引言:为什么 MongoDB 成为现代数据存储的首选?
在大数据和云计算爆发的今天,传统关系型数据库在面对海量非结构化数据时逐渐力不从心。MongoDB 作为 NoSQL 数据库的代表,凭借其灵活的文档模型、强大的横向扩展能力和卓越的读写性能,已成为众多企业的核心数据存储解决方案。
据 DB-Engines 2024 年最新排名,MongoDB 在全球数据库流行度中位列第五,超越了 PostgreSQL、Redis 等知名数据库,在 NoSQL 领域更是稳居第一。从初创公司到财富 500 强企业,MongoDB 正在重塑数据存储的未来。
本文将深入剖析 MongoDB 的核心应用场景,通过 30 + 实战案例带你掌握从设计到优化的全流程技能,无论你是刚入门的开发者还是需要进阶的架构师,都能从中获得实用价值。
一、MongoDB 核心概念与底层原理
1.1 文档模型:超越关系型的灵活存储
MongoDB 采用 BSON(Binary JSON)作为数据存储格式,这是一种类似 JSON 的二进制格式,支持更多数据类型(如日期、二进制数据等)。与关系型数据库的表结构相比,文档模型具有天然优势:
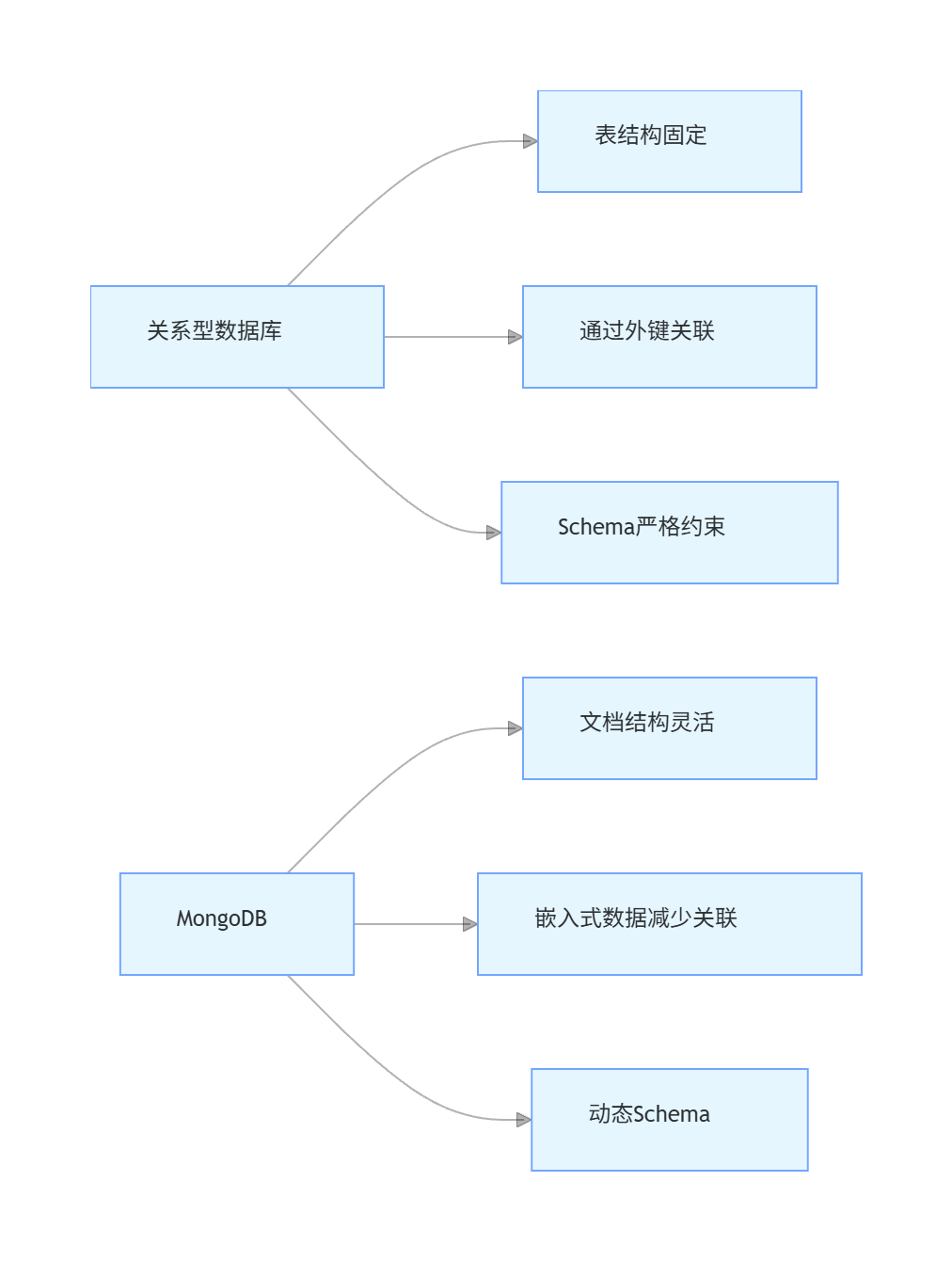
核心区别:关系型数据库需要预先定义表结构,而 MongoDB 的集合(Collection)中的文档(Document)可以有不同的字段,无需统一结构。这种灵活性使得 MongoDB 特别适合需求频繁变化的业务场景。
1.2 数据存储结构解析
MongoDB 的基本存储单元是文档,多个文档组成集合,多个集合组成数据库。其逻辑结构如下:
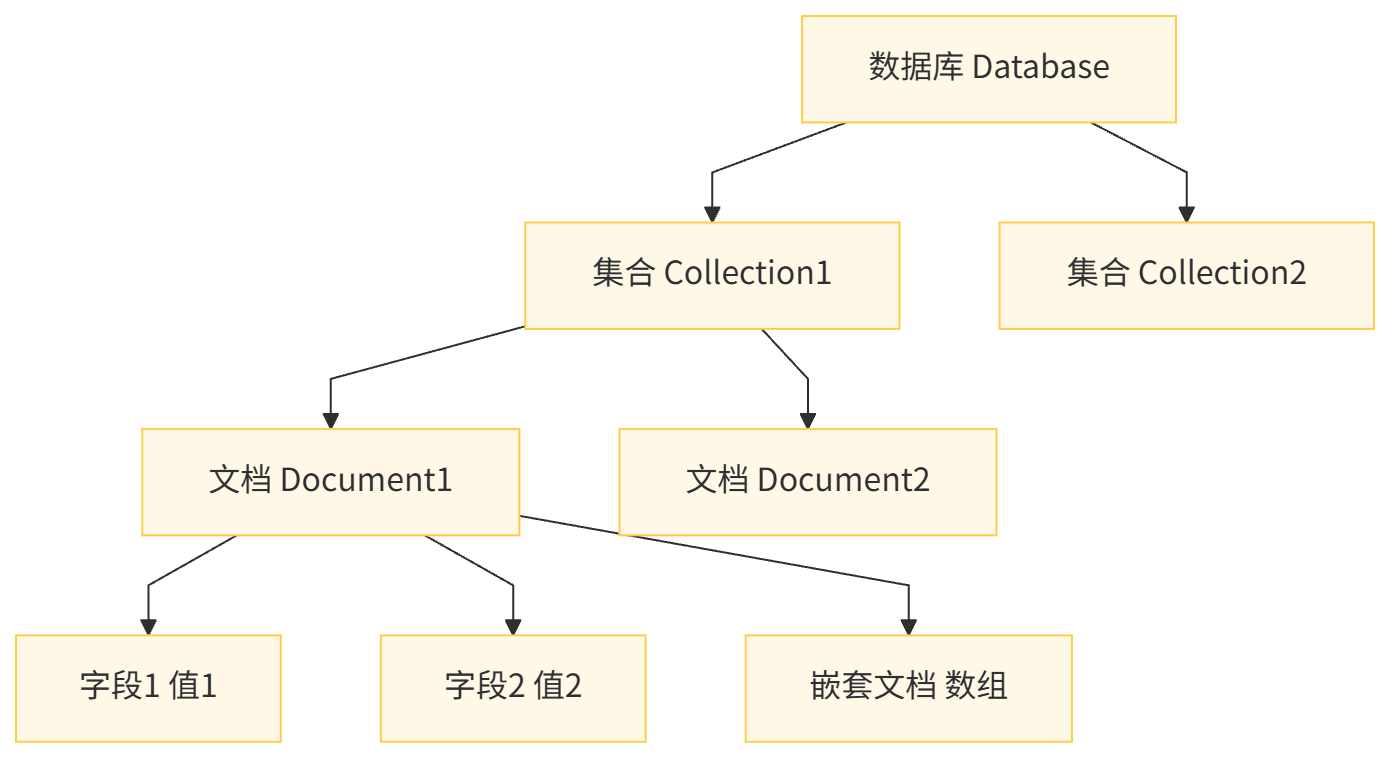
文档示例(一个用户文档):
{
"_id": ObjectId("60d21b4667d0d8992e610c85"),
"username": "johndoe",
"email": "john@example.com",
"age": 30,
"address": {
"street": "123 Main St",
"city": "New York",
"zipcode": "10001"
},
"hobbies": ["reading", "hiking", "coding"],
"createdAt": ISODate("2023-11-01T12:00:00Z")
}注意:每个文档都必须有一个
_id字段作为唯一标识,若未显式指定,MongoDB 会自动生成一个 ObjectId 类型的值。ObjectId 是一个 12 字节的标识符,包含时间戳、机器标识、进程 ID 和计数器,确保了分布式环境下的唯一性。
1.3 索引机制:高性能查询的基石
MongoDB 的索引机制与关系型数据库类似,但支持更多类型的索引,以适应复杂的查询场景:
- 单字段索引:最基本的索引类型,加速单个字段的查询
- 复合索引:包含多个字段的索引,遵循 "最左前缀原则"
- 多键索引:针对数组字段的索引,支持对数组元素的高效查询
- 地理空间索引:用于地理位置查询,如附近的餐厅、商店等
- 文本索引:支持全文搜索功能
- 哈希索引:对字段值进行哈希处理,适合等值查询,不支持范围查询
索引工作原理:MongoDB 使用 B 树作为索引的数据结构,这是一种自平衡的树状结构,能够保持数据有序,并允许在对数时间内进行插入、删除和查找操作。与关系型数据库不同的是,MongoDB 的索引可以直接包含文档数据(覆盖索引),进一步提升查询性能。
二、MongoDB 典型应用场景深度解析
2.1 内容管理系统(CMS)
场景特点:内容结构多样(文章、图片、视频等),字段经常变化,需要快速迭代。
传统数据库痛点:固定表结构难以适应多样内容类型,频繁的 schema 变更需要复杂的迁移操作。
MongoDB 解决方案:
- 使用灵活的文档模型存储不同类型的内容
- 嵌入式文档减少关联查询
- 文本索引支持全文搜索功能
实战案例:博客系统设计
import com.alibaba.fastjson2.JSONObject;
import com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection;
import com.mongodb.client.model.Filters;
import com.mongodb.client.model.Indexes;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.bson.Document;
import org.springframework.util.ObjectUtils;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 博客文章服务类
* 处理文章的CRUD操作及搜索功能
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
public class BlogPostService {
private final MongoCollection<Document> postCollection;
public BlogPostService(MongoCollection<Document> postCollection) {
this.postCollection = postCollection;
// 创建文本索引,支持全文搜索
this.postCollection.createIndex(Indexes.text("title", "content", "tags"));
// 创建创建时间索引,加速按时间查询
this.postCollection.createIndex(Indexes.ascending("createdAt"));
}
/**
* 创建博客文章
* @param title 文章标题
* @param content 文章内容
* @param authorId 作者ID
* @param tags 标签列表
* @param metadata 元数据(如阅读时间、字数等)
* @return 新创建文章的ID
*/
public String createPost(String title, String content, String authorId,
List<String> tags, JSONObject metadata) {
// 参数校验
if (!org.springframework.util.StringUtils.hasText(title)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("文章标题不能为空");
}
if (!org.springframework.util.StringUtils.hasText(content)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("文章内容不能为空");
}
if (!org.springframework.util.StringUtils.hasText(authorId)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("作者ID不能为空");
}
Document post = new Document();
post.append("title", title)
.append("content", content)
.append("authorId", authorId)
.append("tags", tags)
.append("metadata", metadata)
.append("createdAt", Date.from(LocalDateTime.now().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toInstant()))
.append("updatedAt", Date.from(LocalDateTime.now().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toInstant()))
.append("status", "PUBLISHED")
.append("views", 0);
postCollection.insertOne(post);
log.info("创建博客文章成功,ID: {}", post.getObjectId("_id").toHexString());
return post.getObjectId("_id").toHexString();
}
/**
* 全文搜索文章
* @param keyword 搜索关键词
* @param page 页码(从1开始)
* @param size 每页条数
* @return 搜索结果列表
*/
public List<Document> searchPosts(String keyword, int page, int size) {
if (!org.springframework.util.StringUtils.hasText(keyword)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("搜索关键词不能为空");
}
if (page < 1) {
page = 1;
}
if (size < 1 || size > 100) {
size = 20;
}
return postCollection.find(Filters.text(keyword))
.sort(new Document("score", new Document("$meta", "textScore")))
