业务背景
最近,我带的一位新同事跑过来问我,说我们新做的财务项目,他负责的首页模块想使用CompletableFuture来做首页的各部分数据加载,但是里面有个线程池参数不知道怎么给,在我们项目中没看到有封装好的线程池,想直接new一个线程池又不知道核心参数该给多少怎么办?
当我听到他这里的时候,就明白,线程池这东西大多数人都会用,但是并不知道该怎么合理的用;又怕参数给小了,任务处理很耗时,拖慢接口响应;又怕参数给大了影响到其他地方;
想到这里,就考虑到线程池如何才能做成动态的,核心数值参数有没有办法不经过手动编码,而是结合配置中心来解决;
于是,翻了一下ThreadPoolExecutor源码,发现里面给我们提供了一些set和get参数;
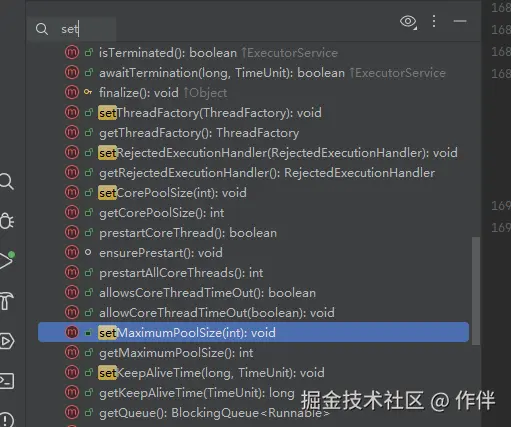
那么看到这几个set顿时就明白了,线程池虽然在Springboot中作为Bean进行了初始化,但是初始化后得到的实例,jdk是允许我们动态修改的。
紧接着,搜了一下百度看是否有这种例子,结果看到了美团的开源框架:dynamic-tp
dynamic-tp官网:dynamictp.cn/
人家给的功能更加全面,更加合适,涵盖监控报警,配置中心等等;
但是,秉着高自由度的原则,我们可以借助他的思想手搓一个jar包,加上公司的Apollo配置中心,同样可以实现动态线程池的作用;
技术设计
初步设想是采用 Apollo + Prometheus + Grafana + starter来实现,我们将线程池内部的参数进行暴露出去给actuator,然后结合监控大板观察有异常任务类型时可以及时的调整线程池的参数;
同时,Apollo上配置每一个组自己的线程池,通过前缀区分,jar包内采用工厂模式对外提供构造好的线程池,这样不同分工之间紧密结合构成一个完整的动态线程池插件;
那么,大致的流程图就是下面的这个样子:
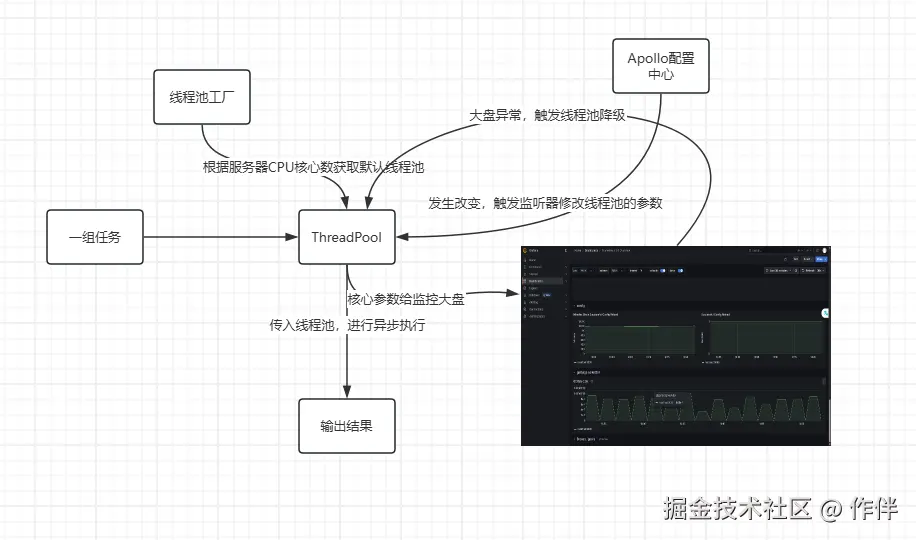
通过这种方式,我们对外提供的始终只是一个被实例化好的Executor,外部也只需要根据拿到的线程池去执行自己的业务;
代码实现
遵循插件化思想,依旧是对外提供jar包,需要引入Springboot的jar包pom 同时jar包内引入Apollo客户端,让线程池能读取Apollo上的配置:
xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Apollo 客户端 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.ctrip.framework.apollo</groupId>
<artifactId>apollo-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 监控指标 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.micrometer</groupId>
<artifactId>micrometer-core</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>线程池任务一般分两个类型:
- IO密集型:比如频繁写入读取文件
- CPU密集型:比如内部有复杂的递归计算
不同的任务类型,默认的线程池参数也不一样,那么从网上了解到的常用公式:
- IO密集型
- coreSize = CPU核心数 * 2
- maxSize = CPU 核心数 × 4 或 CPU 核心数 × (1 + 平均 IO 等待时间 / 平均任务执行时间)
- 不过这里的maxSize是一个理想值,因为平均 IO 等待时间和平均任务执行时间是不固定的,一般就 * 4即可
- keepAlive = 60s
- CPU密集型
- coreSize = CPU核心数 + 1
- maxSize = CPU核心数 * 2
- keepAlive = 30s
例如你机器是8核16g,那么根据上述公式计算,默认的线程池参数 coreSize=16 or 9;maxSize = 32 or 16 ;
借助Java的SPI思想,提供一个自定义的拒绝策略实现,用户可以自定义拒绝策略然后注册到策略管理器中使用:
java
public class RejectedPolicyRegistry {
private static final Map<String, RejectedExecutionHandler> POLICIES = new HashMap<>();
static {
POLICIES.put("AbortPolicy", new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
POLICIES.put("CallerRunsPolicy", new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
POLICIES.put("DiscardOldestPolicy", new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy());
POLICIES.put("DiscardPolicy", new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy());
}
public static void register(String name, RejectedExecutionHandler policy) {
POLICIES.put(name, policy);
}
public static RejectedExecutionHandler getPolicy(String key) {
if (POLICIES.containsKey(key)) {
return POLICIES.get(key);
}
try {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(key);
return (RejectedExecutionHandler) clazz.newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("拒绝策略不存在:" + key, e);
}
}
}然后再自定义线程池的7种参数:
Java
@Data
public class ThreadPoolConfig {
/**
* 线程池名称
*/
private String threadPoolName;
/**
* 核心线程数
*/
private int coreSize;
/**
* 最大线程数
*/
private int maxSize;
/**
* 队列容量
*/
private int queueCapacity;
/**
* 线程空闲时间
*/
private int keepAliveSeconds = 60;
/**
* 线程前缀名称
*/
private String threadNamePrefix = "customerThreadPool";
/**
* 拒绝策略
*/
private RejectedExecutionHandler rejectedPolicy;
}提供对外的properties配置:
java
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "dynamic.thread-pool")
public class ThreadPoolProperties {
/**
* apollo配置命名空间
*/
private String apolloNamespace;
/**
* 线程池默认队列容量
*/
private Integer defaultQueueCapacity;
/**
* 是否启用监控指标
*/
private Boolean metricsEnabled = true;
}提供对外的线程池参数监控:
java
@Component
public class ThreadPoolStatusMonitor {
// 注入线程池工厂(用于获取已创建的线程池)
private final ThreadPoolFactory threadPoolFactory;
@Autowired
public ThreadPoolStatusMonitor(ThreadPoolFactory threadPoolFactory) {
this.threadPoolFactory = threadPoolFactory;
}
/**
* 获取线程池的运行时参数
* @param threadPoolName 线程池名称
* @return 运行时参数(核心线程数、最大线程数等)
*/
public Map<String, Object> getThreadPoolRuntimeStatus(String threadPoolName) {
Map<String, Object> status = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// 获取线程池实例(若未创建则返回空)
ExecutorService executor = threadPoolFactory.build(threadPoolName);
if (!(executor instanceof ThreadPoolExecutor)) {
status.put("error", "线程池不存在或类型不匹配");
return status;
}
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = (ThreadPoolExecutor) executor;
// 线程池运行时参数
status.put("threadPoolName", threadPoolName);
status.put("corePoolSize", threadPool.getCorePoolSize()); // 实际核心线程数
status.put("maximumPoolSize", threadPool.getMaximumPoolSize()); // 实际最大线程数
status.put("activeCount", threadPool.getActiveCount()); // 活跃线程数
status.put("queueSize", threadPool.getQueue().size()); // 队列当前任务数
status.put("completedTaskCount", threadPool.getCompletedTaskCount()); // 已完成任务数
status.put("keepAliveTime", threadPool.getKeepAliveTime(java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit.SECONDS)); // 空闲时间
return status;
}
}定义好线程池工厂,结合meterRegistry和ApolloConfig:
java
@Slf4j
public class ThreadPoolFactory {
private final Map<String, ExecutorService> executorServiceMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final ThreadPoolProperties threadPoolProperties;
private final MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
private final Config apolloConfig;
public ThreadPoolFactory(ThreadPoolProperties threadPoolProperties, MeterRegistry meterRegistry) {
this.threadPoolProperties = threadPoolProperties;
this.meterRegistry = meterRegistry;
this.apolloConfig = ConfigService.getConfig(threadPoolProperties.getApolloNamespace());
}
public ExecutorService build(String threadPoolName) {
return executorServiceMap.computeIfAbsent(threadPoolName, this::createThreadPool);
