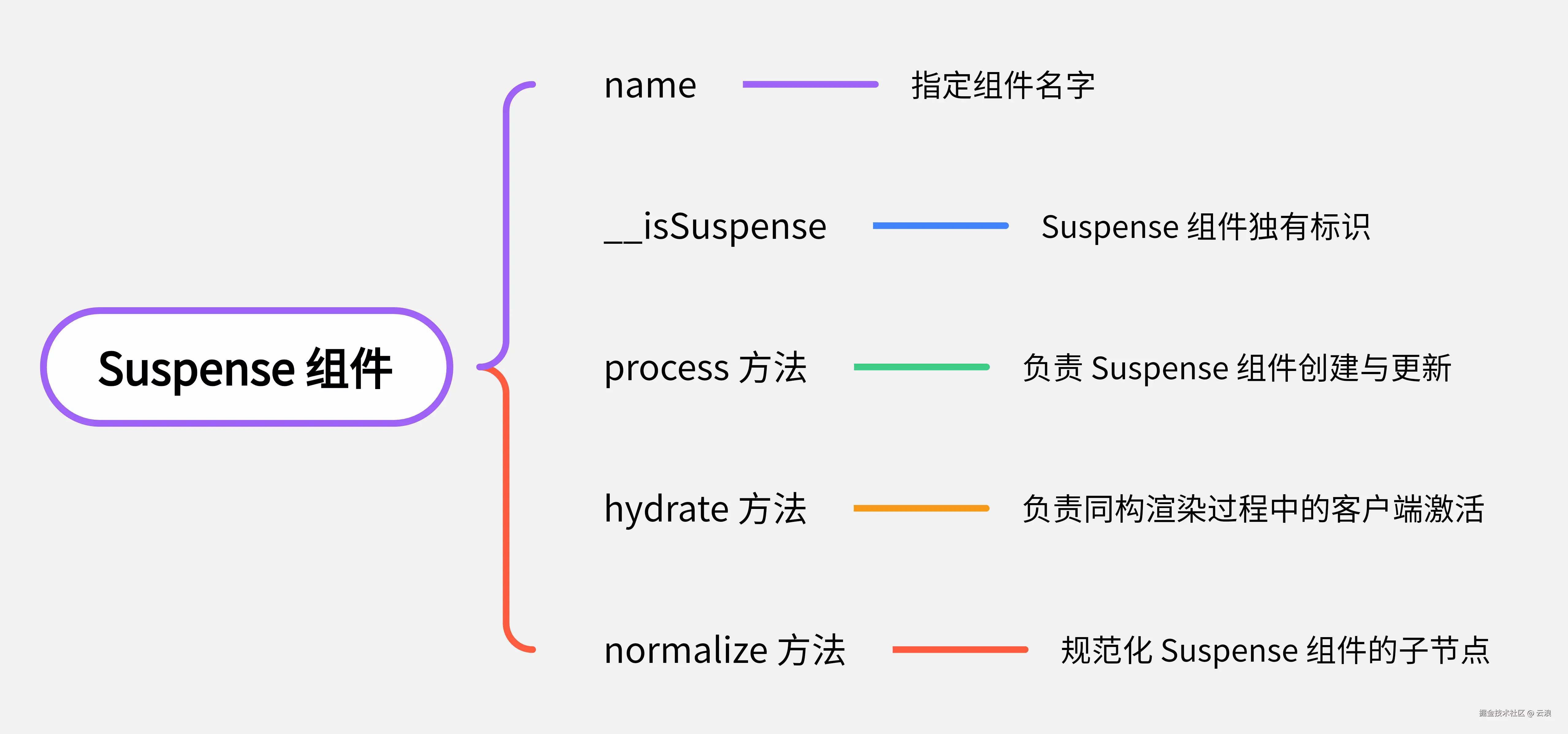
Suspense 组件其实就是对象,该对象包含 2 个属性,3 个方法:
-
name属性很简单,就是指定组件的名字为Suspense。 -
__isSuspense属性值为 true ,是Suspense组件独有标识,可通过该属性来判断组件是否为Suspense组件。
ts
// core/packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
export const isSuspense = (type: any): boolean => type.__isSuspenseprocess方法负责组件的创建和更新逻辑hydrate方法负责同构渲染过程中的客户端激活normalize方法负责规范化Suspense组件的子节点
process 方法分析
process 方法负责组件的创建和更新逻辑。我们看看 process 方法的签名:
ts
// core/packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
process(
n1: VNode | null,
n2: VNode,
container: RendererElement,
anchor: RendererNode | null,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
parentSuspense: SuspenseBoundary | null,
namespace: ElementNamespace,
slotScopeIds: string[] | null,
optimized: boolean,
// platform-specific impl passed from renderer
rendererInternals: RendererInternals,
): void {
// ...
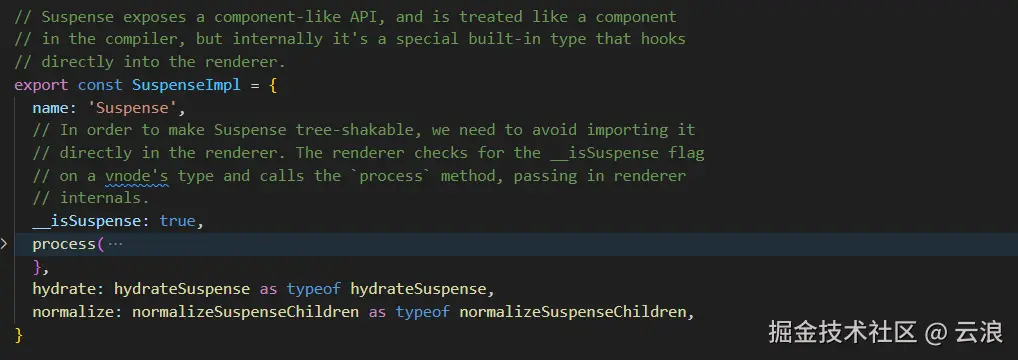
}为了使 Suspense 组件支持摇树优化(tree shaking),需要避免直接在渲染器中导入 Suspense 组件。渲染器会检查虚拟节点(vnode)的类型(type)上是否有 __isSuspense 标志 ,并调用此类型(type)的 process 方法,同时传递渲染器内部对象(rendererInternals)到 process 方法内,这样可以在 process 方法内部调用渲染器中的方法,在 process 方法内部实现 Suspense 组件的挂载与更新。
判断虚拟节点(vnode)的类型(type)上是否有 __isSuspense 标志来判断是否为 Suspense 组件:
ts
// core/packages/runtime-core/src/vnode.ts
const shapeFlag = isString(type)
? ShapeFlags.ELEMENT
: __FEATURE_SUSPENSE__ && isSuspense(type)
? ShapeFlags.SUSPENSE
: isTeleport(type)
? ShapeFlags.TELEPORT
: isObject(type)
? ShapeFlags.STATEFUL_COMPONENT
: isFunction(type)
? ShapeFlags.FUNCTIONAL_COMPONENT
: 0n1旧的虚拟节点(vnode)n2新的虚拟节点(vnode)container渲染的目标容器anchor渲染的锚点parentComponent父组件的实例parentSuspense父Suspense边界namespace元素的命名空间slotScopeIds插槽作用域 IDoptimized是否进行优化rendererInternals渲染器传入的内部对象
当旧的虚拟节点 n1 不存在时,走创建逻辑,否则走更新逻辑:
ts
// core/packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
process(
n1: VNode | null,
n2: VNode,
container: RendererElement,
anchor: RendererNode | null,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
parentSuspense: SuspenseBoundary | null,
namespace: ElementNamespace,
slotScopeIds: string[] | null,
optimized: boolean,
// platform-specific impl passed from renderer
rendererInternals: RendererInternals,
): void {
if (n1 == null) {
// 创建逻辑
} else {
// 更新逻辑
}
}创建节点
创建 Suspense 节点的是 mountSuspense 方法
ts
// core/packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
if (n1 == null) {
mountSuspense(
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
namespace,
slotScopeIds,
optimized,
rendererInternals,
)
}接下来具体看看 mountSuspense 方法的实现。
在创建 Suspense 节点时,依赖了一些渲染器的方法