.skip((page - 1) * size)
.limit(size)
.into(com.google.common.collect.Lists.newArrayList());
}
/**
* 获取指定作者的文章
* @param authorId 作者ID
* @param page 页码
* @param size 每页条数
* @return 文章列表
*/
public List<Document> getPostsByAuthor(String authorId, int page, int size) {
if (!org.springframework.util.StringUtils.hasText(authorId)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("作者ID不能为空");
}
return postCollection.find(Filters.eq("authorId", authorId))
.sort(Filters.desc("createdAt"))
.skip((page - 1) * size)
.limit(size)
.into(com.google.common.collect.Lists.newArrayList());
}
}设计优势:
- 同一集合可以存储不同类型的内容(文章、视频、图片),通过
type字段区分 - 元数据
metadata字段可以灵活存储不同类型内容的特有属性,无需修改结构 - 文本索引支持跨字段全文搜索,比传统数据库的全文搜索更灵活
- 嵌入式结构减少了关联查询,提升读取性能
2.2 实时数据分析与监控
场景特点:高写入吞吐量,数据格式多变,需要实时聚合分析。
传统数据库痛点:写入性能瓶颈,复杂的聚合查询性能差,难以水平扩展。
MongoDB 解决方案:
- 高写入性能支持每秒数万条数据插入
- 聚合管道(Aggregation Pipeline)支持复杂的数据处理和分析
- 分片集群支持海量数据存储和查询
实战案例:用户行为分析系统
import com.mongodb.client.AggregateIterable;
import com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection;
import com.mongodb.client.model.Accumulators;
import com.mongodb.client.model.Aggregates;
import com.mongodb.client.model.Filters;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.bson.Document;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 用户行为分析服务
* 处理用户行为数据的收集和分析
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
public class UserBehaviorAnalysisService {
private final MongoCollection<Document> behaviorCollection;
public UserBehaviorAnalysisService(MongoCollection<Document> behaviorCollection) {
this.behaviorCollection = behaviorCollection;
// 创建复合索引,优化按时间和用户ID的查询
this.behaviorCollection.createIndex(new Document("userId", 1).append("timestamp", -1));
// 创建行为类型和时间的索引,优化统计查询
this.behaviorCollection.createIndex(new Document("action", 1).append("timestamp", -1));
}
/**
* 记录用户行为
* @param userId 用户ID
* @param action 行为类型(如:click, view, purchase等)
* @param details 行为详情(如:点击的按钮,查看的商品ID等)
* @param metadata 元数据(如:设备信息,IP地址等)
*/
public void recordUserBehavior(String userId, String action,
Map<String, Object> details, Map<String, Object> metadata) {
if (!org.springframework.util.StringUtils.hasText(userId)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("用户ID不能为空");
}
if (!org.springframework.util.StringUtils.hasText(action)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("行为类型不能为空");
}
Document behavior = new Document();
behavior.append("userId", userId)
.append("action", action)
.append("timestamp", Date.from(LocalDateTime.now().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toInstant()))
.append("details", details)
.append("metadata", metadata);
behaviorCollection.insertOne(behavior);
log.debug("记录用户行为成功,用户ID: {}, 行为: {}", userId, action);
}
/**
* 统计指定时间段内的用户行为分布
* @param startTime 开始时间
* @param endTime 结束时间
* @return 行为类型及其发生次数
*/
public List<Document> getActionDistribution(LocalDateTime startTime, LocalDateTime endTime) {
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(startTime) || ObjectUtils.isEmpty(endTime)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("开始时间和结束时间不能为空");
}
if (startTime.isAfter(endTime)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("开始时间不能晚于结束时间");
}
Date start = Date.from(startTime.atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toInstant());
Date end = Date.from(endTime.atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toInstant());
List<Document> pipeline = new ArrayList<>();
// 匹配时间范围内的数据
pipeline.add(Aggregates.match(Filters.and(
Filters.gte("timestamp", start),
Filters.lt("timestamp", end)
)));
// 按行为类型分组并计数
pipeline.add(Aggregates.group("$action",
Accumulators.sum("count", 1),
Accumulators.first("firstOccurrence", "$timestamp"),
Accumulators.last("lastOccurrence", "$timestamp")
));
// 按计数降序排序
pipeline.add(Aggregates.sort(new Document("count", -1)));
AggregateIterable<Document> result = behaviorCollection.aggregate(pipeline);
List<Document> resultList = com.google.common.collect.Lists.newArrayList(result);
log.info("统计行为分布完成,时间范围: {} 至 {}, 结果数量: {}",
startTime, endTime, resultList.size());
return resultList;
}
/**
* 分析用户转化漏斗
* @param steps 转化步骤列表(如:["view", "add_to_cart", "purchase"])
* @param startTime 开始时间
* @param endTime 结束时间
* @return 漏斗分析结果,包含每个步骤的用户数和转化率
*/
public List<Document> analyzeConversionFunnel(List<String> steps,
