hello~ 很高兴见到大家! 这次带来的是C++中关于set和map封装这部分的一些知识点,如果对你有所帮助的话,可否留下你宝贵的三连呢?
个 人 主 页 : 默|笙

文章目录
- [一、框架搭建( 如何实现红黑树的复用?)](#一、框架搭建( 如何实现红黑树的复用?))
-
-
- [1. 分析库里set与map的实现(分析RBTree的两个模板参数 Key, Value)](#1. 分析库里set与map的实现(分析RBTree的两个模板参数 Key, Value))
- [2. 分析第三个模板参数KeyofValue](#2. 分析第三个模板参数KeyofValue)
-
- 二、迭代器的实现
-
- [1. 普通迭代器iterator的实现](#1. 普通迭代器iterator的实现)
-
- [1.1 先搭一个基本框架](#1.1 先搭一个基本框架)
- [1.2 operator++与operator- -实现](#1.2 operator++与operator- -实现)
-
- operator++
- [operator- -](#operator- -)
- [2. const_iterator的实现](#2. const_iterator的实现)
- 三、operator[]的实现
- 四、源代码
实现set和map的封装主要有以下步骤:
- 实现红黑树。<红黑树博客>
- 封装set和map框架,解决KeyOfValue。
- 实现iterator。
- 实现const_iterator。
- 实现key不支持修改的问题。
- 实现operator[]。
一、框架搭建( 如何实现红黑树的复用?)
set和map的底层都是红黑树,但由于存储元素的差异(一个只存储key,一个既存储key又存储value),我们要么创造出两棵稍微不一样的红黑树,或者是改变红黑树的结构,使其能完美匹配上set和map。库里面采用了后者。
1. 分析库里set与map的实现(分析RBTree的两个模板参数 Key, Value)
库里面RBTree的实现一共有5个模板参数,分别是 Key,Value,KeyOfValue,Compare和Alloc,我们主要分析前三个模板参数的作用)。Compare是控制比较规则的仿函数类型,Alloc是内存池。
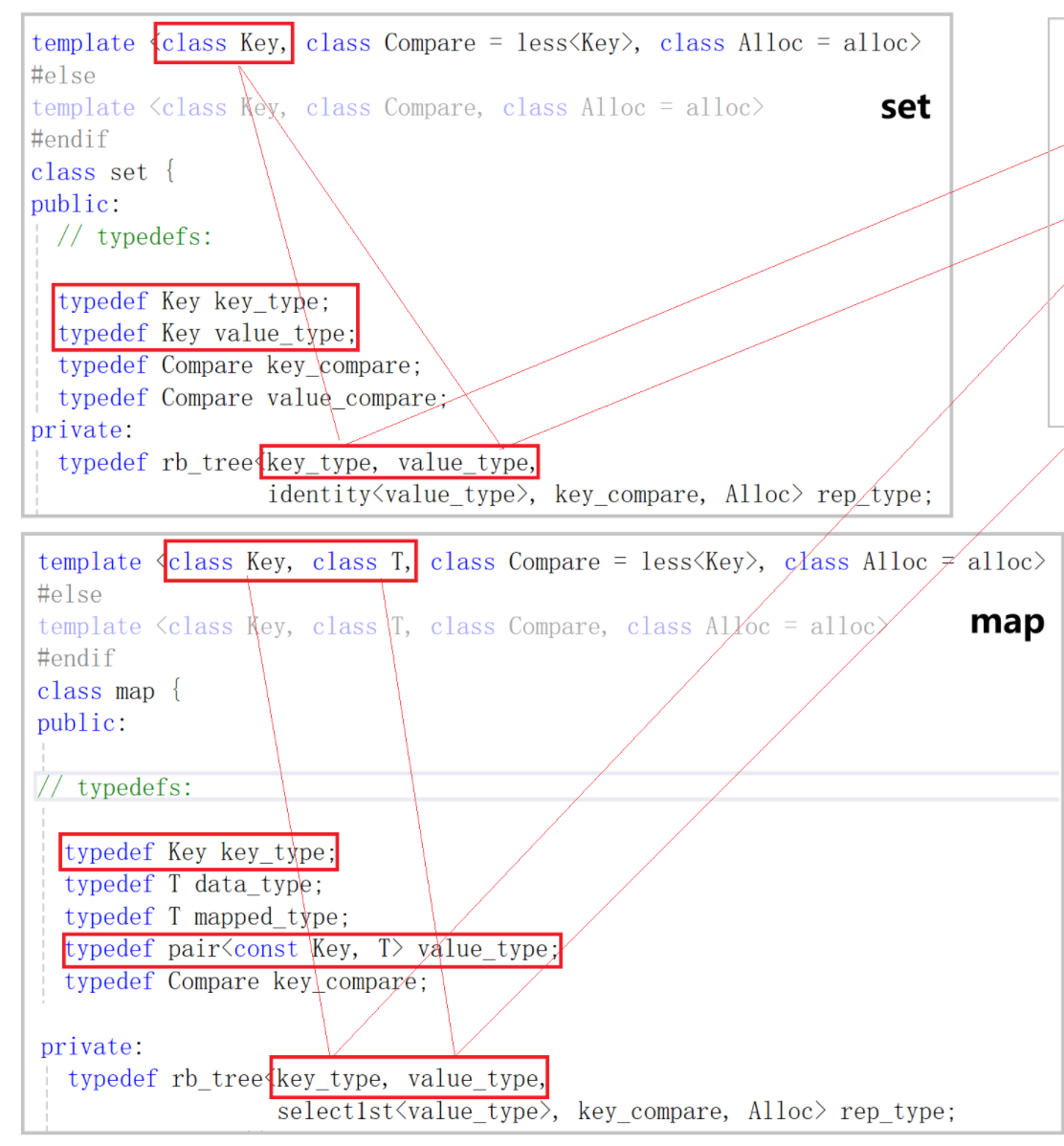
- 对于set,它只有一个用来接收key类型的模板参数Key,并把Key同一个类型命名为key_type与value_type。
- 对于map,它有两个分别用来接收key和 value类型的模板参数Key和T。将Key重命名为key_type,将pair<const Key, T> 重命名为value_type。
- 它们复用同一棵红黑树,将4个类型传给红黑树。
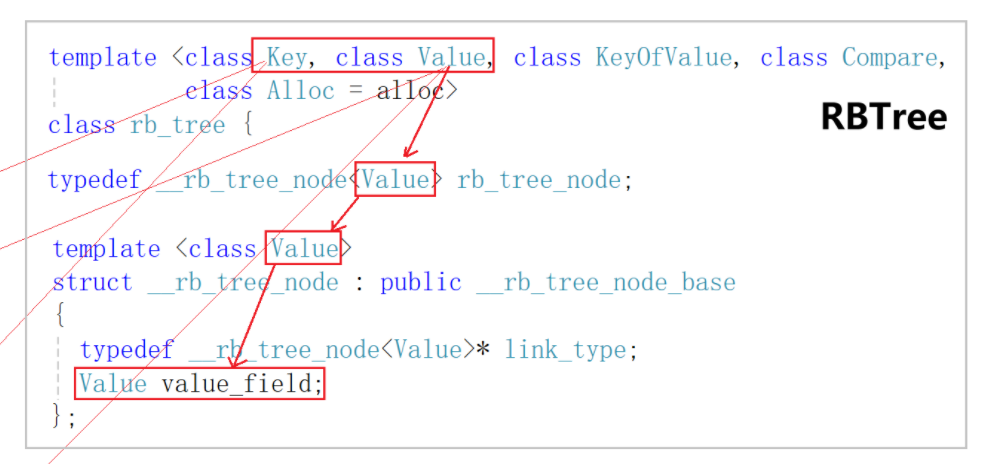
- 重点观察Value这个模板参数,它的类型是节点所存储的元素的类型。set传过来的是Key类型,map传过来的是pair<const Key, T>类型。利用模板来控制红黑树所存储的类型,满足set和map不同的存储需求。
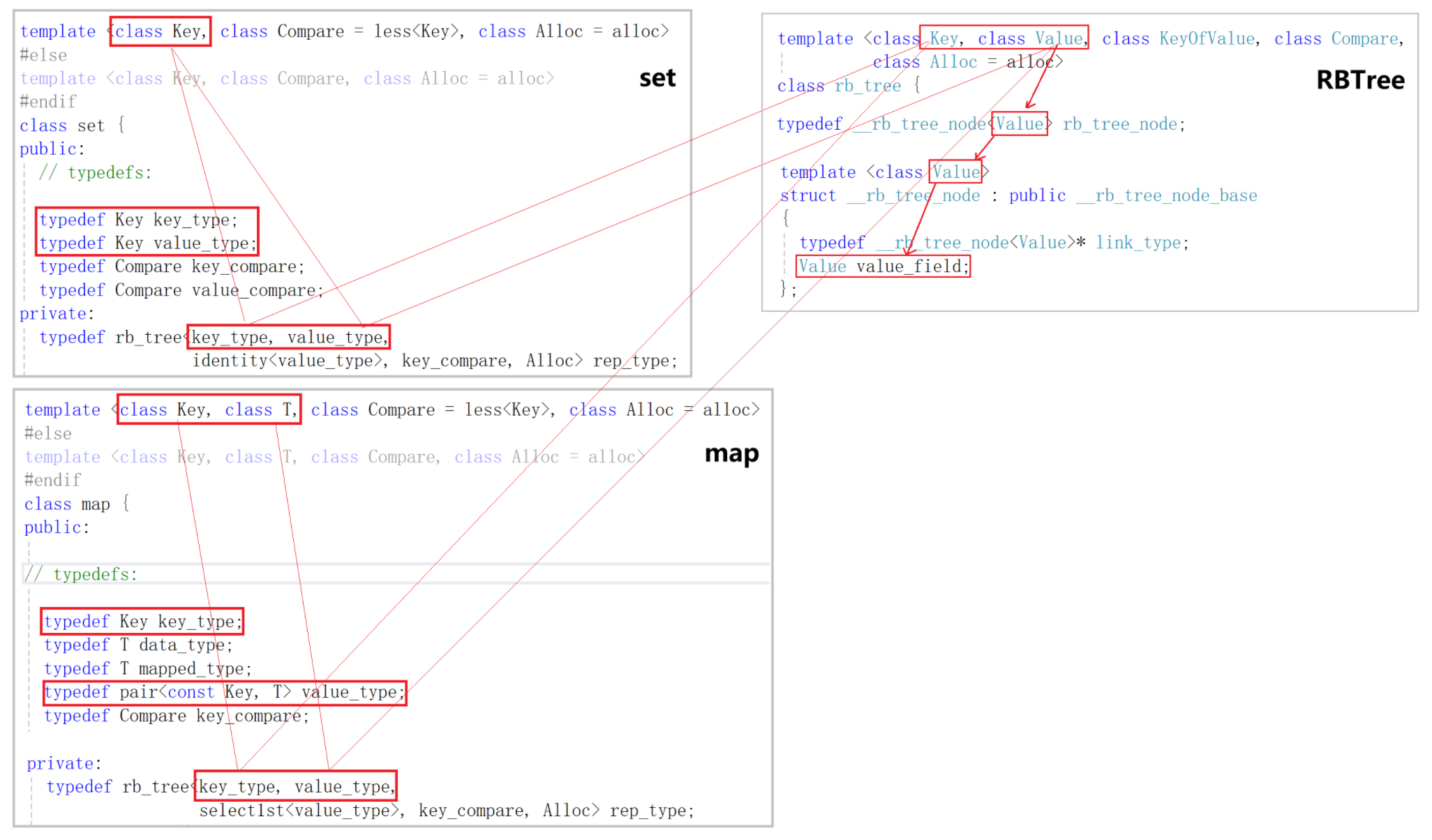
- 我们传递给map的只是key和value的类型,而map要存储的是pair<const key, value>类型(实现key和value的绑定,const实现不可修改以后再加),所以我们需要做一个加工。
- 既然有了接收存储元素类型的Value类型,而为什么不删除第一个用来单独存储key类型的模板参数Key,似乎用不上它,这个以后就能知道了。
2. 分析第三个模板参数KeyofValue
我们在进行插入时,需要根据key的大小来找到插入的位置,而由于set和map存储类型的不同,set直接用Value(key)类型的元素就好,而map则需要取出Value(pair<const key, value>)里面的key值来找到插入的位置。
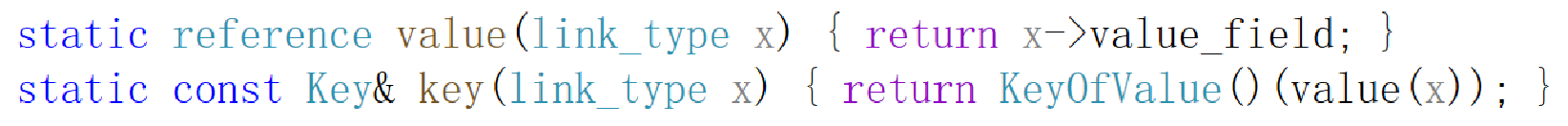
- 而KeyOfValue这个模板参数就是用来接收功能为取出key的仿函数类型,KeyOfValue是匿名对象。可以参照库里的实现大胆猜测。
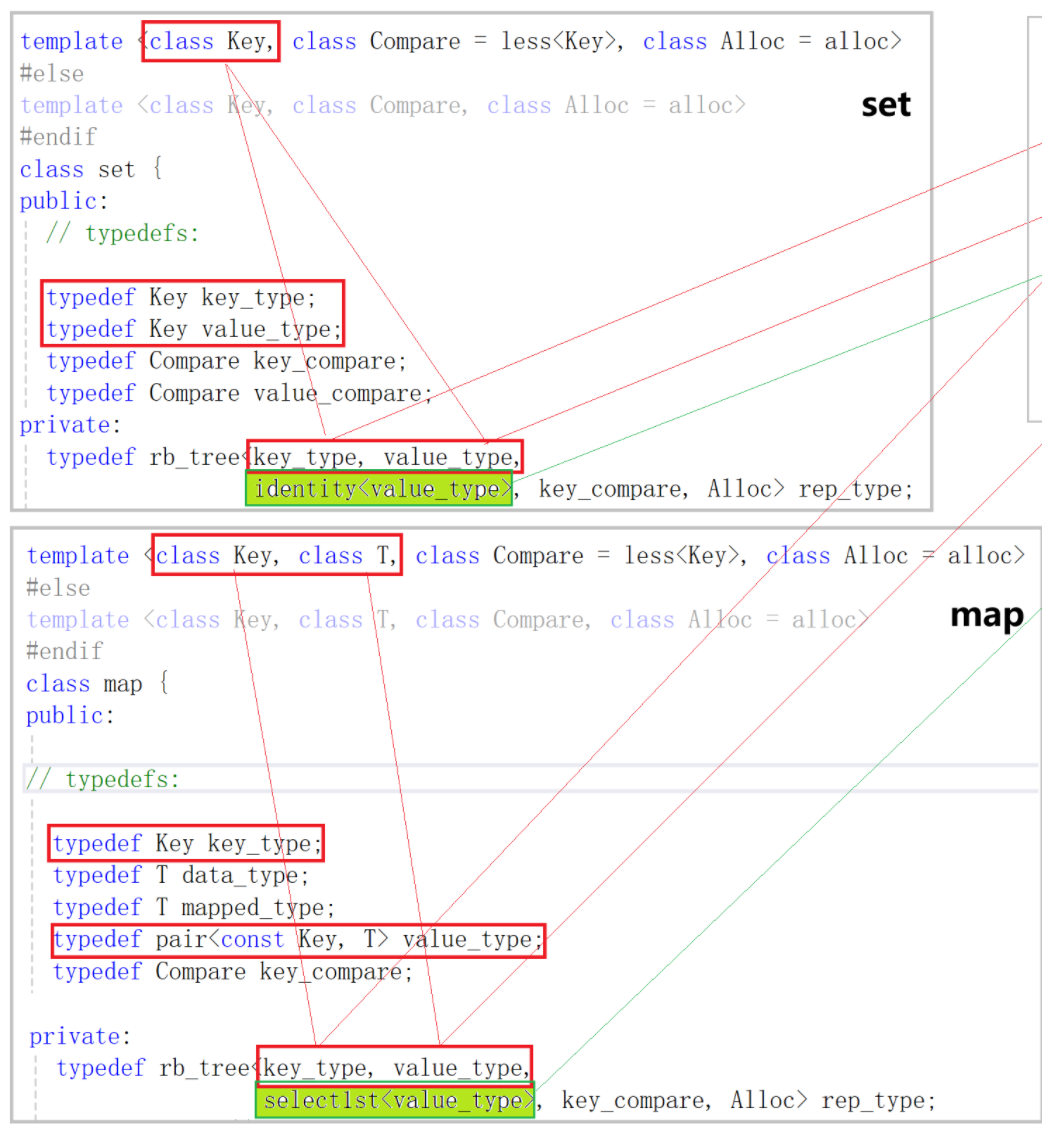
- set里面传给KeyOfValue的是一个ideneity<value_type>类型的仿函数,identity在这里是本身的意思,它的功能就是取出key值就是value_type类型的元素它本身,而map里面传给KeyOfValue的是一个select1st<value_type>类型的仿函数,它的功能就是取出key值就是value_type类型元素里的第一个值。
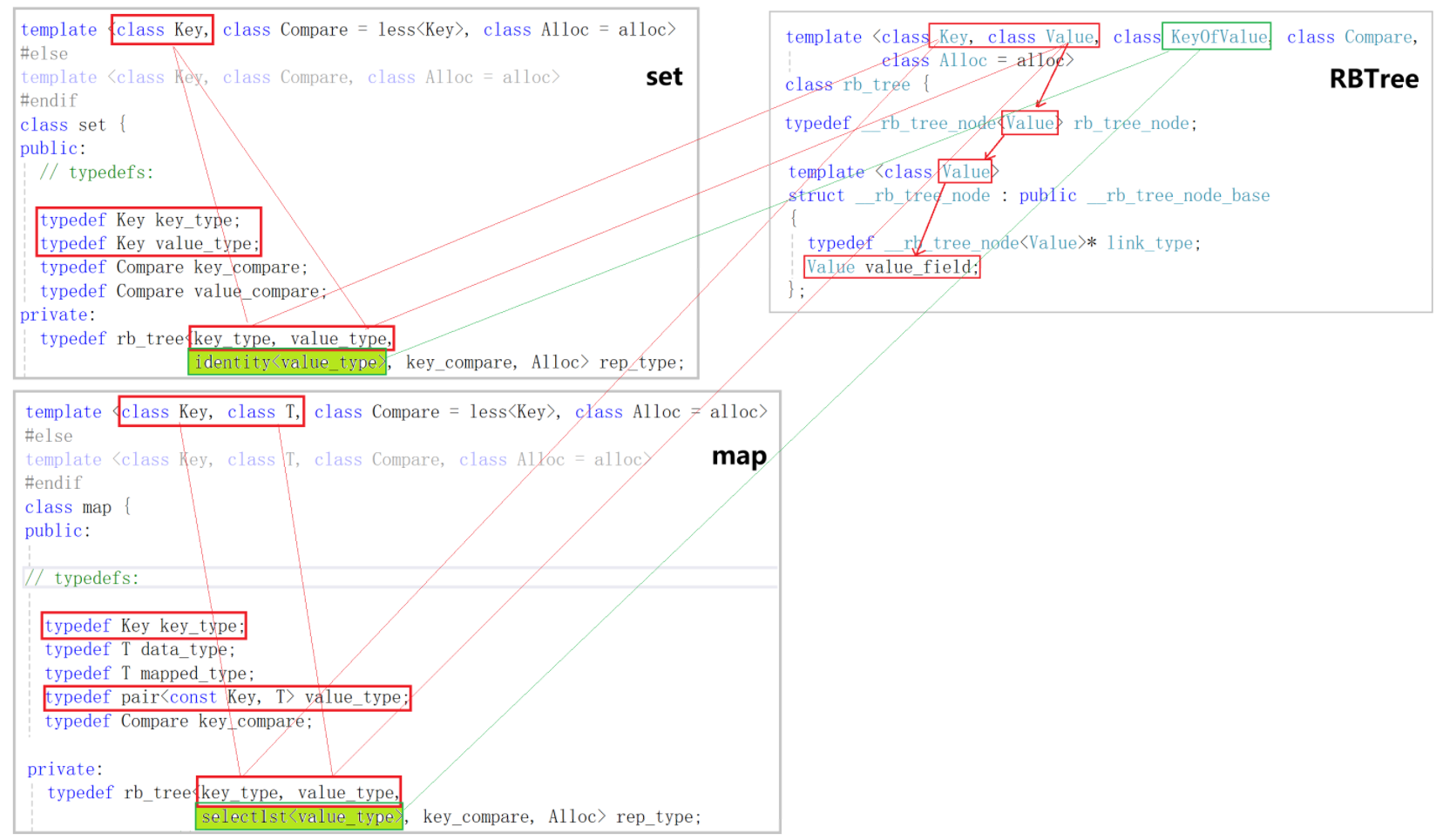
- 所以我们在set和map里面的实现里面都要实现一个仿函数用来传递给KeyOfValue。
set:
cpp
namespace mosheng {
template<class K>
class identity
{
public:
K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