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
const {
p: patch,
o: { createElement },
} = rendererInternalspatch渲染器中挂载与更新组件的方法createElement渲染器中创建元素的方法
在浏览器中,createElement 可以简单的理解为 document.createElement 方法,即创建 html 元素的方法。
创建隐藏容器:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
const hiddenContainer = createElement('div')createSuspenseBoundary 方法创建的对象 suspense 会作为 Suspense 组件的上下文对象。该上下文对象会保存到虚拟 dom (vnode)的 suspense 属性中。该上下文对象记录了当前这个 Suspense 组件的所有信息,例如:是否处于 fallback 阶段、是服务端渲染吗等信息,还有一些操作 Suspense 组件的方法。后面对 Suspense 组件的一系列操作都是以这个对象为中心的。
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
const suspense = (vnode.suspense = createSuspenseBoundary(
vnode,
parentSuspense,
parentComponent,
container,
hiddenContainer,
anchor,
namespace,
slotScopeIds,
optimized,
rendererInternals,
))虚拟节点中 ssContent 是 Suspense 组件默认插槽的内容,即 Suspense 组件最终要渲染的内容。
先将 Suspense 组件默认插槽 ssContent 挂载到隐藏容器(hiddenContainer)中,先不展示出来:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
patch(
null,
(suspense.pendingBranch = vnode.ssContent!),
hiddenContainer, // 隐藏容器
null,
parentComponent,
suspense,
namespace,
slotScopeIds,
)通过判断 Suspense 组件的上下文对象 suspense 的 deps 属性是否大于 0 确定是否存在异步依赖。
存在异步依赖,则会触发 onPending 、onFallback 事件,将 ssFallback 内容渲染到页面。
ssFallback 是后备插槽中的内容,此时页面上就会显示出后备插槽的内容,比如提示正在加载中等。
然后将 ssFallback 后备插槽的虚拟节点(vnode)设置为当前激活分支(activeBranch)
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
if (suspense.deps > 0) {
// has async
// invoke @fallback event
triggerEvent(vnode, 'onPending')
triggerEvent(vnode, 'onFallback')
// mount the fallback tree
patch(
null,
vnode.ssFallback!,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
null, // fallback tree will not have suspense context
namespace,
slotScopeIds,
)
setActiveBranch(suspense, vnode.ssFallback!)
}setActiveBranch 函数用于设置当前激活分支。
activeBranch:激活分支,已经挂载到页面中的vnode,在更新的时候会被卸载,且重新被赋值为新挂载的 vnode
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
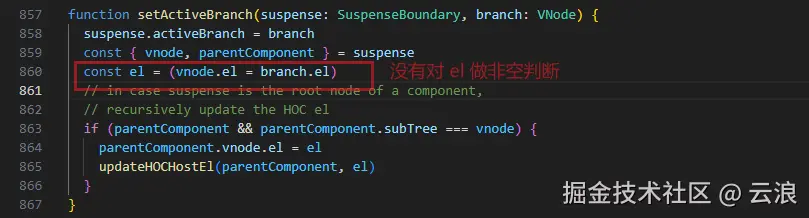
function setActiveBranch(suspense: SuspenseBoundary, branch: VNode) {
suspense.activeBranch = branch
const { vnode, parentComponent } = suspense
let el = branch.el
// if branch has no el after patch, it's a HOC wrapping async components
// drill and locate the placeholder comment node
// 如果 branch 更新之后没有 el 属性,则说明异步组件或 async setup 还没有解析完成,
// 此时需要进一步循环遍历 branch 的 el 属性,找到占位的注释节点。
while (!el && branch.component) {
branch = branch.component.subTree
el = branch.el
}
vnode.el = el
// in case suspense is the root node of a component,
// recursively update the HOC el
