JavaScript原型对象、构造函数、继承与类详解
一、5W2H详细解析
What(什么)
深入解析JavaScript中原型对象、实例对象、构造函数之间的关系,以及它们如何延伸到继承、类和封装等概念。这是理解JavaScript面向对象编程的基础。
Why(为什么)
掌握这些核心概念对于深入理解JavaScript语言特性、进行高效的前端开发以及解决复杂的编程问题至关重要。同时这也是前端面试中的高频考点。
Who(谁)
适用于所有希望深入理解JavaScript面向对象编程的开发者,特别是准备前端面试的求职者。
When(何时)
在学习JavaScript进阶知识、准备技术面试或遇到相关编程问题时。
Where(哪里)
在JavaScript开发环境中的任何地方,特别是在处理对象创建、继承和封装时。
How(如何做)
通过理论讲解结合代码示例的方式,从基础概念开始逐步深入到高级应用。
How much(多少成本/资源)
需要一定的时间投入来理解这些概念,但掌握后将大大提升JavaScript编程能力。
二、图解原型和原型链
原型和原型链是 JS 中不可避免需要碰到的知识点,本文使用图片和文字结合的形式缕一缕原型、原型链、实例、构造函数等等概念之间的关系。
Constructor 构造函数
首先我们先写一个构造函数 Person,构造函数一般为了区别普通函数要求首字母大写:
javascript
function Person(){}prototype 原型
原型指的就是一个对象,实例"继承"那个对象的属性。在原型上定义的属性,通过"继承",实例也拥有了这个属性。"继承"这个行为是在 new 操作符内部实现的。
先不说实例,原型与构造函数的关系就是,构造函数内部有一个名为 prototype 的属性,通过这个属性就能访问到原型:
javascript
function Person(){}
// Person 就是构造函数,Person.prototype 就是原型
console.log(Person.prototype); // {}instance 实例
有个构造函数,我们就可以在原型上创建可以"继承"的属性,并通过 new 操作符创建实例
比方说 Person,我们要创建一个 person 实例,那么使用 new 操作符就可以实现,并通过 instanceof 来检查他们之间的关系:
javascript
function Person(){}
const person = new Person();
console.log(person instanceof Person); // true我们在原型上定义一个属性,那么实例上也就可以"继承"这个属性:
javascript
function Person(){}
Person.prototype.name = "default name";
const person = new Person();
console.log(person.name); // "default name"proto 隐式原型
实例通过 proto 访问到原型,所以如果是实例,那么就可以通过这个属性直接访问到原型:
javascript
function Person(){}
const person = new Person();
// 实例通过 __proto__ 访问到原型
console.log(person.__proto__); // Person.prototype所以这两者是等价的:
javascript
function Person(){}
const person = new Person();
console.log(person.__proto__ === Person.prototype); // trueconstructor 构造函数属性
既然构造函数通过 prototype 来访问到原型,那么原型也应该能够通过某种途径访问到构造函数,这就是 constructor:
javascript
function Person(){}
// 原型通过 constructor 属性访问到构造函数
console.log(Person.prototype.constructor === Person); // true因此两者的关系应该是这样:
javascript
function Person(){}
const person = new Person();
// 关系链
console.log(person.__proto__ === Person.prototype); // true
console.log(Person.prototype.constructor === Person); // true
console.log(person.__proto__.constructor === Person); // true注意这里的 constructor 是原型的一个属性,Person.prototype.constructor 指向的才是真正的构造函数。两者名字不要弄混了。
实例、构造函数、原型之间的关系
这里我们可以看到如果实例想要访问构造函数,那么应当是:
javascript
function Person(){}
const person = new Person();
// 实例 -> 原型 -> 构造函数
console.log(person.__proto__.constructor === Person); // true没有从实例直接访问到构造函数的属性或方法:
javascript
function Person(){}
const person = new Person();
// 这样是访问不到的
// person.constructor === Person 也能访问到,但这是通过原型链查找的实例与原型则是通过上文中提到的 proto 去访问到。
在读取一个实例的属性的过程中,如果属性在该实例中没有找到,那么就会循着 proto 指定的原型上去寻找,如果还找不到,则尝试寻找原型的原型:
javascript
function Person(){}
Person.prototype.name = "default name";
const person = new Person();
// 实例上没有 name 属性,通过 __proto__ 在原型上找到
console.log(person.name); // "default name"
// 如果在实例上定义同名属性,会覆盖原型上的属性
person.name = "custom name";
console.log(person.name); // "custom name"我们把注释删掉,给实例同名属性,可以看到打印出来的属性就指向这个:
javascript
function Person(){}