}
private ExecutorService createThreadPool(String threadPoolName) {
// 根据CPU计算默认的线程池大小配置
ThreadPoolConfig threadPoolConfig = new ThreadPoolConfig();
threadPoolConfig.setThreadPoolName(threadPoolName);
threadPoolConfig.setCoreSize(CpuCoreUtils.getDefaultCoreSize(threadPoolName));
threadPoolConfig.setMaxSize(CpuCoreUtils.getDefaultMaxSize(threadPoolName));
threadPoolConfig.setQueueCapacity(CpuCoreUtils.getDefaultQueueCapacity(threadPoolProperties.getDefaultQueueCapacity()));
threadPoolConfig.setRejectedPolicy(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
// 加载Apollo配置 重写线程池数据
this.loadApolloConfig(threadPoolConfig);
// 加载线程池配置
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = loadThreadPoolExecutor(threadPoolConfig);
// 注册监控
if (meterRegistry != null) {
meterRegistry.gauge("thread.pool.active", executor, ThreadPoolExecutor::getActiveCount);
meterRegistry.gauge("thread.pool.queue.size", executor.getQueue(), java.util.Queue::size);
}
registerApolloListener(threadPoolName);
log.info("线程池[{}]初始化完成: core={}, max={}, queue={}",
threadPoolName, threadPoolConfig.getCoreSize(), threadPoolConfig.getMaxSize(), threadPoolConfig.getQueueCapacity());
return executor;
}
private void loadApolloConfig(ThreadPoolConfig config) {
String prefix = config.getThreadPoolName() + ".";
config.setCoreSize(apolloConfig.getIntProperty(prefix + "coreSize", config.getCoreSize()));
config.setMaxSize(apolloConfig.getIntProperty(prefix + "maxSize", config.getMaxSize()));
config.setQueueCapacity(apolloConfig.getIntProperty(prefix + "queueCapacity", config.getQueueCapacity()));
config.setKeepAliveSeconds(apolloConfig.getIntProperty(prefix + "keepAliveSeconds", 60));
config.setThreadNamePrefix(apolloConfig.getProperty(prefix + "threadNamePrefix", config.getThreadNamePrefix()));
String policy = apolloConfig.getProperty(prefix + "rejectedPolicy", "AbortPolicy");
config.setRejectedPolicy(RejectedPolicyRegistry.getPolicy(policy));
}
private ThreadPoolExecutor loadThreadPoolExecutor(ThreadPoolConfig threadPoolConfig) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(
threadPoolConfig.getCoreSize(),
threadPoolConfig.getMaxSize(),
threadPoolConfig.getKeepAliveSeconds(),
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(threadPoolConfig.getQueueCapacity()),
r -> new Thread(r, threadPoolConfig.getThreadNamePrefix()),
threadPoolConfig.getRejectedPolicy());
}
// 注册Apollo监听器 监听配置变化 重新创建线程池
private void registerApolloListener(String threadPoolName) {
apolloConfig.addChangeListener((ConfigChangeEvent event) -> {
String prefix = threadPoolName + ".";
if (event.changedKeys().stream().anyMatch(key -> key.startsWith(prefix))) {
log.info("线程池[{}]配置变更,重建中...", threadPoolName);
ExecutorService newExecutor = createThreadPool(threadPoolName);
replaceThreadPool(threadPoolName, newExecutor);
