1.基础环境配置
|----------------|-----|-----|
| IP地址 | 主机名 | 节点 |
| 192.168.200.10 | db1 | 主节点 |
| 192.168.200.20 | db2 | 从节点 |
(1)创建两台虚拟机,节点为192.168.200.10(20),分别更改主机名,此处以db1为例
bash
[root@localhost ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname db1
[root@localhost ~]# bash
[root@db1 ~]#(2)两台虚拟机配置本地yum源,此处以db1为例
bash
[root@db1 ~]# mkdir /opt/centos
[root@db1 ~]# mount /dev/cdrom /opt/centos
mount: /dev/sr0 is write-protected, mounting read-only
[root@db1 ~]# mv /etc/yum.repos.d/* /media/
[root@db1 ~]# vi /etc/yum.repos.d/local.repo
[centos]
name=centos
baseurl=file:///opt/centos
gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
[root@db1 ~]# yum clean all
[root@db1 ~]# yum repolist(3)两台虚拟机关闭防火墙和selinux,此处以db1为例
bash
[root@db1 ~]# systemctl stop firewalld
[root@db1 ~]# systemctl disable firewalld
[root@db1 ~]# setenforce 0(4)两台虚拟机修改映射文件,此处以db1为例
bash
[root@db1 ~]# vi /etc/hosts
192.168.200.10 db1
192.168.200.20 db22.初始化MariaDB数据库服务,此处以db1为例
(1)安装MariaDB数据库并启动
bash
[root@db1 ~]# yum install -y mariadb mariadb-server
[root@db1 ~]# systemctl start mariadb
[root@db1 ~]# systemctl enable mariadb(2)初始化MariaDB数据库
bash
[root@db1 ~]# mysql_secure_installation
NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB
SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY!
In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current
password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and
you haven't set the root password yet, the password will be blank,
so you should just press enter here.
Enter current password for root (enter for none): #默认回车
OK, successfully used password, moving on...
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
root user without the proper authorisation.
Set root password? [Y/n] y #确定设置root密码
New password: #输入数据库root密码000000
Re-enter new password: #重复输入设置的root密码
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
... Success!
By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] y #确认删除匿名账户
... Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] n #允许root远程连接
... skipping.
By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] y #删除test数据库
- Dropping test database...
... Success!
- Removing privileges on test database...
... Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] y #确认初始化
... Success!
Cleaning up...
All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB
installation should now be secure.
Thanks for using MariaDB!(3)登录MariaDB数据库
bash
[root@db1 ~]# mysql -uroot -p000000
MariaDB [(none)]>(4)使用Ctrl+C组合键退出MariaDB数据库
bash
MariaDB [(none)]> Ctrl-C -- exit!
Aborted
[root@db1 ~]#3.部署主从复制数据库服务
(1)分别修改db1和db2的/etc/my.cnf数据库配置文件,在[mysqld]下增加三行配置
bash
[root@db1 ~]# vi /etc/my.cnf
[mysqld]
log_bin = mysql-bin #记录操作日志
binlog_ignore_db = mysql #不同步MYSQL系统数据库
server_id = 1 #数据库集群中每个节点的id都要不同
[root@db2 ~]# vi /etc/my.cnf
[mysqld]
log_bin = mysql-bin
binlog_ignore_db = mysql
server_id = 2(2)在db1上重启MariaDB数据库并设置主节点权限
bash
[root@db1 ~]# systemctl restart mariadb
[root@db1 ~]# mysql -uroot -p000000
MariaDB [(none)]> grant all privileges on *.* to root@'localhost' identified by '000000'; #授权本地使用root用户登录到数据库
MariaDB [(none)]> grant all privileges on *.* to root@'%' identified by '000000'; #授权任何客户端机器都可以使用root用户登录到数据库
MariaDB [(none)]> grant replication slave on *.* to 'user'@'db2' identified by '000000'; #创建user用户供从节点db2连接
MariaDB [(none)]> flush privileges; #刷新权限(3)在db2上重启MariaDB数据库并设置从节点权限
bash
[root@db2 ~]# systemctl restart mariadb
[root@db2 ~]# mysql -uroot -p000000
MariaDB [(none)]> change master to master_host='db1',master_user='user',master_password='000000'; #通过user用户连接主节点db1
MariaDB [(none)]> flush privileges; #刷新权限
MariaDB [(none)]> Ctrl-C -- exit!
