ReAct介绍
要介绍ReAct最好要知道它是从哪来的。
ReAct这个概念出自《REACT : SYNERGIZING REASONING AND ACTING IN LANGUAGE MODELS》这篇很牛的论文。
我们先来看下这篇论文的摘要:

翻译:
尽管大型语言模型(LLMs)在语言理解和交互式决策任务中展现了卓越的性能,但其推理能力(如思维链提示)与行为能力(如行动规划生成)以往主要被作为独立课题进行研究。
在本文中,我们探索了一种将LLMs用于以交错方式同时生成推理轨迹与任务特定动作的方法,从而实现两者之间的更强协同效应:推理轨迹帮助模型推导、跟踪和更新行动方案,并处理异常情况;而动作则使模型能够与外部源(如知识库或环境)进行交互并获取额外信息。我们将这一方法命名为ReAct,并将其应用于一系列语言理解和决策任务中,结果表明其性能超越了当前最先进的基线方法,同时显著提升了人类可解释性与可信度。
具体而言,在问答(HotpotQA)和事实验证(Fever)任务中,ReAct通过与简易维基百科API交互,有效克服了思维链推理中普遍存在的幻觉和错误传播问题,并生成了比无推理轨迹的基线方法更具可解释性的人类模仿式问题解决轨迹。此外,在两个交互式决策基准(ALFWorld 和 WebShop)上,ReAct 仅通过一到两个上下文示例的提示,便分别以34%和10%的绝对成功率超越了模仿学习与强化学习方法。
从摘要中我们大概可以知道ReAct是什么,可以把它理解为一种让 AI 一边思考,一边行动的强大框架。
ReAct 是 Reason 和 Act 两个词的缩写,即"推理"和"行动"。
这个"思考 → 行动 → 观察"的循环,会不断重复,直到模型能够给出一个可靠、准确的最终答案。
再来看下这篇论文的结论:

翻译:
我们提出了ReAct,一种简单而有效的用于在大语言模型中协同推理与行动的方法。通过在多跳问答、事实核查和交互式决策任务上的一系列多样化实验,我们表明ReAct能够带来更优的性能,并产生可解释的决策轨迹。尽管我们的方法很简单,但在动作空间较大的复杂任务中,模型需要更多示例才能良好学习,而这不幸很容易超出上下文学习的输入长度限制。我们在HotpotQA上探索了微调方法,取得了初步的积极结果,但未来仍需依赖更多高质量的人类标注数据来进一步提升性能。通过多任务训练扩展ReAct,并将其与强化学习等互补范式结合,有望催生更强大的智能体,进一步释放大语言模型在更多应用场景中的潜力。
在这篇论文中没有图示,不过已经有大佬画了很多图示了,这里我贴一个大佬画的图,结合图示大家可以更好的理解ReAct是怎么样的。
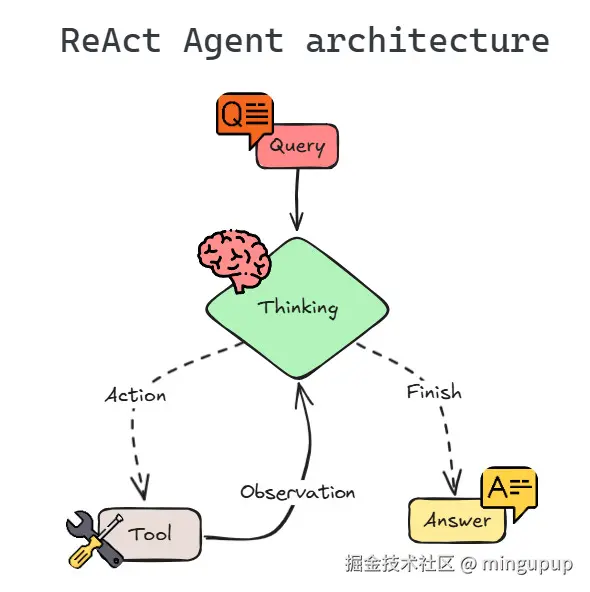
图片来源:mlpills.substack.com/p/diy-14-st...