LocalDateTime startTime, LocalDateTime endTime) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(steps) || steps.size() < 2) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("转化步骤至少需要2个");
}
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(startTime) || ObjectUtils.isEmpty(endTime)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("开始时间和结束时间不能为空");
}
Date start = Date.from(startTime.atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toInstant());
Date end = Date.from(endTime.atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toInstant());
List<Document> pipeline = new ArrayList<>();
// 匹配时间范围内且行为在步骤中的数据
pipeline.add(Aggregates.match(Filters.and(
Filters.gte("timestamp", start),
Filters.lt("timestamp", end),
Filters.in("action", steps)
)));
// 按用户ID分组,收集其所有行为及时间
pipeline.add(Aggregates.group("$userId",
Accumulators.push("actions", new Document("action", "$action").append("time", "$timestamp"))
));
// 处理每个用户的行为序列,判断是否完成转化步骤
Document processUserActions = new Document("$let", new Document()
.append("vars", new Document("sortedActions",
new Document("$sortArray", new Document()
.append("input", "$actions")
.append("sortBy", new Document("time", 1))
)
))
.append("in", new Document("actionSequence",
new Document("$map", new Document()
.append("input", "$sortedActions")
.append("as", "a")
.append("in", "$$a.action")
)
))
);
pipeline.add(Aggregates.addFields(new Document("processed", processUserActions)));
// 匹配完成了所有步骤的用户
Document matchAllSteps = new Document();
for (int i = 0; i < steps.size(); i++) {
String step = steps.get(i);
matchAllSteps.append("$expr", new Document("$and", com.google.common.collect.Lists.newArrayList(
new Document("$in", com.google.common.collect.Lists.newArrayList(step, "$processed.actionSequence"))
)));
}
pipeline.add(Aggregates.match(matchAllSteps));
// 计算每个步骤的转化率(简化版)
pipeline.add(Aggregates.group(null,
Accumulators.sum("totalUsers", 1)
));
AggregateIterable<Document> result = behaviorCollection.aggregate(pipeline);
List<Document> resultList = com.google.common.collect.Lists.newArrayList(result);
log.info("漏斗分析完成,步骤: {}, 结果数量: {}", steps, resultList.size());
return resultList;
}
}设计优势:
- 无 schema 约束,可灵活记录不同类型的用户行为及详情
- 聚合管道支持复杂的数据分析,无需将数据导出到专门的分析工具
- 高写入性能适合处理海量用户行为数据
- 可通过分片将数据分布到多个节点,支持 PB 级数据存储
2.3 物联网(IoT)数据存储
场景特点:海量设备产生的时序数据,高写入低查询,数据按时间分区。
传统数据库痛点:无法高效处理高并发写入,时序数据查询性能差,存储成本高。
MongoDB 解决方案:
- 时间序列集合(Time Series Collections)优化时序数据存储
- 自动过期数据(TTL 索引)降低存储成本
- 高写入性能支持百万级设备并发上报
实战案例:智能设备监控系统
import com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection;
import com.mongodb.client.model.Filters;
import com.mongodb.client.model.Indexes;
import com.mongodb.client.model.TimeSeriesOptions;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.bson.Document;
import org.springframework.util.ObjectUtils;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 物联网设备数据服务
* 处理设备数据的收集、查询和分析
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
public class IoTDataService {
private final MongoCollection<Document> deviceDataCollection;
/**
* 初始化时间序列集合,专门用于存储时序数据
* @param collectionName 集合名称
*/
public IoTDataService(MongoCollection<Document> database, String collectionName) {
// 检查集合是否存在
if (!database.listCollectionNames().into(com.google.common.collect.Lists.newArrayList())
.contains(collectionName)) {
// 创建时间序列集合选项
TimeSeriesOptions timeSeriesOptions = new TimeSeriesOptions("timestamp")
.metaField("deviceId") // 设备ID作为元数据字段
.granularity(TimeSeriesOptions.Granularity.MINUTES); // 数据粒度为分钟
// 创建时间序列集合
database.createCollection(collectionName, new com.mongodb.client.model.CreateCollectionOptions()
.timeSeriesOptions(timeSeriesOptions));
log.info("创建时间序列集合成功: {}", collectionName);
}
this.deviceDataCollection = database.getCollection(collectionName);
// 创建TTL索引,自动删除30天前的数据
this.deviceDataCollection.createIndex(
Indexes.ascending("timestamp"),
new com.mongodb.client.model.IndexOptions()
.expireAfter(30 * 24 * 60 * 60L, java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit.SECONDS)
);
}
/**
* 记录设备数据
* @param deviceId 设备ID
* @param metrics 指标数据(如:温度、湿度、压力等)
* @param timestamp 数据产生时间
*/
public void recordDeviceData(String deviceId, Map<String, Double> metrics, LocalDateTime timestamp) {
if (!org.springframework.util.StringUtils.hasText(deviceId)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("设备ID不能为空");