if (parentComponent && parentComponent.subTree === vnode) {
parentComponent.vnode.el = el
updateHOCHostEl(parentComponent, el)
}
}在更新 Suspense 组件的时候,如果异步组件或 async setup() 没有解析完成,则 Suspense 组件的默认插槽中会渲染空的注释节点,该注释节点仅用于占位。
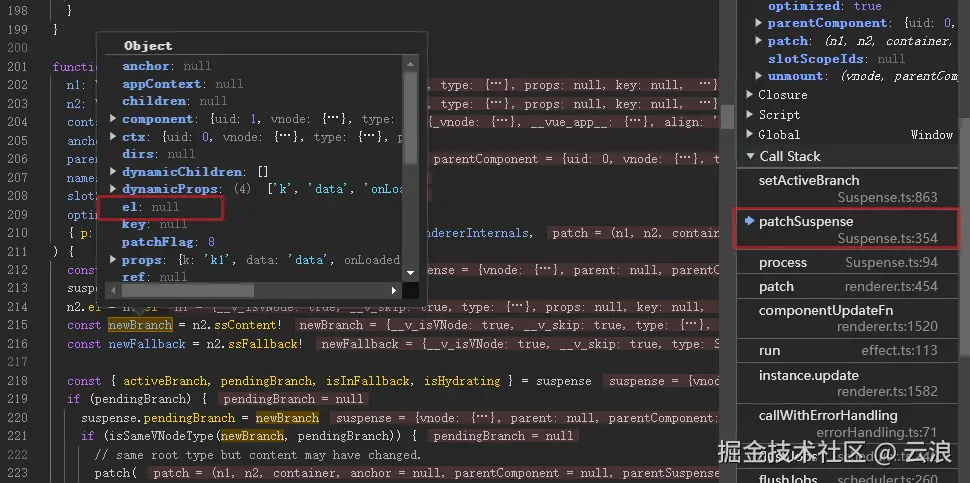
最后在渲染器中执行更新的时候,会通过该 el 拿对应的父级元素,如果 el 为 null ,则会报错:
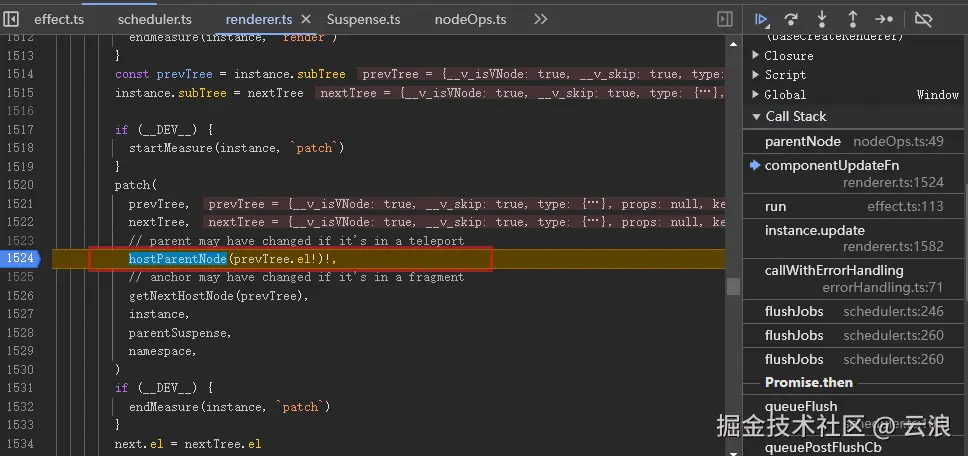
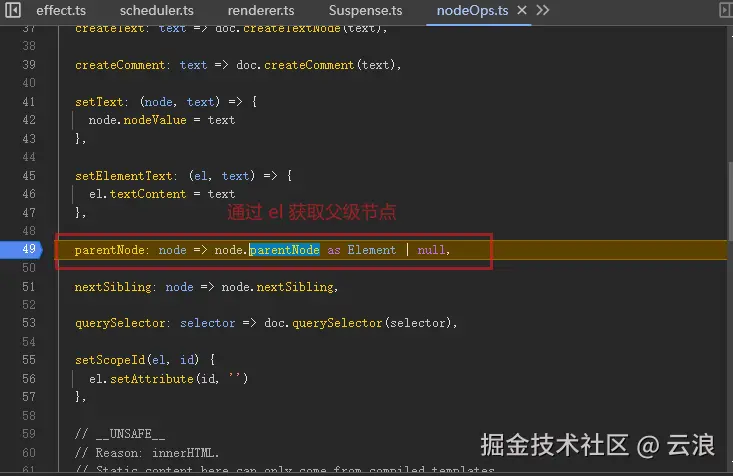
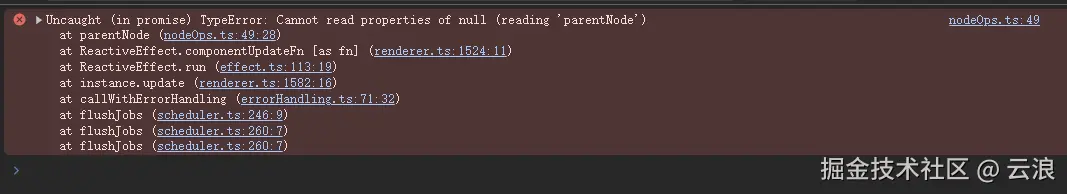
具体可见这个 issue :Crash on 'update' non-resolved async component
不过 Vue 官方在 3.4.8 版本中修复这个 bug ,在检查到 el 为 null 时,会进一步循环遍历 branch 的子组件,直到找到非空的 el 为止:
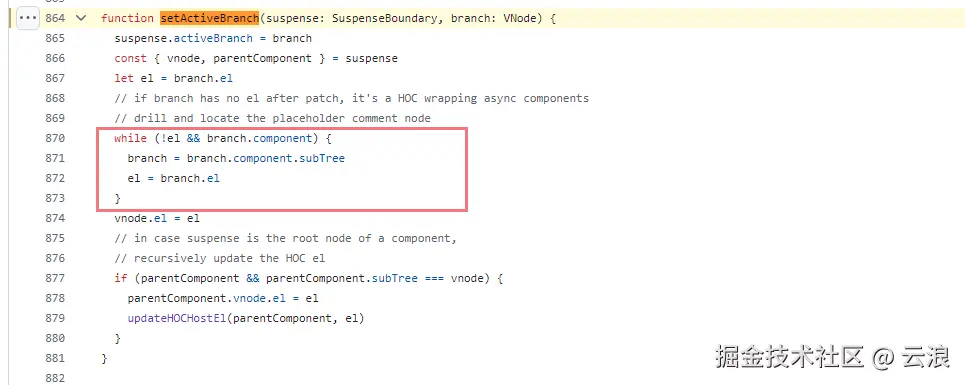
👆 源码链接:github.com/vuejs/core/...
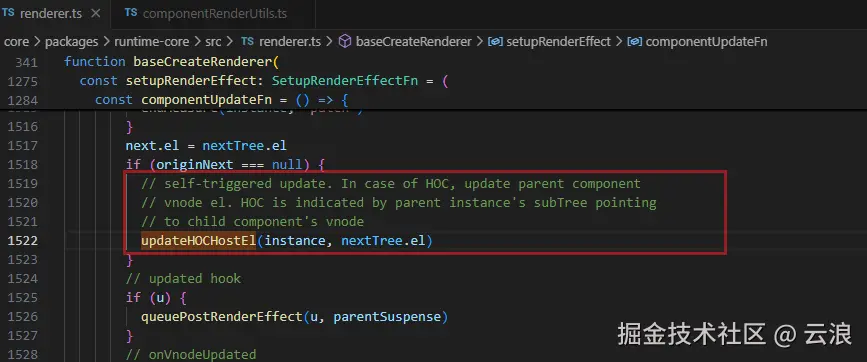
updateHOCHostEl 函数的作用是用于递归更新高阶组件(HOC)的父子关系中的组件节点的宿主元素,确保高阶组件的宿主元素正确映射和更新。这个函数在处理嵌套组件结构时起到了维护和更新宿主元素的作用。
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/componentRenderUtils.ts
export function updateHOCHostEl(
{ vnode, parent }: ComponentInternalInstance,
el: typeof vnode.el, // HostNode
): void {
while (parent) {
const root = parent.subTree
if (root.suspense && root.suspense.activeBranch === vnode) {
root.el = vnode.el
}
// 父组件的 subTree 指向子组件的 vnode ,
// 说明这是一个高阶组件的情况
if (root === vnode) {
;(vnode = parent.vnode).el = el
parent = parent.parent
} else {
break
}
}
}
createSuspenseBoundary 函数分析
接下来详细分析一下 createSuspenseBoundary 函数,createSuspenseBoundary 函数最终返回一个对象,该对象可以称为 Suspense 边界或者是 Suspense 的上下文对象。
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
function createSuspenseBoundary(
vnode: VNode,
parentSuspense: SuspenseBoundary | null,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
container: RendererElement,
hiddenContainer: RendererElement,
anchor: RendererNode | null,
namespace: ElementNamespace,
slotScopeIds: string[] | null,
optimized: boolean,
rendererInternals: RendererInternals,
isHydrating = false,
): SuspenseBoundary {
/* v8 ignore start */
if (__DEV__ && !__TEST__ && !hasWarned) {
hasWarned = true
// @ts-expect-error `console.info` cannot be null error
// eslint-disable-next-line no-console
console[console.info ? 'info' : 'log'](
`<Suspense> is an experimental feature and its API will likely change.`,
)
}
/* v8 ignore stop */
// ...
const initialAnchor = anchor
const suspense: SuspenseBoundary = {
vnode,
parent: parentSuspense,
parentComponent,
namespace,
container,
hiddenContainer,
deps: 0,
pendingId: suspenseId++,
timeout: typeof timeout === 'number' ? timeout : -1,
activeBranch: null,
pendingBranch: null,
isInFallback: !isHydrating,
isHydrating,
isUnmounted: false,
effects: [],
resolve(resume = false, sync = false) {
// ...