实现一个简单的ReAct AI Agent
我使用的是python中的langgraph这个框架。
LangGraph 是一个用于构建有状态、多智能体(multi-agent)应用程序的库,它通过将工作流定义为图(Graph)的形式,让你能够用代码精确地控制应用的执行流程和逻辑。
更多可以从官方上了解。
我学习的那个文章工具是使用维基百科,但我试了一下感觉效果不太行,很多问题找不到,就自己改成了使用duckduckgo_search。
新建一个python环境,安装包:
cmd
pip install -U langgraph langchain-openai wikipedia ddgs导入必要的类和函数:
python
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END
from langchain_core.messages import BaseMessage, SystemMessage, ToolMessage
from typing import TypedDict, Sequence, Annotated
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
import json
from ddgs import DDGS定义状态模型:
python
class AgentState(TypedDict):
"""State of the agent for one turn or conversation."""
messages: Annotated[Sequence[BaseMessage], add_messages]LangGraph 使用一个状态对象来跟踪对话和任何中间数据。对于一个基本的 ReAct 代理,状态可以简单到仅包含一个消息列表(聊天历史)。我们定义一个名为 TypedDict 的状态类型,其中只有一个键 "messages",用于保存一系列消息。我们还为该字段附加了一个归约函数 add_messages ------ 这样做可以确保当节点返回新消息时,这些消息会被追加到状态的消息列表中(而不是覆盖它)。
设置大语言模型和工具:
python
# Initialize the chat model (LLM) - make sure your API key is set
model = ChatOpenAI(
base_url="https://api.siliconflow.cn/v1",
api_key="sk-xxx",
model="Qwen/Qwen3-Next-80B-A3B-Instruct",
temperature=0)
# Define a Wikipedia search tool
#import wikipedia
# @tool
# def wiki_search(query: str) -> str:
# """Search Wikipedia for the query and return a brief summary of the top result."""
# try:
# # Fetch summary of top search result (we set it to 5 sentences)
# summary = wikipedia.summary(query, sentences=5)
# return summary
# except Exception as e:
# return f"Error: {e}"
@tool
def duckduckgo_search(query: str) -> str:
"""Search DuckDuckGo for the query and return a brief summary of the top result."""
try:
# Fetch summary of top search result (we set it to 5 sentences)
summary = DDGS().text(query, max_results=5)
return summary
except Exception as e:
return f"Error: {e}"
# Map tool name to the tool function for easy lookup
tools = [duckduckgo_search]
tools_by_name = {tool.name: tool for tool in tools}
# Give the model access to the tools
model = model.bind_tools(tools) 接下来,初始化大语言模型并定义我们的工具。我们使用 LangChain 中的 ChatOpenAI 来创建一个聊天模型实例,可以使用任何可用的模型(只要其兼容工具调用功能)。
定义 LangGraph 节点和条件逻辑:
推理节点(LLM 调用) :该节点将调用大语言模型,以生成最终答案或决定执行某个工具操作。我们将其实现为一个函数 call_model(state)。该函数接收当前状态(包含迄今为止的对话消息),并返回 LLM 生成的新消息。我们还会加入一个系统提示(例如:"你是一个乐于助人的助手...")来引导 LLM 的行为。用户的查询已包含在状态的消息中,因此我们将系统提示与所有现有消息一并传递给模型进行调用。LangChain 的 ChatOpenAI 可以返回一条包含函数调用的消息------如果模型判断需要使用工具(底层可能利用 OpenAI 的函数调用功能,请求执行 duckduckgo_search 等操作)。
python
def call_model(state: AgentState):
"""LLM reasoning node: call the chat model with system prompt + conversation."""
system_prompt = SystemMessage(content="You are a helpful AI assistant. If needed, you can use the duckduckgo_search tool to build your answer.")