template<class Key>
class set
{
typedef RBTree<Key, Key, identity<Key>> rbType;
};
}map:
cpp
namespace mosheng {
template<class K, class KV>
class select1st
{
public:
K& operator()(const KV& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
template<class Key, class Value>
class map
{
typedef RBTree<Key, std::pair<Key, Value>, select1st<Key, std::pair<Key, Value>> rbType;
};
}- 不要忘了对应的红黑树的修改,主要是修改insert和find还有对应的模板参数,去用KeyOfValue提取key。然后框架搭建完毕。
cpp
#pragma once
enum Colour
{
RED,
BLACK
};
template<class Value>
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode(Value& kv)
:_kv(kv)
, _left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _parent(nullptr)
{
};
Value _kv;
RBTreeNode<Value>* _left;
RBTreeNode<Value>* _right;
RBTreeNode<Value>* _parent;
Colour _col = RED;
};
template<class Key, class Value, class KeyOfValue>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<Value> Node;
public:
bool Insert(Value& kv)
{
//处理空树的情况
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(kv);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
//找到要插入的位置
else
{
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur)
{
if (KeyOfValue()(kv) < KeyOfValue()(cur->_kv))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (KeyOfValue()(kv) > KeyOfValue()(cur->_kv))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
//插入新节点
cur = new Node(kv);
if (KeyOfValue()(parent->_kv) > KeyOfValue()(kv))
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
//父节点为红色的情况下需要进行处理
if (parent->_col == RED)
{
while (parent && parent->_col == RED)
{
//记录节点
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
Node* uncle = nullptr;
if (grandfather->_left == parent)
{
uncle = grandfather->_right;
}
else
{
uncle = grandfather->_left;
}
//uncle为红色的情况
//仅变色
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
uncle->_col = parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
//更新
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
//uncle为黑色或为空的情况
else
{
//右旋转
if (grandfather->_left == parent && parent->_left == cur)
{
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
break;
}
//左旋转
else if (grandfather->_right == parent && parent->_right == cur)
{
RotateL(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
break;
}//左右双旋
else if (grandfather->_left == parent && parent->_right == cur)
