目录
[九、扑克牌顺子(排序+模拟 /位图+模拟)](#九、扑克牌顺子(排序+模拟 /位图+模拟))
[十、最长回文子串(动规回文串问题)](#十、最长回文子串(动规回文串问题))
[十一、买卖股票的最佳时机I (贪心)](#十一、买卖股票的最佳时机I (贪心))
十四、买卖股票的最佳时机II(双指针/贪心/简单多状态dp)
一*、大数加法(高精度加法模拟)

cpp
string solve(string s, string t) {
int m=s.size(),n=t.size();
string ret;
int sum=0,cur1=m-1,cur2=n-1;
while(cur1>=0||cur2>=0||sum)
{
if(cur1>=0){sum+=s[cur1]-'0';--cur1;}
if(cur2>=0){sum+=t[cur2]-'0';--cur2;}
ret+=to_string(sum%10);
sum/=10;
}
reverse(ret.begin(),ret.end());
return ret;
}二*、链表相加(高精度加法模拟)
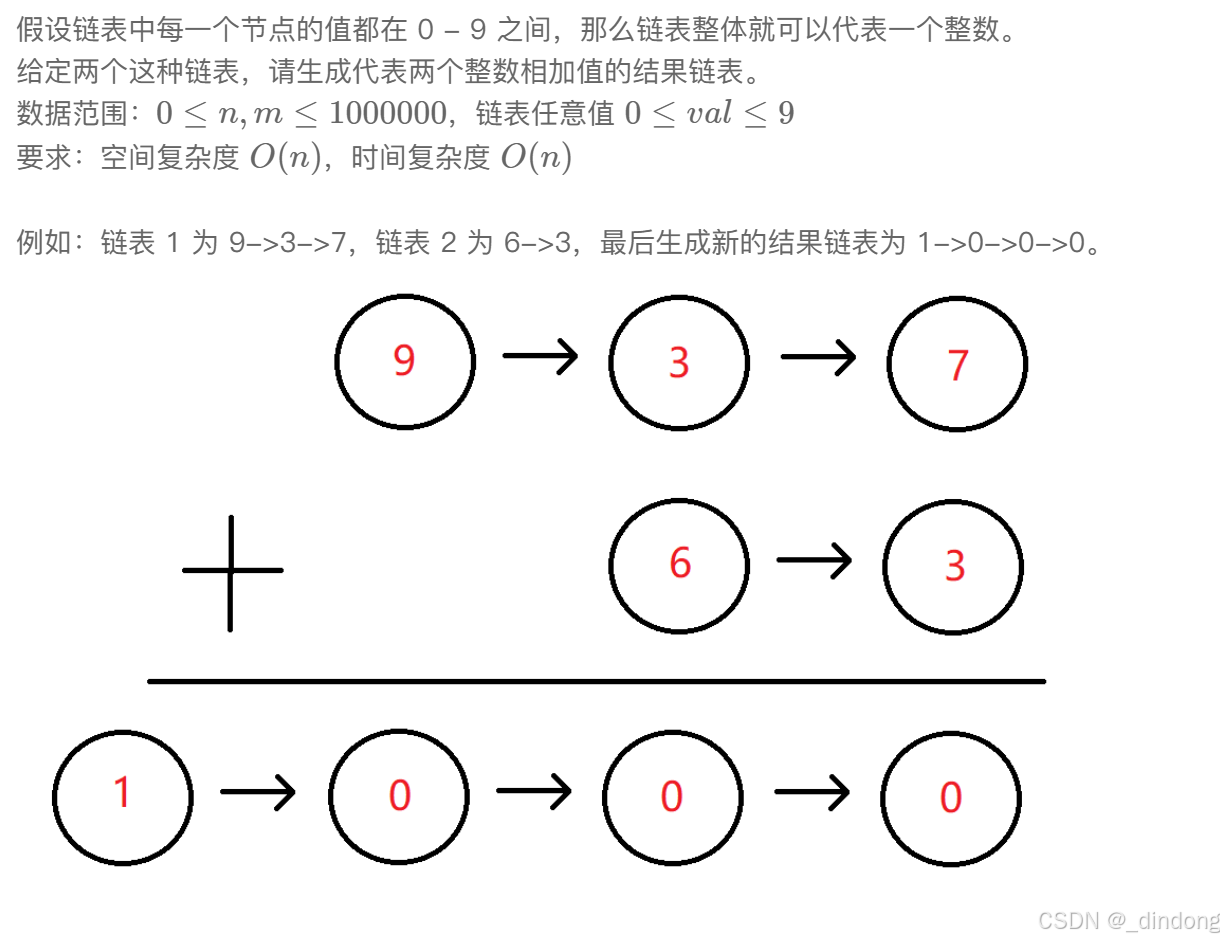

