VoiceRAG
链接:Azure AI 搜索 - 检索增强生成 | Microsoft Azure
引言
本报告基于 Azure-Samples/aisearch-openai-rag-audio 项目,分析 VoiceRAG(语音增强检索生成)这一新兴应用模式。
VoiceRAG 结合了检索增强生成(RAG)技术与语音交互界面,利用 Azure AI Search 和 GPT-4o 实时音频 API 构建交互式语音生成 AI 体验。
发现 :VoiceRAG 代表了人机交互的重要进步,通过将传统的文本 RAG 模式扩展到语音领域,为用户提供了更自然、直观的知识查询体验。
该模式在保持 RAG 技术准确性的同时,显著提升了用户体验的便利性和可访问性。
1:技术架构与核心特性
架构设计原理
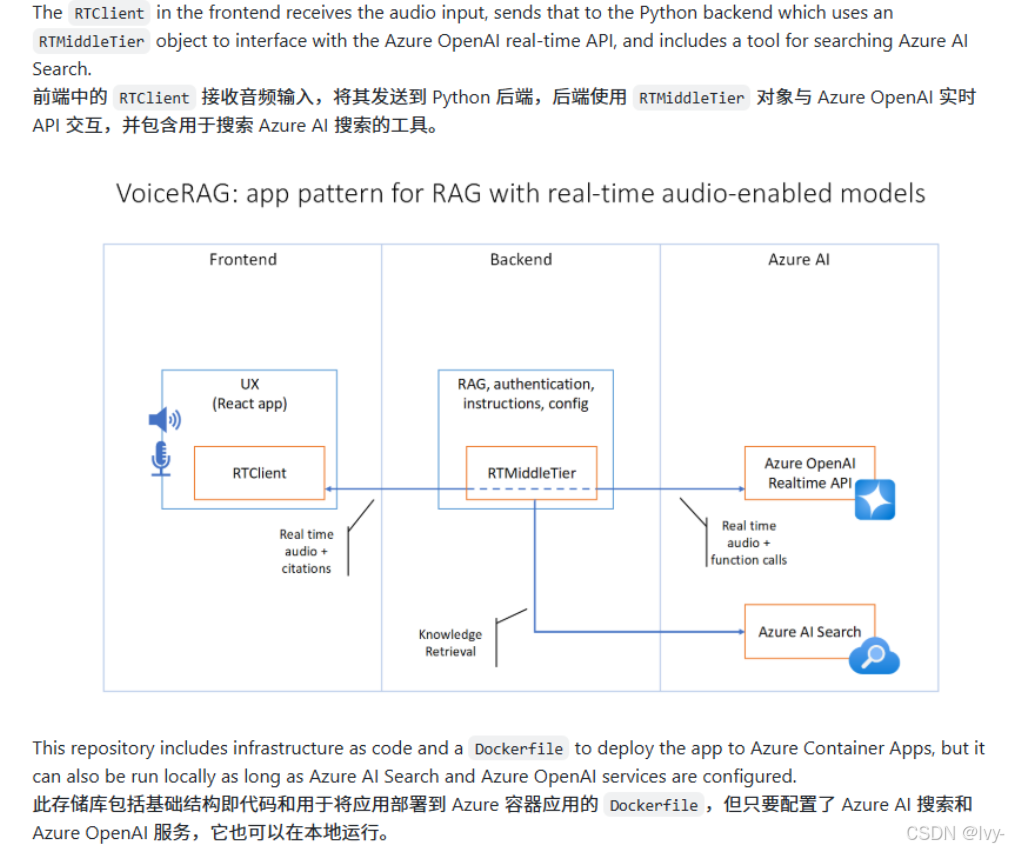
- 三层架构模式 :
- 前端 RTClient 负责音频输入采集
- Python 后端通过 RTMiddleTier 对象
- Azure OpenAI 实时 API 接口,集成 Azure AI Search 工具进行知识检索
- 实时音频处理:利用浏览器麦克风捕获语音输入,通过 GPT-4o 实时 API 进行音频处理和响应生成
- 容器化部署:提供完整的基础设施即代码(IaC)和 Dockerfile,支持 Azure Container Apps 部署
核心功能特性
- 语音交互界面:完全基于语音的用户交互,消除了传统文本输入的障碍
- RAG 集成 :通过 Azure AI Search 服务查询知识库,将检索到的文档发送给 GPT-4o 实时 API 生成响应
- 音频输出 :直接播放 GPT-4o 实时 API 的音频响应,提供流畅的对话体验
- 引用展示:显示生成响应时使用的搜索结果,确保信息可追溯性
2:技术实现与部署方案
开发环境支持
- 多平台兼容:支持 GitHub Codespaces、VS Code Dev Containers 和本地环境三种开发方式
- 工具链要求:需要 Azure Developer CLI、Node.js、Python >=3.11、Git 等基础工具
- 快速启动 :通过
GitHub Codespaces可实现一键式环境配置,降低了技术门槛
部署流程优化
- 自动化部署 :单一命令
azd up即可完成资源配置、代码部署和示例数据的集成向量化 - 资源配置:自动创建 Azure Container Apps、OpenAI 服务、AI Search 等必要资源
- 环境变量管理:支持自定义部署配置,包括现有服务集成和语音选择定制
本地开发支持
- 开发服务器:提供本地运行能力,支持连接已部署的 Azure 服务或现有服务
- 环境配置 :通过
.env文件管理必要的环境变量,包括 OpenAI 端点、部署名称、API 密钥等 - 跨平台兼容:提供 Windows 和 Linux/Mac 的启动脚本
3:成本效益与安全考量
成本结构分析
- 主要成本来源:Azure AI Search(标准层)产生持续费用,即使在中断部署的情况下也可能产生成本
- 资源定价模型 :
- Azure Container Apps:按使用量付费的消费计划
- Azure OpenAI:按每 1K 令牌使用量计费
- Azure AI Search:按小时计费的标准层
- Azure Blob Storage:基于存储和读取操作的标准层定价
- 成本优化建议:可切换到免费 SKU 降低成本,但功能会受到限制
安全实践
- 托管身份认证:使用 Managed Identity 消除开发者管理凭据的需求,提高安全性
- 无凭据架构:应用程序可通过托管身份获取 Microsoft Entra 令牌,无需管理任何凭据
- 代码安全扫描:建议启用 GitHub 密钥扫描功能,确保代码库安全最佳实践
4:应用场景与技术价值
实际应用示例