Person.prototype.name = "default name";
const person = new Person();
person.name = "custom name";
console.log(person.name); // "custom name" - 实例属性
console.log(person.__proto__.name); // "default name" - 原型属性原型链示意图
javascript
实例对象 (person)
↓ __proto__
构造函数的原型对象 (Person.prototype)
↓ __proto__
Object.prototype
↓ __proto__
null原型链
原型同样也可以通过 proto 访问到原型的原型,比方说这里有个构造函数 Person 然后"继承"前者的有一个构造函数 People,然后 new People 得到实例 p
javascript
function Person(){}
function People(){}
// 设置继承关系
People.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype);
People.prototype.constructor = People;
const p = new People();当访问 p 中的一个非自有属性的时候,就会通过 proto 作为桥梁连接起来的一系列原型、原型的原型、原型的原型的原型直到 Object 构造函数为止。
这个搜索的过程形成的链状关系就是原型链:
javascript
p (实例)
↓ __proto__
People.prototype
↓ __proto__
Person.prototype
↓ __proto__
Object.prototype
↓ __proto__
null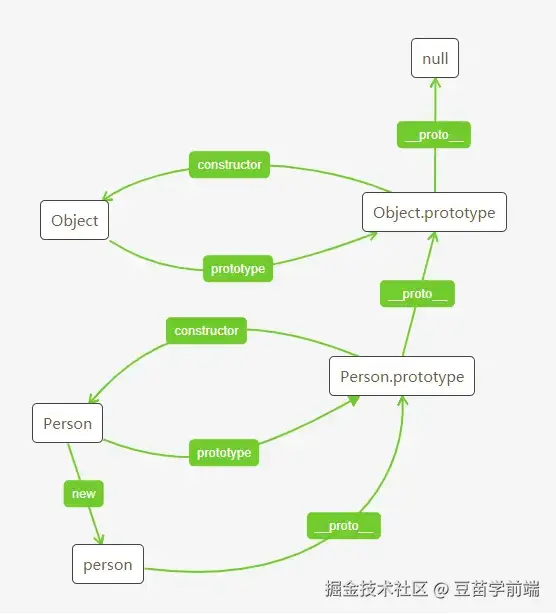
看到 null 了么,原型链搜索搜到 null 为止,搜不到那访问的这个属性就是不存在的:
javascript
function Person(){}
function People(){}
People.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype);
People.prototype.constructor = People;
const p = new People();
// 搜索路径: p -> People.prototype -> Person.prototype -> Object.prototype -> null
console.log(p.toString); // 找到了 Object.prototype.toString
// 搜索不存在的属性
console.log(p.nonExistentProperty); // undefined以上,这就是原型、原型链、构造函数、实例、null 之间的关系。
三、完整的技术落地方案
1. 原型对象、实例对象与构造函数详解
基本概念
构造函数(Constructor Function) : 构造函数是用于创建特定类型对象的函数。在JavaScript中,任何函数都可以作为构造函数使用,只要通过new关键字调用。
javascript
// 构造函数示例
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
Person.prototype.sayHello = function() {
console.log(`Hello, my name is ${this.name}`);
};
// 使用构造函数创建实例
const person1 = new Person("Alice", 25);
const person2 = new Person("Bob", 30);实例对象(Instance Object) : 通过构造函数和new关键字创建的具体对象称为实例对象。
javascript
// person1和person2都是实例对象
console.log(person1 instanceof Person); // true
console.log(person2 instanceof Person); // true原型对象(Prototype Object) : 每个函数都有一个prototype属性,这个属性指向一个对象,这个对象就是原型对象。原型对象包含可以由特定类型的所有实例共享的属性和方法。
javascript
// 访问原型对象
console.log(Person.prototype); // 原型对象
console.log(person1.__proto__); // 实例对象通过__proto__指向原型对象
console.log(Person.prototype === person1.__proto__); // true三者关系图解
scss
构造函数(Person) <------constructor-------- 原型对象(Person.prototype)
| |
| new |
| |
v |
实例对象(person1) <------------------- __proto__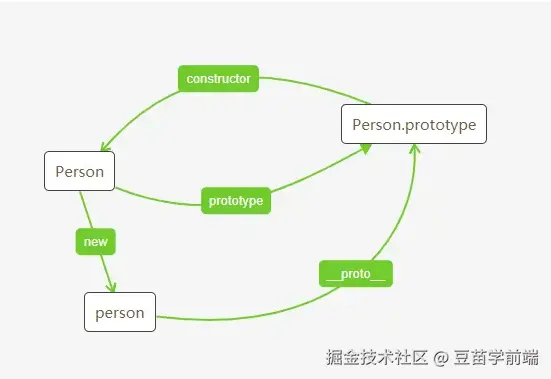
详细代码示例
javascript
// 定义构造函数
function Animal(name, type) {
// 实例属性
this.name = name;
this.type = type;
this.energy = 100;
}
// 原型方法
Animal.prototype.eat = function(food) {
console.log(`${this.name} is eating ${food}`);
this.energy += 10;
};
Animal.prototype.sleep = function() {
console.log(`${this.name} is sleeping`);
this.energy += 20;
};
Animal.prototype.getInfo = function() {
return `${this.name} is a ${this.type} with ${this.energy} energy`;
};
// 创建实例对象
const dog = new Animal("Buddy", "Dog");
const cat = new Animal("Whiskers", "Cat");
// 使用方法
dog.eat("bone"); // Buddy is eating bone
cat.sleep(); // Whiskers is sleeping