}
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(metrics)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("指标数据不能为空");
}
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(timestamp)) {
timestamp = LocalDateTime.now();
}
Document data = new Document();
data.append("deviceId", deviceId)
.append("timestamp", Date.from(timestamp.atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toInstant()))
.append("metrics", metrics);
// 批量插入优化(实际应用中可使用批量插入)
deviceDataCollection.insertOne(data);
log.debug("记录设备数据成功,设备ID: {}, 时间: {}", deviceId, timestamp);
}
/**
* 批量记录设备数据
* @param deviceDataList 设备数据列表
*/
public void batchRecordDeviceData(List<Document> deviceDataList) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(deviceDataList)) {
log.warn("批量记录设备数据时,数据列表为空");
return;
}
deviceDataCollection.insertMany(deviceDataList);
log.info("批量记录设备数据成功,数量: {}", deviceDataList.size());
}
/**
* 查询设备指定时间范围内的指标数据
* @param deviceId 设备ID
* @param metricName 指标名称(如:temperature)
* @param startTime 开始时间
* @param endTime 结束时间
* @param interval 时间间隔(分钟),用于数据降采样
* @return 指标数据列表,包含时间和值
*/
public List<Document> queryDeviceMetric(String deviceId, String metricName,
LocalDateTime startTime, LocalDateTime endTime,
int interval) {
if (!org.springframework.util.StringUtils.hasText(deviceId)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("设备ID不能为空");
}
if (!org.springframework.util.StringUtils.hasText(metricName)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("指标名称不能为空");
}
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(startTime) || ObjectUtils.isEmpty(endTime)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("开始时间和结束时间不能为空");
}
if (interval <= 0) {
interval = 5; // 默认5分钟间隔
}
Date start = Date.from(startTime.atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toInstant());
Date end = Date.from(endTime.atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toInstant());
// 构建聚合管道
List<Document> pipeline = com.google.common.collect.Lists.newArrayList();
// 匹配条件:设备ID和时间范围
pipeline.add(new Document("$match", new Document("$and", com.google.common.collect.Lists.newArrayList(
new Document("deviceId", deviceId),
new Document("timestamp", new Document("$gte", start).append("$lte", end))
))));
// 按时间间隔分组,计算每个间隔的平均值
pipeline.add(new Document("$group", new Document()
.append("_id", new Document(
"$dateTrunc", new Document()
.append("date", "$timestamp")
.append("unit", "minute")
.append("binSize", interval)
))
.append("avgValue", new Document("$avg", " $metrics." + metricName))
.append("count", new Document("$sum", 1))
));
// 按时间排序
pipeline.add(new Document("$sort", new Document("_id", 1)));
// 格式化输出
pipeline.add(new Document("$project", new Document()
.append("time", "$_id")
.append("avgValue", 1)
.append("count", 1)
.append("_id", 0)
));
return com.google.common.collect.Lists.newArrayList(
deviceDataCollection.aggregate(pipeline)
);
}
/**
* 查询设备的异常数据(超出正常范围的指标)
* @param deviceId 设备ID
* @param metricName 指标名称
* @param minThreshold 最小值阈值
* @param maxThreshold 最大值阈值
* @param hours 过去几小时
* @return 异常数据列表
*/
public List<Document> queryAnomalyData(String deviceId, String metricName,
Double minThreshold, Double maxThreshold,
int hours) {
if (hours <= 0) {
hours = 24; // 默认查询过去24小时
}
LocalDateTime endTime = LocalDateTime.now();
LocalDateTime startTime = endTime.minusHours(hours);
Date start = Date.from(startTime.atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toInstant());
Date end = Date.from(endTime.atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toInstant());
// 构建查询条件
Document filter = new Document("$and", com.google.common.collect.Lists.newArrayList(
new Document("deviceId", deviceId),
new Document("timestamp", new Document("$gte", start).append("$lte", end))
));
// 添加指标范围条件
Document metricFilter = new Document();
if (minThreshold != null) {
metricFilter.append("$lt", minThreshold);
}
if (maxThreshold != null) {
metricFilter.append("$gt", maxThreshold);
}
if (!metricFilter.isEmpty()) {
filter.get("$and", List.class).add(
new Document("metrics." + metricName, metricFilter)
);
}
return com.google.common.collect.Lists.newArrayList(
deviceDataCollection.find(filter)
.sort(new Document("timestamp", -1))
.projection(new Document("deviceId", 1)
.append("timestamp", 1)
.append("metrics." + metricName, 1)