},
fallback(fallbackVNode) {
// ...
},
move(container, anchor, type) {
// ...
},
next() {
return suspense.activeBranch && next(suspense.activeBranch)
},
registerDep(instance, setupRenderEffect, optimized) {
// ...
},
unmount(parentSuspense, doRemove) {
// ...
},
}
return suspense
}/* v8 ignore start */ 和 /* v8 ignore stop */ 注释用于忽略测试覆盖率计算
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
/* v8 ignore start */
if (__DEV__ && !__TEST__ && !hasWarned) {
hasWarned = true
// @ts-expect-error `console.info` cannot be null error
// eslint-disable-next-line no-console
console[console.info ? 'info' : 'log'](
`<Suspense> is an experimental feature and its API will likely change.`,
)
}
/* v8 ignore stop */从渲染器传入的对象中取出相关方法以备后续使用:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
const {
p: patch,
m: move,
um: unmount,
n: next,
o: { parentNode, remove },
} = rendererInternals如果用户传入了 suspensible 为 true 的 prop ,则将当前组件的异步依赖作为父级 Suspense 的依赖项。
使用 isVNodeSuspensible() 函数判断用户是否设置了 suspensible 为 true 。如果返回的变量 isSuspensible 为 true ,则将父级的 Suspense 组件的 pendingId 赋值给 parentSuspenseId ,并增加父级 Suspense 组件的依赖计数(deps):
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
// if set `suspensible: true`, set the current suspense as a dep of parent suspense
let parentSuspenseId: number | undefined
const isSuspensible = isVNodeSuspensible(vnode)
if (isSuspensible) {
if (parentSuspense && parentSuspense.pendingBranch) {
parentSuspenseId = parentSuspense.pendingId
parentSuspense.deps++
}
}如果传入的虚拟 DOM 节点的 suspensible 不为空且不是 false ,则说明 suspensible 为 true :
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
function isVNodeSuspensible(vnode: VNode) {
const suspensible = vnode.props && vnode.props.suspensible
return suspensible != null && suspensible !== false
}获取用户传入的 timeout prop ,并做数字转换:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
const timeout = vnode.props ? toNumber(vnode.props.timeout) : undefinedtoNumber() 函数是 Vue.js 源码中公共方法,用于将数字类型的字符串转为数字,对于数字 或者无法转换为数字的字符串则原样返回:
ts
// packages/shared/src/general.ts
/**
* Only concerns number-like strings
* "123-foo" will be returned as-is
*/
export const toNumber = (val: any): any => {
const n = isString(val) ? Number(val) : NaN
return isNaN(n) ? val : n
}记录锚点元素,后续移动挂起分支(pendingBranch)时使用:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
const initialAnchor = anchor接下来,构造 Suspense 组件的上下文对象:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
const suspense: SuspenseBoundary = {
vnode,
parent: parentSuspense,
parentComponent,
namespace,
container,
hiddenContainer,
deps: 0,
pendingId: suspenseId++,
timeout: typeof timeout === 'number' ? timeout : -1,
activeBranch: null,
pendingBranch: null,
isInFallback: !isHydrating,
isHydrating,
isUnmounted: false,
effects: []
// ...
}-
vnode,当前 Suspense 组件的虚拟 DOM -
parent,父级 Suspense 组件的上下文对象 -
parentComponent,父级组件的实例对象 -
namespace,表示元素的命名空间。在 HTML 中,命名空间可以用于区分不同的 XML 命名空间或特定的 HTML 版本(如 SVG 的命名空间) -
container,代表当前 Suspense 上下文对象关联的容器元素 -
hiddenContainer,用于挂载未解析完成的默认插槽中的内容 -
deps,异步依赖的数量 -
pendingId,标识异步依赖(默认插槽中的内容)的唯一标识,用于区分不同的异步依赖 -
timeout,解析异步依赖的超时时间,表示等待多长时间后展示后备内容,若timeout为 0 ,则 Suspense 组件回退到挂起状态后立马展示后备内容 -
activeBranch,激活分支,已经挂载到页面中的虚拟 DOM ,在更新的时候会被卸载,且重新被赋值为新挂载的虚拟 DOM -
pendingBranch,挂起分支,指默认插槽(#default)中的内容。因为存在异步依赖,在异步依赖处理完毕之后,将activeBranch卸载完毕后,进入挂载 -
isInFallback,表示当前是否处于后备状态(即等待异步依赖加载期间显示的状态)。如果为true,表示正在显示后备内容 -
isHydrating,表示当前是否处于水合状态。水合状态是在客户端渲染过程中,将服务器端渲染的内容与客户端的状态同步的过程 -
isUnmounted,表示当前 Suspense 组件是否已卸载 -
effects,存储 Suspense 组件中的副作用函数的数组,这些副作用可能是在渲染过程中需要执行的,比如数据获取、事件监听等
解释完 Suspense 组件上下文对象(SuspenseBoundary)中的属性后,来看看 Suspense 组件上下文对象中的方法:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
const suspense: SuspenseBoundary = {
// ...
resolve(resume = false, sync = false) {
// 异步依赖解析完成后调用的方法
},
fallback(fallbackVNode) {
// 用于展示后备插槽中的内容
},
move(container, anchor, type) {
// 移动 activeBranch 内容到指定容器
},
next() {
// 返回 activeBranch 的相邻兄弟元素
},
registerDep(instance, setupRenderEffect, optimized) {
// 注册异步依赖,异步依赖增加则 deps 计数相应增加,
// 异步依赖解析完成,deps 计数相应减少
},
unmount(parentSuspense, doRemove) {
// 卸载 activeBranch 或 pendingBranch 的内容
}
}接下来我们来看看各个方法的具体实现。
resolve 方法
首先来看 resolve 方法的实现,resolve 方法是异步依赖解析完成后调用的方法:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
const suspense: SuspenseBoundary = {
// ...
resolve(resume = false, sync = false) {
// ...
