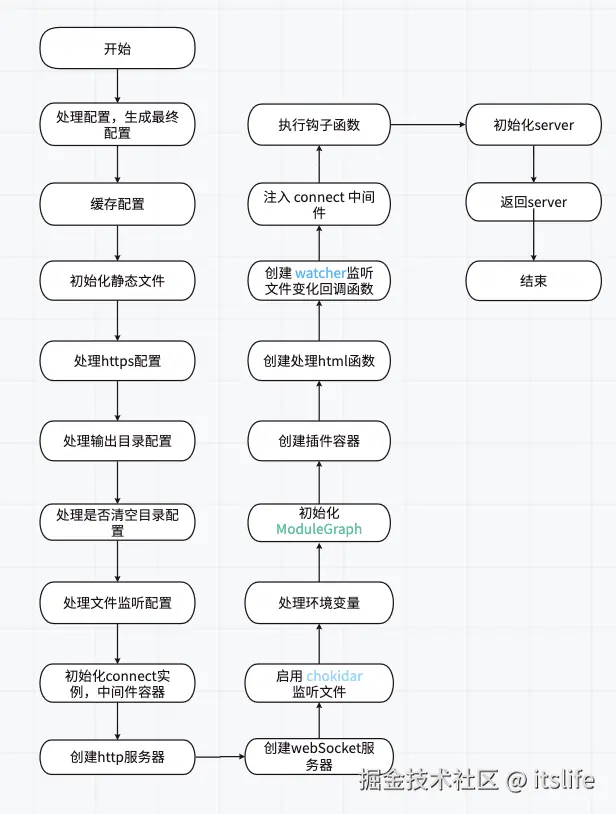
监听文件变化
js
// 如果开启监听,则调用 chokidar.watch,否则返回假的监听实例
const watcher = watchEnabled
? (chokidar.watch(
// config file dependencies and env file might be outside of root
[
root,
...config.configFileDependencies,
...getEnvFilesForMode(config.mode, config.envDir),
// Watch the public directory explicitly because it might be outside
// of the root directory.
...(publicDir && publicFiles ? [publicDir] : []),
],
resolvedWatchOptions,
) as FSWatcher)
: createNoopWatcher(resolvedWatchOptions)环境配置
vite 支持多环境构建,允许一个项目同时构建多个目标,如:
client:前端浏览器代码ssr:服务端渲染代码worker:Web Workercustom:自定义环境(如 Electron 主进程)
每个环境可以有:
- 独立的入口(
input) - 独立的插件
- 独立的构建选项(
build.rollupOptions、resolve等)
typescript
const environments: Record<string, DevEnvironment> = {}
for (const [name, environmentOptions] of Object.entries(
config.environments,
)) {
environments[name] = await environmentOptions.dev.createEnvironment(
name,
config,
{
ws,
},
)
}
for (const environment of Object.values(environments)) {
const previousInstance = options.previousEnvironments?.[environment.name]
// 初始化环境
await environment.init({ watcher, previousInstance })
}这里先不管具体实现,先记住 vite 在这里处理了多环境,对每个环境进行了初始化,并且共用一个 ws 服务。
ModuleGraph 初始化(模块图)
js
// 为了向后兼容,使用 ModuleGraph 类做代理,真正的 ModuleGraph 为 EnvironmentModuleGraph
let moduleGraph = new ModuleGraph({
client: () => environments.client.moduleGraph,
ssr: () => environments.ssr.moduleGraph,
})现在可以将 EnvironmentModuleGraph 简单理解为一个 map,key 为 字符串,value 为 EnvironmentModuleNode | Set<EnvironmentModuleNode>。对应四个 map。
typescript
export class EnvironmentModuleGraph {
environment: string
urlToModuleMap = new Map<string, EnvironmentModuleNode>()
idToModuleMap = new Map<string, EnvironmentModuleNode>()
etagToModuleMap = new Map<string, EnvironmentModuleNode>()
// a single file may corresponds to multiple modules with different queries
fileToModulesMap = new Map<string, Set<EnvironmentModuleNode>>()
// 省略
}创建插件容器
vite 调用 createPluginContainer 函数创建一个 PluginContainer 类实例。
javascript
export function createPluginContainer(
environments: Record<string, Environment>,
): PluginContainer {
return new PluginContainer(environments)
}
let pluginContainer = createPluginContainer(environments)创建处理 html 函数
通过调用 createDevHtmlTransformFn 函数创建处理 html 的函数。 createDevHtmlTransformFn 函数主要定义了需要执行的插件和插件的上下文,并返回一个函数,这个函数中执行 applyHtmlTransforms 函数对 html 做处理。
php
export function createDevHtmlTransformFn(
config: ResolvedConfig,
): (
server: ViteDevServer,
url: string,
html: string,
originalUrl?: string,
) => Promise<string> {
const [preHooks, normalHooks, postHooks] = resolveHtmlTransforms(
config.plugins,
)
const transformHooks = [
preImportMapHook(config),
injectCspNonceMetaTagHook(config),
...preHooks,
htmlEnvHook(config),
devHtmlHook,
...normalHooks,
...postHooks,
injectNonceAttributeTagHook(config),
postImportMapHook(),
]
const pluginContext = new BasicMinimalPluginContext(
{ ...basePluginContextMeta, watchMode: true },
config.logger,
)
return (
server: ViteDevServer,
url: string,
html: string,
originalUrl?: string,
): Promise<string> => {
return applyHtmlTransforms(html, transformHooks, pluginContext, {
path: url,
filename: getHtmlFilename(url, server),
server,
originalUrl,
})
}
}
const devHtmlTransformFn = createDevHtmlTransformFn(config)创建文件监听回调函数
对于文件监听,这里有三种情况,分别是:
- 增加
- 修改
- 删除
dart
watcher.on('change', async (file) => {
file = normalizePath(file)
reloadOnTsconfigChange(server, file)
await pluginContainer.watchChange(file, { event: 'update' })
// invalidate module graph cache on file change
for (const environment of Object.values(server.environments)) {
environment.moduleGraph.onFileChange(file)
}
await onHMRUpdate('update', file)
})
watcher.on('add', (file) => {
onFileAddUnlink(file, false)
})
watcher.on('unlink', (file) => {
onFileAddUnlink(file, true)
})可以看出,这里是 vite 的核心机制,在开发时,修改文件后会触发这里的回调函数,但是先记住这里,继续主流程。
注入 connect 中间件
接下来, vite 会把一系列的中间件注入 connect 中间件容器中。
scss
// request timer
if (process.env.DEBUG) {