.append("_id", 0))
);
}
}设计优势:
- 时间序列集合针对时序数据进行了特殊优化,比普通集合节省约 50% 的存储空间
- TTL 索引自动删除过期数据,降低存储成本
- 按设备 ID 和时间分区,大幅提升查询性能
- 聚合管道支持实时数据降采样和分析,适合监控仪表盘展示
2.4 电商平台商品管理
场景特点:商品类型多样,属性差异大,需要支持复杂查询和快速迭代。
传统数据库痛点:表结构难以适配多样商品类型,大量的关联查询影响性能。
MongoDB 解决方案:
- 文档模型支持多样商品属性
- 复合索引优化多条件查询
- 地理位置索引支持 "附近的商品" 等场景
实战案例:电商商品管理系统
import com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection;
import com.mongodb.client.model.Filters;
import com.mongodb.client.model.Indexes;
import com.mongodb.client.model.geojson.Point;
import com.mongodb.client.model.geojson.Position;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.bson.Document;
import org.springframework.util.ObjectUtils;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 电商商品服务
* 处理商品的CRUD、搜索和推荐
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
public class ProductService {
private final MongoCollection<Document> productCollection;
public ProductService(MongoCollection<Document> productCollection) {
this.productCollection = productCollection;
// 创建复合索引:分类+价格,优化按分类筛选并按价格排序的查询
this.productCollection.createIndex(Indexes.compoundIndex(
Indexes.ascending("category"),
Indexes.ascending("price")
));
// 创建文本索引:名称+描述+标签,支持商品搜索
this.productCollection.createIndex(Indexes.text(
"name", "description", "tags"
));
// 创建地理位置索引,支持按位置搜索
this.productCollection.createIndex(Indexes.geo2dsphere("location"));
// 创建创建时间索引,优化新品查询
this.productCollection.createIndex(Indexes.descending("createdAt"));
}
/**
* 创建商品
* @param name 商品名称
* @param description 商品描述
* @param category 商品分类
* @param price 商品价格
* @param attributes 商品属性(不同类型商品有不同属性)
* @param tags 商品标签
* @param location 商品存放位置(经纬度)
* @return 商品ID
*/
public String createProduct(String name, String description, String category,
BigDecimal price, Map<String, Object> attributes,
List<String> tags, double longitude, double latitude) {
// 参数校验
if (!org.springframework.util.StringUtils.hasText(name)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("商品名称不能为空");
}
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(price) || price.compareTo(BigDecimal.ZERO) <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("商品价格必须大于0");
}
if (!org.springframework.util.StringUtils.hasText(category)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("商品分类不能为空");
}
Document product = new Document();
product.append("name", name)
.append("description", description)
.append("category", category)
.append("price", price)
.append("attributes", attributes)
.append("tags", tags)
.append("stock", 0) // 初始库存为0
.append("sales", 0) // 初始销量为0
.append("rating", 0.0) // 初始评分
.append("reviewCount", 0) // 初始评论数
.append("location", new Document(
"type", "Point"
).append("coordinates", new double[]{longitude, latitude}))
.append("createdAt", Date.from(LocalDateTime.now().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toInstant()))
.append("updatedAt", Date.from(LocalDateTime.now().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toInstant()))
.append("status", "ACTIVE");
productCollection.insertOne(product);
String productId = product.getObjectId("_id").toHexString();
log.info("创建商品成功,ID: {}", productId);
return productId;
}
/**
* 商品高级搜索
* @param keyword 搜索关键词
* @param category 商品分类(null表示不限制)
* @param minPrice 最低价格(null表示不限制)
* @param maxPrice 最高价格(null表示不限制)
* @param attributes 属性筛选(如:{"brand": "Apple", "storage": "128GB"})
* @param sortField 排序字段
* @param sortDirection 排序方向(1:升序,-1:降序)
* @param page 页码
* @param size 每页条数
* @return 商品列表
*/
public List<Document> searchProducts(String keyword, String category,
BigDecimal minPrice, BigDecimal maxPrice,
Map<String, Object> attributes,
String sortField, int sortDirection,
int page, int size) {
// 构建查询条件
List<Document> filters = com.google.common.collect.Lists.newArrayList();
// 关键词筛选
if (org.springframework.util.StringUtils.hasText(keyword)) {
filters.add(new Document("$text", new Document("$search", keyword)));
}
// 分类筛选
if (org.springframework.util.StringUtils.hasText(category)) {
filters.add(new Document("category", category));
}
// 价格范围筛选
if (minPrice != null || maxPrice != null) {
Document priceFilter = new Document();
if (minPrice != null) {
priceFilter.append("$gte", minPrice);
}
if (maxPrice != null) {
priceFilter.append("$lte", maxPrice);
}
filters.add(new Document("price", priceFilter));
}