逆转链表,然后模拟
cpp
ListNode* ReverseNode(ListNode*head)
{
if(!head||!head->next)return head;
ListNode* newhead=ReverseNode(head->next);
head->next->next=head;
head->next=nullptr;
return newhead;
}
// ListNode* ReverseNode(ListNode*head)
// {
// ListNode*prev=nullptr;
// ListNode*cur=head;
// while(cur)
// {
// ListNode*t=cur->next;
// cur->next=prev;
// prev=cur;
// cur=t;
// }
// return prev;
// }
ListNode* addInList(ListNode* head1, ListNode* head2) {
//逆转链表
ListNode*cur1=ReverseNode(head1),*cur2=ReverseNode(head2);
int add=0;
ListNode*newhead=new ListNode(-1);
while(cur1||cur2||add)
{
if(cur1)
{
add+=cur1->val;
cur1=cur1->next;
}
if(cur2)
{
add+=cur2->val;
cur2=cur2->next;
}
//头插
ListNode*Node=new ListNode(add%10);
Node->next=newhead->next;
newhead->next=Node;
add/=10;
}
ListNode*prev=newhead->next;
delete newhead;
return prev;
}三*、大数乘法(高精度乘法模拟)

cpp
string solve(string s, string t) {
if(s=="0"||t=="0")return "0";
int m=s.size(),n=t.size();
vector<int> res(m+n);
for(int i=m-1;i>=0;--i)
{
for(int j=n-1;j>=0;--j)
{
int p1=i+j,p2=i+j+1;
int mul=(s[i]-'0')*(t[j]-'0');
int sum=mul+res[p2];
res[p2]=sum%10;
res[p1]+=sum/10;
}
}
string ret;
for(int i=0;i<m+n;++i)
{
if(ret.empty()&&res[i]==0)continue;
ret+=to_string(res[i]);
}
return ret;
}四*、求最小公倍数(数学)

先求最大公约数tmp,那么返回a*b/tmp即可
求最大公约数有以下两种方法:
1:暴力枚举
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a, b;cin>>a>>b;
int n=min(a,b),tmp;
for(int i=n;i>=1;--i)
{
if(a%i==0&&b%i==0)
{
tmp=i;break;
}
}
cout<<a*b/tmp;
return 0;
}2.辗转相除法(非常高效,学习)

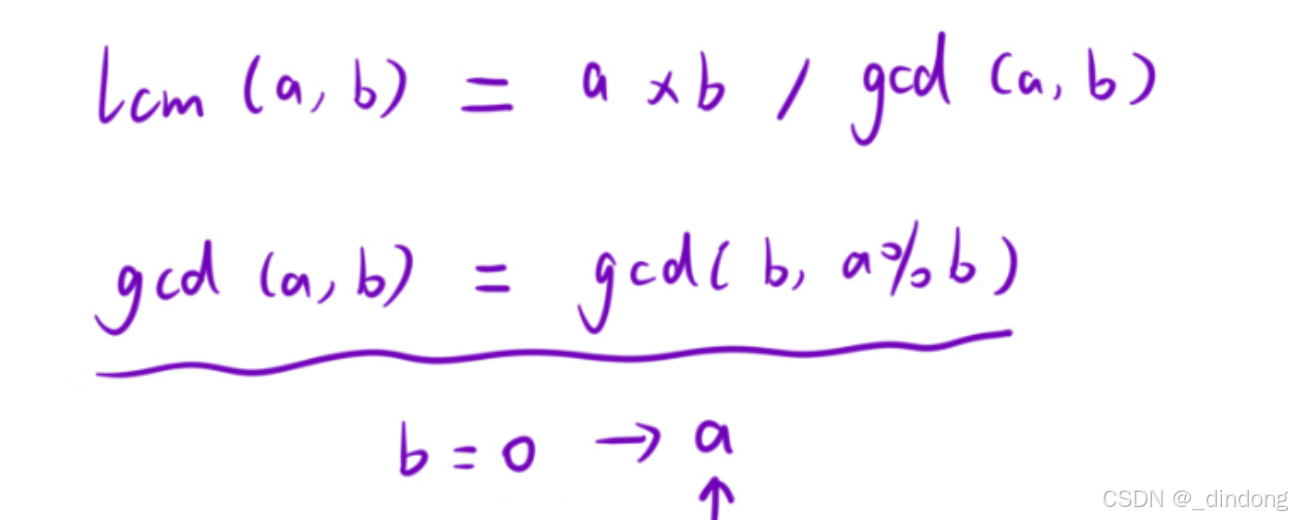

cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int gcd(int a,int b)
{
if(b==0)return a;
return gcd(b,a%b);
}
int main() {
int a, b;cin>>a>>b;
cout<<a*b/gcd(a,b)<<endl;
return 0;
}五、数组中的最长连续子序列(排序+双指针)