[root@db2 ~]# systemctl restart mariadb #再次重启MariaDB数据库
[root@db2 ~]# mysql -uroot -p000000
MariaDB [(none)]> start slave; #开启从节点服务
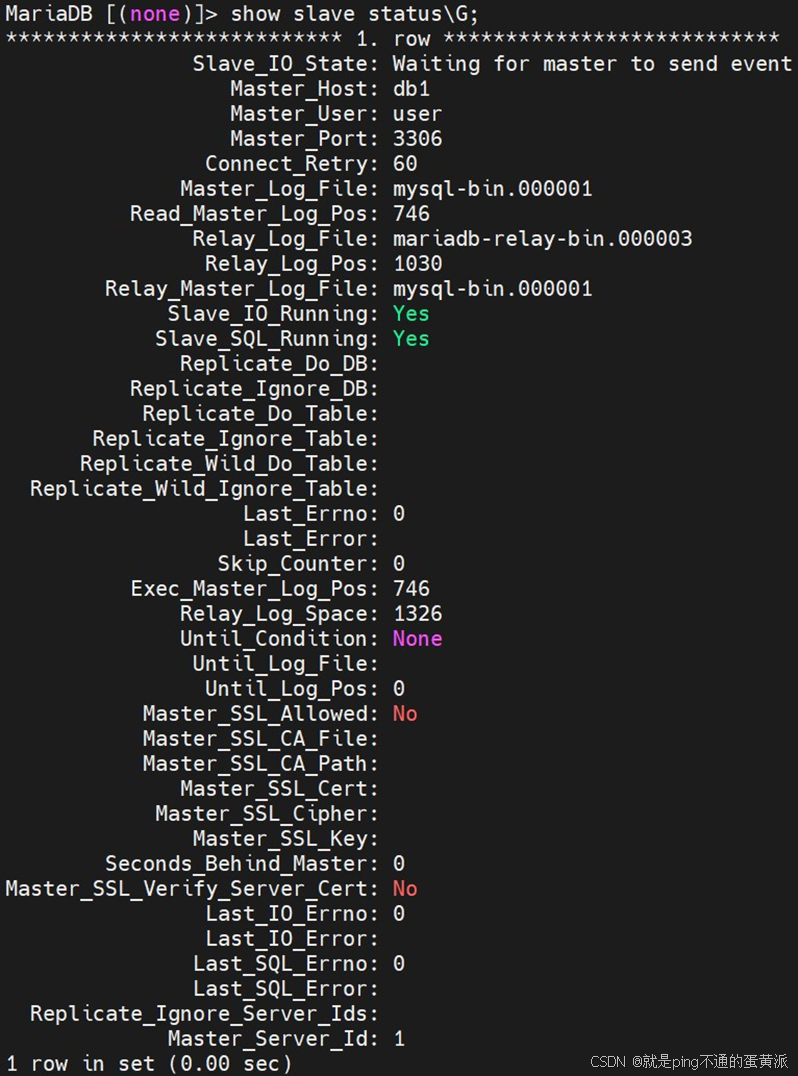
MariaDB [(none)]> show slave status\G; #查看从节点服务状态当Slave_IO_Running和Slave_SQL_Running的状态都为YES,则说明主从数据库搭建成功
4.验证主从数据库功能
(1)在主节点db1上创建库test
bash
[root@db1 ~]# mysql -uroot -p000000
MariaDB [(none)]> create database test;
MariaDB [(none)]> use test
MariaDB [test]> create table company(id int not null primary key,name varchar(50),addr varchar(255));
MariaDB [test]> insert into company values(1,"baidu","china");
MariaDB [test]> select * from company;
+----+-------+-------+
| id | name | addr |
+----+-------+-------+
| 1 | baidu | china |
+----+-------+-------+(2)在从节点db2上查看,其会自动同步db1上创建的库
bash
[root@db2 ~]# mysql -uroot -p000000
MariaDB [(none)]> use test;
MariaDB [test]> select * from company;
+----+-------+-------+
| id | name | addr |
+----+-------+-------+
| 1 | baidu | china |
+----+-------+-------+