// 属性筛选
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(attributes)) {
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : attributes.entrySet()) {
filters.add(new Document("attributes." + entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()));
}
}
// 组合查询条件
Document query = new Document();
if (!filters.isEmpty()) {
query.append("$and", filters);
}
// 构建排序条件
Document sort = new Document();
if (org.springframework.util.StringUtils.hasText(sortField)) {
sort.append(sortField, sortDirection);
} else {
// 默认按评分降序排序
sort.append("rating", -1);
}
// 分页处理
if (page < 1) {
page = 1;
}
if (size < 1 || size > 100) {
size = 20;
}
int skip = (page - 1) * size;
// 执行查询
return com.google.common.collect.Lists.newArrayList(
productCollection.find(query)
.sort(sort)
.skip(skip)
.limit(size)
);
}
/**
* 查找附近的商品
* @param longitude 经度
* @param latitude 纬度
* @param maxDistance 最大距离(米)
* @param category 商品分类(null表示不限制)
* @param limit 最大结果数
* @return 附近的商品列表,按距离排序
*/
public List<Document> findNearbyProducts(double longitude, double latitude,
double maxDistance, String category,
int limit) {
if (maxDistance <= 0) {
maxDistance = 5000; // 默认5公里
}
if (limit <= 0 || limit > 100) {
limit = 20;
}
// 构建地理位置查询
Document geoQuery = new Document("$nearSphere", new Document(
"$geometry", new Document(
"type", "Point"
).append("coordinates", new double[]{longitude, latitude})
).append("$maxDistance", maxDistance));
// 构建查询条件
Document query = new Document("location", geoQuery);
// 添加分类筛选
if (org.springframework.util.StringUtils.hasText(category)) {
query.append("category", category);
}
// 执行查询并计算距离
List<Document> pipeline = com.google.common.collect.Lists.newArrayList();
pipeline.add(new Document("$match", query));
pipeline.add(new Document("$addFields", new Document(
"distance", new Document("$geoDistance", new Document(
"near", new Document(
"type", "Point"
).append("coordinates", new double[]{longitude, latitude})
).append("distanceField", "distance")
.append("spherical", true)
)
)));
pipeline.add(new Document("$sort", new Document("distance", 1)));
pipeline.add(new Document("$limit", limit));
return com.google.common.collect.Lists.newArrayList(
productCollection.aggregate(pipeline)
);
}
/**
* 更新商品库存
* @param productId 商品ID
* @param quantity 变动数量(正数增加,负数减少)
* @return 更新后的库存
*/
public int updateStock(String productId, int quantity) {
if (!org.springframework.util.StringUtils.hasText(productId)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("商品ID不能为空");
}
// 使用原子操作更新库存,避免并发问题
Document result = productCollection.findOneAndUpdate(
Filters.eq("_id", new org.bson.types.ObjectId(productId)),
new Document("$inc", new Document("stock", quantity)),
new com.mongodb.client.model.FindOneAndUpdateOptions().returnDocument(com.mongodb.client.model.ReturnDocument.AFTER)
);
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(result)) {
throw new RuntimeException("商品不存在或已被删除,ID: " + productId);
}
int newStock = result.getInteger("stock");
log.info("更新商品库存成功,商品ID: {}, 变动数量: {}, 新库存: {}",
productId, quantity, newStock);
return newStock;
}
}设计优势:
attributes字段存储不同商品的特有属性,无需为每种商品创建单独的集合- 复合索引优化多条件筛选和排序,提升搜索性能
- 地理位置索引支持 "附近的商品" 等 LBS 场景
- 原子操作
$inc确保库存更新的线程安全
三、MongoDB 与关系型数据库的选择策略
在实际项目中,MongoDB 并非万能,与关系型数据库(如 MySQL)各有优势。选择合适的数据库需要根据具体业务场景进行权衡。
3.1 核心差异对比
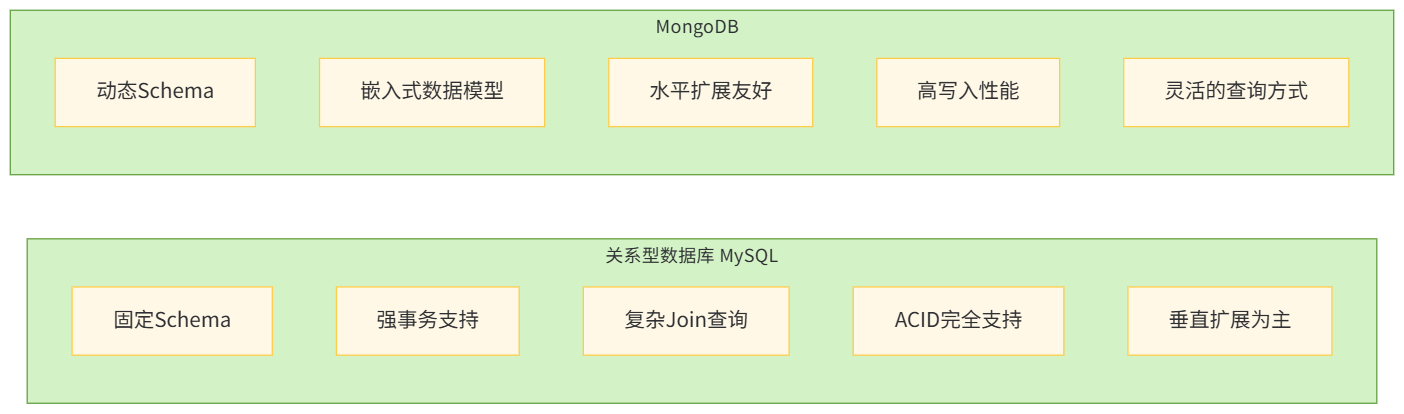
| 特性 | 关系型数据库 | MongoDB |
|---|---|---|
| 数据模型 | 表、行、列 | 文档、集合 |
| Schema | 固定,预先定义 | 动态,灵活 |
| 事务支持 | 完全支持 ACID | 支持多文档事务(4.0+) |
| 关联处理 | 外键约束,Join 操作 | 嵌入式文档,引用 |
| 查询语言 | SQL | MongoDB 查询语言 |
| 扩展性 | 垂直扩展为主 | 水平扩展(分片) |
| 适用场景 | 结构化数据,复杂事务,多表关联 | 非结构化 / 半结构化数据,快速迭代,高写入场景 |
3.2 混合使用策略
在很多复杂系统中,最佳实践是混合使用关系型数据库和 MongoDB,发挥各自优势:
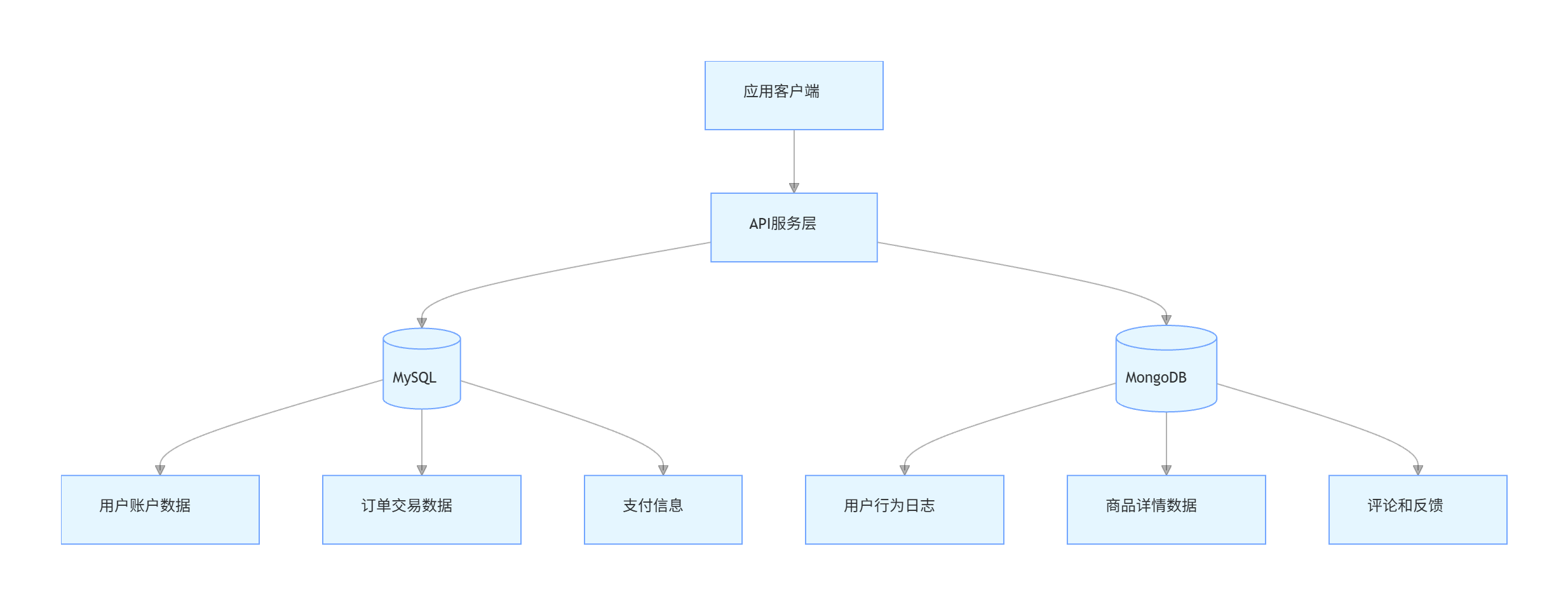
典型混合架构场景:
- 用户账户、订单、支付等核心交易数据存储在 MySQL 中,确保事务一致性
- 商品详情、用户行为日志、评论等非结构化或半结构化数据存储在 MongoDB 中,提高灵活性和写入性能
- 通过应用层实现两种数据库的协同工作
四、MongoDB 性能优化实战
即使使用 MongoDB,若设计不当也会导致性能问题。以下是经过实战验证的性能优化策略:
4.1 索引优化
索引设计原则:
- 为常用查询字段创建索引
- 复合索引遵循 "最左前缀原则"
- 避免创建过多索引(影响写入性能)
- 使用
explain()分析查询性能
索引优化示例:
/**
* 分析查询性能并优化索引
* @author ken
*/
public class IndexOptimizer {
private final MongoCollection<Document> collection;
public IndexOptimizer(MongoCollection<Document> collection) {
this.collection = collection;
}
/**
* 分析查询性能
* @param query 查询条件
* @return 执行计划
*/
public Document analyzeQuery(Document query) {