console.log(dog.getInfo()); // Buddy is a Dog with 110 energy
console.log(cat.getInfo()); // Whiskers is a Cat with 120 energy
// 验证关系
console.log(dog.constructor === Animal); // true
console.log(dog.__proto__ === Animal.prototype); // true
console.log(Animal.prototype.constructor === Animal); // true原型关系及原型链总结
-
构造函数 → 原型对象 :
- 图中绿色箭头标记为"constructor",表示 Person 构造函数通过其 prototype 属性指向 Person.prototype 原型对象
- 每个函数在创建时都会自动拥有一个 prototype 属性,指向其原型对象
-
原型对象 → 构造函数 :
- 图中绿色箭头标记为"prototype",表示 Person.prototype 原型对象通过其 constructor 属性指回 Person 构造函数
- 这形成了一个循环引用关系
-
实例 → 原型对象 :
- 图中绿色箭头标记为" proto "和"proto",表示通过 new Person() 创建的 person 实例通过其内部的 [[Prototype]] 链接(即 proto )指向 Person.prototype
- 当使用 new 关键字创建对象时,新对象的 proto 会自动链接到构造函数的 prototype
prototype和__proto__属性的作用
-
prototype :
- 只存在于构造函数上的属性
- 指向该构造函数的原型对象
- 用于定义所有实例共享的属性和方法
-
proto :
- 存在于所有对象上的内部属性(ES6之前是非标准的,现在已标准化)
- 指向创建该对象的构造函数的原型对象
- 是对象实例访问原型链的入口点
原型链工作机制
当我们访问一个对象的属性或方法时,JavaScript引擎会:
- 首先检查对象自身是否有该属性/方法
- 如果没有,则沿着 proto 链向上查找到对象的原型
- 如果原型上也没有,则继续沿着原型的 proto 向上查找
- 这个查找过程会一直持续到找到属性/方法或到达原型链的末端( Object.prototype.proto === null )
2. 继承详解
原型链继承
javascript
// 父类
function Animal(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Animal.prototype.speak = function() {
console.log(`${this.name} makes a sound`);
};
// 子类
function Dog(name, breed) {
Animal.call(this, name); // 调用父类构造函数
this.breed = breed;
}
// 设置继承关系
Dog.prototype = Object.create(Animal.prototype);
Dog.prototype.constructor = Dog;
// 子类特有方法
Dog.prototype.bark = function() {
console.log(`${this.name} barks`);
};
// 使用
const dog = new Dog("Buddy", "Golden Retriever");
dog.speak(); // Buddy makes a sound
dog.bark(); // Buddy barks借用构造函数继承
javascript
function Parent(name) {
this.name = name;
this.hobbies = ["reading", "swimming"];
}
function Child(name, age) {
Parent.call(this, name); // 借用父类构造函数
this.age = age;
}
const child1 = new Child("Alice", 10);
const child2 = new Child("Bob", 12);
child1.hobbies.push("dancing");
console.log(child1.hobbies); // ["reading", "swimming", "dancing"]
console.log(child2.hobbies); // ["reading", "swimming"]组合继承
javascript
function Parent(name) {
this.name = name;
this.colors = ["red", "blue"];
}
Parent.prototype.getName = function() {
return this.name;
};
function Child(name, age) {
Parent.call(this, name); // 借用构造函数继承属性
this.age = age;
}
// 原型链继承方法
Child.prototype = Object.create(Parent.prototype);
Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
Child.prototype.getAge = function() {
return this.age;
};
const child1 = new Child("Alice", 10);
const child2 = new Child("Bob", 12);
child1.colors.push("green");
console.log(child1.colors); // ["red", "blue", "green"]
console.log(child2.colors); // ["red", "blue"]
console.log(child1.getName()); // Alice
console.log(child2.getName()); // Bob3. 类(Class)详解
ES6引入了类语法,使JavaScript的面向对象编程更加直观。
基本类定义
javascript
class Person {
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// 原型方法
sayHello() {