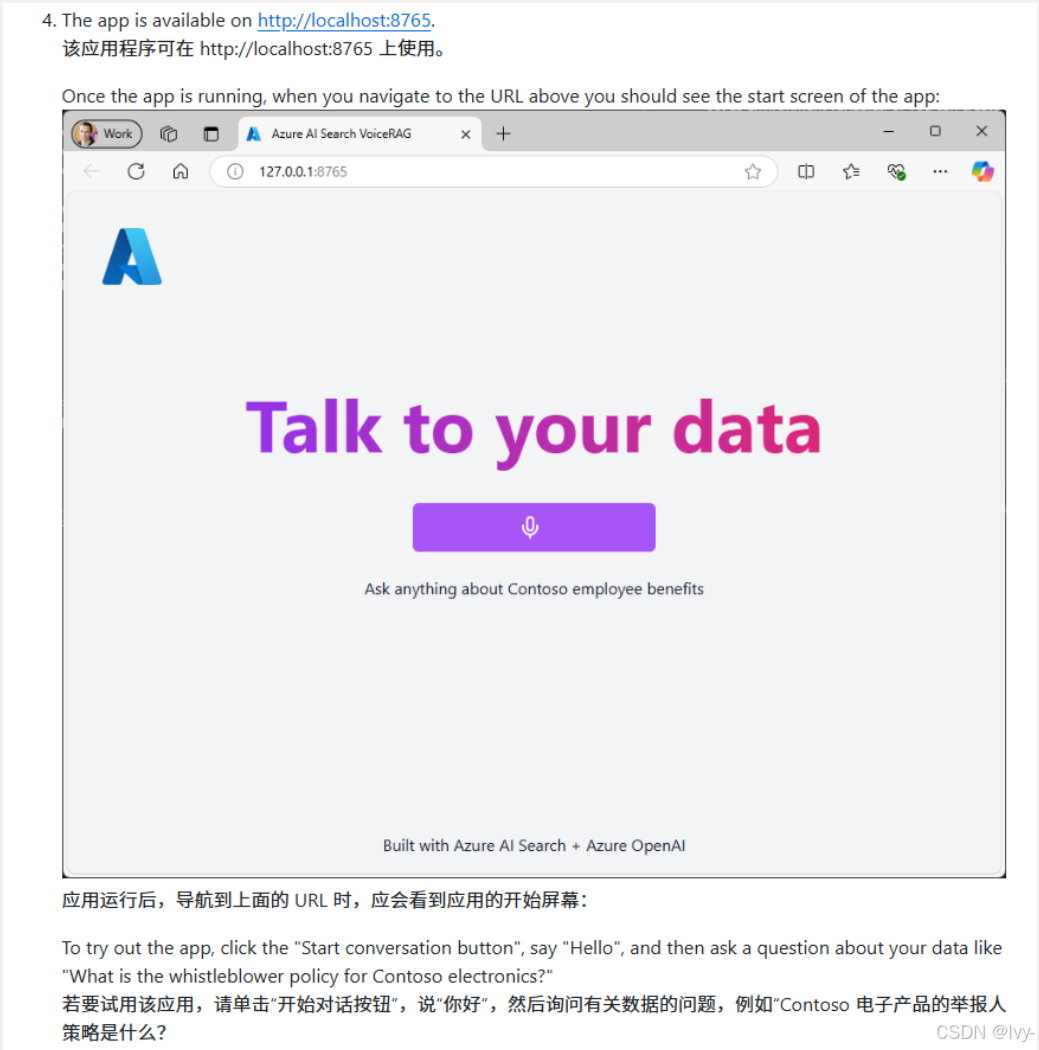
- 企业知识查询:用户可通过语音询问"Contoso electronics 的举报人政策是什么?"等企业相关问题
- 文档检索优化:将传统的文本搜索转换为自然语言对话,提高信息获取效率
- 无障碍访问:为视觉障碍用户或需要免手操作的场景提供更好的可访问性
技术创新价值
- 模式创新 :VoiceRAG 模式代表了 RAG 技术向多模态交互的重要扩展
- 用户体验提升:通过语音交互降低了技术使用门槛,提高了用户参与度
- 集成生态:展示了 Azure 生态系统中多个 AI 服务的有效整合能力
结论
VoiceRAG 应用模式代表了检索增强生成技术的重要演进,成功地将传统的文本 RAG 扩展到语音交互领域。
通过 Azure AI Search 和 GPT-4o 实时音频 API 的深度集成,该模式不仅保持了 RAG 技术在信息准确性方面的优势,还显著提升了用户交互体验的自然性和便利性。
主要技术价值:
- 交互模式创新:实现了从文本到语音的交互范式转换
- 技术集成优化:展示了多个 Azure AI 服务的有效协同
- 部署便利性:提供了完整的开发到部署工具链支持
- 成本可控性:通过灵活的资源配置选项平衡功能与成本
该项目为企业级语音 AI 应用提供了可行的技术路径,特别适用于需要结合专业知识库进行语音交互的场景。
随着语音 AI 技术的持续发展,VoiceRAG 模式有望成为下一代智能助手和知识管理系统的重要技术基础
docs:aisearch-openai-rag-audio
本项目支持与AI助手进行实时语音对话 ,该助手能基于定制知识库回答问题。
系统通过浏览器麦克风获取输入,并以音频形式播放AI响应。在生成答案前,系统会智能地从文档中检索相关信息 ,确保准确性并提供来源引用。
可视化
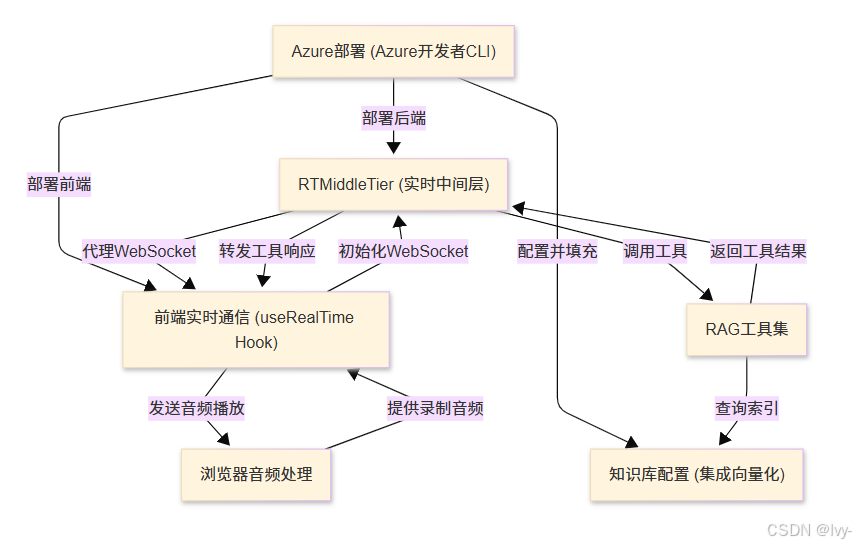
章节
第1章:知识库配置(集成向量化)
想象你拥有大量重要文档------就像一座装满书籍、报告和笔记的图书馆。如果你希望AI仅基于这个特定图书馆的信息(而非其通用互联网知识)回答问题,它如何快速找到正确答案?显然不能每次提问时都从头开始阅读每份文档
这正是"知识库配置(集成向量化)"的意义所在。它将原始文档组织成一个高效、可搜索的图书馆,使AI能够理解。
这一过程自动预处理信息,让AI能快速找到相关细节并提供准确答案。
核心问题:海量文本的智能化处理
根本问题在于计算机(以及AI)并不像人类那样天然"理解"语言,它们只处理数字。如何将文档中的文字转化为AI可搜索和理解的形式?
解决方案:集成向量化
传统检索-专栏传送: ElasticSearch
本项目通过在Azure AI Search中建立自动化系统来解决这个问题,将文档转换为强大的可搜索格式。该过程涉及几个协同工作的关键概念:
1. Azure AI Search:智能图书馆系统
将Azure AI Search视为先进的数字图书馆系统
它不仅是文件存储库,更是专为海量信息快速检索设计的服务,作为知识库的核心枢纽。
2. 索引:高级目录
在Azure AI Search中,索引如同图书馆的高级目录
与传统仅记录书名和作者的目录不同,该索引存储文档的实际内容(分解为小片段)以及捕捉语义的特殊数字"指纹"。
3. 技能集:专家级图书管理员
技能集如同一位自动处理新增文档的专家图书管理员,执行以下关键任务:
- 分块:不试图一次性概括整本书,而是将文档分解为更易管理的片段(如章节),帮助AI搜索时聚焦相关内容。
- 嵌入 :为每个文本块生成称为嵌入 的数字表示。这相当于将文本块的含义转换为独特的数字指纹。语义相似的块将具有相似的数值指纹。这些嵌入由Azure OpenAI生成。
4. 集成向量化:自动化魔法
"集成向量化"指Azure AI Search自动协调上述所有步骤。你只需将原始文档上传至存储位置(Azure Blob Storage),Azure AI Search便会自动:
- 连接文档
- 分解为小块
- 使用Azure OpenAI为每块生成数值嵌入
- 将块及其嵌入存储至搜索索引
这是将非结构化文本转化为高度可搜索、AI就绪知识库的全自动流水线。
项目中的实现
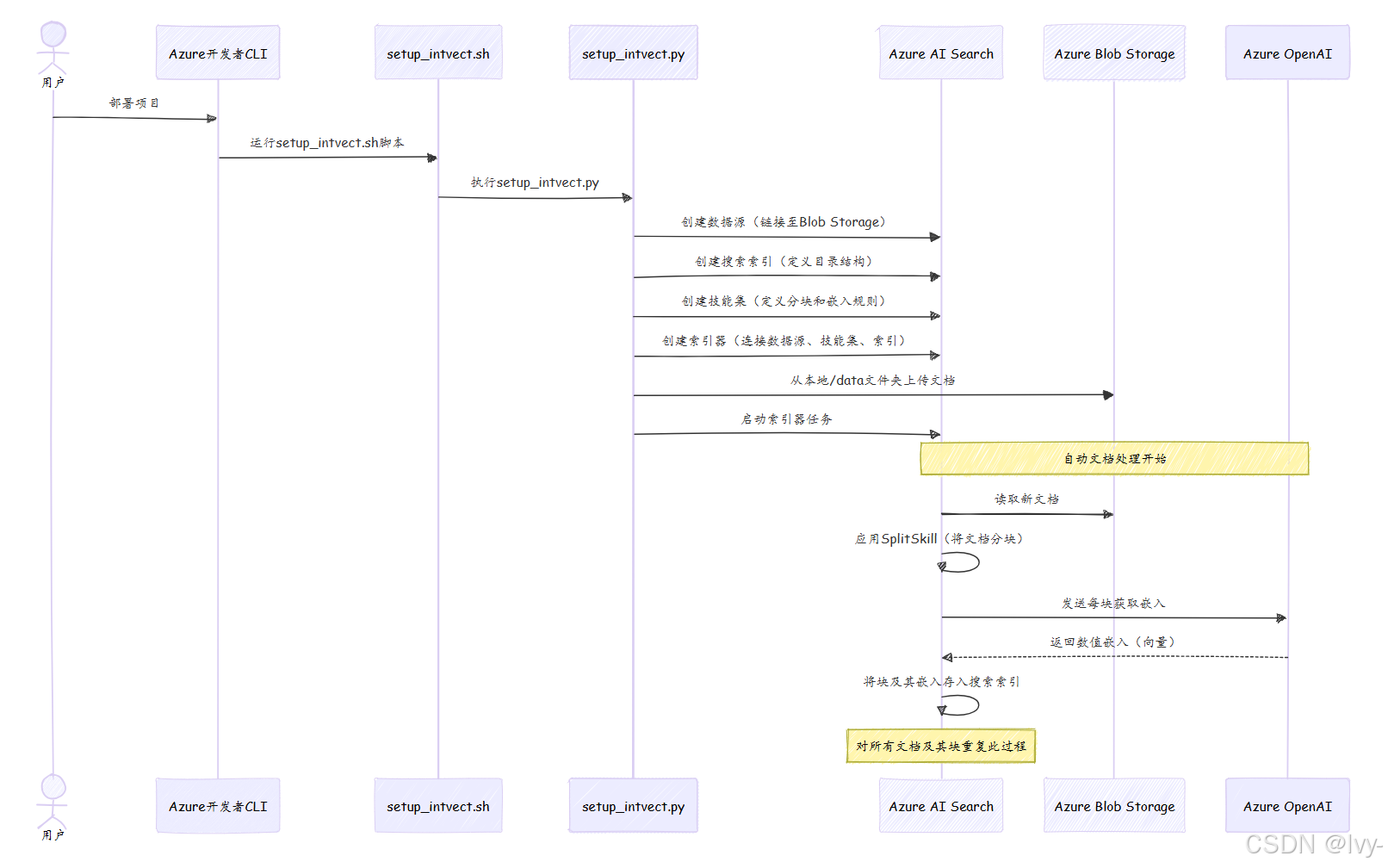
在aisearch-openai-rag-audio项目中,app/backend/setup_intvect.py脚本(由scripts/setup_intvect.sh或.ps1脚本协调)处理整个配置。部署项目时,它会定义Azure AI Search应如何处理文档并启动流程。
步骤1:加载环境变量
首先,项目需要知道Azure服务的位置及访问方式。load_azd_env()函数加载这些关键设置。
python
# app/backend/setup_intvect.py
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import subprocess
import json
def load_azd_env():
# 查找由'azd'(Azure开发者CLI)创建的'.env'文件
# 并加载其中变量(如Azure端点URL和密钥)
# 以便脚本使用
result = subprocess.run("azd env list -o json", shell=True, capture_output=True, text=True)
env_json = json.loads(result.stdout)
env_file_path = None
for entry in env_json:
if entry["IsDefault"]:
env_file_path = entry["DotEnvPath"]
if not env_file_path:
raise Exception("未找到默认azd环境文件")
load_dotenv(env_file_path, override=True) # 加载环境变量步骤2:配置Azure AI Search组件
setup_index函数(篇幅较长,分段说明)负责创建或更新Azure AI Search中的所有必要部分。
连接文档(数据源)
这部分代码告诉Azure AI Search原始文档的存储位置------具体是Azure Blob Storage容器。
python
# app/backend/setup_intvect.py(setup_index函数简化片段)
from azure.search.documents.indexes import SearchIndexerClient
from azure.search.documents.indexes.models import (
SearchIndexerDataSourceConnection, SearchIndexerDataContainer, SearchIndexerDataSourceType
)
def create_data_source(index_name, azure_search_endpoint, azure_credential, azure_storage_connection_string, azure_storage_container):
indexer_client = SearchIndexerClient(azure_search_endpoint, azure_credential)
if index_name not in [ds.name for ds in indexer_client.get_data_source_connections()]:
print(f"创建数据源连接: {index_name}")
indexer_client.create_data_source_connection(