看完题解以及示例一之后,其实也就可以转换成双指针问题了,记得先排序,
此外,示例2在暗示我们,如果后一个数和前一个数一样,都记作一次
所以用例没过的时候一定要看看你忽略的示例,示例一定是有意义的。
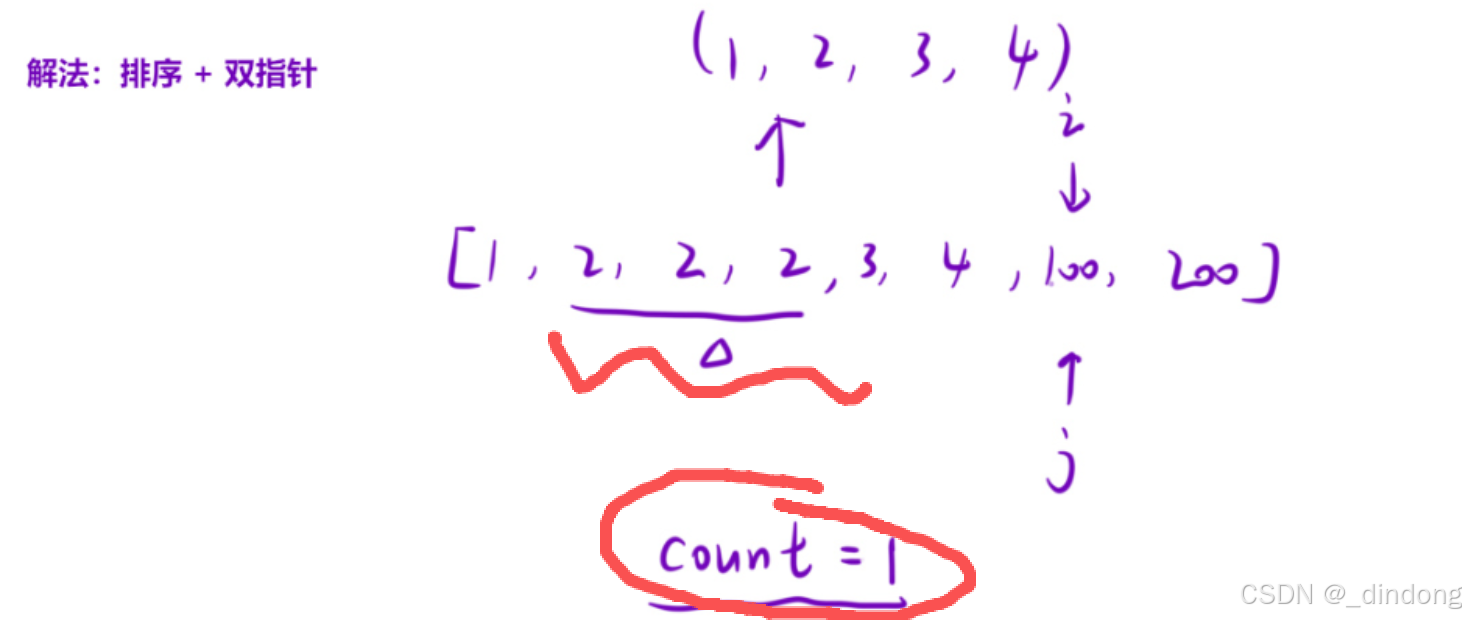
六、字母收集(路径dp)


先创建一个int数组表,存信息,l的话就代表4,o就代表3
然后正常dp就行,很简单,不过自己想出来了很开心。
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n,m;cin>>n>>m;
vector<vector<int>> num(n,vector<int>(m));
char ch;
for(int i=0;i<n;++i)
{
for(int j=0;j<m;++j)
{
cin>>ch;
if(ch=='l')num[i][j]=4;
else if(ch=='o')num[i][j]=3;
else if(ch=='v')num[i][j]=2;
else if(ch=='e')num[i][j]=1;
}
}
vector<vector<int>> dp(n+1,vector<int>(m+1));
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
for(int j=1;j<=m;++j)
{
//注意映射
dp[i][j]=num[i-1][j-1];
dp[i][j]+=max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1]);
}
}
cout<<dp[n][m];
return 0;
}上面是自己写的思路很清晰,也可以按下面这种方法写
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N=501;
char nums[N][N];
int dp[N][N];
int main() {
int m,n;
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
for(int j=1;j<=m;++j)
cin>>nums[i][j];
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
for(int j=1;j<=m;++j){
int t=0;
if(nums[i][j]=='l') t=4;
else if(nums[i][j]=='o') t=3;
else if(nums[i][j]=='v') t=2;
else if(nums[i][j]=='e') t=1;
dp[i][j]=max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1])+t;
}
cout<<dp[n][m]<<endl;
return 0;
}
// 64 位输出请用 printf("%lld")七、添加逗号(模拟)

斗宗强者恐怖如斯,本人写的代码丑陋无比写了三十多行,(begin存下标然后不断取substr)没想到标答这么简洁。
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s;
cin>>s;
string ret;//统计最后结果
int n=s.size();
for(int i=0;i<n;++i){
ret+=s[i];
if((n-i-1)%3==0&&i!=n-1) ret+=',';
}
cout<<ret<<endl;
return 0;
}
// 64 位输出请用 printf("%lld")本人写的,貌似不用判断前导0???还真是,修改了一下代码,/(ㄒoㄒ)/~~
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string N;cin>>N;
int n=N.size();
int begin=0;
if(n<=3)
{
cout<<N.substr(begin,n);
return 0;
}
string ret;
if(n%3)ret+=(N.substr(begin,n%3)+",");
begin+=n%3;
while(begin+2<n)
{
ret+=N.substr(begin,3);
begin+=3;
if(begin<n)ret+=",";
}
cout<<ret<<endl;
return 0;
}八、跳台阶(dp斐波那契数列模型)

很简单第一题,这里直接上空间优化代码
注意特判
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;cin>>n;
if(n==1||n==2){cout<<n;return 0;}
int a=1,b=2,c;
for(int i=3;i<=n;++i)
{
c=a+b;
a=b;
b=c;
}
cout<<c;
return 0;
}九、扑克牌顺子(排序+模拟 /位图+模拟)