return collection.find(query).explain();
}
/**
* 推荐优化索引
* @param query 查询条件
* @return 推荐的索引列表
*/
public List<Document> recommendIndexes(Document query) {
List<Document> recommendedIndexes = com.google.common.collect.Lists.newArrayList();
// 分析查询条件,提取查询字段
List<String> queryFields = com.google.common.collect.Lists.newArrayList();
for (String key : query.keySet()) {
// 跳过逻辑运算符
if (!key.startsWith("$")) {
queryFields.add(key);
}
}
// 为单字段查询推荐单字段索引
if (queryFields.size() == 1) {
String field = queryFields.get(0);
recommendedIndexes.add(new Document(field, 1));
}
// 为多字段查询推荐复合索引
else if (queryFields.size() > 1) {
Document compoundIndex = new Document();
for (String field : queryFields) {
compoundIndex.append(field, 1);
}
recommendedIndexes.add(compoundIndex);
}
return recommendedIndexes;
}
/**
* 清理无用索引
* @return 被删除的索引名称列表
*/
public List<String> cleanUnusedIndexes() {
List<String> droppedIndexes = com.google.common.collect.Lists.newArrayList();
// 获取所有索引
List<Document> indexes = com.google.common.collect.Lists.newArrayList(collection.listIndexes());
for (Document index : indexes) {
String indexName = index.getString("name");
// 跳过默认的_id索引
if (indexName.equals("_id_")) {
continue;
}
// 在实际应用中,这里应该检查索引是否被使用过
// 简化处理:假设所有非默认索引都需要被检查
boolean isUsed = false; // 实际应用中需要通过监控数据判断
if (!isUsed) {
collection.dropIndex(indexName);
droppedIndexes.add(indexName);
log.info("删除无用索引: {}", indexName);
}
}
return droppedIndexes;
}
}4.2 读写分离与分片
对于大规模应用,单节点 MongoDB 难以满足性能需求,需要采用集群架构:
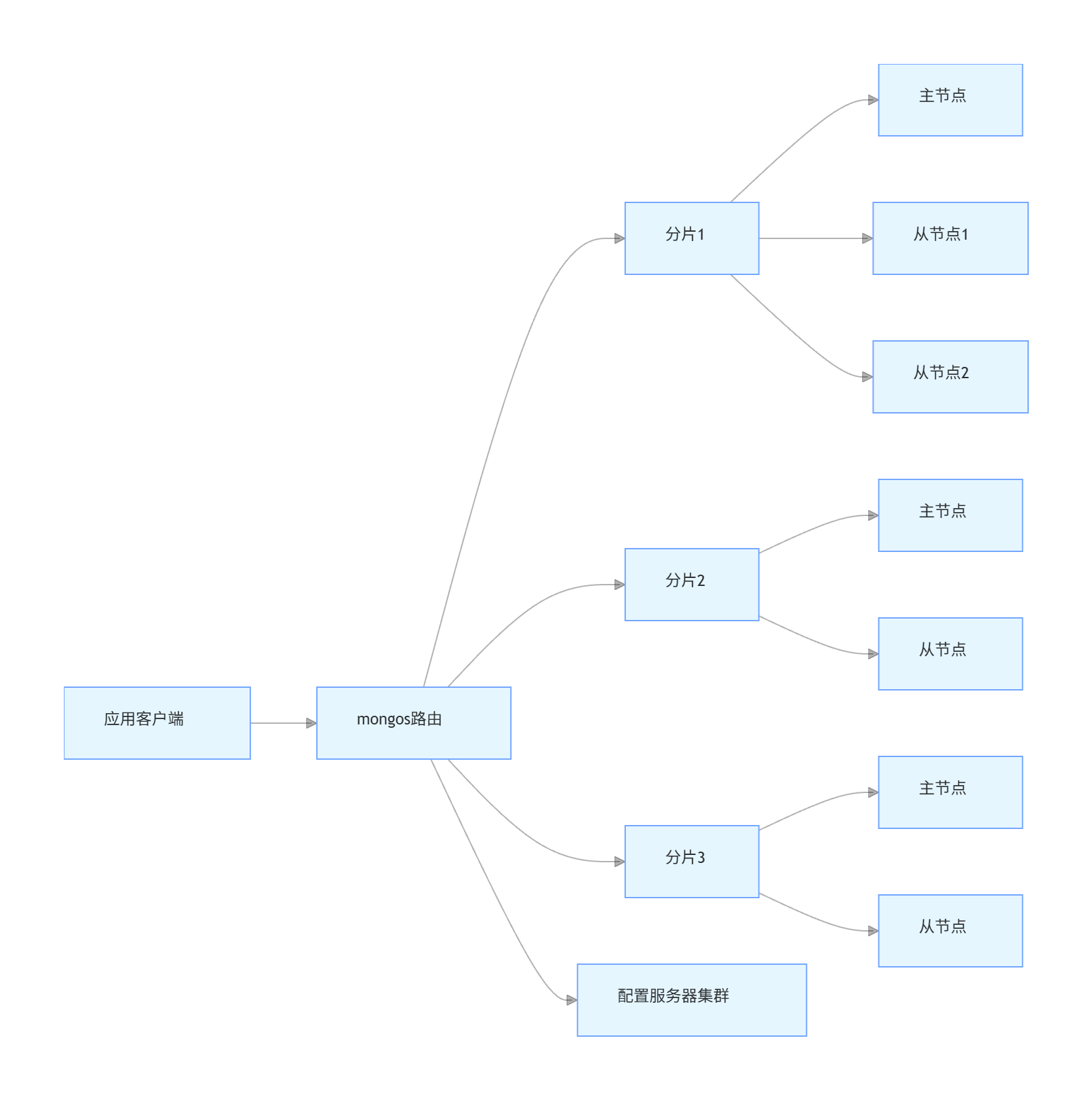
分片策略:
- 范围分片:适合按范围查询的场景(如时间范围)
- 哈希分片:适合随机访问,负载更均衡
- Zone 分片:根据地理位置等因素将数据分布到特定分片
分片实战代码:
import com.mongodb.client.MongoClient;
import com.mongodb.client.MongoDatabase;
import com.mongodb.client.model.CreateCollectionOptions;
import com.mongodb.client.model.ShardingOptions;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
/**
* MongoDB分片管理工具
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
public class ShardingManager {
private final MongoClient mongoClient;
private final String databaseName;
public ShardingManager(MongoClient mongoClient, String databaseName) {
this.mongoClient = mongoClient;
this.databaseName = databaseName;
}
/**
* 启用数据库分片
*/
public void enableSharding() {
MongoDatabase adminDb = mongoClient.getDatabase("admin");
adminDb.runCommand(new Document("enableSharding", databaseName));
log.info("启用数据库分片成功: {}", databaseName);
}
/**
* 创建分片集合(范围分片)
* @param collectionName 集合名称
* @param shardKey 分片键
*/
public void createRangeShardedCollection(String collectionName, String shardKey) {
// 先启用数据库分片
enableSharding();
MongoDatabase db = mongoClient.getDatabase(databaseName);
// 创建集合
db.createCollection(collectionName);
// 创建分片键索引
db.getCollection(collectionName).createIndex(new Document(shardKey, 1));
// 配置分片
MongoDatabase adminDb = mongoClient.getDatabase("admin");
adminDb.runCommand(new Document("shardCollection", databaseName + "." + collectionName)
.append("key", new Document(shardKey, 1)));
log.info("创建范围分片集合成功: {}.{},分片键: {}", databaseName, collectionName, shardKey);
}
/**
* 创建分片集合(哈希分片)
* @param collectionName 集合名称
* @param shardKey 分片键
*/
public void createHashShardedCollection(String collectionName, String shardKey) {
// 先启用数据库分片
enableSharding();
MongoDatabase db = mongoClient.getDatabase(databaseName);
// 创建集合
db.createCollection(collectionName);
// 创建哈希索引作为分片键
db.getCollection(collectionName).createIndex(new Document(shardKey, "hashed"));
// 配置分片
MongoDatabase adminDb = mongoClient.getDatabase("admin");
adminDb.runCommand(new Document("shardCollection", databaseName + "." + collectionName)
.append("key", new Document(shardKey, "hashed")));
log.info("创建哈希分片集合成功: {}.{},分片键: {}", databaseName, collectionName, shardKey);
}
/**
* 配置Zone分片
* @param zoneName 区域名称
* @param shardNames 该区域包含的分片
* @param min 分片键最小值
* @param max 分片键最大值
* @param collectionName 集合名称
*/
public void configureZoneSharding(String zoneName, List<String> shardNames,
Object min, Object max, String collectionName) {
MongoDatabase adminDb = mongoClient.getDatabase("admin");
// 创建Zone
adminDb.runCommand(new Document("addShardToZone", shardNames.get(0))
.append("zone", zoneName));
// 添加更多分片到Zone
for (int i = 1; i < shardNames.size(); i++) {
adminDb.runCommand(new Document("addShardToZone", shardNames.get(i))
.append("zone", zoneName));
}