data_source_connection=SearchIndexerDataSourceConnection(
name=index_name,
type=SearchIndexerDataSourceType.AZURE_BLOB, # 文档存储在Azure Blob Storage
connection_string=azure_storage_connection_string,
container=SearchIndexerDataContainer(name=azure_storage_container)))
else:
print(f"数据源连接 {index_name} 已存在")定义高级目录(搜索索引)
接下来定义SearchIndex的结构,即目录中每个"条目"包含的信息类型。
python
# app/backend/setup_intvect.py(setup_index函数简化片段)
from azure.search.documents.indexes import SearchIndexClient
from azure.search.documents.indexes.models import (
SearchIndex, SearchableField, SearchField, SearchFieldDataType,
VectorSearch, AzureOpenAIVectorizer, AzureOpenAIParameters, VectorSearchProfile,
SemanticSearch, SemanticConfiguration, SemanticPrioritizedFields, SemanticField
)
def create_search_index(index_name, azure_search_endpoint, azure_credential, embeddings_dimensions, openai_endpoint, openai_deployment, openai_model):
index_client = SearchIndexClient(azure_search_endpoint, azure_credential)
if index_name not in [idx.name for idx in index_client.list_indexes()]:
print(f"创建索引: {index_name}")
index_client.create_index(
SearchIndex(
name=index_name,
fields=[ # 目录中的列
SearchableField(name="chunk_id", key=True),
SearchableField(name="chunk"), # 存储实际文本块
SearchField(name="text_vector", # 存储数值嵌入
type=SearchFieldDataType.Collection(SearchFieldDataType.Single),
vector_search_dimensions=embeddings_dimensions,
vector_search_profile_name="vp", stored=True)
],
vector_search=VectorSearch( # 处理数值摘要(向量)的方式
vectorizers=[
AzureOpenAIVectorizer(name="openai_vectorizer", # 使用OpenAI创建嵌入
azure_open_ai_parameters=AzureOpenAIParameters(
resource_uri=openai_endpoint, deployment_id=openai_deployment, model_name=openai_model))