}
}-
resume,如果为 true ,强制进行更新 -
sync,如果为 true ,同步进行状态更新
如果在开发环境,在解析前先进行一些前提条件的判断,如果不符合这些条件判断,则抛出异常:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
resolve(resume = false, sync = false) {
if (__DEV__) {
if (!resume && !suspense.pendingBranch) {
throw new Error(
`suspense.resolve() is called without a pending branch.`,
)
}
if (suspense.isUnmounted) {
throw new Error(
`suspense.resolve() is called on an already unmounted suspense boundary.`,
)
}
}
// ...
}从 Suspense 组件上下文对象中取出一系列数据方便后面使用:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
const {
vnode,
// activeBranch 是后备插槽(#fallback)中的内容
activeBranch,
// pendingBranch 是默认插槽(#default)中的内容
pendingBranch,
pendingId,
effects,
parentComponent,
container,
} = suspense下面就是一个挂载默认插槽(#default)的操作,主要针对的是客户端渲染,处理离开和进入过渡,在离开过渡完成后,将解析好的异步依赖,即默认插槽中的内容移动到指定容器,完成默认插槽内容的挂载。
如果有过渡,我们需要等待过渡完成再将默认插槽的内容移动到页面容器中:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
// if there's a transition happening we need to wait it to finish.
let delayEnter: boolean | null = false如果是服务端渲染,不进行过渡的处理,因为过渡动效在客户端环境下才能执行:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
if (suspense.isHydrating) {
suspense.isHydrating = false
}resume 为 false 表示不强制进行更新。如果 pendingBranch ,即异步依赖解析后的内容存在进入过渡,则 activeBranch ,后备插槽的内容就会有一个离开过渡,此时需要等待离开过渡完成后,再将 pendingBranch 移动到指定容器中:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
if (suspense.isHydrating) {
suspense.isHydrating = false
} else if (!resume) {
// 非强制更新
// pendingBranch 存在进入过渡,则 activeBranch 有离开过渡
delayEnter =
activeBranch &&
pendingBranch!.transition &&
pendingBranch!.transition.mode === 'out-in'
if (delayEnter) {
// 构造 Transition 组件离开过渡函数
activeBranch!.transition!.afterLeave = () => {
if (pendingId === suspense.pendingId) {
// 等离开过渡执行完成后,再将 pendingBranch 移动到指定容器中
move(
pendingBranch!,
container,
anchor === initialAnchor ? next(activeBranch!) : anchor,
MoveType.ENTER,
)
// 执行 Suspense 组件的副作用函数
queuePostFlushCb(effects)
}
}
}
// ...
}
afterLeave是 Transition 组件相关的事件,会在离开过渡完成、且元素已从 DOM 中移除时调用
out-in是 Transition 组件的模式,表示先执行离开动画,后执行进入动画
Suspense 从 fallback 状态切换到主内容时,安全卸载当前显示的 fallback 内容并更新 DOM 锚点。
父级 Suspense 可能移动了当前 fallback 的 DOM 位置,需要获取最新的锚点位置保证新内容插入正确位置。
当使用 out-in 过渡模式时(delayEnter=true),过渡期间可能发生分支切换。导致 activeBranch 和 pendingBranch 同时存在于 hiddenContainer ,此时 next(activeBranch) 可能错误返回 pendingBranch.el ,从而意外地将 pendingBranch 卸载掉了。
在不需要延迟插入的情况下,立即将异步加载完成的内容移动到实际容器中显示。
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
if (suspense.isHydrating) {
suspense.isHydrating = false
} else if (!resume) {
// ...
// unmount current active tree
if (activeBranch) {
// if the fallback tree was mounted, it may have been moved
// as part of a parent suspense. get the latest anchor for insertion
// #8105 if `delayEnter` is true, it means that the mounting of
// `activeBranch` will be delayed. if the branch switches before
// transition completes, both `activeBranch` and `pendingBranch` may
// coexist in the `hiddenContainer`. This could result in
// `next(activeBranch!)` obtaining an incorrect anchor
// (got `pendingBranch.el`).
// Therefore, after the mounting of activeBranch is completed,
// it is necessary to get the latest anchor.
// activeBranch 是否在原始容器 ?
if (parentNode(activeBranch.el!) === container) {
// 获取 activeBranch 的下一个节点作为锚点
anchor = next(activeBranch)
}
// 卸载当前内容
unmount(activeBranch, parentComponent, suspense, true)
}
if (!delayEnter) {
// move content from off-dom container to actual container
// 在不需要延迟插入的情况下,立即将异步加载完成的内容移动到实际容器中显示
move(pendingBranch!, container, anchor, MoveType.ENTER)
}
}完成 Suspense 边界(Suspense 组件上下文对象)的状态转换并处理相关副作用。
将加载完成的内容分支(pendingBranch)设置为当前活动分支,清空待处理分支指针,标记 Suspense 不再处于 fallback 状态:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
setActiveBranch(suspense, pendingBranch!)
suspense.pendingBranch = null
suspense.isInFallback = false向上遍历父级 Suspense 边界,查找 pending 状态的祖先,如果有 pending 状态的祖先 Suspense ,将当前副作用合并到祖先的队列中,否则且没有延迟进入时,异步执行副作用函数,然后清空当前 Suspense 的副作用队列:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
// flush buffered effects
// check if there is a pending parent suspense
let parent = suspense.parent
let hasUnresolvedAncestor = false
while (parent) {
if (parent.pendingBranch) {
// found a pending parent suspense, merge buffered post jobs
// into that parent
parent.effects.push(...effects)
hasUnresolvedAncestor = true
break
}
parent = parent.parent
}
// no pending parent suspense nor transition, flush all jobs
if (!hasUnresolvedAncestor && !delayEnter) {
queuePostFlushCb(effects)
}
suspense.effects = []如果当前 Suspense 可被父级捕获(suspensible),减少父级 Suspense 的依赖计数,当父级依赖降为 0 时,调用父级 resolve 方法
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
// resolve parent suspense if all async deps are resolved
if (isSuspensible) {
if (
parentSuspense &&
parentSuspense.pendingBranch &&
parentSuspenseId === parentSuspense.pendingId
) {
parentSuspense.deps--
if (parentSuspense.deps === 0 && !sync) {
parentSuspense.resolve()
}
}
}调用用户定义的 onResolve 函数:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
// invoke @resolve event
triggerEvent(vnode, 'onResolve')fallback 方法
检查 pendingBranch 是否存在(即是否有异步加载中的内容分支),如果没有待处理的异步分支,则直接退出方法(避免不必要的 fallback 操作)
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
if (!suspense.pendingBranch) {
return
}从 Suspense 边界对象( Suspense 上下文对象)中提取后续操作必需的5个关键属性:
vnode:当前 Suspense 组件对应的虚拟节点activeBranch:当前正在显示的内容分支(可能是主内容或前一个 fallback )parentComponent:父组件实例(用于组件上下文传递)container:DOM 容器元素(用于挂载 fallback 内容)namespace:元素命名空间(处理 SVG 等特殊命名空间场景)
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
const { vnode, activeBranch, parentComponent, container, namespace } =
suspense调用用户定义的 onFallback 回调:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
// invoke @fallback event
triggerEvent(vnode, 'onFallback')获取当前活动分支的下一个 DOM 节点作为锚点,定义挂载函数(延迟执行或立即执行)
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
const anchor = next(activeBranch!)