法一:排序+模拟,自己想出来了很开心
排序,边遍历边统计0的个数count,非0元素统计一下下一个元素减去这个元素再减去1,就是这期间需要填补的数gap,最后判断count==gap?出错->只考虑了非零元素区间,如果非零元素区间刚好是+1+1递增,只需把0修改一下就行,也是符合的,所以应该是count>=gap。还是没全部通过,查看用例,具有相同元素会就是false,此时gap会等于-1,如果遇到这种情况直接返回false即可。大功告成。
cpp
bool IsContinuous(vector<int>& numbers) {
sort(numbers.begin(), numbers.end());
int count = 0, gap = 0, cur = 0;
while (cur < 5) {
if (numbers[cur] == 0) {
++count;
++cur;
} else {
if (cur + 1 < 5) {
int x=numbers[cur + 1] - numbers[cur] - 1;
if(x<0)return false;
gap += x;
}
++cur;
}
}
return count >= gap;
}法二:找规律+位图
看完思路也是直呼666
cpp
class Solution {
public:
bool IsContinuous(vector<int>& nums) {
int flag=0;
int _min=14,_max=0;
for(auto&e:nums){
if(e==0) continue;
if(flag&(1<<e)) return false;//说明重复了
flag|=(1<<e);//标记这张票出现过了
_min=min(_min,e);//最小牌
_max=max(_max,e);//最大牌
}
return _max-_min<5;
}
};十、最长回文子串(动规回文串问题)
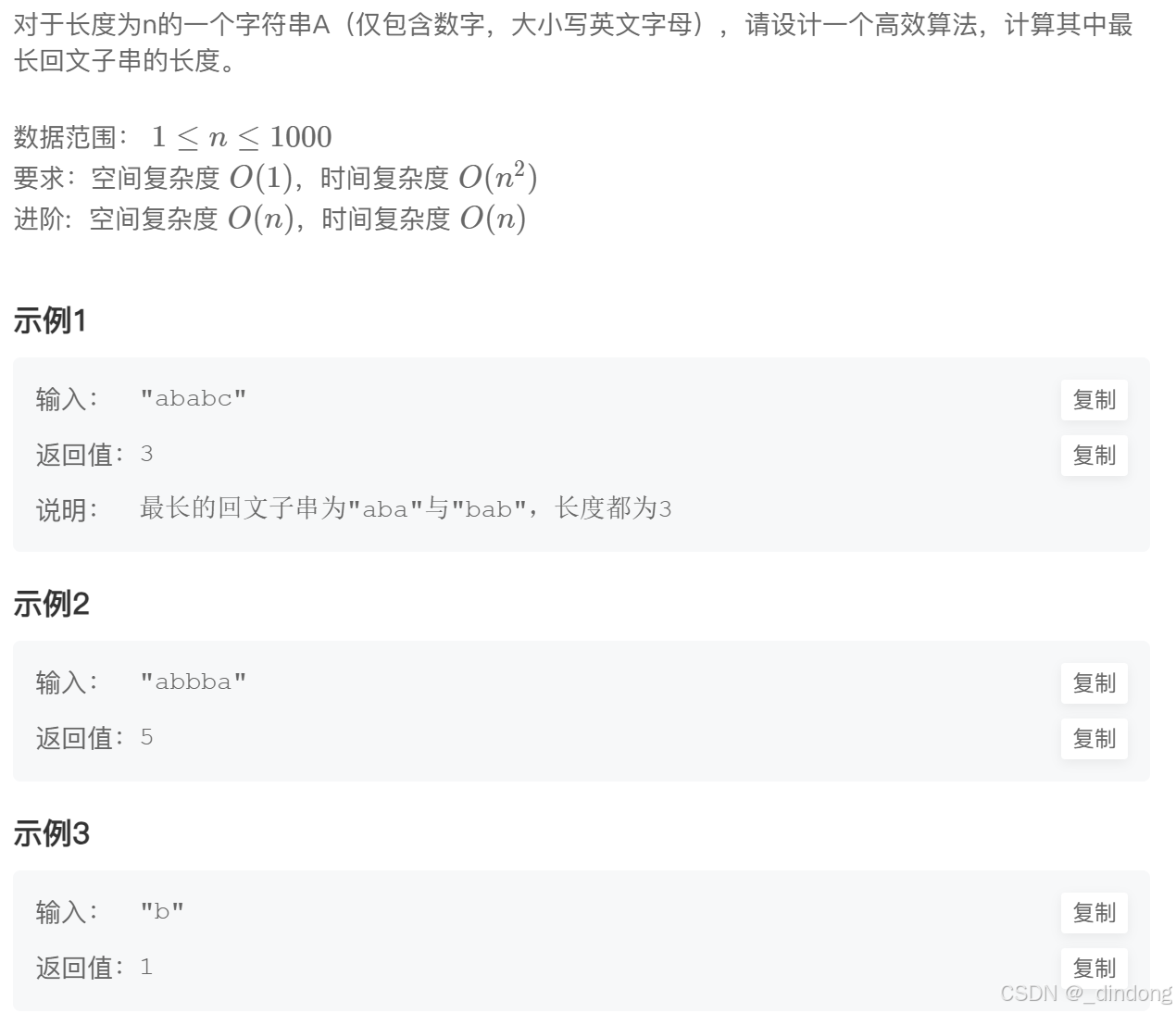
不久前一刷过这题,再次碰见完全没思路了
在动规专栏里有总结回文串问题->动态规划回文串问题汇总
dp[i][j]表示i~j闭区间,是否是回文串,判断是不是就从两端不断往内,
如果s[i]==s[j],如果i==j,返回true,如果i恰好是j左边一个数也就是i+1==j返回true
其他情况就要看dp[i+1][j-1],因为需要后边的数据,所以i层需要倒着填
cpp
int getLongestPalindrome(string A) {
int n=A.size();
vector<vector<bool>> dp(n,vector<bool>(n));
int len=1;
for(int i=n-1;i>=0;--i)
{
for(int j=i;j<n;++j)
{
//默认就是false这里不用再写
//if(A[i]!=A[j])dp[i][j]=false;
if(A[i]==A[j])dp[i][j]=i+1<j?dp[i+1][j-1]:true;
if(dp[i][j]&&len<j-i+1)len=j-i+1;
}
}
return len;
}十一、买卖股票的最佳时机I (贪心)


