鸿蒙实现可以上下左右滑动的表格-摆脱大量ListScroller
前言: 好久没写过文章了,最近在开发鸿蒙项目,于是乎想简单记录一下开发过程中遇到的一些好玩的东西或者经常会遇到的功能开发。
开发过程中经常遇到需要做可以上下左右滑动的类型的表格的实现,写之前也在华为论坛搜索了下相关的,官方文档提供了一种方案,创建了大量的ListScroller,个人感觉数据量大了就不是很好用,这里提供一种自己实现的方案
鉴于这个功能难度不是很大,仅仅就是布局和联动的实现,所以代码很少
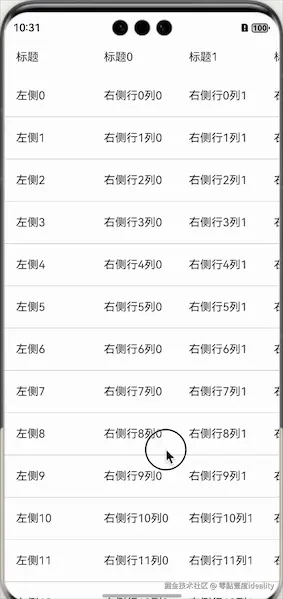
效果
废话不多说,先上效果
布局
根据表格滑动的结构,可以看到布局结构如下,分别是横向滑动的标题,横向滑动的内容和上下滑动的标题+内容。
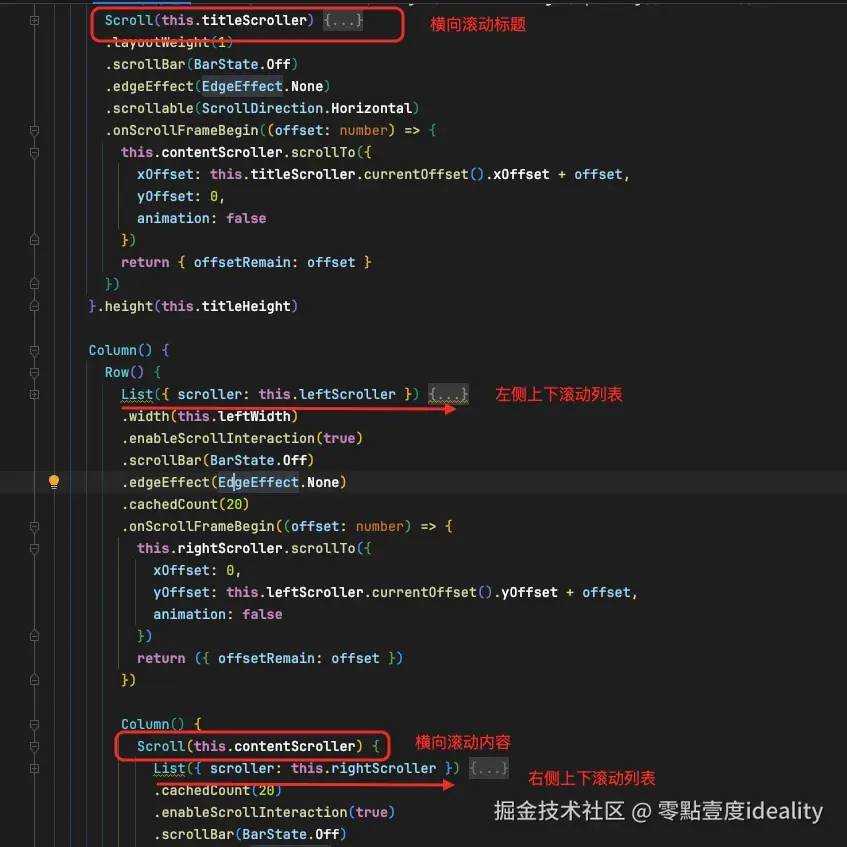
完整代码如下
ts
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct Index {
leftWidth: number = 140
cellWidth: number = 120
cellHeight: number = 60
titleHeight: number = 50
private titleScroller: Scroller = new Scroller()
private contentScroller: Scroller = new Scroller()
private leftScroller: Scroller = new Scroller()
private rightScroller: Scroller = new Scroller()
titleList: string[] = []
leftData: string[] = []
rightData: string[] = []
aboutToAppear(): void {
for (let index = 0; index < 20; index++) {
this.titleList.push(`标题${index}`)
}
for (let index = 0; index < 100; index++) {
this.leftData.push(`左侧${index}`)
this.rightData.push(`右侧行${index}`)
}
}
build() {
Column() {
Row() {
Text('标题').width(this.leftWidth).height(this.titleHeight).padding({ left: 16 })
Scroll(this.titleScroller) {
Row() {
ForEach(this.titleList, (item: string) => {
Text(item).width(this.cellWidth).height(this.titleHeight)
})
}
}
.layoutWeight(1)
.scrollBar(BarState.Off)
.edgeEffect(EdgeEffect.None)
.scrollable(ScrollDirection.Horizontal)
.onScrollFrameBegin((offset: number) => {
this.contentScroller.scrollTo({
xOffset: this.titleScroller.currentOffset().xOffset + offset,
yOffset: 0,
animation: false
})
return { offsetRemain: offset }
})
}.height(this.titleHeight)
Column() {
Row() {
List({ scroller: this.leftScroller }) {
Repeat<ESObject>(this.leftData).virtualScroll().each((ri: RepeatItem<ESObject>) => {
ListItem() {
Text(ri.item)
}
.height(this.cellHeight)
.width(this.leftWidth)
.itemBorder()
.align(Alignment.Start)
.padding({ left: 16 })
})
ListItem().height(this.cellHeight)
}
.width(this.leftWidth)
.enableScrollInteraction(true)
.scrollBar(BarState.Off)
.edgeEffect(EdgeEffect.None)
.cachedCount(20)
.onScrollFrameBegin((offset: number) => {
this.rightScroller.scrollTo({
xOffset: 0,
yOffset: this.leftScroller.currentOffset().yOffset + offset,
animation: false
})
return ({ offsetRemain: offset })
})
Column() {
Scroll(this.contentScroller) {
List({ scroller: this.rightScroller }) {
Repeat<string>(this.rightData).virtualScroll().each((ri: RepeatItem<ESObject>) => {
ListItem() {
Row() {
ForEach(this.titleList, (item: string, index: number) => {
Text(`${ri.item}列${index}`).width(this.cellWidth).height(this.cellHeight)
})
}
}.height(this.cellHeight).itemBorder()
})
ListItem().height(this.cellHeight)
}
.cachedCount(20)
.enableScrollInteraction(true)
.scrollBar(BarState.Off)
.edgeEffect(EdgeEffect.None)
.onScrollFrameBegin((offset: number) => {
this.leftScroller.scrollTo({
xOffset: 0,
yOffset: this.rightScroller.currentOffset().yOffset + offset,
animation: false
})
return ({ offsetRemain: offset })
})
}
.scrollBar(BarState.Off)
.edgeEffect(EdgeEffect.None)
.scrollable(ScrollDirection.Horizontal)
.onScrollFrameBegin((offset: number) => {
if (!this.contentScroller.isAtEnd()) {
this.titleScroller.scrollTo({
xOffset: this.contentScroller.currentOffset().xOffset + offset,
yOffset: 0,
animation: false
})
}
return { offsetRemain: offset }
})
}.layoutWeight(1)
}
}
}
.height('100%')
.width('100%')
}
}
@Styles
function itemBorder() {
.border({
color: '#cccccc',
width: {
left: 0,
top: 0,
right: 0,
bottom: 1
}
})
}