console.log(`Hello, my name is ${this.name}`);
}
// 静态方法
static getSpecies() {
return "Homo sapiens";
}
// Getter
get description() {
return `${this.name} is ${this.age} years old`;
}
// Setter
set nickname(value) {
this._nickname = value;
}
get nickname() {
return this._nickname || this.name;
}
}
const person = new Person("Alice", 25);
person.sayHello(); // Hello, my name is Alice
console.log(Person.getSpecies()); // Homo sapiens
console.log(person.description); // Alice is 25 years old
person.nickname = "Ali";
console.log(person.nickname); // Ali类继承
javascript
class Animal {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
speak() {
console.log(`${this.name} makes a sound`);
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
constructor(name, breed) {
super(name); // 调用父类构造函数
this.breed = breed;
}
speak() {
super.speak(); // 调用父类方法
console.log(`${this.name} barks`);
}
getInfo() {
return `${this.name} is a ${this.breed}`;
}
}
const dog = new Dog("Buddy", "Golden Retriever");
dog.speak();
// Buddy makes a sound
// Buddy barks
console.log(dog.getInfo()); // Buddy is a Golden Retriever4. 封装类详解
javascript
class BankAccount {
constructor(accountNumber, initialBalance) {
this.accountNumber = accountNumber;
this._balance = initialBalance; // 私有属性约定
}
// 存款
deposit(amount) {
if (amount > 0) {
this._balance += amount;
return this._balance;
}
throw new Error("Deposit amount must be positive");
}
// 取款
withdraw(amount) {
if (amount > 0 && amount <= this._balance) {
this._balance -= amount;
return this._balance;
}
throw new Error("Invalid withdrawal amount");
}
// 获取余额
getBalance() {
return this._balance;
}
// 转账
transfer(amount, targetAccount) {
this.withdraw(amount);
targetAccount.deposit(amount);
}
}
// 使用示例
const account1 = new BankAccount("123456", 1000);
const account2 = new BankAccount("789012", 500);
account1.deposit(200);
console.log(account1.getBalance()); // 1200
account1.transfer(300, account2);
console.log(account1.getBalance()); // 900
console.log(account2.getBalance()); // 800四、技术重点难点列表及其解决办法
1. 原型链理解难点
难点 :理解原型链的查找机制和__proto__与prototype的区别。
解决办法:
- 通过可视化图解理解原型链结构
- 多做代码实验验证原型链查找过程
- 理解
__proto__是实例对象的属性,prototype是构造函数的属性
javascript
// 原型链查找示例
function Foo() {}
const foo = new Foo();
console.log(foo.__proto__ === Foo.prototype); // true
console.log(Foo.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype); // true
console.log(Object.prototype.__proto__ === null); // true2. 继承实现难点
难点:正确实现各种继承方式,避免引用类型属性被共享的问题。
解决办法:
- 理解组合继承的优势和不足
- 掌握寄生组合式继承的实现方式
- 使用ES6的class语法简化继承实现
javascript
// 寄生组合式继承
function inheritPrototype(subType, superType) {
const prototype = Object.create(superType.prototype);
prototype.constructor = subType;
subType.prototype = prototype;
}
function Parent(name) {
this.name = name;
this.colors = ["red", "blue"];
}
Parent.prototype.sayName = function() {
console.log(this.name);
};
function Child(name, age) {
Parent.call(this, name);
this.age = age;
}
inheritPrototype(Child, Parent);