笔试场上只想到暴力,实在不应该。遍历中途不断更新0~当前位置最小值,然后ret=max(ret,num[i]-prevMin)
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+1;
int num[N];
int main() {
int n;cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;++i)cin>>num[i];
int prevMin=num[0],ret=0;
for(int i=1;i<n;++i)
{
int jud=num[i]-prevMin;
if(jud>ret)ret=jud;
prevMin=min(prevMin,num[i]);
}
cout<<ret;
return 0;
}十二、过河卒(路径dp)
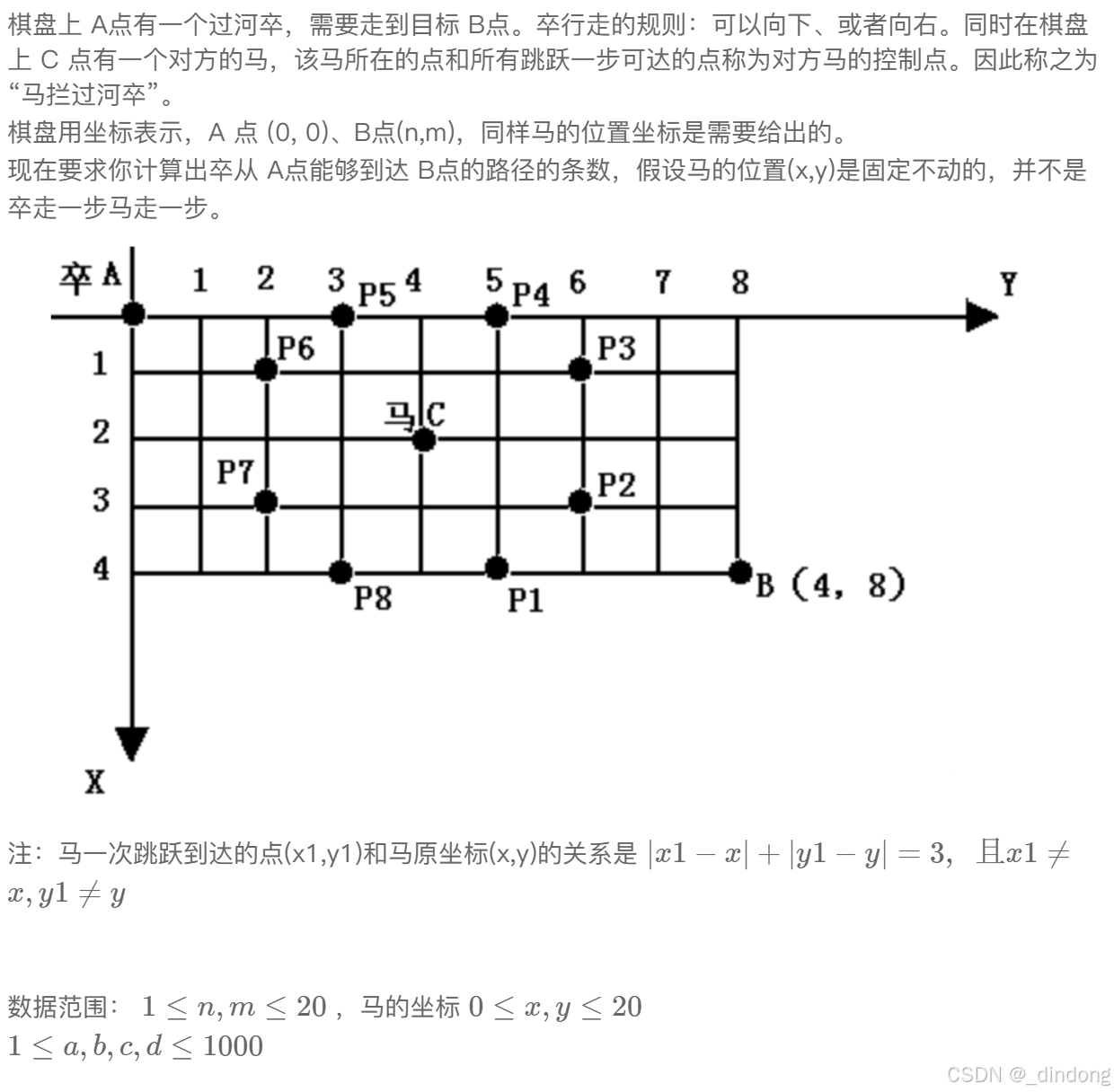