],
profiles=[VectorSearchProfile(name="vp", vectorizer="openai_vectorizer")]
),
semantic_search=SemanticSearch( # 提升自然语言查询的相关性
configurations=[SemanticConfiguration(name="default",
prioritized_fields=SemanticPrioritizedFields(content_fields=[SemanticField(field_name="chunk")]))]
)
)
)
else:
print(f"索引 {index_name} 已存在")设置专家规则(技能集)
这部分定义Skillset------对每份文档执行的自动化任务系列。
python
# app/backend/setup_intvect.py(setup_index函数简化片段)
from azure.search.documents.indexes import SearchIndexerClient
from azure.search.documents.indexes.models import (
SearchIndexerSkillset, SplitSkill, AzureOpenAIEmbeddingSkill,
InputFieldMappingEntry, OutputFieldMappingEntry,
SearchIndexerIndexProjections, SearchIndexerIndexProjectionSelector, IndexProjectionMode
)
def create_skillset(index_name, azure_search_endpoint, azure_credential, openai_endpoint, openai_deployment, openai_model, embeddings_dimensions):
indexer_client = SearchIndexerClient(azure_search_endpoint, azure_credential)
if index_name not in [sk.name for sk in indexer_client.get_skillsets()]:
print(f"创建技能集: {index_name}")
indexer_client.create_skillset(
skillset=SearchIndexerSkillset(
name=index_name,
skills=[
SplitSkill( # 技能1:将文档分页(块)
text_split_mode="pages", maximum_page_length=2000, page_overlap_length=500,
inputs=[InputFieldMappingEntry(name="text", source="/document/content")],
outputs=[OutputFieldMappingEntry(name="textItems", target_name="pages")]),
AzureOpenAIEmbeddingSkill( # 技能2:使用Azure OpenAI为每块生成嵌入
context="/document/pages/*", resource_uri=openai_endpoint,
deployment_id=openai_deployment, model_name=openai_model,
dimensions=embeddings_dimensions,
inputs=[InputFieldMappingEntry(name="text", source="/document/pages/*")],