{
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
break;
}
//右左双旋
else
{
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
//处理根节点颜色
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
Node* Find(const Key& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (KeyOfValue()(cur->_kv) < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (KeyOfValue()(cur->_kv) > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
Node* _root = nullptr;
};-
可以使用匿名对象,但推荐构造一个对象kof来使用仿函数KefOfValue。
-
为什么保留第一个Key的模板参数在find函数上就有所体现:我们需要Key的类型,因为要根据Key的类型来寻找。KefOfValue无法提取出类型。
二、迭代器的实现
迭代器的实现也就是在节点指针的基础之上做封装操作,并重载一些运算符。map和set的迭代器是双向迭代器,关键是需要实现++和--的重载。
1. 普通迭代器iterator的实现
1.1 先搭一个基本框架
cpp
template<class Value>
class TreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<Value> Node;
typedef TreeIterator<Value> Self;
public:
TreeIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
Value& operator* ()
{
return _node->_kv;
}
Value* operator->()
{
return &(_node->_kv);
}
bool operator==(const Self& s)const
{
return _node == s->_node;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)const
{
return _node != s->_node;
}
private:
Node* _node;
};1.2 operator++与operator- -实现
operator++
我们希望达成的效果是++从当前节点移动到下一个按照中序遍历的节点。- -则是反过来。++只需要知道当前节点的下一个节点是哪一个。
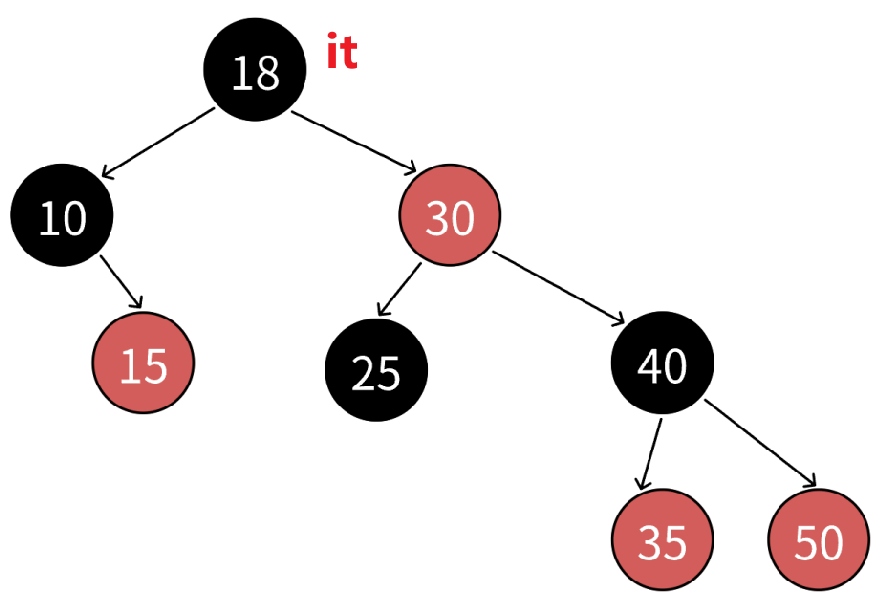
- 现在我们有一棵红黑树,若当前节点为18,那么我们希望节点18++后的节点是节点25,节点25++后的节点是节点30,以此类推。
- 首先看节点10,它不是叶子节点,++后需要跳到节点15,也就是它的右节点,这是因为它的右子树不为空,按照中序遍历顺序,可以认为它的左子树是遍历完成的,只需要看它的右子树就行。所以首先要判断当前节点的右子树是否为空 。再来看节点30,++后需要跳到节点35,是其右子树的最左节点。若不为空就会跳到节点30的左孩子节点40,节点40的左子树是还未访问过的,所以需要访问它的左子树,一直到最左端。
-
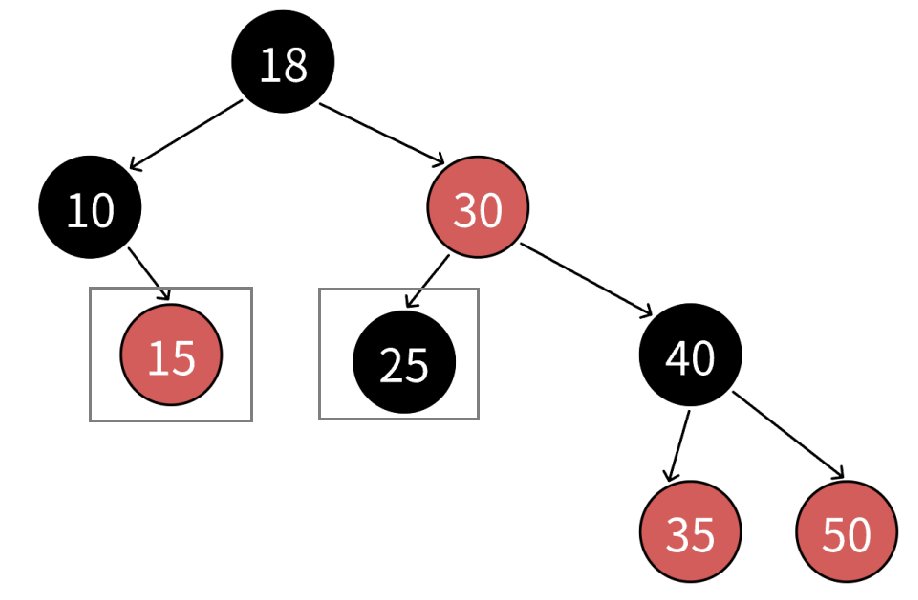
我们再来看节点15和节点25,它们都是叶子节点,节点15++后需要跳到节点18,这是其parent的_parent所指向的节点。节点25++后需要跳到节点30,也就是它的parent节点。为什么会有这样的区别?可以发现:节点15是节点10的右孩子,而节点25是节点30的左孩子,由于左节点的值<当前节点的值<右节点的值,左中右也是中序遍历的顺序,所以对于当前节点15,可以将它的父亲节点节点10以及父亲节点的左子树看作是遍历完成的,而++之后节点15也将访问完,即代表以节点10为根节点的这棵子树就遍历完了,接下来就需要回溯,回溯到节点10,节点10是节点18的左孩子,代表以节点18为根节点的树左子树已经遍历完成,按照中序遍历顺序,下一个就是节点18;对于节点25,它直接是节点30的左孩子,代表30还未遍历,接下来遍历节点30。
-
所以可以总结为:
- 判断当前节点的右节点是否为空,不为空则迭代器内部指针指向当前节点右子树的最左节点,为空则进行下一步。
- 判断当前节点是其父节点的左孩子还是右孩子,如果是左孩子,++之后就跳到其父亲节点,迭代器内部指针指向其父亲节点;
- 如果是右孩子,就需要回溯到其父亲点,再判断父节点是其_parent节点的左孩子还是右孩子,如此往复(循环),直到回溯的节点为其_parent节点的左孩子或_parent为空(说明整棵树已经访问完了,根节点的_parent是为空的),迭代器内部指针指向当前回溯节点父节点。
- 返回解引用之后的this指针。