看完就能明白是很明显的路径dp,dp值表示到达该点的总路线条数,遇到拦截点置0,dp值等于上+左。但是注意马不能直着走,判断距离的时候映射的位置不能在同一行,同一列。
此外,int会爆,保险还是开long long
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<cmath>
int main() {
int n,m,x,y;
cin>>n>>m>>x>>y;
vector<vector<long long>> dp(n+2,vector<long long>(m+2));
dp[0][1]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n+1;++i)
{
for(int j=1;j<=m+1;++j)
{
//注意映射,也可以循环外x,y都+=1这样就不用老是写减1
if(i-1==x&&j-1==y)dp[i][j]=0;
//马不能直着走
else if(i-1!=x&&j-1!=y&&abs(i-1-x)+abs(j-1-y)==3)dp[i][j]=0;
else dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j]+dp[i][j-1];
}
}
cout<<dp[n+1][m+1];
return 0;
}十三?、游游的水果大礼包(枚举)
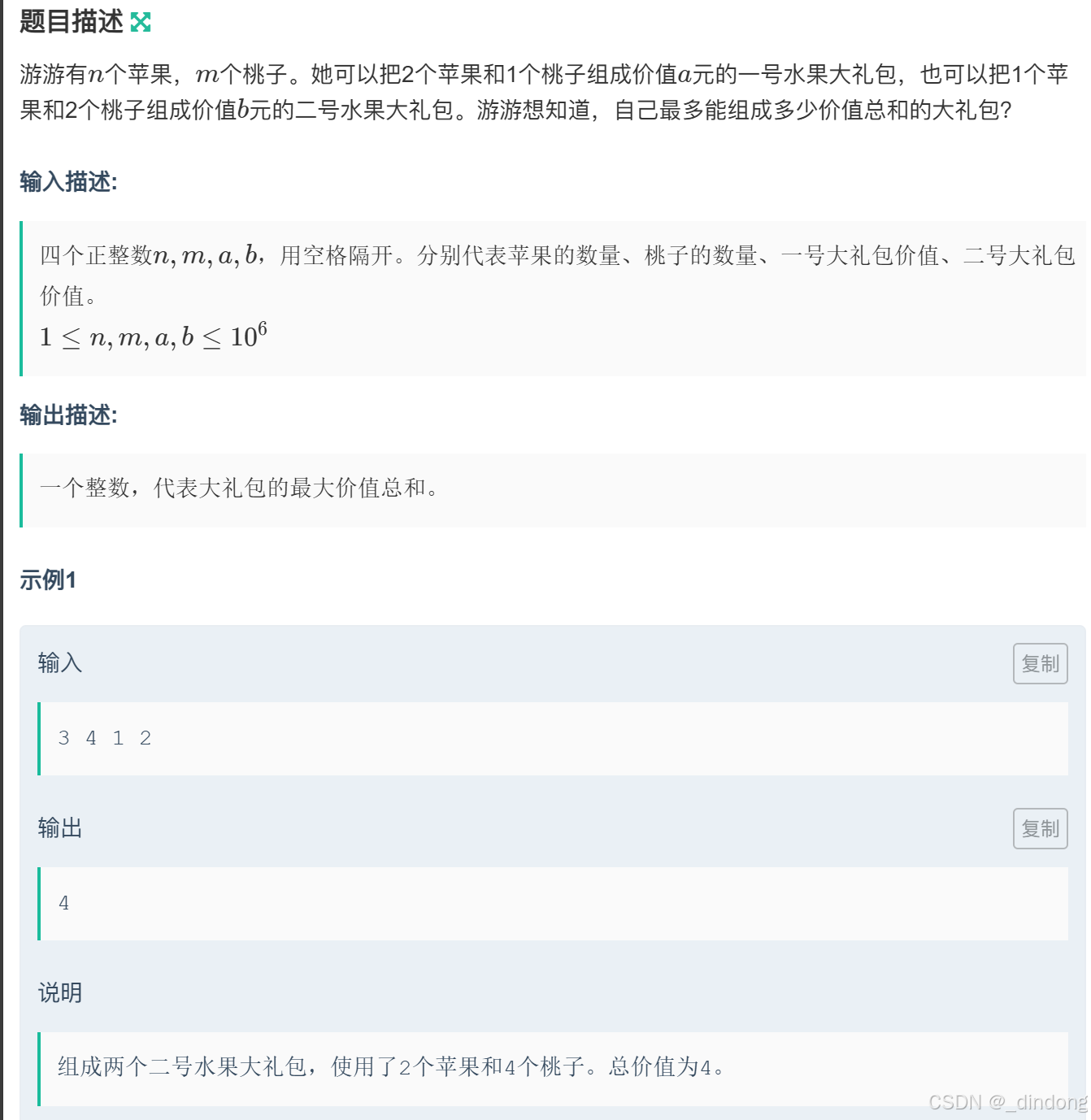

其实按贪心也是能写的,不过没枚举这么简洁,还不如直接枚举
made这里int会爆,要开long long,之后看到即使只有相加都要想到先开long long
cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
long long n,m,a,b;
cin>>n>>m>>a>>b;
long long ret=0;
//我们先尝试枚举1号
for(int x=0;x<=min(n/2,m);++x){
int y=min(n-x*2,(m-x)/2);
ret=max(ret,a*x+b*y);
}
cout<<ret<<endl;
}十四、买卖股票的最佳时机II(双指针/贪心/简单多状态dp)