}
});
}
private void replaceThreadPool(String threadPoolName, ExecutorService newExecutor) {
ExecutorService oldExecutor = executorServiceMap.get(threadPoolName);
if (oldExecutor == null) {
executorServiceMap.put(threadPoolName, newExecutor);
return;
}
executorServiceMap.replace(threadPoolName, newExecutor);
new Thread(() -> {
try {
oldExecutor.shutdown();
if (!oldExecutor.awaitTermination(5, TimeUnit.MINUTES)) {
oldExecutor.shutdownNow();
log.warn("线程池[{}]强制关闭超时任务", threadPoolName);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
oldExecutor.shutdownNow();
}
}).start();
}
}将ThreadPoolFactory放在Configuration中:
java
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ThreadPoolProperties.class)
public class ThreadPoolAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public ThreadPoolFactory threadPoolFactory(ThreadPoolProperties properties,
MeterRegistry meterRegistry) {
ThreadPoolFactory threadPoolFactory = new ThreadPoolFactory(properties, meterRegistry);
ThreadPoolUtils.init(threadPoolFactory);
return threadPoolFactory;
}
}然后就只需要对外提供一个线程池工具类:
java
public class ThreadPoolUtils {
private static volatile ThreadPoolFactory threadPoolFactory;
private ThreadPoolUtils() {
throw new AssertionError("工具类不允许实例化");
}
static void init(ThreadPoolFactory factory) {
if (threadPoolFactory == null) {
synchronized (ThreadPoolUtils.class) {
if (threadPoolFactory == null) {
threadPoolFactory = factory;
}
}
}
}
// 静态工具方法:执行任务
public static void execute(String threadPoolName, Runnable task) {
getExecutor(threadPoolName).execute(task);
}
public static <T> Future<T> submit(String threadPoolName, Callable<T> task) {
return getExecutor(threadPoolName).submit(task);
}
public static void executeWithTimeout(String threadPoolName, Runnable task, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws TimeoutException, InterruptedException {
Future<?> future = getExecutor(threadPoolName).submit(task);
try {
future.get(timeout, unit);
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
future.cancel(true);
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("任务执行失败", e);
}
}
// 获取线程池(校验初始化状态)
private static ExecutorService getExecutor(String threadPoolName) {
if (threadPoolFactory == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("线程池工厂未初始化,请检查Spring配置");
}
return threadPoolFactory.build(threadPoolName);
}
}经历了上述所有步骤后,我们就可以在项目中配置好Apollo和线程池默认数据进行测试
测试效果
在Apollo中定义好一组线程池数据:
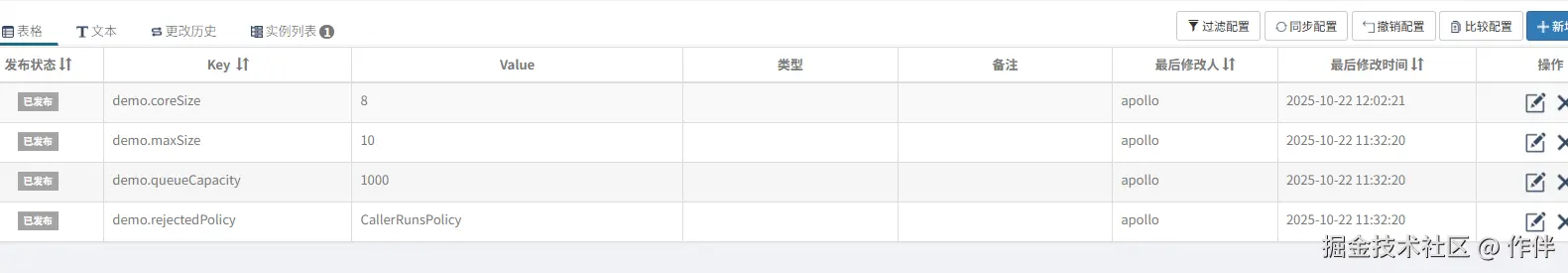
随后,采用api的形式注入我们的monitor,修改Apollo上的参数观察效果:
java
@RestController
public class TestThreadPoolApi {
@Autowired
private ThreadPoolStatusMonitor statusMonitor;
@GetMapping
public String getThreadPool() {
Map<String, Object> demo = statusMonitor.getThreadPoolRuntimeStatus("demo");
return JSONUtil.toJsonStr( demo);
}
}
至此,我们就实现了一个简单,可插拔形式的动态线程池;