# Call the chat model with system + existing messages (user question is included in state["messages"])
response = model.invoke([system_prompt] + list(state["messages"]))
# Return the response as a list (to be appended to state's messages via reducer)
return {"messages": [response]}工具节点(执行工具):此节点用于执行大语言模型所请求的任何工具。我们实现 tool_node(state) 来检查大语言模型最新消息中是否存在工具调用。如果存在工具调用,我们将调用相应的工具函数,并将其结果封装为一个特殊的 ToolMessage。该 ToolMessage 将被添加到状态中,以便大语言模型在下一次迭代中能够看到工具的输出。
python
def tool_node(state: AgentState):
"""Tool execution node: execute any tool calls the LLM asked for."""
outputs = []
# Check the last message from the LLM for tool calls
last_message = state["messages"][-1]
if hasattr(last_message, "tool_calls") and last_message.tool_calls:
# If the model requested one or more tool calls, execute each
for tool_call in last_message.tool_calls:
tool_name = tool_call["name"]
tool_args = tool_call["args"]
if tool_name in tools_by_name:
# Invoke the corresponding tool function with provided arguments
result = tools_by_name[tool_name].invoke(tool_args)
else:
result = f"Tool '{tool_name}' not found."
# Wrap the result in a ToolMessage for the LLM to read
outputs.append(
ToolMessage(
content=json.dumps(result, ensure_ascii=False), # tool result as JSON string, preserve Chinese characters
name=tool_name,
tool_call_id=tool_call.get("id") # use id if provided
)
)
# Return the tool outputs to be added to messages
return {"messages": outputs}条件边(should_continue):在每次LLM推理步骤之后,我们需要决定代理是应该以答案结束,还是通过使用工具继续。我们定义一个函数 should_continue(state),用于检查LLM的最后一条消息。如果LLM没有请求任何工具(即没有函数调用),则表示它已经生成了最终答案,此时代理可以结束工作;如果请求了工具,则应继续前往工具节点。该函数将返回一个标志(例如"continue"或"end"),LangGraph将据此选择下一个节点。
python
def should_continue(state: AgentState) -> str:
"""Decide whether to continue the ReAct loop or end it, based on last LLM message."""
last_message = state["messages"][-1]
print(last_message)
# If the LLM's last message did not request a tool, we're done
if not (hasattr(last_message, "tool_calls") and last_message.tool_calls):
return "end"
else:
# There is a tool request, so continue to the tool node
return "continue"构建和编译图:
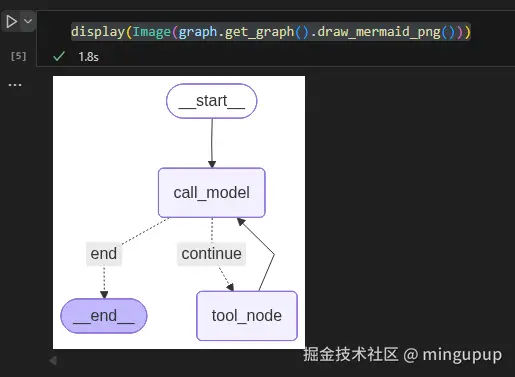
现在,我们使用 LangGraph 的 StateGraph 来构建图。我们添加了两个节点:"agent"(用于 LLM 推理)和 "tool"(用于工具执行),设置入口点,并定义节点间的转换关系。关键部分是从 LLM 节点添加一条条件边,根据 should_continue 函数的输出,决定走向工具节点或图的结束节点。我们将"continue"信号映射到"tool"节点,将"end"信号映射到 END(一个特殊标记,表示图应终止)。同时,我们从工具节点添加一条普通边返回到 LLM 节点,从而形成一个循环:在使用工具后,智能体将返回 LLM 以整合新获取的信息。
python
graph_builder = StateGraph(AgentState)
graph_builder.add_node("call_model", call_model)
graph_builder.add_node("tool_node", tool_node)
graph_builder.set_entry_point("call_model")
graph_builder.add_edge("tool_node", "call_model")
graph_builder.add_conditional_edges("call_model",
should_continue,
{"continue": "tool_node", "end": END})
graph = graph_builder.compile()如果你使用的是NoteBook,添加from IPython.display import Image, display、display(Image(graph.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png())),还可以看到这个图的结构:
使用这个简单的ReAct AI Agent:
通过上面的几个步骤,我们就构建了这个简单的ReAct AI Agent,现在我们来试试它的效果吧!!
