1、
答:字符串是以空字符('\0')结尾的一系列字符,故上述声明的是一个字符数组,不是字符串。
2、
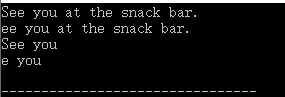
3、

4、
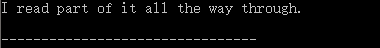
5、
a.
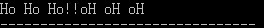
b.
指向 char 类型的指针
c.
字符串 "Ho Ho Ho!" 的首地址。
d.
*--pc : 表示指针先前移动一位,然后取指针指向的值。
--*pc : 先取指针指向的值,然后值减1.
e.
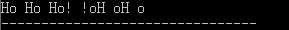
f.
第 1 个 while 循环用来测试是否到达字符串末尾的空字符('\0') ;
第 2 个 do{}while 循环用来测试是否到达该字符串的首字符.
g.
由于 *pc 为空字符('\0'),不会进入第 1 个 while 循环,第二个 do{}while 循环先对 pc 递减,则表达式 pc - str 永远为负,循环一直进行下去。
h.
主调函数需调用pr()前要声明函数 char *pr(char *str);
主调函数需要声明指针 char 类型变量 x,即 char *x 。
6、
sign 是 char 类型变量,占 1 个字节的内存。
'$' 是 char 字面值常量,占 1 个字节的内存。
"$" 是字符串字面值,末尾还有空字符('\0'),占 2 个字节的内存。
7、
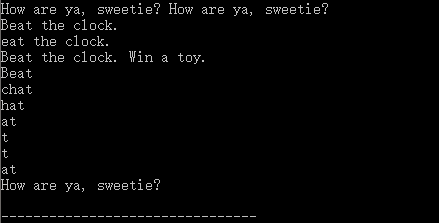
8、

9、
char *s_gets(char *st, int n)
{
char *ret_val;
char *ptr;
ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin);
if(ret_val)
{
ptr = st;
while(*ptr != '\n' && *ptr != '\0')
ptr++;
if(*ptr == '\n')
*ptr = '\0';
else
while(getchar() != '\n')
continue;
}
return ret_val;
}10、
int strlen(char *st)
{
int i = 0;
while(*st++)
i++;
return i;
}11、
#include <string.h> // 有 strchr() 函数
char *s_gets(char *st, int n)
{
char *ret_val;
char *find;
ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin);
if (ret_val)
{
find = strchr(st, '\n');
if (find)
*find = '\0';
else
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
}
return ret_val;
} 12、
#include <stdio.h>
char *find_first_space(const char *str)
{
if (str == NULL)
return NULL;
while (*str != '\0')
{
if (*str == ' ')
return (char *)str;
str++;
}
return NULL;
}
/*
括号 (char *) 是 C 语言类型转换操作符的固定语法格式。它告诉编译器:"将 str 从 const char * 类型转换为 char * 类型"。
*/13、
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#define ANSWER "Grant"
#define SIZE 40
char *s_gets(char *st, int n);
void upper(char *str);
int main()
{
char try[SIZE];
puts("Who is buried in Grant's tomb?");
s_gets(try, SIZE);
upper(try);
while(strcmp(try, ANSWER) != 0)
{
puts("No, that's wrong. Try again.");
s_gets(try, SIZE);
upper(try);
}
puts("That's right);
return 0;
}
char *s_gets(char *st, int n)
{
char *ret_val;
char *find;
ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin);
if (ret_val)
{
find = strchr(st, '\n');
if(find)
*find = '\0';
else
while(getchar() != '\n')
continue;
}
return ret_val;
}
void upper(char *str)
{
while(*str)
{
*str = toupper(*str);
++str;
}
}