Child.prototype.sayAge = function() {
console.log(this.age);
};3. 类与构造函数的区别
难点:理解ES6类与ES5构造函数的区别和联系。
解决办法:
- 理解类本质上仍然是基于原型的语法糖
- 掌握类的静态方法、getter/setter等特性
- 理解类必须使用new调用的限制
javascript
// 类与构造函数的等价实现
// ES5构造函数
function PersonES5(name) {
this.name = name;
}
PersonES5.prototype.sayHello = function() {
console.log(`Hello, ${this.name}`);
};
// ES6类
class PersonES6 {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
sayHello() {
console.log(`Hello, ${this.name}`);
}
}
// 两者创建的对象行为基本一致
const person1 = new PersonES5("Alice");
const person2 = new PersonES6("Bob");
person1.sayHello(); // Hello, Alice
person2.sayHello(); // Hello, Bob4. 私有属性实现难点
难点:JavaScript中没有真正的私有属性,如何实现封装。
解决办法:
- 使用命名约定(下划线前缀)表示私有属性
- 使用Symbol创建私有属性
- 使用ES2022的私有字段语法(#)
javascript
// 方法1:命名约定
class MyClass1 {
constructor() {
this._privateProp = "private";
}
}
// 方法2:Symbol
const privateProp = Symbol("private");
class MyClass2 {
constructor() {
this[privateProp] = "private";
}
}
// 方法3:ES2022私有字段(需要现代浏览器支持)
class MyClass3 {
#privateProp = "private";
getPrivateProp() {
return this.#privateProp;
}
}五、场景或业务的痛难点及其解决方案
1. 对象创建的灵活性需求
痛点:在复杂的业务场景中,需要灵活地创建具有不同属性和方法的对象。
解决方案:
- 使用工厂模式创建对象
- 结合原型继承实现代码复用
- 使用ES6类简化对象创建
javascript
// 工厂模式示例
class ShapeFactory {
static createShape(type, ...args) {
switch(type) {
case 'circle':
return new Circle(...args);
case 'rectangle':
return new Rectangle(...args);
default:
throw new Error('Unknown shape type');
}
}
}
class Circle {
constructor(radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
area() {
return Math.PI * this.radius ** 2;
}
}
class Rectangle {
constructor(width, height) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
area() {
return this.width * this.height;
}
}
// 使用工厂创建对象
const circle = ShapeFactory.createShape('circle', 5);
const rectangle = ShapeFactory.createShape('rectangle', 4, 6);
console.log(circle.area()); // 78.53981633974483
console.log(rectangle.area()); // 242. 继承体系的维护困难
痛点:随着业务复杂度增加,继承体系变得复杂,难以维护和扩展。
解决方案:
- 优先使用组合而非继承
- 合理设计抽象基类
- 使用接口或混入(mixin)实现多重继承效果
javascript
// 混入模式示例
const Flyable = {
fly() {
console.log(`${this.name} is flying`);
}
};
const Swimmable = {
swim() {
console.log(`${this.name} is swimming`);
}
};
class Duck {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
// 扩展Duck类的功能
Object.assign(Duck.prototype, Flyable, Swimmable);
const duck = new Duck("Donald");
duck.fly(); // Donald is flying
duck.swim(); // Donald is swimming3. 内存优化需求
痛点:大量相似对象的创建导致内存占用过高。
解决方案:
- 使用原型共享方法以节省内存
- 实现对象池模式复用对象
- 及时清理不需要的对象引用
javascript
// 对象池模式示例
class ObjectPool {
constructor(createFn, resetFn) {
this.createFn = createFn;
this.resetFn = resetFn;
this.pool = [];
}
acquire() {
if (this.pool.length > 0) {
return this.pool.pop();
}
return this.createFn();
}
release(obj) {
this.resetFn(obj);
this.pool.push(obj);
}
}
// 使用对象池
const particlePool = new ObjectPool(
() => ({ x: 0, y: 0, vx: 0, vy: 0 }), // 创建函数
(particle) => { // 重置函数
particle.x = 0;
particle.y = 0;
