因为web的便利性,很多传统功能都有了web端的实现,WebSSH就是其中之一,我是第一次接触,所以来记录一下使用。
WebSSH支持终端交互,主要可以分为两部分,第一是页面输入命令行并传递给远程终端,第二是展示命令执行结果,这两部分现在都已经有具体实现的库了,所以我们只需要把它们组合起来。
在具体实现之前,需要先准备一个远程终端,我这里用的是VMware创建的虚拟机

可以在Mac的终端直接登录
接下来我们就来看代码的实现,前端页面使用三方库xtermjs实现终端界面,远程连接使用nodejs的ssh2模块。
前端实现
我们先来看web端的实现。
前端代码主要做三件事,第一初始化终端对象terminal,第二增加监听事件监听用户的输入,第三建立web socket连接实现实时交互。我这里用react项目做简单的演示。
先在页面上准备一个div,模拟终端背景。
jsx
import React, {useEffect, useRef, useState} from 'react';
import { Terminal } from 'xterm';
import 'xterm/css/xterm.css';
const FontSize = 14;
const Col = 80;
const WebTerminal = () => {
const terminalRef = useRef(null);
const webTerminal = useRef(null);
const ws = useRef(null);
useEffect(() => {
const ele = terminalRef.current;
if (ele) {
}
}, [terminalRef.current]);
return <div ref={terminalRef} style={{ backgroundColor: '#000', width: '100vw', height: '100vh' }}/>;
};
export default WebTerminal;然后我们对终端进行初始化。
jsx
import React, {useEffect, useRef, useState} from 'react';
import { Terminal } from 'xterm';
import 'xterm/css/xterm.css';
const FontSize = 14;
const Col = 80;
const WebTerminal = () => {
const terminalRef = useRef(null);
const webTerminal = useRef(null);
const ws = useRef(null);
useEffect(() => {
const ele = terminalRef.current;
if (ele && !webTerminal.current) {
const height = ele.clientHeight; // +
const terminal = new Terminal({ // +
cursorBlink: true, // +
cols: Col, // +
rows: Math.ceil(height / FontSize), // +
}); // +
// +
terminal.open(ele); // +
// +
webTerminal.current = terminal; // +
}
}, [terminalRef.current]);
return <div ref={terminalRef} style={{ backgroundColor: '#000', width: '100vw', height: '100vh' }}/>;
};
export default WebTerminal;这个时候可以看到页面上出现了一个闪烁的光标,就像input输入框被聚焦时候的状态,cols属性指定了一行可以输入的字符数,rows指定了展示的行数,这里做了一个简单的取整的计算。这个时候还不能输入内容,因为还没加上事件监听,那么现在我们给它加上。
jsx
import React, {useEffect, useRef, useState} from 'react';
import { Terminal } from 'xterm';
import 'xterm/css/xterm.css';
const FontSize = 14;
const Col = 80;
const WebTerminal = () => {
const terminalRef = useRef(null);
const webTerminal = useRef(null);
const ws = useRef(null);
useEffect(() => {
const ele = terminalRef.current;
if (ele && !webTerminal.current) {
const height = ele.clientHeight;
const terminal = new Terminal({
cursorBlink: true,
cols: Col,
rows: Math.ceil(height / FontSize),
});
terminal.open(ele);
webTerminal.current = terminal;
terminal.onData((val) => { // 键盘输入 // +
if (val === '\x03') { // +
// nothig todo // +
} else { // +