python
def main():
inputs = {
"messages": [("user", "桦加沙是什么?")],
"intermediate_steps": [],
}
print_stream(graph.stream(inputs, stream_mode="values"))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()效果:
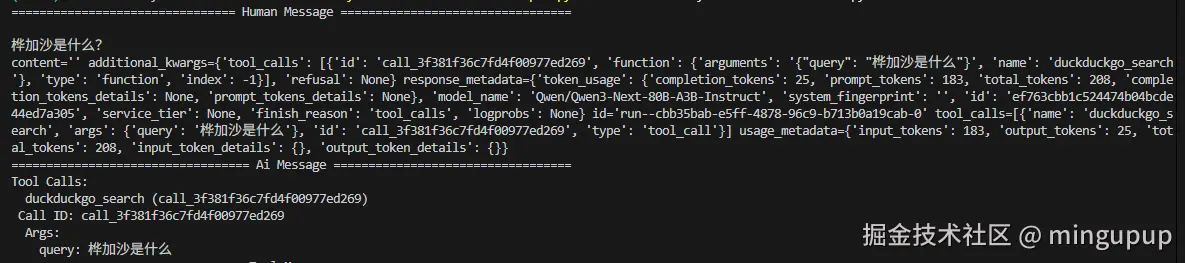
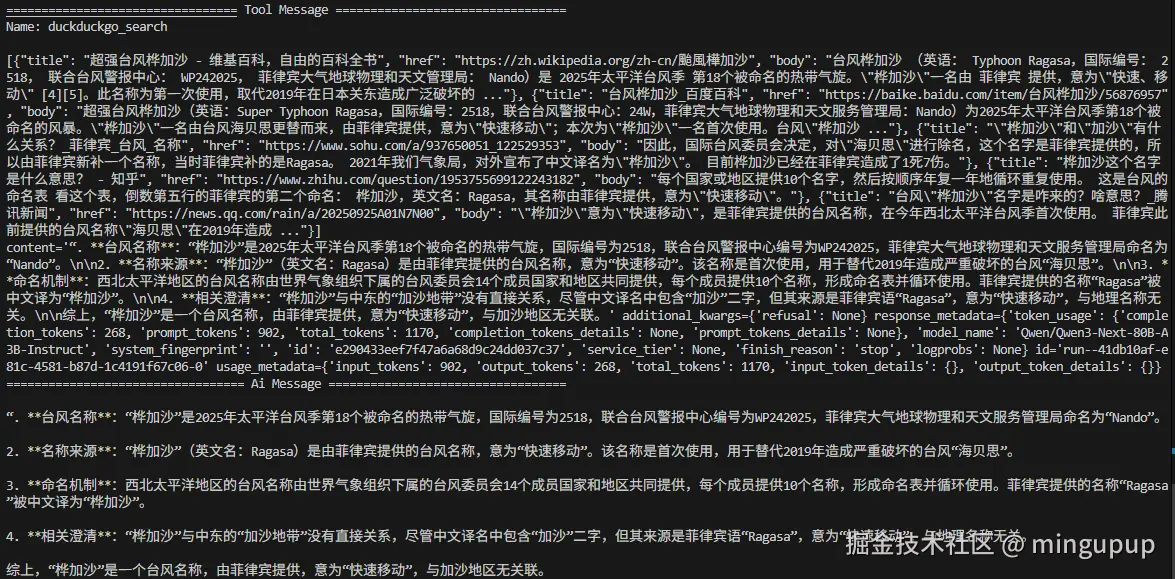
这个简单的ReAct AI Agent调用了工具来回答这个问题。
以上就是本期的全部内容,期待跟你一起进步,每天学习一点,希望对你有所帮助。