- 所以对于红黑树iterator的起点begin和终点end:起点指向最左节点,终点为空。或者也可以增加一个头节点,其左指针指向最左节点,其右指针指向最右节点,父亲指针指向根节点,这个头节点为终点。这里实现第一种。
++重载实现
cpp
Self& operator++()
{
if (_node->_right)
{
Node* min = _node;
while (min->left)
{
min = min->_left
}
_node = min;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && parent->_right == cur)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}operator- -
相较于operator++,operator- - 的思路就是++的逆思路。
- 判断当前节点是否存在左子树,若存在左子树,存在则迭代器内部指针指向左子树最右节点。不存在则继续之后的步骤。
- 判断当前节点是其父节点的左孩子还是右孩子,如果是右孩子则迭代器内部指针指向其父节点。
- 如果是左孩子,则回溯到parent,再判断parent是其_parent节点的左孩子还是右孩子,如此往复(循环),直到回溯节点是其父节点的右孩子或其父节点为最左节点。最后迭代器内部指针指向回溯节点的父节点。
- 返回解引用之后的this指针。
- 有一点需要注意的是,由于我们将终点设置为nullptr,如果希望空指针- - 之后指向最右节点的话,就需要做特殊处理。
- operator- - 的实现相较于operator++要更加复杂,要么通过实现头节点来实现(推荐),也可以在迭代器里面保存根节点指针来实现。这里就不实现了。
2. const_iterator的实现
我们通过模板来实现对迭代器的复用,这样就不用单独再实现一个跟iterator十分有九分像的const_iterator迭代器了。
cpp
template<class Value, class Ref, class Ptr>
class TreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<Value> Node;
typedef TreeIterator<Value> Self;
public:
TreeIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
Ref operator* ()
{
return _node->_kv;
}
Ref operator* ()const
{
return _node->_kv;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &(_node->_kv);
}
Ptr operator->()const
{
return &(_node->_kv);
}
bool operator==(const Self& s)const
{
return _node == s._node;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)const
{
return _node != s._node;
}
//++重载
Self& operator++()
{
if (_node->_right)
{
Node* min = _node->_right;
while (min->_left)
{
min = min->_left;
}
_node = min;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && parent->_right == cur)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
private:
Node* _node;
};
template<class Key, class Value, class KeyOfValue>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<Value> Node;
typedef TreeIterator<Value, Value&, Value*> iterator;
typedef TreeIterator<Value, const Value&, const Value*> const_iterator;
public:
iterator begin()
{
Node* it = _root;
while (it->left)
{
it = it->_left;
}
return iterator(it);
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
Node* it = _root;
while (it->left)
{
it = it->_left;
}
return iterator(it);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr);
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return iterator(nullptr);