middlewares.use(timeMiddleware(root))
}
// disallows request that contains `#` in the URL
middlewares.use(rejectInvalidRequestMiddleware())
// cors
const { cors } = serverConfig
if (cors !== false) {
middlewares.use(corsMiddleware(typeof cors === 'boolean' ? {} : cors))
}
// host check (to prevent DNS rebinding attacks)
const { allowedHosts } = serverConfig
// no need to check for HTTPS as HTTPS is not vulnerable to DNS rebinding attacks
if (allowedHosts !== true && !serverConfig.https) {
middlewares.use(hostValidationMiddleware(allowedHosts, false))
}
// apply configureServer hooks ------------------------------------------------
const configureServerContext = new BasicMinimalPluginContext(
{ ...basePluginContextMeta, watchMode: true },
config.logger,
)
const postHooks: ((() => void) | void)[] = []
for (const hook of config.getSortedPluginHooks('configureServer')) {
postHooks.push(await hook.call(configureServerContext, reflexServer))
}
// Internal middlewares ------------------------------------------------------
middlewares.use(cachedTransformMiddleware(server))
// proxy
const { proxy } = serverConfig
if (proxy) {
const middlewareServer =
(isObject(middlewareMode) ? middlewareMode.server : null) || httpServer
middlewares.use(proxyMiddleware(middlewareServer, proxy, config))
}
// base
if (config.base !== '/') {
middlewares.use(baseMiddleware(config.rawBase, !!middlewareMode))
}
// open in editor support
middlewares.use('/__open-in-editor', launchEditorMiddleware())
// ping request handler
// Keep the named function. The name is visible in debug logs via `DEBUG=connect:dispatcher ...`
middlewares.use(function viteHMRPingMiddleware(req, res, next) {
if (req.headers['accept'] === 'text/x-vite-ping') {
res.writeHead(204).end()
} else {
next()
}
})
// serve static files under /public
// this applies before the transform middleware so that these files are served
// as-is without transforms.
if (publicDir) {
middlewares.use(servePublicMiddleware(server, publicFiles))
}
// main transform middleware
middlewares.use(transformMiddleware(server))
// serve static files
middlewares.use(serveRawFsMiddleware(server))
middlewares.use(serveStaticMiddleware(server))
// html fallback
if (config.appType === 'spa' || config.appType === 'mpa') {
middlewares.use(htmlFallbackMiddleware(root, config.appType === 'spa'))
}同样这里也先不管中间件的具体作用。
执行钩子函数
需要让用户的 configureServer 钩子函数先执行。确保这些中间件在 Vite 内置的 HTML fallback 中间件之前生效,从而让开发者能完全控制请求处理流程。
javascript
const postHooks: ((() => void) | void)[] = []
for (const hook of config.getSortedPluginHooks('configureServer')) {
postHooks.push(await hook.call(configureServerContext, reflexServer))
}
postHooks.forEach((fn) => fn && fn())
// 内置 html 中间件
if (config.appType === 'spa' || config.appType === 'mpa') {
// transform index.html
middlewares.use(indexHtmlMiddleware(root, server))
// handle 404s
middlewares.use(notFoundMiddleware())
}初始化 server
对于普通模式,即 vite 直接启动,vite 会在服务启动前做依赖预构建。
typescript
const initServer = async (onListen: boolean) => {
if (serverInited) return
if (initingServer) return initingServer
initingServer = (async function () {
// For backward compatibility, we call buildStart for the client
// environment when initing the server. For other environments
// buildStart will be called when the first request is transformed
await environments.client.pluginContainer.buildStart()
// ensure ws server started
if (onListen || options.listen) {
await Promise.all(
Object.values(environments).map((e) => e.listen(server)),
)
}
initingServer = undefined
serverInited = true
})()
return initingServer
}
if (!middlewareMode && httpServer) {
// overwrite listen to init optimizer before server start
const listen = httpServer.listen.bind(httpServer)
httpServer.listen = (async (port: number, ...args: any[]) => {
try {
await initServer(true)
} catch (e) {
httpServer.emit('error', e)
return
}
return listen(port, ...args)
}) as any
} else {
await initServer(false)
}结束
主流程大概结束,接下来从单步调试数据流来分析 vite 在启动时具体做了什么。