terminal.write(val); // +
} // +
}); // +
}
}, [terminalRef.current]);
return <div ref={terminalRef} style={{ backgroundColor: '#000', width: '100vw', height: '100vh' }}/>;
};
export default WebTerminal;这里我们利用terminal对象的onData方法对用户输入进行监听,然后调用terminal的write方法将内容输出到页面上,这里因为x03代表了Ctrl+C的组合键,所以把它做了过滤。这个时候你可能会发现一个问题,就是我们点击回退键删除内容的时候,控制台会出现报错,这是因为编码的问题,onData返回的是utf16/ucs2编码的内容,需要转换为utf8编码,这个后面我们交给node端去处理。
最后我们来实现web socket的实时交互,这块因为需要建立web socket链接,需要web和node一起配合实现。
Webscoket实现
我们先写node端的代码。
ts
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const expressWs = require('express-ws')(app);
import { createNewServer } from './utils/createNewServer';
app.get('/', function (req: any, res: any, next: any) {
res.end();
});
app.ws('/', function (ws: any, req: any) {
createNewServer({
host: '172.16.215.129',
username: 'root',
password: '123456'
}, ws);
});
app.listen(3001)这里我们使用express-ws模块来实现socket通信,监听3001端口,接下来我们主要看createNewServer方法的实现。
首先引入ssh2模块,构造一个ssh客户端,并与远程主机、也就是我前面创建的虚拟机建立连接。
ts
const SSHClient = require('ssh2').Client;
const utf8 = require('utf8');
const termCols = 80;
const termRows = 30;
export const createNewServer = (machineConfig: any, socket: any) => {
const ssh = new SSHClient(); // +
const { host, username, password } = machineConfig; // +
// +
ssh.connect({ // +
port: 22, // +
host, // +
username, // +
password, // +
}).on('ready', function() { // +
console.log('ssh连接已建立'); // +
}) // +
}这里端口22是SSH提供远程连接服务的默认端口,当ssh连接建立成功后,就会打印出"ssh连接已建立"。现在我们到web端去创建web socket连接来查看效果。
jsx
import React, {useEffect, useRef, useState} from 'react';
import { Terminal } from 'xterm';
import 'xterm/css/xterm.css';
const FontSize = 14;
const Col = 80;
const WebTerminal = () => {
const terminalRef = useRef(null);
const webTerminal = useRef(null);
const ws = useRef(null);
useEffect(() => {
const ele = terminalRef.current;
if (ele && !webTerminal.current) {
const height = ele.clientHeight;
const terminal = new Terminal({
cursorBlink: true,
cols: Col,
rows: Math.ceil(height / FontSize),
});
terminal.open(ele);
webTerminal.current = terminal;
terminal.onData((val) => { // 键盘输入
if (val === '\x03') {
// nothig todo
} else {
terminal.write(val);
}
});
const socket = new WebSocket(`ws://127.0.0.1:3001`); // +
socket.onopen = () => { // +
socket.send('connect success'); // +
}; // +
ws.current = socket; // +
}
}, [terminalRef.current]);
return <div ref={terminalRef} style={{ backgroundColor: '#000', width: '100vw', height: '100vh' }}/>;