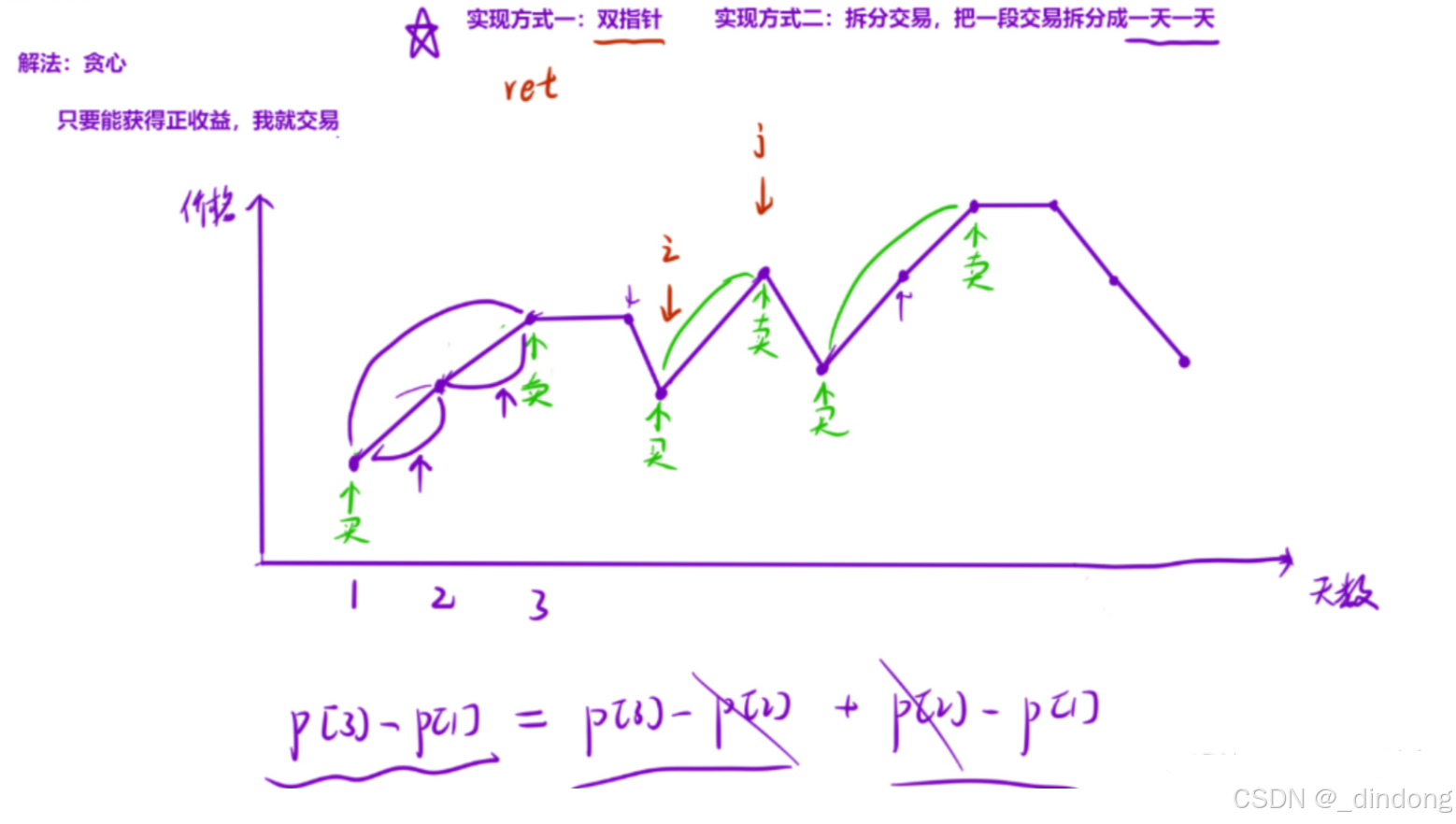
解法一:双指针:
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+3;
int a[N];
int n;
int main() {
cin>>n;
int ret=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;++i) cin>>a[i];
for(int i=0;i<n;++i){
int j=i;
while(j+1<n&&a[j+1]>a[j]) ++j;
//此时j正好在顶点
ret+=a[j]-a[i];
i=j;
}
cout<<ret<<endl;
}
// 64 位输出请用 printf("%lld")解法二:贪心,有正收益我就加,相当于是解法一的思路拆分成一天一天
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+3;
int a[N];
int n;
int main() {
cin>>n;
int ret=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;++i) cin>>a[i];
for(int i=1;i<n;++i)
if(a[i]>a[i-1]) ret+=a[i]-a[i-1];
cout<<ret<<endl;
}
// 64 位输出请用 printf("%lld")解法三:简单多状态dp,f表示买入状态最大利润,g表示卖出状态最大利润
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+1;
int f[N],g[N],price[N];
int main() {
int n;cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;++i)cin>>price[i];
f[0]=-price[0];
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
f[i]=max(f[i-1],g[i-1]-price[i-1]);
g[i]=max(g[i-1],f[i-1]+price[i-1]);
}
cout<<g[n];
return 0;
}十五?、倒置字符串(双指针)
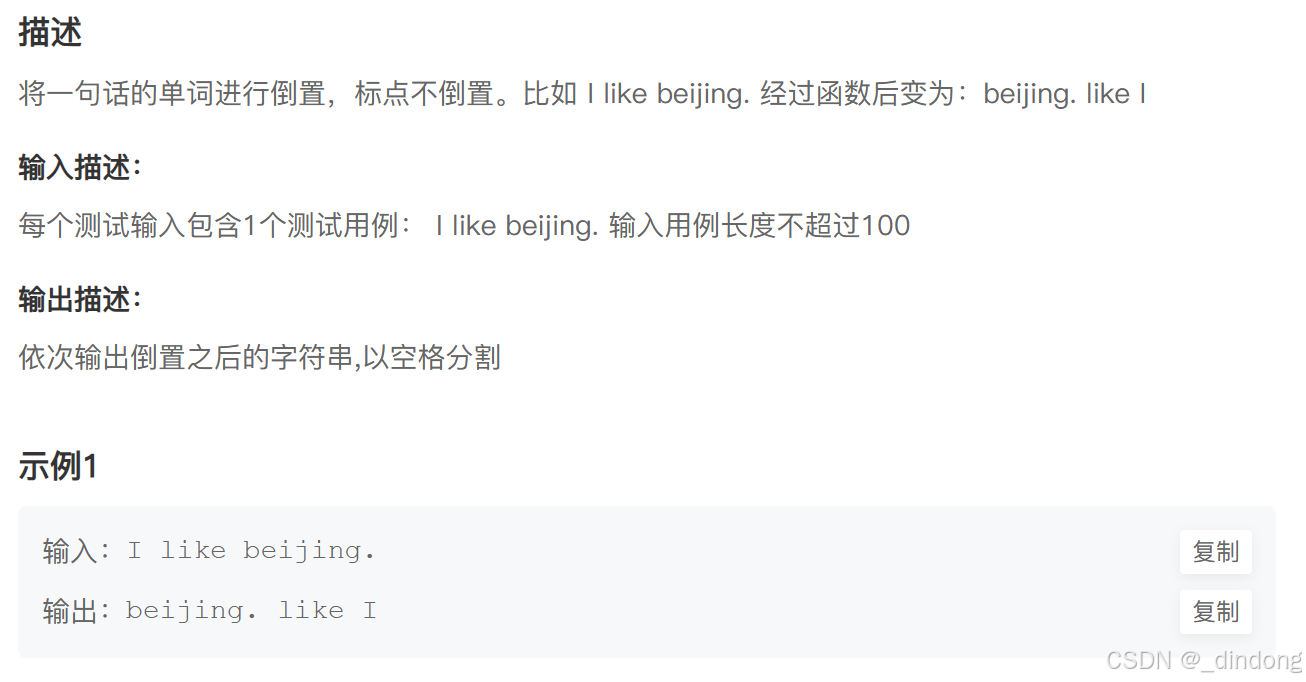
刷过一遍就理解了,这种题目就得先刷一遍,╰(艹皿艹 )。先整体逆转,再局部逆转即可
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s;
//先整体逆置 在局部逆置
getline(cin,s);
reverse(s.begin(),s.end());
int n=s.size();
for(int left=0;left<n;++left){
int right=left;
while(right<n&&s[right]!=' ') ++right;
//开始逆置
reverse(s.begin()+left,s.begin()+right);
left=right;
}
cout<<s<<endl;
}
// 64 位输出请用 printf("%lld")十六、删除公共字符(哈希表)
因为原字符串有空格,cin读取不到空格,所以我们用getline
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<unordered_map>
int main() {
string s1,s2;
//空格也要读取
getline(cin,s1);
getline(cin,s2);
unordered_map<char, int> hash;
for(auto ch:s2)hash[ch]++;
int n=s1.size();
string ret;
for(int i=0;i<n;++i)
{
if(!hash.count(s1[i]))
ret+=s1[i];
}
cout<<ret;
return 0;
}注意这里哈希表可以用数组模拟
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s,t;
getline(cin,s);
getline(cin,t);
bool hash[128]={0};
for(char ch:t) hash[ch]=true;
string ret;
for(auto&ch:s) if(!hash[ch]) ret+=ch;
cout<<ret;
return 0;
}十七、两个链表的第一个公告结点(双指针)