}
然后实现Key不可修改的问题。在set和map头文件里传递要存储的类型的时候加上const就行。
三、operator[]的实现
就是在insert的基础之上进行实现,是insert的复用。
set:
cpp
#pragma once
#include "RBTree.h"
namespace mosheng {
template<class K>
class identity
{
public:
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
template<class Key>
class set
{
typedef RBTree<Key, const Key, identity<Key>> rbType;
public:
typedef typename RBTree<Key, const Key, identity<Key>>::Iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<Key, Key, identity<Key>>::const_Iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return _t.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const Key& key)
{
return _t.Insert(key);
}
private:
rbType _t;
};
}map:
cpp
#pragma once
#include "RBTree.h"
namespace mosheng {
template<class K, class KV>
class select1st
{
public:
const K& operator()(const KV& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
template<class Key, class Value>
class map
{
typedef RBTree<Key, pair<const Key, Value>, select1st<Key, pair<const Key, Value>>> rbType;
public:
typedef typename RBTree<Key, pair<const Key, Value>, select1st<Key, pair<const Key, Value>>>::Iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree < Key, pair<const Key, Value>, select1st<Key, pair<const Key, Value>>>::const_Iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return _t.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<Key, Value>& kv)
{
return _t.Insert(kv);
}
Value& operator[](const Key& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = _t.Insert({key, Value()});
return ret.first->second;
}
private:
rbType _t;
};
}四、源代码
Myset.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include "RBTree.h"
namespace mosheng {
template<class K>
class identity
{
public:
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
template<class Key>
class set
{
typedef RBTree<Key, const Key, identity<Key>> rbType;
public:
typedef typename RBTree<Key, const Key, identity<Key>>::Iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<Key, const Key, identity<Key>>::const_Iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return _t.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const Key& key)
{
return _t.Insert(key);
}
private:
rbType _t;
};
}Mymap.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include "RBTree.h"