const mountFallback = () => {
if (!suspense.isInFallback) {
return
}
// mount the fallback tree
patch(
null,
fallbackVNode,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
null, // fallback tree will not have suspense context
namespace,
slotScopeIds,
optimized,
)
setActiveBranch(suspense, fallbackVNode)
}检查 fallback 内容是否有 out-in 过渡模式,若有,延迟挂载直到当前内容离开动画完成:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
const delayEnter =
fallbackVNode.transition && fallbackVNode.transition.mode === 'out-in'
if (delayEnter) {
activeBranch!.transition!.afterLeave = mountFallback
}标记 Suspense 进入 fallback 状态,卸载当前显示的内容:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
suspense.isInFallback = true
// unmount current active branch
unmount(
activeBranch!,
parentComponent,
null, // no suspense so unmount hooks fire now
true, // shouldRemove
)若无过渡动画要求,立即挂载 fallback 内容:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
if (!delayEnter) {
mountFallback()
}move 方法
当 Suspense 有当前显示的激活分支(activeBranch)时,调用渲染器内部的 move 方法(来自 rendererInternals),将激活分支对应的 DOM 移动到传入的容器(container)的指定锚点位置(anchor):
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
move(container, anchor, type) {
suspense.activeBranch &&
move(suspense.activeBranch, container, anchor, type)
suspense.container = container
}该移动方法会提供给渲染器调用:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts
const move: MoveFn = (
vnode,
container,
anchor,
moveType,
parentSuspense = null,
) => {
if (__FEATURE_SUSPENSE__ && shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.SUSPENSE) {
vnode.suspense!.move(container, anchor, moveType)
return
}
}next 方法
获取当前激活分支(activeBranch)对应的 DOM 节点的下一个相邻节点:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
next() {
return suspense.activeBranch && next(suspense.activeBranch)
}registerDep 方法
当 Suspense 处于等待状态时(pendingBranch 存在),增加依赖计数 deps++
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
const isInPendingSuspense = !!suspense.pendingBranch
if (isInPendingSuspense) {
suspense.deps++
}异步组件返回的结果是一个 Promise ,Promise 可以由 then 回调中得到解析结果。在 catch 回调中捕获异步组件加载过程中的错误:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
instance
.asyncDep!.catch(err => {
handleError(err, instance, ErrorCodes.SETUP_FUNCTION)
})
.then(asyncSetupResult => {
// ...
})不知道异步组件返回的 Promise 什么时候返回结果,但是在返回的时候可能组件已经被卸载,如果已经被卸载或者是 Suspense 被卸载以及如果不是等待的异步和处理的异步不是同一个,直接结束当前的 Promise 解析:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
// retry when the setup() promise resolves.
// component may have been unmounted before resolve.
if (
instance.isUnmounted ||
suspense.isUnmounted ||
suspense.pendingId !== instance.suspenseId
) {
return
}设置组件实例的 asyncResolved 标志,表示该异步组件的 setup 函数已完成解析:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
instance.asyncResolved = true处理异步 setup 函数的返回结果:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
handleSetupResult(instance, asyncSetupResult, false)恢复原始 DOM 引用。在异步组件加载期间,组件可能因状态更新被重新渲染,重新渲染会创建新的 vnode,其 vnode.el 会被更新为客户端临时节点(通常是注释占位符)这会导致原始服务器渲染的 DOM 引用丢失。
因此在异步组件结果返回前,将 DOM 元素先保存到 hydratedEl 中。
在异步组件结果返回后,再将原始的 DOM 元素重置回 vnode.el 中。确保客户端激活(hydration)时能正确匹配服务器渲染的 DOM 结构:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
if (hydratedEl) {
// vnode may have been replaced if an update happened before the
// async dep is resolved.
vnode.el = hydratedEl
}在纯客户端渲染(CSR)场景中,异步组件加载期间会生成注释占位符节点(即 <!---->):
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
const placeholder = !hydratedEl && instance.subTree.elsetupRenderEffect 的作用是创建和管理组件的响应式渲染/更新逻辑,在 Suspense 场景中,它确保了异步组件解析后能正确挂载到 DOM 并保持响应式更新能力:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
setupRenderEffect(
instance,
vnode,
// component may have been moved before resolve.
// if this is not a hydration, instance.subTree will be the comment
// placeholder.
parentNode(hydratedEl || instance.subTree.el!)!,
// anchor will not be used if this is hydration, so only need to
// consider the comment placeholder case.
hydratedEl ? null : next(instance.subTree),
suspense,
namespace,
optimized,
)移除客户端渲染时生成的注释占位节点:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
if (placeholder) {
remove(placeholder)
}当异步组件被高阶组件(HOC)包裹时,需要确保 HOC 的根 DOM 元素引用 (vnode.el) 能正确指向最终渲染的真实 DOM 元素,避免因异步加载导致元素引用错位:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
updateHOCHostEl(instance, vnode.el)isInPendingSuspense 标识当前是否处于 Suspense 的 pending 状态。
suspense.deps 为 Suspense 边界(Suspense 上下文对象)内未完成的异步依赖计数。
Suspense 的异步任务中嵌套了其他异步任务,每减少一个 deps 代表一个异步任务结束。只有到了最后一个异步任务结束,Suspense 才会进入 resolve 状态:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
// only decrease deps count if suspense is not already resolved
if (isInPendingSuspense && --suspense.deps === 0) {
suspense.resolve()
}unmount 方法
标记 Suspense 组件为已卸载状态,卸载 Suspense 组件激活分支或 fallback 分支:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
unmount(parentSuspense, doRemove) {
suspense.isUnmounted = true
if (suspense.activeBranch) {
unmount(
suspense.activeBranch,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
doRemove,
)
}
if (suspense.pendingBranch) {
unmount(
suspense.pendingBranch,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
doRemove,
)
}
}完成挂载
挂载默认插槽的内容到离屏容器中,在离屏容器中初始化异步内容:
-
pendingBranch:存储默认插槽内容(需异步加载的组件) -
hiddenContainer: 通过createElement('div')创建的离屏容器
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
patch(
null,
(suspense.pendingBranch = vnode.ssContent!), // 设置 pendingBranch 为默认插槽内容
hiddenContainer, // 离屏容器(不在 DOM 树中)
null,
parentComponent,
suspense,
namespace,
slotScopeIds,
)检查异步依赖状态,
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
if (suspense.deps > 0) {
// 处理异步场景
} else {
// Suspense 没有异步依赖,则直接调用 resolve 方法
suspense.resolve(false, true)
}触发 onPending 、onFallback 回调函数:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
if (suspense.deps > 0) {
// has async
// invoke @fallback event
triggerEvent(vnode, 'onPending')
triggerEvent(vnode, 'onFallback')
// ...
}挂载 fallback 插槽内容,将 fallback 内容设置为当前活动分支:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
if (suspense.deps > 0) {
// ...