outputs=[OutputFieldMappingEntry(name="embedding", target_name="text_vector")])
],
index_projections=SearchIndexerIndexProjections( # 处理数据存入索引的方式
selectors=[SearchIndexerIndexProjectionSelector(
target_index_name=index_name,
source_context="/document/pages/*", # 应用于每个块
mappings=[
InputFieldMappingEntry(name="chunk", source="/document/pages/*"),
InputFieldMappingEntry(name="text_vector", source="/document/pages/*/text_vector"),
InputFieldMappingEntry(name="title", source="/document/metadata_storage_name") # 文档文件名作为标题
])],
parameters=SearchIndexerIndexProjectionsParameters(projection_mode=IndexProjectionMode.SKIP_INDEXING_PARENT_DOCUMENTS)
)
)
)
else:
print(f"技能集 {index_name} 已存在")调度处理任务(索引器)
Indexer是整合数据源(文档)、技能集(处理规则)和搜索索引(存储结果)的实际任务。
python
# app/backend/setup_intvect.py(setup_index函数简化片段)
from azure.search.documents.indexes import SearchIndexerClient
from azure.search.documents.indexes.models import SearchIndexer, FieldMapping
def create_indexer(index_name, azure_search_endpoint, azure_credential):
indexer_client = SearchIndexerClient(azure_search_endpoint, azure_credential)
if index_name not in [idxer.name for idxer in indexer_client.get_indexers()]:
print(f"创建索引器: {index_name}")
indexer_client.create_indexer(
indexer=SearchIndexer(
name=index_name,
data_source_name=index_name, # 链接到存储室(数据源)
skillset_name=index_name, # 链接到图书管理规则(技能集)
target_index_name=index_name, # 链接到高级目录(搜索索引)
field_mappings=[FieldMapping(source_field_name="metadata_storage_name", target_field_name="title")]
)
)
else:
print(f"索引器 {index_name} 已存在")步骤3:上传文档并运行索引器
配置完所有组件后,最后一步是将文档导入系统并启动Indexer。
python
# app/backend/setup_intvect.py(简化片段)
import os
from azure.storage.blob import BlobServiceClient