之前刷抖音的时候刷到过这题hehehe
cpp
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};*/
#include <cmath>
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* FindFirstCommonNode( ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2) {
if(!pHead1||!pHead2)return nullptr;
ListNode*cur1=pHead1,*cur2=pHead2;
//用题给最大次数当作循环条件
int n=1000;
while(n--)
{
//可能存在没有公共结点的情况,所以在相等时才返回
if(cur1==cur2)return cur1;
cur1=cur1->next?cur1->next:pHead2;
cur2=cur2->next?cur2->next:pHead1;
}
return nullptr;
}
};十八*、mari和shiny(状态dp+空间优化)

总感觉编题目的有点皮皮的o(* ̄▽ ̄*)o
最先想到的当然是暴力咯,不过只能通过百分之40用例,超时了
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;cin>>n;
string s;cin>>s;
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i<n-2;++i)
{
if(s[i]=='s')
{
for(int j=i+1;j<n-1;++j)
{
if(s[j]=='h')
{
for(int k=j+1;k<n;++k)
{
if(s[k]=='y')++count;
}
}
}
}
}
cout<<count;
return 0;
}下面我们用dp优化。

唉,做的时候也往这方面想了,但就是不知道代码怎么写,不得不说这代码真是太妙了
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
string str;
cin>>n>>str;
long long s=0,h=0,y=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;++i){
char ch=str[i];
if(ch=='s')++s;
else if(ch=='h')h+=s;
else if(ch=='y')y+=h;
}
cout<<y<<endl;
}第二周完结撒花\^o^/
Week2 ending...