particle.vx = 0;
particle.vy = 0;
}
);
const particle1 = particlePool.acquire();
particle1.x = 10;
particle1.y = 20;
particlePool.release(particle1); // 归还到池中六、知识延伸与扩展
1. 从原型到现代JavaScript特性
装饰器(Decorators)
javascript
// 装饰器示例(需要Babel支持)
function readonly(target, name, descriptor) {
descriptor.writable = false;
return descriptor;
}
class Person {
@readonly
name = "Alice";
}代理(Proxy)
javascript
// 使用Proxy实现数据绑定
const target = {
name: "Alice",
age: 25
};
const proxy = new Proxy(target, {
get(obj, prop) {
console.log(`Getting ${prop}`);
return obj[prop];
},
set(obj, prop, value) {
console.log(`Setting ${prop} to ${value}`);
obj[prop] = value;
return true;
}
});
proxy.name = "Bob"; // Setting name to Bob
console.log(proxy.age); // Getting age \n 252. 设计模式与原型
单例模式
javascript
class Singleton {
constructor() {
if (Singleton.instance) {
return Singleton.instance;
}
this.data = [];
Singleton.instance = this;
}
addData(item) {
this.data.push(item);
}
getData() {
return this.data;
}
}
const instance1 = new Singleton();
const instance2 = new Singleton();
console.log(instance1 === instance2); // true观察者模式
javascript
class Subject {
constructor() {
this.observers = [];
}
addObserver(observer) {
this.observers.push(observer);
}
removeObserver(observer) {
const index = this.observers.indexOf(observer);
if (index > -1) {
this.observers.splice(index, 1);
}
}
notify(data) {
this.observers.forEach(observer => observer.update(data));
}
}
class Observer {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
update(data) {
console.log(`${this.name} received: ${data}`);
}
}
// 使用观察者模式
const subject = new Subject();
const observer1 = new Observer("Observer 1");
const observer2 = new Observer("Observer 2");
subject.addObserver(observer1);
subject.addObserver(observer2);
subject.notify("Hello World");
// Observer 1 received: Hello World
// Observer 2 received: Hello World3. 函数式编程与原型
高阶函数与原型方法
javascript
// 扩展数组原型以支持函数式编程
Array.prototype.groupBy = function(keyFn) {
return this.reduce((groups, item) => {
const key = keyFn(item);
if (!groups[key]) {
groups[key] = [];
}
groups[key].push(item);
return groups;
}, {});
};
const people = [
{ name: "Alice", age: 25, department: "Engineering" },
{ name: "Bob", age: 30, department: "Marketing" },
{ name: "Charlie", age: 35, department: "Engineering" }
];
const grouped = people.groupBy(person => person.department);
console.log(grouped);
// {
// Engineering: [
// { name: "Alice", age: 25, department: "Engineering" },
// { name: "Charlie", age: 35, department: "Engineering" }
// ],
// Marketing: [
// { name: "Bob", age: 30, department: "Marketing" }
// ]
// }4. 性能优化与原型
原型方法与实例方法的性能对比
javascript
// 性能测试示例
function PerformanceTest() {
this.instanceMethod = function() {
return "instance method";
};
}
PerformanceTest.prototype.prototypeMethod = function() {
return "prototype method";
};
const test = new PerformanceTest();
// 测试原型方法性能
console.time("Prototype Method");