from azure.search.documents.indexes import SearchIndexerClient
from azure.core.exceptions import ResourceExistsError
def upload_and_process_documents(indexer_name, azure_search_endpoint, azure_credential, azure_storage_endpoint, azure_storage_container):
# 1. 将本地'data'文件夹中的文档上传至Azure Blob Storage
blob_service_client = BlobServiceClient(account_url=azure_storage_endpoint, credential=azure_credential)
container_client = blob_service_client.get_container_client(azure_storage_container)
if not container_client.exists():
container_client.create_container()
existing_blobs = [blob.name for blob in container_client.list_blobs()]
for file in os.scandir("data"): # 假设'data'文件夹包含你的文档
filename = os.path.basename(file.path)
if filename not in existing_blobs:
print(f"上传文件: {filename}")
with open(file.path, "rb") as opened_file:
container_client.upload_blob(filename, opened_file, overwrite=True)
else:
print(f"文件已存在,跳过: {filename}")
# 2. 启动索引器处理新上传文档
indexer_client = SearchIndexerClient(azure_search_endpoint, azure_credential)
try:
indexer_client.run_indexer(indexer_name)
print("索引器已启动。文档将很快处理。")
except ResourceExistsError:
print("索引器已在运行,无需重启。")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# ...(先前配置调用)...
upload_and_process_documents(
indexer_name=AZURE_SEARCH_INDEX,
azure_search_endpoint=AZURE_SEARCH_ENDPOINT,
azure_credential=azure_credential,
azure_storage_endpoint=AZURE_STORAGE_ENDPOINT,
azure_storage_container=AZURE_STORAGE_CONTAINER
)整体流程(底层原理)
总结
本章学习了如何通过Azure AI Search将原始文档转化为智能、可搜索的知识库
这包括设置核心搜索索引(高级目录)、定义技能集(专家图书管理员)以使用Azure OpenAI自动分块文档并生成数值嵌入,最后通过索引器协调整个过程
这种称为集成向量化的自动化流程,使数据准备好被AI高效理解和响应。
知识库智能准备就绪后,下一步是了解AI如何实际使用该配置回答问题。在第2章:RAG工具集中,我们将探索如何从该知识库检索信息并生成有意义的响应。