// 配置Zone范围
String fullCollectionName = databaseName + "." + collectionName;
Document range = new Document();
if (min != null) {
range.append("min", new Document("userId", min));
}
if (max != null) {
range.append("max", new Document("userId", max));
}
adminDb.runCommand(new Document("updateZoneKeyRange", fullCollectionName)
.append("zone", zoneName)
.append("range", range));
log.info("配置Zone分片成功: 区域={}, 分片={}, 范围={}", zoneName, shardNames, range);
}
}4.3 数据生命周期管理
对于海量数据,合理管理数据生命周期可以大幅降低存储成本:
- TTL 索引:自动删除过期数据
- 数据归档:将历史数据迁移到低成本存储
- 分片集群扩展:根据数据增长动态添加分片
数据生命周期管理示例:
import com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection;
import com.mongodb.client.model.Indexes;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.bson.Document;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 数据生命周期管理服务
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
public class DataLifecycleManager {
private final MongoCollection<Document> primaryCollection;
private final MongoCollection<Document> archiveCollection;
public DataLifecycleManager(MongoCollection<Document> primaryCollection,
MongoCollection<Document> archiveCollection) {
this.primaryCollection = primaryCollection;
this.archiveCollection = archiveCollection;
// 为主要集合创建TTL索引,自动删除30天前的数据
this.primaryCollection.createIndex(
Indexes.ascending("createdAt"),
new com.mongodb.client.model.IndexOptions()
.expireAfter(30 * 24 * 60 * 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.name("ttl_createdAt")
);
}
/**
* 归档历史数据
* 将超过指定天数的数据从主集合迁移到归档集合
* @param days 天数阈值
* @return 归档的数据量
*/
public long archiveOldData(int days) {
if (days <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("天数阈值必须大于0");
}
// 计算 cutoff 时间
LocalDateTime cutoffTime = LocalDateTime.now().minusDays(days);
Date cutoffDate = Date.from(cutoffTime.atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toInstant());
// 查询需要归档的数据
List<Document> oldData = com.google.common.collect.Lists.newArrayList(
primaryCollection.find(new Document("createdAt", new Document("$lt", cutoffDate)))
.limit(10000) // 每次归档最多10000条,避免过大操作
);
if (oldData.isEmpty()) {
log.info("没有需要归档的数据,阈值: {}天", days);
return 0;
}
// 批量插入到归档集合
archiveCollection.insertMany(oldData);
// 删除主集合中的已归档数据
List<Object> ids = com.google.common.collect.Lists.transform(oldData, doc -> doc.get("_id"));
primaryCollection.deleteMany(new Document("_id", new Document("$in", ids)));
log.info("数据归档完成,数量: {}, 阈值: {}天", oldData.size(), days);
return oldData.size();
}
/**
* 清理过期的归档数据
* 删除超过指定天数的归档数据
* @param days 天数阈值
* @return 清理的数据量
*/
public long cleanExpiredArchiveData(int days) {
if (days <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("天数阈值必须大于0");
}
// 计算 cutoff 时间
LocalDateTime cutoffTime = LocalDateTime.now().minusDays(days);
Date cutoffDate = Date.from(cutoffTime.atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toInstant());
// 删除过期的归档数据
com.mongodb.client.result.DeleteResult result = archiveCollection.deleteMany(
new Document("createdAt", new Document("$lt", cutoffDate))
);
log.info("清理过期归档数据完成,数量: {}, 阈值: {}天", result.getDeletedCount(), days);
return result.getDeletedCount();
}
/**
* 统计集合数据量和大小
* @return 统计信息
*/
public Document stats() {
Document primaryStats = primaryCollection.stats();
Document archiveStats = archiveCollection.stats();
return new Document("primary", new Document(
"count", primaryStats.getLong("count")
).append("size", primaryStats.getLong("size")))
.append("archive", new Document(
"count", archiveStats.getLong("count")
).append("size", archiveStats.getLong("size")))
.append("total", new Document(
"count", primaryStats.getLong("count") + archiveStats.getLong("count")
).append("size", primaryStats.getLong("size") + archiveStats.getLong("size")));
}
}五、MongoDB 最佳实践与陷阱规避
5.1 数据模型设计最佳实践
-
嵌入式 vs 引用:
- 一对一关系优先使用嵌入式
- 一对多关系根据访问模式选择:频繁一起访问则嵌入,否则使用引用
- 多对多关系必须使用引用
-
避免过大文档:MongoDB 文档大小限制为 16MB,避免存储大型二进制数据(建议使用 GridFS)
-
合理使用数组:数组适合存储有序数据,但过大的数组会影响性能,考虑拆分
-
预聚合数据:对于频繁查询的统计数据,考虑在写入时预计算并存储
5.2 常见性能陷阱及解决方案
| 陷阱 | 解决方案 |
|---|---|
| 全表扫描 | 创建合适的索引,使用explain()分析查询 |
| 过多的索引 | 定期清理无用索引,平衡读写性能 |
| 大文档频繁更新 | 拆分文档,只更新必要的部分 |
| 未使用批量操作 | 使用批量插入、更新操作减少网络往返 |
| 忽略分片键设计 | 选择基数高、分布均匀的字段作为分片键 |
| 不适当的索引顺序 | 复合索引中,将选择性高的字段放在前面 |
六、总结与展望
MongoDB 作为一款成熟的 NoSQL 数据库,凭借其灵活的文档模型、强大的查询能力和出色的扩展性,已成为现代应用开发的重要选择。本文从核心概念、应用场景、实战案例到性能优化,全面解析了 MongoDB 的使用之道。