for (let i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
test.prototypeMethod();
}
console.timeEnd("Prototype Method");
// 测试实例方法性能
console.time("Instance Method");
for (let i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
test.instanceMethod();
}
console.timeEnd("Instance Method");5. 模块化与原型
ES6模块与类的结合
javascript
// person.js
export class Person {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
greet() {
return `Hello, I'm ${this.name}`;
}
}
export class Employee extends Person {
constructor(name, position) {
super(name);
this.position = position;
}
work() {
return `${this.name} is working as ${this.position}`;
}
}
// main.js
import { Person, Employee } from './person.js';
const person = new Person("Alice");
const employee = new Employee("Bob", "Developer");
console.log(person.greet()); // Hello, I'm Alice
console.log(employee.work()); // Bob is working as Developer6. 错误处理与原型
自定义错误类型
javascript
class CustomError extends Error {
constructor(message, code) {
super(message);
this.name = "CustomError";
this.code = code;
}
}
class ValidationError extends CustomError {
constructor(message, field) {
super(message, "VALIDATION_ERROR");
this.name = "ValidationError";
this.field = field;
}
}
try {
throw new ValidationError("Invalid email format", "email");
} catch (error) {
if (error instanceof ValidationError) {
console.log(`Validation failed for ${error.field}: ${error.message}`);
}
}七、面试常见问题与解答
1. 原型链相关问题
Q: 如何判断一个属性是实例属性还是原型属性?
A:
javascript
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.species = "Homo sapiens";
const person = new Person("Alice");
// 判断方法
console.log(person.hasOwnProperty("name")); // true - 实例属性
console.log(person.hasOwnProperty("species")); // false - 原型属性
console.log("species" in person); // true - 存在于原型链中Q: instanceof 和 isPrototypeOf 的区别?
A:
javascript
function Animal() {}
function Dog() {}
Dog.prototype = Object.create(Animal.prototype);
const dog = new Dog();
console.log(dog instanceof Dog); // true
console.log(dog instanceof Animal); // true
console.log(Animal.prototype.isPrototypeOf(dog)); // true
console.log(Dog.prototype.isPrototypeOf(dog)); // true2. 继承相关问题
Q: ES6类继承与ES5构造函数继承有什么区别?
A:
javascript
// ES5继承
function Parent(name) {
this.name = name;
}
function Child(name, age) {
Parent.call(this, name); // 必须手动调用
this.age = age;
}
Child.prototype = Object.create(Parent.prototype);
Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
// ES6继承
class ParentES6 {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
class ChildES6 extends ParentES6 {
constructor(name, age) {
super(name); // 必须先调用super
this.age = age;
}
}3. 类相关问题
Q: 类的静态方法可以被实例调用吗?
A:
javascript
class MyClass {
static staticMethod() {
return "static method";
}
instanceMethod() {
return "instance method";
}
}
const instance = new MyClass();
console.log(MyClass.staticMethod()); // "static method"
console.log(instance.instanceMethod()); // "instance method"
// console.log(instance.staticMethod()); // TypeError