// mount the fallback tree
patch(
null,
vnode.ssFallback!,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
null, // fallback tree will not have suspense context
namespace,
slotScopeIds,
)
setActiveBranch(suspense, vnode.ssFallback!)
}更新节点
更新 Suspense 组件的逻辑主要在 patchSuspense ,但是在执行更新 Suspense 逻辑前,会进行一些必要的判断,用于避免嵌套 Suspense 场景下重复渲染问题。
-
parentSuspense:存在父级 Suspense 组件 -
parentSuspense.deps > 0:父级 Suspense 存在未完成的异步依赖 -
!n1.suspense!.isInFallback当前 Suspense 不在 fallback 状态
因为父级 Suspense 的 pendingBranch 包含了当前这个已经 resolve 的 Suspense。如果现在直接 patch 它,会导致它里面的子组件被 mount 一次;而当父级 resolve 时,又会再次 mount,造成重复挂载的问题。
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
if (
parentSuspense &&
parentSuspense.deps > 0 &&
!n1.suspense!.isInFallback
) {
n2.suspense = n1.suspense! // 复用旧的 suspense 实例
n2.suspense.vnode = n2 // 更新 vnode 引用为新的 vnode
n2.el = n1.el // 复用已有的真实 DOM 元素(el)。
return // 直接返回,跳过 patch 流程,防止重复渲染
}下面正式分析 patchSuspense 函数的代码实现
patchSuspense
从旧节点 n1 复用 suspense 实例到新节点 n2,避免重新创建 Suspense 边界(Suspense 上下文对象),保持状态连续性:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
const suspense = (n2.suspense = n1.suspense)!将 SuspenseBoundary 关联的 vnode 更新为最新节点,确保后续操作基于最新组件状态:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
suspense.vnode = n2直接复用旧节点的 DOM 元素引用,避免不必要的 DOM 创建操作,优化性能:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
n2.el = n1.el获取新 Suspense 节点默认插槽和 fallback 插槽的内容
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
const newBranch = n2.ssContent!
const newFallback = n2.ssFallback!完成上述准备工作后,patchSuspense 函数大体上分为两种情况的处理,一种是存在 pendingBranch 的情况,另一种是 pendingBranch 不存在的情况:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
if (pendingBranch) {
// ...
} else {
// ...
}存在 pendingBranch 的情况
当存在待处理分支 pendingBranch 时,将新的异步内容分支设置为当前待处理分支:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
suspense.pendingBranch = newBranch当新内容分支与 pendingBranch 类型相同时,在离屏 dom 中对新旧分支进行更新:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
if (isSameVNodeType(newBranch, pendingBranch)) {
// same root type but content may have changed.
patch(
pendingBranch,
newBranch,
suspense.hiddenContainer, // 在隐藏容器中更新
null,
parentComponent,
suspense,
namespace,
slotScopeIds,
optimized,
)
}若所有异步依赖完成(deps <= 0),立即触发 resolve() :
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
if (suspense.deps <= 0) {
suspense.resolve()
}当 Suspense 处于显示 fallback 内容的状态,且非 hydration(SSR 激活)过程时,对 fallback 内容执行 patch 更新:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
else if (isInFallback) {
// It's possible that the app is in hydrating state when patching the
// suspense instance. If someone updates the dependency during component
// setup in children of suspense boundary, that would be problemtic
// because we aren't actually showing a fallback content when
// patchSuspense is called. In such case, patch of fallback content
// should be no op
if (!isHydrating) {
patch(
activeBranch,
newFallback,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
null, // fallback tree will not have suspense context
namespace,
slotScopeIds,
optimized,
)
// 更新活跃分支为新的 fallback
setActiveBranch(suspense, newFallback)
}Suspense 在异步加载过程中根节点类型被切换时,递增全局 suspenseId 作为新分支的唯一标识,使之前注册的异步回调失效:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
// toggled before pending tree is resolved
// increment pending ID. this is used to invalidate async callbacks
suspense.pendingId = suspenseId++如果 isHydrating 为 true ,则说明是在 SSR 激活完成前,用户强制切换内容,这时服务端渲染的 DOM 不再有效,需中断 SSR 激活的过程,所以需要将 isHydrating 设置为 false,将原分支(pendingBranch)标记为 activeBranch ,确保后续能正确卸载该分支,避免残留无效 DOM 节点:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
if (isHydrating) {
// if toggled before hydration is finished, the current DOM tree is
// no longer valid. set it as the active branch so it will be unmounted
// when resolved
suspense.isHydrating = false
suspense.activeBranch = pendingBranch
} else {
unmount(pendingBranch, parentComponent, suspense)
}重置 Suspense 组件状态:
-
deps = 0:重置异步依赖计数器,新分支需重新收集依赖 -
effects.length = 0:清除旧分支的副作用队列,避免残留影响 -
新建隐藏容器:隔离新旧分支的 DOM 操作,防止冲突
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
// reset suspense state
suspense.deps = 0
// discard effects from pending branch
suspense.effects.length = 0
// discard previous container
suspense.hiddenContainer = createElement('div')如果 Suspense 还在 fallback 状态,则挂载新分支到隐藏容器:
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
if (isInFallback) {
// already in fallback state
// 挂载新分支到隐藏容器
patch(
null,
newBranch,
suspense.hiddenContainer,
null,
parentComponent,
suspense,
namespace,
slotScopeIds,
optimized,
)
if (suspense.deps <= 0) {
// 无异步依赖立即完成
suspense.resolve()
} else {
// 更新 fallback 插槽内容
patch(
activeBranch,
newFallback,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
null, // fallback tree will not have suspense context
namespace,
slotScopeIds,
optimized,
)
setActiveBranch(suspense, newFallback)
}
}场景一,切换回当前活跃分支,即新分支 newBranch 与当前活跃分支 activeBranch 类型相同(isSameVNodeType) ,例如从 ComponentA 切换到另一个 ComponentA 实例。直接更新现有分支,强制立即 resolve 。强制立即 resolve 会跳过 DOM 卸载/移动流程。
场景二,切换到第三方分支,新分支既不同于待处理分支(pendingBranch),也不同于活跃分支,例如从 ComponentA 切换到全新的 ComponentC 。将新分支挂载到离屏 dom (hiddenContainer)中,检查异步依赖,无依赖(deps <= 0),调用 resolve() 显示内容。
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
else if (activeBranch && isSameVNodeType(newBranch, activeBranch)) {
// toggled "back" to current active branch
// 切换回当前活跃分支
patch(
activeBranch,
newBranch,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
suspense,
namespace,
slotScopeIds,
optimized,
)
// force resolve
// 强制 resolve
suspense.resolve(true)
} else {
// switched to a 3rd branch
// 切换到第三方分支
patch(
null,
newBranch,
suspense.hiddenContainer, // 离屏 dom
null,
parentComponent,
suspense,
namespace,
slotScopeIds,
optimized,
)
if (suspense.deps <= 0) {
suspense.resolve()
}
}不存在 pendingBranch 的情况
如果 activeBranch 存在且 newBranch 与 activeBranch 是同类型节点(isSameVNodeType),说明只是内容更新,不涉及根节点切换,直接 patch 并设置新的 activeBranch。
否则,说明根节点发生了切换(如异步内容和 fallback 互换),则触发 onPending 事件,通知外部 Suspense 进入 pending 状态。
将新的内容分支 newBranch 作为 pendingBranch,并分配唯一的 pendingId。
如果新分支是被 KeepAlive 包裹的组件(即 shapeFlag 包含 COMPONENT_KEPT_ALIVE),则直接复用该组件实例上的 suspenseId,保证同一个被缓存的组件在多次切换时 pendingId 一致,有利于缓存和恢复。
否则,为当前 Suspense 分支分配一个全局自增的 suspenseId,确保每次切换分支时 pendingId 唯一。
然后,将新分支内容挂载到离屏 dom 中,避免异步的内容在加载完成前影响真实的 dom,之后检查异步依赖计数(suspense.deps),如果为 0,说明新分支没有异步依赖,直接 resolve,将加载完成的异步内容移动到真实 dom 容器中。
如果大于 0,说明有异步依赖,进入等待流程,如果设置了 timeout ,则在超时后自动调用 suspense.fallback(newFallback),切换到 fallback 分支。如果 timeout 为 0,立即切换到 fallback 分支。
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
if (activeBranch && isSameVNodeType(newBranch, activeBranch)) {
// root did not change, just normal patch
// 根节点未改变,仅执行标准虚拟 DOM 更新流程
patch(
activeBranch,
newBranch,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
suspense,
namespace,
slotScopeIds,
optimized,
)
setActiveBranch(suspense, newBranch)
} else {
// root node toggled
// 根节点被切换了
// invoke @pending event
triggerEvent(n2, 'onPending')
// mount pending branch in off-dom container
suspense.pendingBranch = newBranch
// 分配唯一的 pendingId
if (newBranch.shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.COMPONENT_KEPT_ALIVE) {
suspense.pendingId = newBranch.component!.suspenseId!