namespace mosheng {
template<class K, class KV>
class select1st
{
public:
const K& operator()(const KV& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
template<class Key, class Value>
class map
{
typedef RBTree<Key, pair<const Key, Value>, select1st<Key, pair<Key, Value>>> rbType;
public:
typedef typename RBTree<Key, pair<const Key, Value>, select1st<Key, pair<const Key, Value>>>::Iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree < Key, pair<const Key, Value>, select1st<Key, pair<const Key, Value>>>::const_Iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return _t.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<Key, Value>& kv)
{
return _t.Insert(kv);
}
Value& operator[](const Key& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = _t.Insert({key, Value()});
return ret.first->second;
}
private:
rbType _t;
};
}RBTree.h
cpp
#pragma once
enum Colour
{
RED,
BLACK
};
template<class Value>
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode(const Value& kv)
:_kv(kv)
, _left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _parent(nullptr)
{
};
Value _kv;
RBTreeNode<Value>* _left;
RBTreeNode<Value>* _right;
RBTreeNode<Value>* _parent;
Colour _col = RED;
};
template<class Value, class Ref, class Ptr>
class TreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<Value> Node;
typedef TreeIterator<Value, Ref, Ptr> Self;
public:
TreeIterator(Node* node = nullptr)
:_node(node)
{}
Ref operator* ()
{
return _node->_kv;
}
Ref operator* ()const
{
return _node->_kv;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &(_node->_kv);
}
Ptr operator->()const
{
return &(_node->_kv);
}
bool operator==(const Self& s)const
{
return _node == s._node;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)const
{
return _node != s._node;
}
//++重载
Self& operator++()
{
if (_node->_right)
{
Node* min = _node->_right;
while (min->_left)
{
min = min->_left;
}
_node = min;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && parent->_right == cur)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
private:
Node* _node;
};
template<class Key, class Value, class KeyOfValue>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<Value> Node;
public:
typedef TreeIterator<Value, Value&, Value*> Iterator;