};
export default WebTerminal;这个时候我们去刷新页面,就可以看到nodejs的控制台打印出了"ssh连接已建立"这句话。
与远程主机建立连接后,我们就可以使用ssh2客户端的shell方法,与主机终端开启交互。
ts
const SSHClient = require('ssh2').Client;
const utf8 = require('utf8');
const termCols = 80;
const termRows = 30;
export const createNewServer = (machineConfig: any, socket: any) => {
const ssh = new SSHClient();
const { host, username, password } = machineConfig;
ssh.connect({
port: 22,
host,
username,
password,
}).on('ready', function() {
console.log('ssh连接已建立');
ssh.shell({ // +
cols: termCols, // +
rows: termRows, // +
}, function(err: any, stream: any) { // +
if (err) { // +
return socket.send('\r\n*** SSH SHELL ERROR: ' + err.message + ' ***\r\n');
} // +
console.log('开启交互'); // +
}); // +
})
}此时nodejs的控制台就打印出了"开启交互"这句话,stream用于控制终端的输入输出。现在我们需要在web和nodejs两端都加上对消息的监听和发送,这样才能开始真正的交互,我们就接着先写node端的监听和发送。
在node端接收到socket消息后,用on-message对前端传递过来的内容进行编码转换处理,并转换为原始字节流写入终端。
ts
const SSHClient = require('ssh2').Client;
const utf8 = require('utf8');
const termCols = 80;
const termRows = 30;
export const createNewServer = (machineConfig: any, socket: any) => {
const ssh = new SSHClient();
const { host, username, password } = machineConfig;
ssh.connect({
port: 22,
host,
username,
password,
}).on('ready', function() {
console.log('ssh连接已建立');
ssh.shell({
cols: termCols,
rows: termRows,
}, function(err: any, stream: any) {
if (err) {
return socket.send('\r\n*** SSH SHELL ERROR: ' + err.message + ' ***\r\n');
}
console.log('开启交互');
socket.on('message', function (data: any) { // +
stream.write(Buffer.from(data, 'utf8')); // +
}); // +
// +
stream.on('data', function (d: Buffer) { // +
socket.send(d.toString('binary')); // +
}); // +
});
})
}同时监听终端的输出,对前端输入的内容进行处理,并通过socket连接返回给前端。toString binary表示保持原始字节,避免utf8解码异常。
接着我们来完成web端对socket的处理,首先把原来的用户输入显示到屏幕上改为发送socket消息。
jsx
terminal.onData((val) => { // 键盘输入
if (val === '\x03') {
// nothig todo
} else {
socket.send(val); // M
}
});并增加对socket消息的监听。
jsx
socket.onmessage = e => {
terminal.write(e.data);
};将socket返回的消息输出到页面模拟的终端容器上。
这个时候我们刷新页面看到如下图所示,就表示我们实现了最基本的交互功能。

这样就可以愉快地和远程终端开始交互了。

到这里我们还可以简单优化一下,就是socket连接断开后,如果不退出终端,会在远程主机保留很多进程,我们可以用这个命令ps -aux | grep ssh看到。
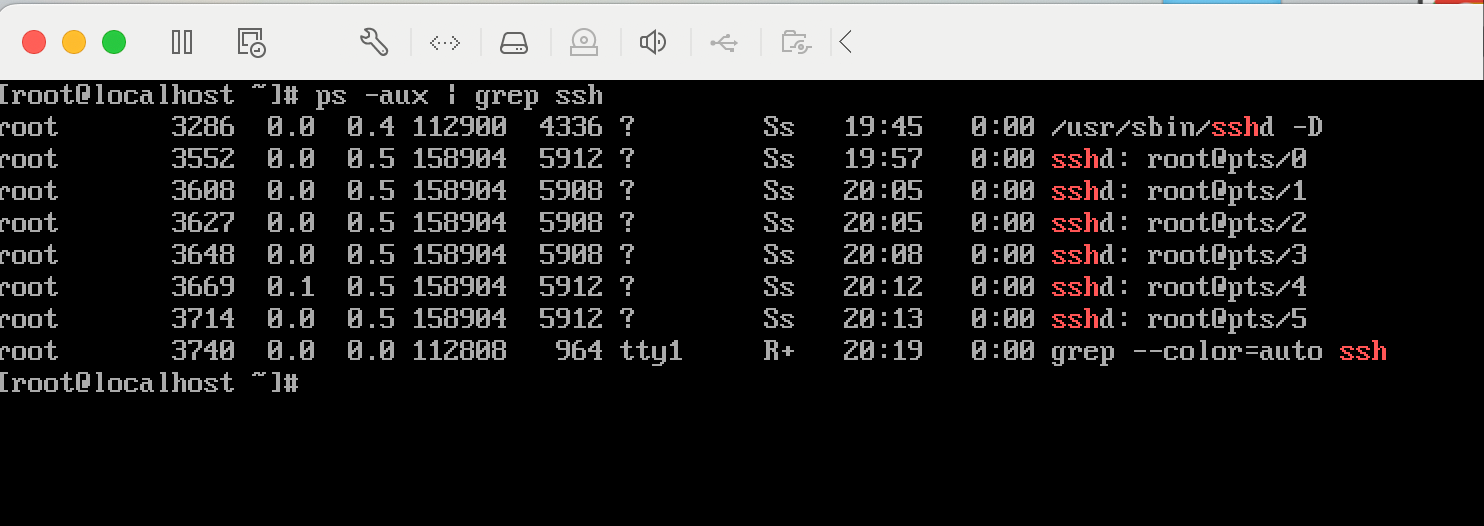
为了避免占用内存,我们可以对socket的关闭进行监听,在socket连接关闭的时候调用end方法来结束ssh连接服务。
ts
socket.onclose = (event: any) => {
ssh.end();
}这样我们再去查看的时候,就会看到只剩下一个正在运行的ssh服务。
到这里我们就实现了一个简单的WebSSH的交互了。当然这个例子比较简单,类似浏览器窗口尺寸变化对输出显示的影响这里也没有处理,以及node端ssh2模块的其他功能方法也没有涉及到,感兴趣的同学们可以去查阅文档自己尝试一下。