} else {
suspense.pendingId = suspenseId++
}
// 将新分支内容挂载到离屏 dom 中
patch(
null,
newBranch,
suspense.hiddenContainer,
null,
parentComponent,
suspense,
namespace,
slotScopeIds,
optimized,
)
if (suspense.deps <= 0) {
// incoming branch has no async deps, resolve now.
suspense.resolve()
} else {
const { timeout, pendingId } = suspense
if (timeout > 0) {
setTimeout(() => {
if (suspense.pendingId === pendingId) {
suspense.fallback(newFallback)
}
}, timeout)
} else if (timeout === 0) {
suspense.fallback(newFallback)
}
}
}hydrate 方法分析
hydrate 方法由 hydrateSuspense 方法实现。
hydrateSuspense 方法的作用是:在 SSR(服务端渲染)场景下,将服务端渲染好的 Suspense 组件内容与客户端的虚拟节点(VNode)进行"水合"对齐,并调用 createSuspenseBoundary 方法创建 Suspense 上下文对象。
然后,调用 hydrateNode 方法对 Suspense 默认插槽,即内容分支(vnode.ssContent!)进行水合,将服务端渲染生成的 DOM 节点与虚拟节点(VNode)关联起来。
判断异步依赖计数(suspense.deps),如果异步依赖计数为 0,则调用 resolve 方法,Suspense 组件进入 resolved 状态。
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
function hydrateSuspense(
node: Node,
vnode: VNode,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
parentSuspense: SuspenseBoundary | null,
namespace: ElementNamespace,
slotScopeIds: string[] | null,
optimized: boolean,
rendererInternals: RendererInternals,
hydrateNode: (
node: Node,
vnode: VNode,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
parentSuspense: SuspenseBoundary | null,
slotScopeIds: string[] | null,
optimized: boolean,
) => Node | null,
): Node | null {
// 创建 Suspense 上下文对象
const suspense = (vnode.suspense = createSuspenseBoundary(
vnode,
parentSuspense,
parentComponent,
node.parentNode!,
// eslint-disable-next-line no-restricted-globals
document.createElement('div'),
null,
namespace,
slotScopeIds,
optimized,
rendererInternals,
true /* hydrating */,
))
// there are two possible scenarios for server-rendered suspense:
// - success: ssr content should be fully resolved
// - failure: ssr content should be the fallback branch.
// however, on the client we don't really know if it has failed or not
// attempt to hydrate the DOM assuming it has succeeded, but we still
// need to construct a suspense boundary first
// 尝试水合 Suspense 默认插槽,即内容分支,将现有 DOM 节点与虚拟节点关联起来。
const result = hydrateNode(
node,
(suspense.pendingBranch = vnode.ssContent!),
parentComponent,
suspense,
slotScopeIds,
optimized,
)
if (suspense.deps === 0) {
// 异步依赖计数为 0 ,直接进入 resolved 状态
suspense.resolve(false, true)
}
return result
}normalize 方法分析
normalize 方法由 normalizeSuspenseChildren 方法实现。
normalizeSuspenseChildren 方法的作用是规范化 Suspense 组件的子节点,将其拆分为内容分支(ssContent)和fallback 分支(ssFallback),以便后续渲染和切换。
首先判断子节点类型,如果 vnode.shapeFlag 包含 SLOTS_CHILDREN ,说明 children 是插槽对象,分别取 default 和 fallback 作为内容和 fallback 分支。
否则,直接将 children 作为内容分支,fallback 分支用注释节点(createVNode(Comment))占位。
调用 normalizeSuspenseSlot 进一步规范化内容和 fallback 分支,确保它们都是单根节点的 VNode。
结果赋值到 vnode.ssContent 和 vnode.ssFallback,供 Suspense 运行时逻辑使用。
ts
// packages/runtime-core/src/components/Suspense.ts
function normalizeSuspenseChildren(vnode: VNode): void {
const { shapeFlag, children } = vnode
const isSlotChildren = shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.SLOTS_CHILDREN
vnode.ssContent = normalizeSuspenseSlot(
isSlotChildren ? (children as Slots).default : children,
)
vnode.ssFallback = isSlotChildren
? normalizeSuspenseSlot((children as Slots).fallback)
: createVNode(Comment)
}总结
Suspense 是用于处理异步组件的场景,处理异步,自然会用到 Promise 。其实 Suspense 的本质就是使用 Promise 来处理异步组件的场景。
整体的实现流程是,Suspense 发现有异步依赖时,由于异步依赖本质是 Promise ,则会在 then 回调中获取异步依赖最终解析的结果,在异步依赖解析期间,则会把 fallback 的内容展示到页面上,当在 then 回调中拿到异步依赖最终解析的结果后,则会用异步依赖解析后的内容替换掉 fallback 的内容。
异步依赖指的是带有异步
setup()钩子的组件和异步组件
Suspense 内部有个变量叫 deps ,用于记录异步依赖的个数,每解析完成一个异步依赖,则 deps 数减 1 ,当 deps 为 0 时,表示异步依赖已经全部解析完成,此时就可以把 fallback 的内容替换掉。Suspense 组件使用这种方式实现对多个异步依赖的等待。