typedef TreeIterator<Value, const Value&, const Value*> const_Iterator;
Iterator begin()
{
Node* it = _root;
while (it->_left)
{
it = it->_left;
}
return Iterator(it);
}
const_Iterator begin()const
{
Node* it = _root;
while (it->_left)
{
it = it->_left;
}
return Iterator(it);
}
Iterator end()
{
return Iterator(nullptr);
}
const_Iterator end()const
{
return Iterator(nullptr);
}
pair<Iterator, bool> Insert(const Value& kv)
{
//处理空树的情况
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(kv);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return { Iterator(_root), true };
}
//找到要插入的位置
else
{
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur)
{
if (KeyOfValue()(kv) < KeyOfValue()(cur->_kv))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (KeyOfValue()(kv) > KeyOfValue()(cur->_kv))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return { Iterator(cur), false };
}
}
//插入新节点
cur = new Node(kv);
Node* newnode = cur;
if (KeyOfValue()(parent->_kv) > KeyOfValue()(kv))
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
//父节点为红色的情况下需要进行处理
if (parent->_col == RED)
{
while (parent && parent->_col == RED)
{
//记录节点
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
Node* uncle = nullptr;
if (grandfather->_left == parent)
{
uncle = grandfather->_right;
}
else
{
uncle = grandfather->_left;
}
//uncle为红色的情况
//仅变色
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
uncle->_col = parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
//更新
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
//uncle为黑色或为空的情况
else
{
//右旋转
if (grandfather->_left == parent && parent->_left == cur)
{
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
break;
}
//左旋转
else if (grandfather->_right == parent && parent->_right == cur)
{
RotateL(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
break;
}//左右双旋
else if (grandfather->_left == parent && parent->_right == cur)
{
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
break;
}
//右左双旋
else
{
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
break;
}
}
}
}
//处理根节点颜色
_root->_col = BLACK;
return { Iterator(newnode), true };
}
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
bool IsBalance()
{
if (_root && _root->_col == RED)
{
return false;
}
int leftMost = 0;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_col == BLACK)
{
leftMost++;
}
cur = cur->_left;
}
return _check(_root, 0, leftMost);
}
int Height()
{
return _Height(_root);
}
int Size()
{
return _Size(_root);
}
Node* Find(const Key& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (KeyOfValue()(cur->_kv) < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (KeyOfValue()(cur->_kv) > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
private:
int _Size(Node* root)
{
return root == nullptr ? 0 : _Size(root->_left) + _Size(root->_right) + 1;
}
int _Height(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
int leftHeight = _Height(root->_left);
int rightHeight = _Height(root->_right);
return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
}
bool _check(Node* cur, int BlackNum, const int leftMost)
{
if (cur == nullptr)
{
if (BlackNum != leftMost)
{
return false;
cout << "黑色节点的数量不相等" << endl;
}
else
return true;
}
if (cur->_col == RED && cur->_parent && cur->_parent->_col == RED)
{
cout << cur->_kv.first << "->" << "连续的红色节点" << endl;
return false;
}
if (cur->_col == BLACK)
{
BlackNum++;
}
return _check(cur->_left, BlackNum, leftMost) && _check(cur->_right, BlackNum, leftMost);
}
void _InOrder(const Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_kv.first << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
//记录节点
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;
//改变指针
parent->_left = subLR;
subL->_right = parent;
if (parentParent == nullptr)
{
_root = subL;
subL->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (parentParent->_left == parent)
{
parentParent->_left = subL;
}
else
{
parentParent->_right = subL;
}
subL->_parent = parentParent;
}
//避免subLR = nullptr出现空指针解引用的情况
if (subLR)
{
subLR->_parent = parent;
}
parent->_parent = subL;
}
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
//记录节点
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;
//改变指针指向
subR->_left = parent;
parent->_right = subRL;
if (parentParent == nullptr)
{
_root = subR;
subR->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (parentParent->_left == parent)
{
parentParent->_left = subR;
}
else
{
parentParent->_right = subR;
}
subR->_parent = parentParent;
}
if (subRL)
{
subRL->_parent = parent;
}
parent->_parent = subR;
}
Node* _root = nullptr;
};今天的分享就到此结束啦,如果对读者朋友们有所帮助的话,可否留下宝贵的三连呢~~
让我们共同努力, 一起走下去!